Communication Sciences Exam #1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Newton's 1st Law of motion
An object at rest or in motion will remain unless acted upon by an outside force
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
Acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon it, and i inversely proportional to mass
-F=MxA
Newton's 3rd law of motion
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Brownian Motion
Random movement of particles in fluids such as a liquid or gas, resulting from collision with fast-moving atoms or particles.
-nature of sound waves
Velocity
Speed of something in a given direction
What is velocity measured in ?
m/s
Force
Strength or energy as an attribute of physical action or movement
Pressure
Force applied perpendicular to a surface per unit square area
What is pressure measured in?
Kpa and centimeters
Wave
disturbance traveling through medium, transferring energy from one point to another without transporting matter itself
Medium
A material substance that transmits energy from one point to another
Psychoacoustics
The study of the relationship between physical properties and our perception of those properties
Frequency
Cycle, one alternating compression and rarefaction, cycles per second, frequency is a measurement perceived as pitch by a listener
What is frequency measured in?
Hz
Period
Duration of one cycle
-Time measurement
What is period measured in?
seconds
-T(period in seconds= 1 sec/f
-T(period in milliseconds)= 1000/f
Brownian Motion
Random movement of particles in fluids such as a liquid or gas, resulting from collision with fast-moving atoms or particles.
-nature of sound waves
Velocity
Speed of something in a given direction
What is velocity measured in
m/s
Relationship between period and frequency
longer period--> lower frequency
Relationship between amplitude and intensity
amplitude doubles, intensity quadruples
Transverse Waves
Particle movement perpendicular
ex. fans in the stadium doing a wave
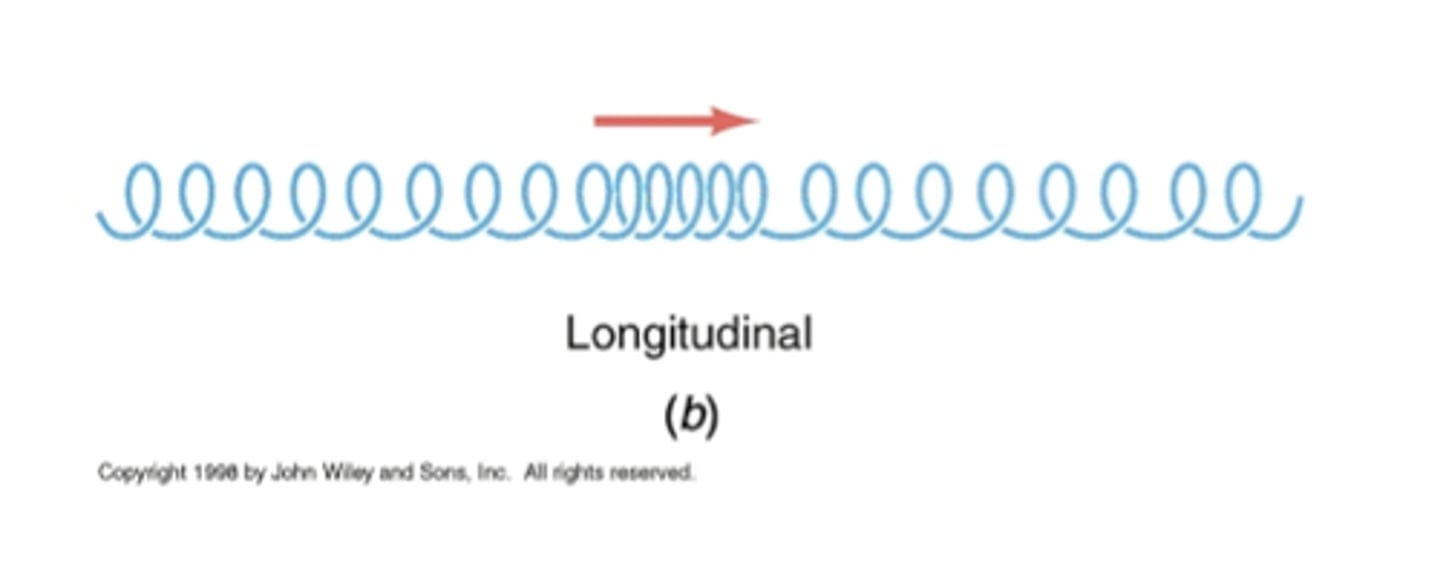
Longitudinal waves
Particle movement parallel
ex. slinkey
Pulse waves
Single disturbance
ex. clapping hands, /t/, /k/, African (Zulu/Chosa), click sound
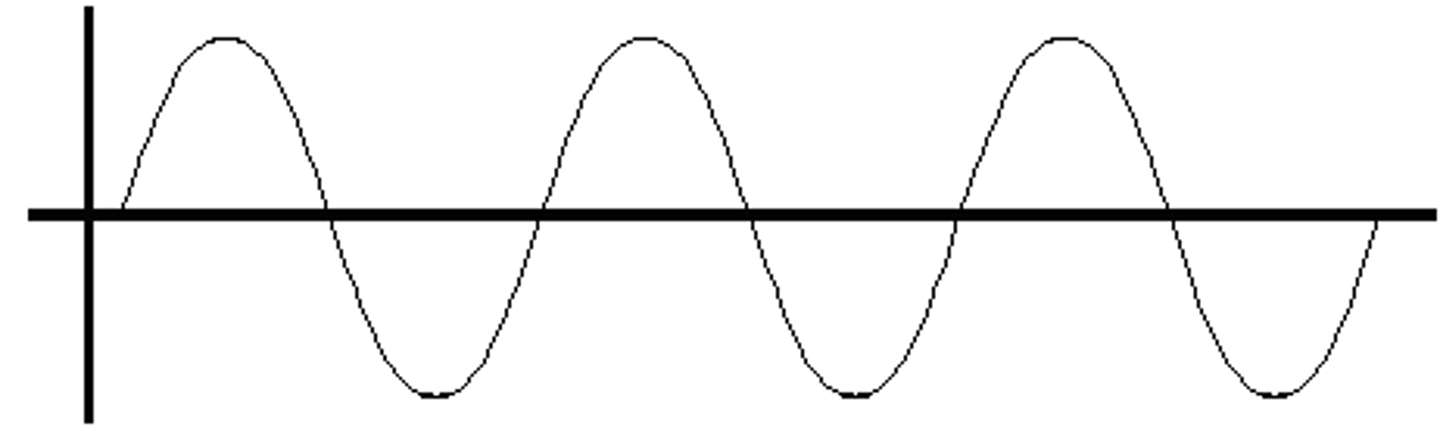
Sinusoidal eaves
Simple harmonic motion, back/ forth motion repeats, periodic, the resulting sound is a pure tone, single frequency
Compression
Positive pressure
Rarefaction
Negative pressure
X-axis
time
Y-axis
Pressure
Inverse square law
-Intensity diminishes further away from the source
-Energy spreads out
Relationship: take the factor by which distance increases, intensit