ap precalc test prep
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
rate of change formula
y₂-y₁/x₂-x₁
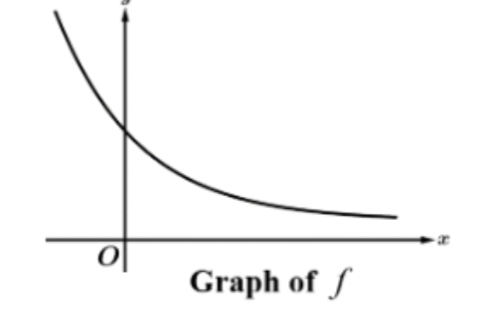
positive or negative, increasing or decreasing
positive and decreasing
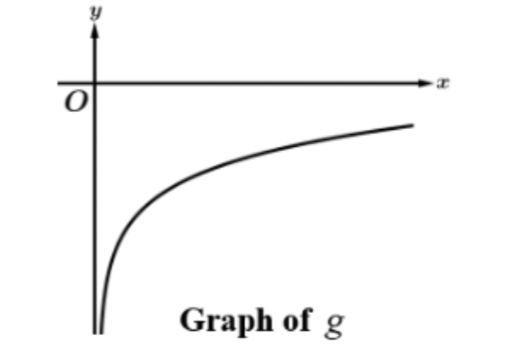
positive or negative, increasing or decreasing
negative and increasing
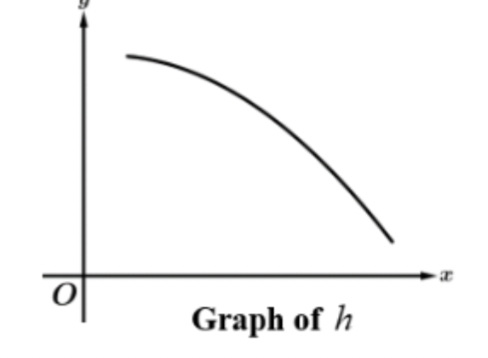
positive or negative, increasing or decreasing
positive and decreasing
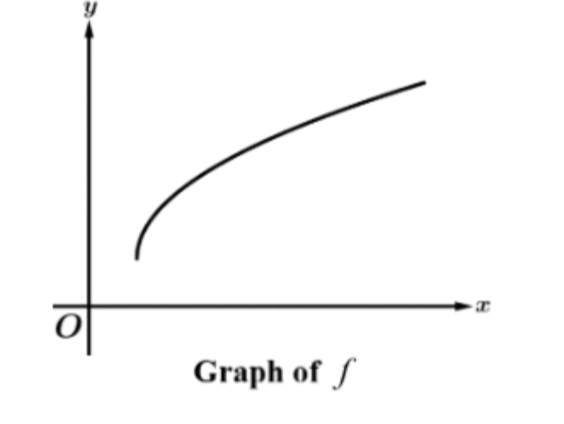
positive or negative, increasing or decreasing
positive and decreasing
what is multiplicity?
the degree of the factor
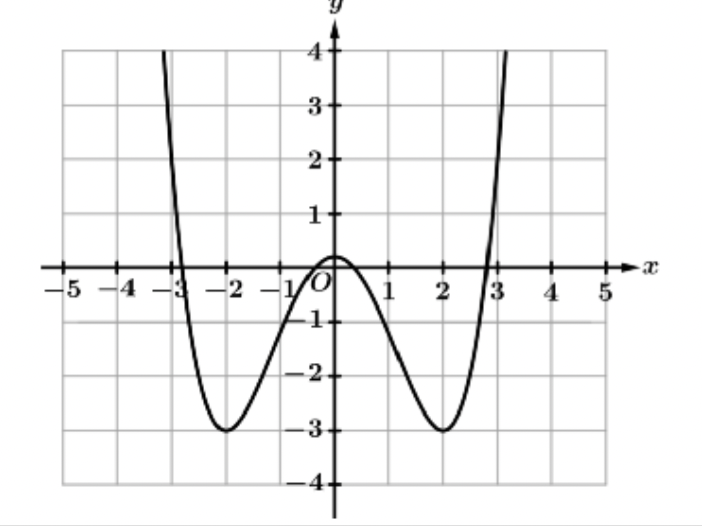
even functions
an even function is symmetric over the y axis
f(-x)=f(x)
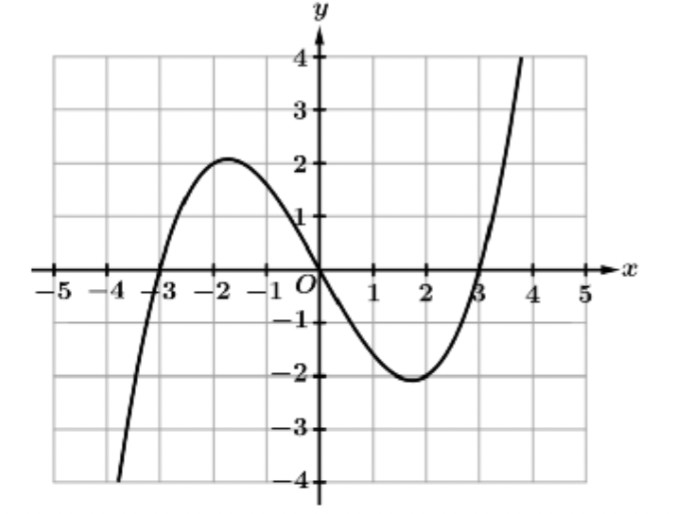
odd function
an odd function is symmetric about the origin
g(-x)=-g(x)
what translation/dilation is f(x)+k
vertical dilation of k units
what translation/dilation is f(x+k)
horizontal translation of -h units
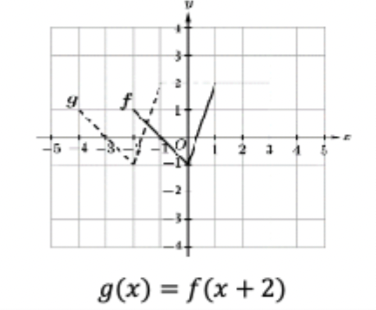
what translation/dilation af(x)
f has a vertical dilation by a factor of |a|, if a<0, f is reflected over the x-axis
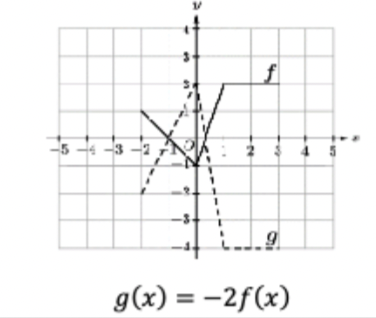
what translation/dilation is f(bx)
f has a horizontal dilation by a factor of |1/b|. if b<0, f is reflected over the y-axis
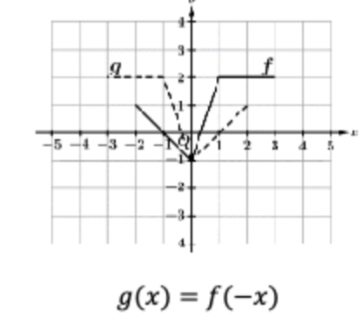
vertical asymptote
when function is undefined, set the denominator=0 and let each factor in the denominator=0
holes
when you cancel a factor in the numerator and denominator. set the cancelled factor to 0
horizontal asymptote
if the power of the numerator is ___ than the denominator
n<d, HA y=0
n>d, no HA
n=d, HA = leading coefficient on the numerator/leading coefficient on the denominator
slant asymptote
when n>d, there is a slant asymptote. divide numerator by denominator
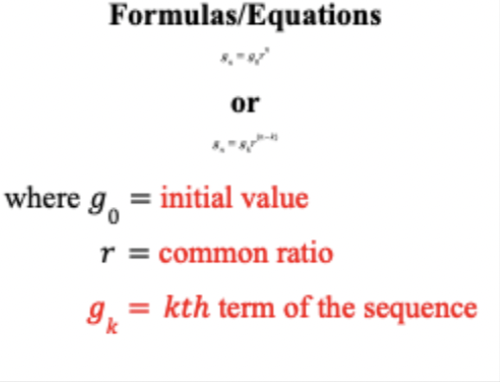
arithmetic sequence
common difference
behave like linear functions, except they’re not continuous.
increasing arithmetic sequences increase equally each step (slope stays the same)

geometric sequence
common ratio/constant proportional change
behave like exponential functions, except they’re not continous
increaisng geometric sequences increase by a larger amount each step (% increase always stays the same)
exponential functions
a(b)^x, b>0
a represents the initial amount
b represents the base of common ratio
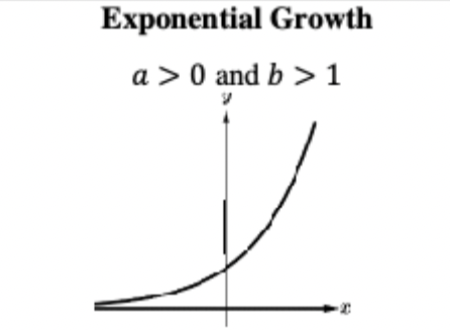
exponential growth, a and b values
a>0, b>1
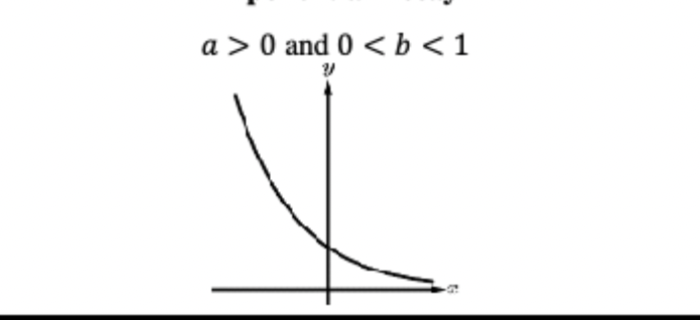
exponential decay, a and b values
a>0, 0<b<1
product property exponent rule

power property exponent rule

negative exponent property rule

how to calculate residentuals
residual=observed value-predicted value
this is also referred to as the error in the model
how to know if the residual model is appropriate
they will have points randomly scattered above and belove the x axi. think of the sum of the residuals being 0
2 ways composite functions can be written
(f o g)(x) or f(g(x))
inverse functions
these can be found by switching x and y.
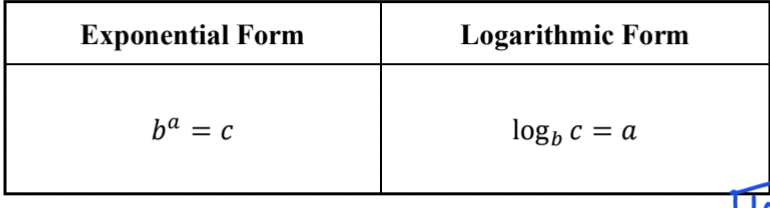
exponential and logarithmic form of log functions
log function characteristics
always concave up or concave down
always increasing or decreasing
vertically asymptotic to x=0
domain is typically (0,infinity)
range is typically (-infinity, infinity)
product property

quotient property

power property

change of base property
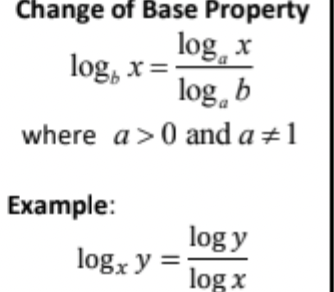
period
a period is the length of the x values that it takes for the function to complete 1 cycle
standard position
in the coordinate plane, an angle is in the standard position when its vertex is at the origin and one ray of the angle lies on the positive x-axis
terminal ray
the terminal ray is the second ray of an angle in standard position
positive angles
counterclockwise direction
negative angles
clockwise direction
reference angle
the distance between the terminal ray and nearest x-axis (must be a positive acute angle)
sin displacement
sin is the ratio of vertical displacement
sin⍬ = y/r
cos displacement
cos is the ratio of horizontal displacement
cos⍬ = x/r
tan displacement
tan is the slope of the terminal ray
the ratio of the vertical displacement to the horizontal displacement
tan⍬ = y/x
tan⍬ = sin⍬/cos⍬
coordinates of a point on a circle centered at the origin
cos⍬ = x/r
sin⍬ = y/r
unit circle quadrant one (1) values
0 = (1,0
π/6 = √3/2, 1/2
π/4 = √2/2, √2/2
π/3 = 1/2, √3/2
π/2 = 0,1
unit circle quadrant two (2) values
2π/3 = -1/2, √3/2
3π/4 = -√2/2, √2/2
5π/6 = -√3/2, 1/2
π = (-1,0)
unit circle quadrant three (3) values
7π/6 = -√3/2, -1/2
5π/4 = -√2/2, -√2/2
4π/3 = -1/2, -√3/2
3π/2 = 0, -1
unit circle quadrant four (4) values
5π/3 = 1/2, -√3/2
7π/4 = √2/2, -√2/2
11π/6 = √3/2, 1/2
2π = 1,0
properties of f(⍬) = sin⍬
average period with no shifts: 2π
frequency is the reciprocal of the period, 1/2π
the graph of f(⍬) = sin⍬ oscillates between concave down and concave up
properties of g(⍬) = cos⍬
period with no shifts: 2π
frequency is the reciprocal of the period, 1/2π
the graph of g(⍬) = cos⍬ oscillates between concave down and concave up
sinusoidal functions
a sinusoidal function is any function that involves additive and multiplicative transformations of f(⍬) = sin⍬
the sin and cosin functions are both sinusoidal functions because g(⍬) = cos⍬ = sin(⍬+π/2)
transformations of a sin function
the midline is a vertical translation
the amplitude is a vertical dilation
the period is the result of a horizontal dilation
phase shift of a sinusoidal function
a horizontal translation of a sinusoidal function is called the phase shift
the graph of g(x) = sin(x+c) is a phase shift of the graph of f(x) = sin(x) by -c units
the same result can be applied to the cos function
properties of the tan function
domain is all real x values, x ≠ π/2 +nπ (n E Z)
range is -infinity, infinity
period: π
vertical asymptotes: x ≠ π/2 +nπ (n E Z)
tangent equation
y=atanb(x-c)+d
a reprsents the vertical stretch/compression and indicates positive or negative to find the relative max/min
b is the frequency and helps you find the period, π/b
c is the phase shift
d is the vertical shift and midline
the asyptotes of a tangent function can be found by -π/2 < b(x-c) < π/2
tangent 5 point patter: asymptote, relative min, mid, relative max, asymptote
inverse trig functions
always consider the domain restrctions
the range of inverse sin is -π/2, π/2
the range of inverse cos is [0, π]
the range of inverse tan is -π/2, π/2
![<p>always consider the domain restrctions</p><p>the range of inverse sin is -π/2, π/2 </p><p>the range of inverse cos is [0, π]</p><p>the range of inverse tan is -π/2, π/2 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/574d04a4-beff-49cf-ae9b-8fb1160699b5.png)
general solutions to sin functions
sinx = ½
x = π/6 +2πk, where k is an interger
x = 5π/6 + 2πk, where k is an integer
general solutions to cos functions
cosx = ½
x = π/3 + 2πk, where k is an integer
x = 5π/3 + 2πk, where is an interger
general solutions to tan functions
tanx = 1
x = π/4 +πk, where k is an integer
since the period of tangent is π, one equation will capture all solutions
secant reciprocal function
secx = 1/cosx, where cosx ≠ 0
secant is the reciprocal of the cosine function
cosecant reciprocal function
cscx = 1/sinx, where sinx ≠ 0
cosecant is the reciprocal of the sin function
cotangent
cotx = 1/tanx, where tanx ≠ 0
cotx = cosx/sinx, where sinx ≠ 0
pythagorean identity and equivalent forms
sin²⍬ + cos²⍬ = 1
1 + tan²⍬ = sec²⍬
1 + cot²⍬ = csc²⍬
sum and difference identities
sin (α ± β) = sinαcosβ ± cosαsinβ
cos (α ± β) = cosαcosβ ± sinαsinβ
double angle identities
sin(2⍬) = 2sin⍬cos⍬
cos(2⍬) = cos²⍬ - sin²⍬ = 1-2sin²⍬ = 2cos²⍬-1
polar coordinates
(r, ⍬)
converting from polar to rectangular
we know that cos⍬ = x/r and sin⍬ = y/r
x=rcos⍬
y=rsin⍬
converting from rectangular to polar coordinates
(x,y) to (r,⍬)
we know that x²+y²=r²
tan⍬ = y/x to find the value of ⍬