Final exam review
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
what areas are considered blind spots for horses
directly between their eyes on the forehead, directly behind them, directly below their nose
what is the term for a baby horse that is no longer nursing
weanling
what is the term for a female parent of a horse
dam
what is the term for a intact male donkey
jack
what is the term for a offspring of a female horse and a male donkey
mule
what is the term for a offspring of a female donkey and a male horse
Hinny
what is the term for a female donkey
jenny
what is the term for a male parent of a horse
sirei
what are alpha 2 agonists that can be used on a horse
xylazine, detomidine
what are opioids that can be used on horses
butorphanol, morphine
what are tranquilizer that can be used on horses
acepromazine
what are hypnotics that can be used on horses
Diazepam
where in the digestive tract does fermentation occur
cecum
what is the equine vertebral formula
C7, T18, L6, S5, Cy15-21
what is the most common arrhythmia found in horses
second degree AV block
what could cause a CRT of 3 seconds
hypotension, hypovolemia, dehydration
upon auscultating the LLQ, you appreciate what sounds like waves at the beach. this could indicate a build up of what in the GI tract
sand
what can be heard in the 4 quadrants during abdominal auscultation
RUQ: base of cecum
LUQ: small intestine
RLQ: right ventral colon
LLQ: left ventral colon
what is a possible cause of a yellow MM
fasting hyperbilirubinemia
what is a possible cause of a blanched/white MM
hemorrhage
what is a possible cause of red/purple MM
endotoxemia
what is a possible cause of brown MM
red maple leaf toxicosis
what are the best sites for obtaining a pulse rate
transverse facial artery, submandibular artery
what is the ‘bean’
smegma buildup within the urethral diverticulum of a gelding
horse dental formula
2(13/3, C0-1/0-1, PM3-4/3, M3/3) = 40-42
what kind of teeth do horses have
hypsodont teeth
what kind of teeth do foals have
deciduous teeth
what are cups in relation to equine teeth
infolding of enamel that decrease with age
when it comes to aging horses, the ________ _______ appears near the gum line on the lateral surface of the _______ _____ _______ at approximately ___ ____ of age
Galvayne’s Groove, upper third incisor, 10 years
an alteration of the horse’s gait, attitude or performance is defined as
lameness
During an In motion evaluation you notice has an uneven gait. It appears their head bobs downward when stepping on its right front. This could indicate a problem with which limb?
left front
what is the function of a flexion test?
accentuates pain and localizes lameness
what are some parts of an ophthalmic exam
Maze Test, Dazzle reflex, Menace Response
what are the equine core vaccines
EEE, WEE, VEE; rabies; tetanus; west nile virus
what are the three sites that IM injections can be administered
semimembranousus/tendinosis, triangle of the neck, pectoral
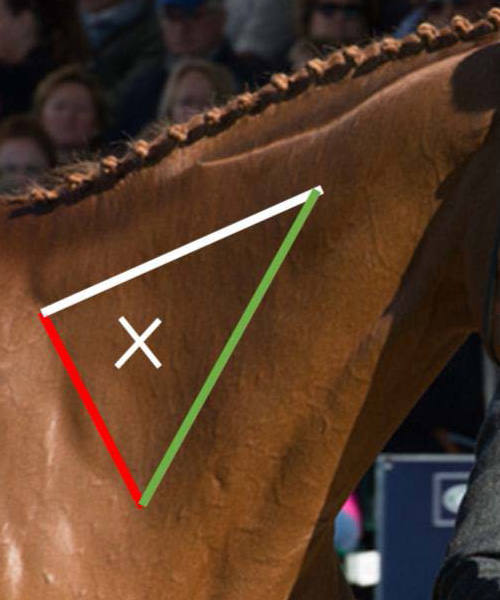
what does the white line represent
nuchal ligament
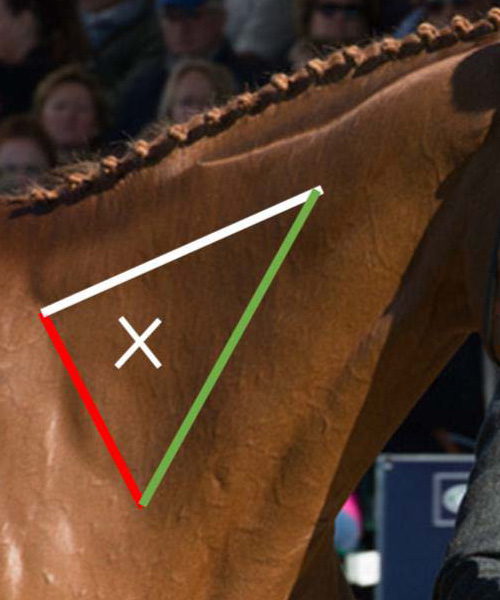
what does the green line represent
cervical vertebrae
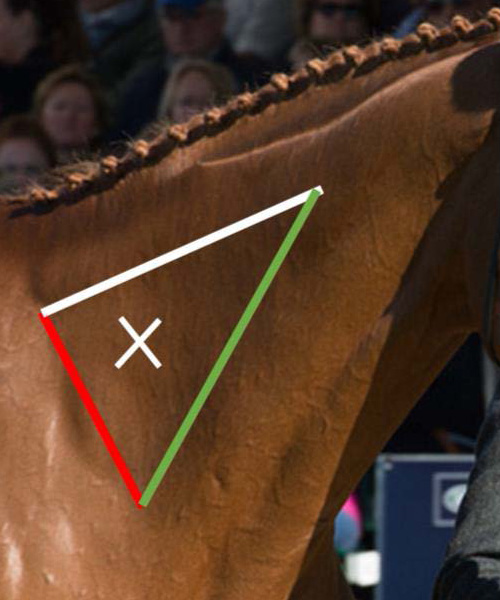
what does the red line represent
scapula
what are the most common sites for equine venipuncture
jugular vein, transverse facial venous sinus
when giving an IV injections, it is important to position the needle in the _____ ____ of the jugular vein. This is due to is close proximity to the ______ _______ on the ______ aspect of the neck.
cranial 1/3, carotid artery, caudal
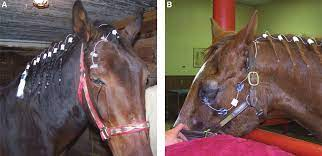
what do you call the system set up on the horse that allows continuous administration of topical medication to the eye?
subpalpebral lavage sytem
what are normal findings in urine testing
mucus strands, calcium carbonate crystals, USG of 1.020-1.050
what is urine coloration
pale to dark yellow
what could bright red urine mean
hematuria
what could brownish red urine mean
myoglobinuria
what could pinkish red urine mean
hemoglobinuria
what is the sample collected during an arthrocentesis
synovial fluid
what is the sample collected during a cystocentesis
urine
what is the sample collected during an abdominocentesis
peritoneal fluid
what is the sample collected during a spinal tap
CSF
what is the sample collected during an apheresis
bone marrow/stem cells
what is the sample collected during a bronchoalveolar lavage
upper respiratory samples
a belly tap is performed to obtain ______ _______. If the sample is a ______ ____ color, it indicates ischemia or necrosis. If there is an intestinal rupture there may be _____ present in the sample
peritoneal fluid, red/brown, feed
define laceration
torn or ragged wound of varying degree of damage
define puncture wound
sharp object passes through skin into underlying tissues
define complicated wound
wound involving multiple structures and tissues
define contusion
skin injury that includes bruising
define abrasion
area of the body surface denuded of skin or mucous membrane by some abnormal mechanical process
define incised wound
skin edges are cleanly cut by a sharp object
what are the degrees of contamination of a wound from least to most infected
clean, clean-contaminated, contaminated, infected
layers of Robert Jones bandage in order
primary layer: telfa, kling
secondary layer: cast padding/sheet cotton, brown gauze
third layer: vet wrap, elastikon
what happens in the inflammatory/Debridement phase of wound healing
1-3 days post injury, WBCs enter area and attack extracellular bacteria, fibric clot formation to help with hemostasis
what happens in the proliferative/repair phase of wound repair
3 days to 1-3 weeks, granulation tissue, fibroblasts begin to appear which synthesizes collagen
what is the maturation phase of wound healing
3 weeks - fully healed, epithelialization and contraction, collagen fibers cross-link and reorient along lines of tension
what is the proper form to administrate an IN injection
central and ventral
what is the proper form to administrate an IM injection
insert perpendicular to site
what is the proper form to administrate an IV injection
align parallel to site and insert at a 45 degree angle
what is the proper form to administrate a PO injection
insert at diastema and aim caudally
what is the proper form to administrate SQ injections
align parallel to site and tent skin to insert superficially

what tool is A
hoof nippers

what tool is B
hoof rasp

what tool is C
hoof knife
what gauge catheter is used in the horse
14 ga 5 ½ in
what is the maintenance fluid requirement for an adult horse
50 ml/kg/day
what is one reason why the IVC insertion site should be monitored Q6 hours
patency
what is a puffy swelling that occurs on either side of the tendons above the fetlock
wind puff
what is osteoarthritis of the joints of the pastern
ringbone
what is enlarged, stretched DDFT behind the cannon
bowed tendon
what is a bony growth usually on medial and distal portion of the hock
bone spavin
what is inflammation or degradation of the distal sesamoid and surrounding tissues
navicular disease
what is a soft swelling occurring on the medial part of hock
bog spavin
what is atrophy of single muscle or group of muscles
sweeney
what is inflammation of the subcutaneous bursa
capped elbow/capped hock
what are bony deposits on the upper part of the cannon
splints
what is ossification of the lateral cartilages
sidebones
what is separation of hoof wall from laminae at the white line
white line disease/seedy toe
what is failure of the interdigitation of the laminae between hoof wall and coffin bone
laminitis
what happens in laminitis cases
separation of the hoof wall laminae from the sensitive laminae, chronic cases may have slipper foot or rings on the hoof fall, heel to toe gait
what happens in cases of navicular disease
due to compression of the bone under the deep digital flexor and short pastern, toe heel gait
what non-infectious disease, secondary to any inflammatory process, would cause separation of the hoof wall and coffin bone
laminitis
what happens in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis cases
prevents muscle spasms and weakness due to sodium channel leaking, episodes tend to occur when there is lack of exercise, treatment and prevention includes exercise, get them walking and moving
what happens in Exertional Rhabdomyolysis cases
also called Monday Morning Sickness, episodes tend to occur after physical activity, treatment includes stop exercise, don’t force to walk and analgesia, severe cases can have severe muscle necrosis and myoglobinuria
what condition would cause insulin resistance, having a BCS >6; even when on diet restriction and have a cresty neck
Equine Metabolic Syndrome
what condition would cause an increase in ACTH, have a cresty neck and hirsutism (curly coat)
PPID/Cushings Disease
what happens in Choke
coughing, nasal discharge with feed particles, food lodged in esophagus
what happens in Exercise Induced Pulmonary hemorrhage (EIPH)
can see epistaxis, coughing, bronchoalveolar lavage cytology shows hemosiderin within macrophages, due to excessive negative pressure during inhalation
what happens during Recurrent Airway Obstruction
narrowing of the bronchi, tends to be triggered by allergies dust pollens, heave line, cough
what bacteria causes pigeon fever
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
what bacteria causes thrush
Fusobacterium necrophorum
what bacteria causes strangles
Streptococcus equi