Osteoporosis - Lewis
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What are the risk factors that increase risk of osteoporosis?
Low BMD
Age (≥65 years for women)
Female sex
Race/ethnicity
Low BMI
Smoking
Menopause
+3 drinks/day
Genetics
Inadequate nutrition/exercise
Weight bearing exercise
History of fracture
Falls
What medications are risk factors of osteoporosis?
Anti-epileptics
Medications that lower estrogen (aromatase inhibitors)
Chemotherapy
Medroxyprogesterone
PPIs
Glucocorticoids
SSRIs
SGLT2i
TZD (pioglitazone)
T4
Diuretics
What lab values do you look at to test for osteoporosis?
CMP
25(OH) vitamin D (low)
TSH (low)
Total testosterone (men)
24 hour urine calcium and creatinine concentrations
CBC
Evaluate patients’ need for bone-remodeling medication treatment
Women aged ≥65 years
Postmenopausal women aged <65 with ≥1 clinical risk factor
Should get a central DXA when the FRAX major osteoporotic fracture risk score is >8.4%
Men aged ≥50 years with ≥1 clinical risk factor
If no secondary cause of osteoporosis or history of a low-trauma fracture, BMD screening not recommended for children, premenopause, males younger than 50
What does a DEXA scan do?
Assesses bone mineral density
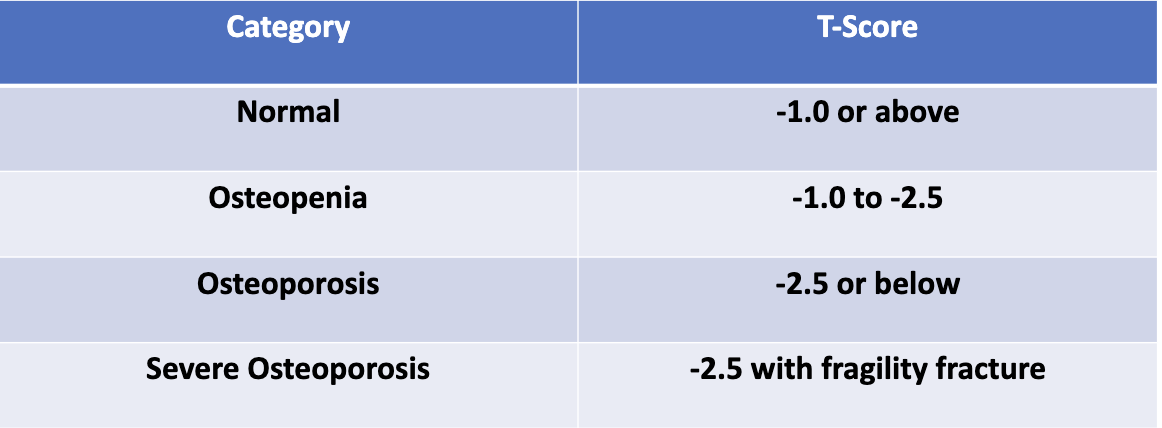
What is a T-score?
Number of SD from the mean of the reference population
What DEXA score is used for diagnosis of osteoporosis?
T-score ≤ -2.5
What does the T-score compare the patient’s BMD to?
A healthy young white female
What does the Z-score compare the patient’s BMD to?
The BMD of someone of the same age and gender
How often should you do routine checkups (DEXA) for BMD?
Every 1-3 years if treated for osteoporosis
Every 2-5 years at low risk of fracture and not receiving treatment
What do the different T-score values indicate?
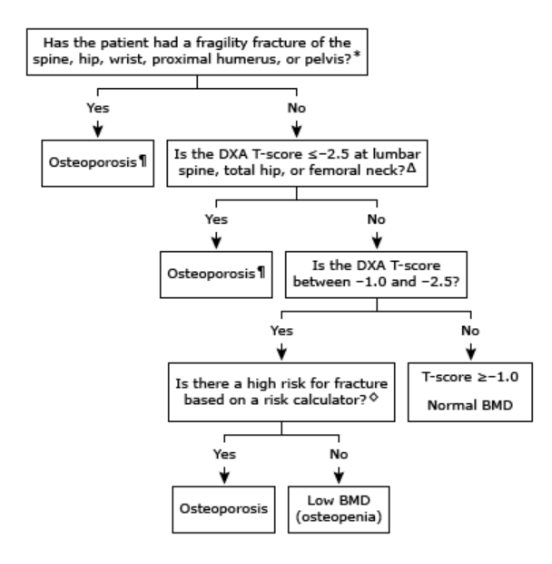
How do you diagnose osteoporosis in postmenopausal women?
What are the goals of treatment for osteoporosis?
Not curable
Strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk
Minimize bone loss
Reduce fall risk
Pain management
What are some lifestyle modifications to prevent osteoporosis?
Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
Diet
Weight-bearing/resistance exercises
Smoking cessation
Avoid heavy drinking
Reduce fall risks (BEERs meds)
What are the recommended calcium daily intakes for men?
19-70 years old: 1000 mg calcium/day
>70 years old: 1200 mg calcium/day
What are the recommended calcium daily intakes for women?
19-50 years old: 1000 mg calcium/day
>50 years old: 1200 mg calcium/day
What are the ADRs associated with calcium?
Dyspepsia
Constipation
Kidney stones
What should you separate calcium from?
Thyroid hormones and irons
Which calcium supplements are most widely used? What are the pros and cons?
Calcium carbonate (first choice)
Cheapest
Must take with meals
Not recommended in patients taking PPIs/H2RAs
Calcium citrate:
More expensive
Can be taken with or without meals
Good for patients on PPIs/H2RAs
What is the difference between Ergocalciferol (D2) and Cholecalciferol (D3)?
D3 is preferred because it increases serum 25(OH)D more efficiently than D2
D2 does not accurately measure all vitamin D assays
Both can be taken with or without food
Who should be given vitamin D supplementation?
Adults with osteoporosis or at high risk of it
What are the suggested vitamin D intakes?
AACE: 1000-2000 IU daily
NOF: 800-1000 IU daily
IM: 600 IU daily
When do you give pharmacological treatment assuming postmenopausal females and males 50+ years old?
T-score ≤ -2.5 at lumbar spine, femoral neck, total hip
History of fragility fracture of vertebrae (clinical or subclinical), hip, wrist, pelvis, humerus
T-score between -1 and -2.5 at femoral neck or spine AND
10-year probability of hip fracture ≥ 3% OR
10-year probability of major osteporosis related fracture ≥ 20%
What are the FDA approved medications for prevention of osteoporosis on postmenopausal women?
Estrogens
Bisphosphonates: alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, zoledronic acid
SERMs: raloxifene, bazedoxifene
none for men
What are pharmacological treatment options for patients with high risk but no prior fractures?
Alendronate, denosumab, risedronate, zoledronic acid
Can try ibandronate and raloxifene
If BMD worsens, switch to injectable or anabolic agent
What are pharmacological treatment options for patients with very high risk and prior fractures?
PTH analogs, romosozumab, zoledronic acid
Can also try alendronate, risedronate
What drugs are most commonly used in osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates
Which bisphosphonate is given IV only?
Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
Which bisphosphonate can be given PO or IV?
Ibandronate (Boniva)
Which bisphosphonate is only for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women?
Ibandronate (Boniva)
What do you have to consider when initiating bisphosphonates?
Do not use alendronate or zoledronic acid if CrCl <35 mL/min
Do not use risedronate or ibandronate if CrCl <30 mL/min
What types of osteoporosis can bisphonates be used for?
Alendronate, risedronate, zoledronic acid: treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis, treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis, glucocorticoids-induced osteoporosis
Ibandronate: treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis ONLY
How should you counsel patients on taking bisphosphonates?
Take on empty stomach with 6-8 ounces of water
Do not lie down, eat/drink for at least 30 minutes (60 minutes for ibandronate)
What are the side effects associated with bisphosphonates?
Common: abdominal pain, dyspepsia, hypocalcemia
Rare: osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), ulcers, bone pain, atypical fractures
Recommend routine dental exams
Dental procedures should be done before therapy
What is ONJ?
Overgrowth of bone in the jaw
Seen in high doses of IV bisphosphonates
What is an atypical femoral fracture?
Seen in long term bisphosphonate use but not exclusive to bisphosphonates
May be caused by slow bone turnover
Why should patients go on a bisphosphonate drug holiday?
Bisphosphonates tend to reside in the bones for continued efficacy after discontinuation
Going on holiday decreases risk of side effects like ONJ and atypical fractures
How long should bisphosphonates be used for?
5-10 years
3-6 years for zoledronic acid
What medications can you initiate during a bisphosphonate holiday?
Teriparatide or raloxifene
What medications can you initiate for other drug holidays?
Anabolic agents: denosumab, bisphosphonates, raloxifene
Denosumab: antiresorptive agents (don’t use anabolic agents)
How is denosumab (Prolia) administered?
60 mg SC every 6 months
What is the BBW for denosumab?
Severe hypocalcemia in patients with advanced kidney disease
What are the side effects associated with denosumab?
Hypocalcemia
Injection site reaction
ONJ
atypical fractures
Infection
What should you do after discontinuing denosumab?
Initiate another antiresportive agent since the BMD will decline
What medication is only indicated for treatment ONLY for postmenopausal women, typically for patients who have failed bisphosphonates and denosumab?
Calcitonin (Miacalcin, Fortical)
How is calcitonin administered?
Intranasal: 1 spray into one nostril only
SC
What are the side effects of calcitonin?
Rhinitis (if intranasal)
Hypocalcemia
potentially increased risk of malignancy
Which medication should not be used if the patient has a salmon allergy?
Calcitonin
What treatment is used in prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women but is not FDA indicated?
Estrogen
If a patient does not have a hysterectomy, what do you have to add to estrogen regimens? Why?
Progesterone
Estrogen alone causes uterine cancer
What is the BBW of estrogens?
Do not use for prevention of CVD or prevention of dementia, increases risk of breast cancer
What are the common side effects of estrogen?
Headaches, weight gain
What is bazedoxifene/estrogen (Duavee) used for?
Prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
When would bazedoxifene/estrogen (Duavee) be contraindicated?
History of/current VTE, pregnancy, carcinoma of the breast
What is the BBW of bazedoxifene/estrogen (Duavee)?
Increased risk of stroke/DVT
Do not use to reduce risk of CVD/dementia
Do not take with other estrogen products
Increases risk of endometrial cancer in patients with a uterus who use unopposed estrogens (basically means estrogen without progesterone)
What are the common side effects of bazedoxifene/estrogen (Duavee)?
Nausea, dizziness, muscle spasm, leg cramps
When is raloxifene (Evista) contraindicated?
History of/current VTE, pregnancy
Why is raloxifene better than estrogen based products?
Is a mixed estrogen agonist/antagonist so prevents bone loss and decreases risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women
What is the BBW for raloxifene (Evista)?
Increased risk of DVT/PE/stroke
What are common side effects of raloxifene (Evista)?
Hot flashes, peripheral edema, leg cramps, muscle spasms
What are PTH analogs indicated for?
Osteoporosis treatment
How do you store PTH analogs?
Teriparatide: refrigerate
Abaloparatide: refrigerate, but can store at RT for 30 days once opened
How are PTH analogs administered and for how long?
SC and up to 2 years
What is the BBW for PTH analogs?
Potential risk of osteosarcoma (malignant bone tumor)
What are common side effects of PTH analogs?
Rapid bone loss after discontinuation, transient hypercalcemia, orthostatic hypotension, nausea
What is romosozumab (Evenity) indicated for?
Osteoporosis in post-menpausal women
How is romosozumab (Evenity) administered and for how long?
Two consecutive injections monthly
Used up to 1 year
What is the BBW for romosozumab (Evenity)?
Increased risk of MI, stroke, cardiovascular disease
Do not initiate in patients with MI/stroke within a year
What are the side effects of romosozumab (Evenity)?
Arthralgia, headache, hypersensitivity, injection site reactions
What do you monitor for in any osteoporosis treatment?
Monitor BMD every 1-3 years while on treatment
Goal: increased/stable BMD