Biological Bases of Behavior Flashcards
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and definitions from the lecture notes on the biological bases of behavior.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Neuropsychologists
Those who explore the relationships between brain/nervous systems and behavior; also called biological psychologists, biopsychologists, behavioral geneticists, physiological psychologists, and behavioral neuroscientists.
Lesions
Precise destruction of brain tissue, enables more systematic study of the loss of function resulting from surgical removal (also called ablation), cutting of neural connections, or destruction by chemical applications.
Computerized axial tomography (CAT or CT)
Creates a computerized image using X-rays passed through the brain to show structure and/or the extent of a lesion.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Creates more detailed computerized images using a magnetic field and pulses of radio waves that cause emission of signals that depend upon the density of tissue.
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified tracing of brain activity produced when electrodes positioned over the scalp transmit signals about the brain's electrical activity ("brain waves") to an electroencephalograph machine.
Evoked potentials
EEGs resulting from a response to a specific stimulus presented to the subject.
Positron emission tomography (PET)
Shows brain activity when radioactively tagged glucose rushes to active neurons and emits positrons.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Shows brain activity at higher resolution than the PET scan when changes in oxygen concentration near active neurons alter magnetic qualities.
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Portion of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord; includes all of the sensory and motor neurons, and subdivisions called the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Subdivision of PNS that includes motor nerves that innervate smooth (involuntary) and heart muscle. Its sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for "fight or flight"; the parasympathetic nervous system causes bodily changes for maintenance or rest.
Sympathetic nervous system
Subdivision of PNS and ANS whose stimulation results in responses that help your body deal with stressful events.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Subdivision of PNS and ANS whose stimulation calms your body following sympathetic stimulation by restoring normal body processes.
Somatic nervous system
Subdivision of PNS that includes motor nerves that stimulate skeletal (voluntary) muscles.
Spinal cord
Portion of the central nervous system below the level of the medulla.
Brain
Portion of the central nervous system above the spinal cord.
Convolutions
Folding-in and out of the cerebral cortex that increases surface area of the brain.
Contralaterality
Control of one side of your body by the other side of your brain.
Medulla oblongata
Regulates heart rhythm, blood flow, breathing rate, digestion, vomiting.
Pons
Includes portion of reticular activating system or reticular formation critical for arousal and wakefulness; sends information to and from medulla, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex.
Cerebellum
Controls posture, equilibrium, and movement.
Basal ganglia
Regulates initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture, and functions in processing of implicit memories.
Thalamus
Relays visual, auditory, taste, and somatosensory information to/from appropriate areas of cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus
Controls feeding behavior, drinking behavior, body temperature, sexual behavior, threshold for rage behavior, activation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, and secretion of hormones of the pituitary.
Amygdala
Influences emotions such as aggression, fear, and self-protective behaviors.
Hippocampus
Enables formation of new long-term memories.
Cerebral cortex
Center for higher-order processes such as thinking, planning, judgment; receives and processes sensory information and directs movement.
Association areas
Areas of the cerebral cortex that do not have specific sensory or motor functions but are involved in higher mental functions such as thinking, planning, and communicating.
Occipital lobes
Primary area for processing visual information.
Parietal lobes
Front strip is somatosensory cortex that processes sensory information including touch, temperature, and pain from body parts; association areas perceive objects.
Frontal lobes
Interpret and control emotional behaviors, make decisions, carry out plans; motor cortex strip just in front of somatosensory cortex initiates movements and integrates activities of skeletal muscles; produces speech (Broca's area).
Temporal lobes
Primary area for hearing, understanding language (Wernicke's area), understanding music/tonality, processing smell.
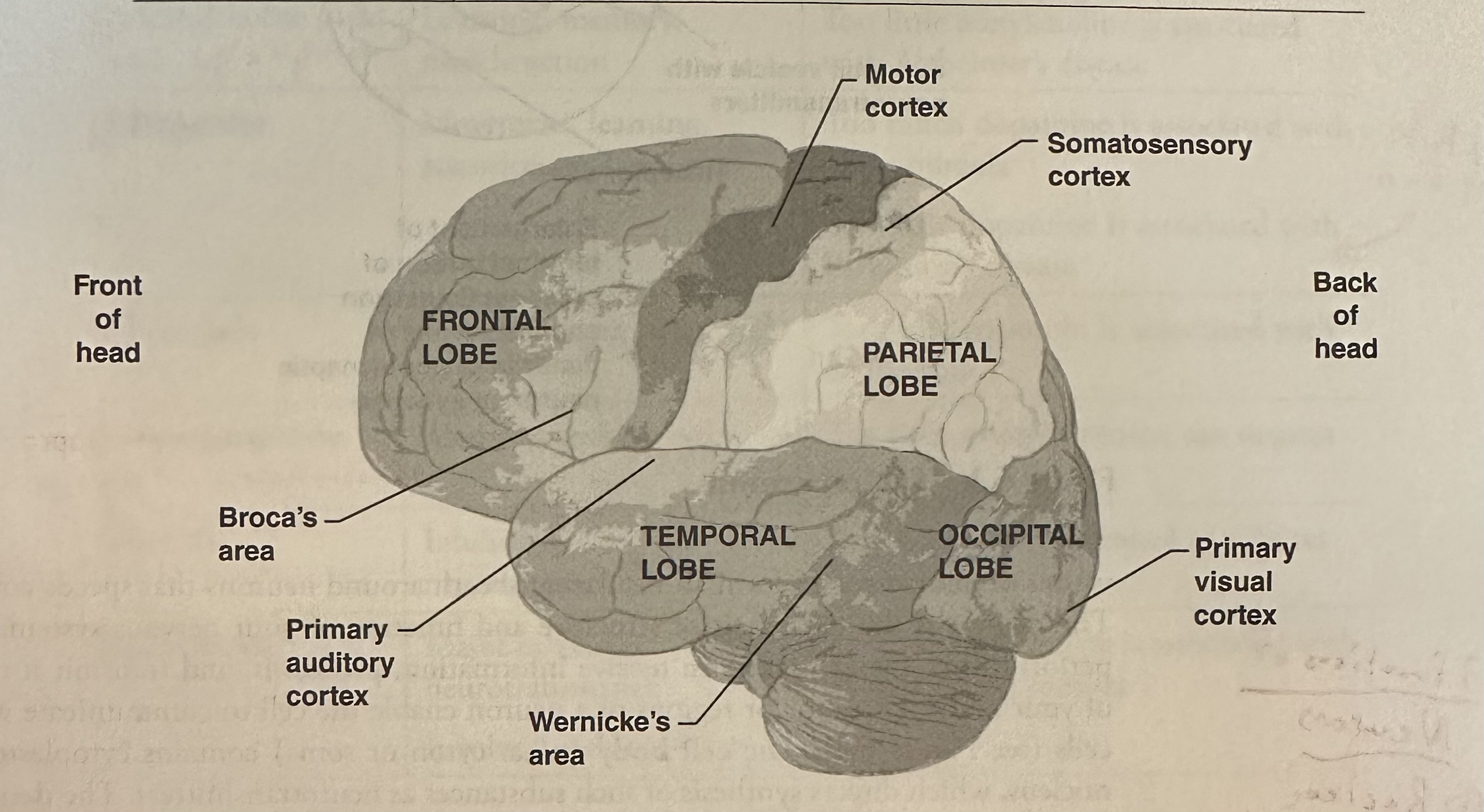
Aphasia
Impairment of the ability to understand or use language.
Glial cells
Supportive cells of the nervous system that guide the growth of developing neurons, help provide nutrition for and get rid of wastes of neurons, and form an insulating sheath around neurons that speeds conduction.
Neuron
The basic unit of structure and function of your nervous system. Neurons perform three major functions: receive information, process it, and transmit it to the rest of your body.
Cell body
Also called the cyton or soma; the part of the neuron that contains cytoplasm and the nucleus, which directs synthesis of such substances as neurotransmitters.
Dendrites
Branching tubular processes of a neuron that have receptor sites for receiving information.
Axon
A long, single conducting fiber extending from the cell body of a neuron that transmits an action potential and that branches and ends in tips called terminal buttons (a.k.a. axon terminals, or synaptic knobs), which secrete neurotransmitters.
Myelin sheath
A fatty covering of the axon made by glial cells, which speeds up conduction of the action potential.
Terminal buttons (a.k.a. axon terminals, end bulbs, or synaptic knobs)
Tips at the end of axons that secrete neurotransmitters when stimulated by the action potential.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers released by the terminal buttons of the presynaptic neuron into the synapse.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that causes contraction of skeletal muscles, helps regulate heart muscles, is involved in memory, and also transmits messages between the brain and spinal cord. A lack of ACh is associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter that stimulates the hypothalamus to synthesize hormones and affects alertness, attention, and movement. A lack of dopamine is associated with Parkinson's disease; too much is associated with schizophrenia.
Glutamate
A neurotransmitter that stimulates cells throughout the brain, but especially in the hypothalamus, and is associated with memory formation and information processing.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter associated with arousal, sleep, appetite, moods, and emotions. A lack of serotonin is associated with depression.
Endorphin
A neurotransmitter similar to the opiate morphine that relieves pain and may induce feelings of pleasure.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
A neurotransmitter that inhibits firing of postsynaptic neurons. Huntington's disease and seizures are associated with malfunctioning GABA systems.
Action potential
Also called an impulse, the "firing" of a neuron; a net flow of sodium ions into the cell that causes a rapid change in potential across the membrane when stimulation reaches threshold.
All-or-none principle
The law that the neuron either generates an action potential when the stimulation reaches threshold or doesn't fire when stimulation is below threshold. The strength of the action potential is constant whenever it occurs.
Nodes of Ranvier
Spaces between segments of myelin on the axons of neurons.
Saltatory conduction
Rapid conduction of impulses when the axon is myelinated since depolarizations jump from node (of Ranvier) to node.
Synapse
Region of communication between the transmitting presynaptic neuron and receiving postsynaptic neuron, muscle, or gland, consisting of the presynaptic terminal buttons, a tiny space, and receptor sites typically on the postsynaptic dendrites.
Excitatory neurotransmitter
Chemical secreted at terminal button that causes the neuron on the other side of the synapse to generate an action potential (to fire).
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Chemical secreted at terminal button that reduces or prevents neural impulses in the postsynaptic dendrites.
Reflex
The simplest form of behavior.
Reflex arc
The path over which the reflex travels.
Sensory receptor
Cell typically in sense organs that initiates action potentials, which then travel along sensory/afferent neurons to the CNS.
Afferent neuron
Also called sensory neuron; nerve cell in your PNS that transmits impulses from receptors to the brain or spinal cord.
Interneuron
Nerve cell in the CNS that transmits impulses between sensory and motor neurons. Neural impulses travel one way along the neuron from dendrites to axons to terminal buttons, and among neurons from the receptor to the effector.
Efferent neuron
Also called motor neuron; nerve cell in your PNS that transmits impulses from sensory or interneurons to muscle cells that contract or gland cells that secrete.
Effector
Muscle cell that contracts or gland cell that secretes.
Endocrine system
Ductless glands that typically secrete hormones directly into the blood, which help regulate body and behavioral processes.
Hormone
Chemical messenger that travels through the blood to a receptor site on a target organ.
Pineal gland
Endocrine gland in brain that produces melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythms and is associated with seasonal affective disorder.
Hypothalamus
Portion of brain part that acts as endocrine gland and produces hormones that stimulate (releasing factors) or inhibit secretion of hormones by the pituitary.
Pituitary gland (sometimes called "master gland")
Endocrine gland in brain that produces stimulating hormones, which promote secretion by other glands including TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone); ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), which stimulates the adrenal glands; FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), which stimulates egg or sperm production; ADH (antidiuretic hormone) to help retain water in your body; and HGH (human growth hormone).
Thyroid gland
Endocrine gland in neck that produces thyroxine, which stimulates and maintains metabolic activities.
Parathyroids
Endocrine glands in neck that produce parathyroid hormone, which helps maintain calcium ion level in blood necessary for normal functioning of neurons.
Adrenal glands
Endocrine glands atop kidneys.
Adrenal cortex
The outer layer-produces steroid hormones such as cortisol, which is a stress hormone.
Adrenal medulla
The core-secretes adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine), which prepare the body for "fight or flight" like the sympathetic nervous system.
Pancreas
Gland near stomach that secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar that fuels all behavioral processes. Imbalances result in diabetes and hypoglycemia.
Ovaries and testes
Gonads in females and males, respectively, that produce hormones necessary for reproduction and development of secondary sex characteristics.
Evolutionary psychologists
Study how Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection favored behaviors that contributed to survival and spread of our ancestors' genes; evolutionary psychologists look at universal behaviors shared by all people.
Behavioral geneticists
Study the role played by our genes and our environment in mental ability, emotional stability, temperament, personality, interests, etc.; they look at the causes of our individual differences.
Zygote
Fertilized egg.
Identical twins
Also called monozygotic twins; two individuals who share all the same genes/heredity because they develop from the same zygote.
Fraternal twins
Also called dizygotic twins; siblings that share about half of the same genes because they develop from two different zygotes.
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals in a population that is due to genetic causes.
Gene
Each DNA segment of a chromosome that determines a trait.
Chromosome
Structure in the nucleus of cells that contains genes determined by DNA sequences.
Turner syndrome
Females with only one X sex chromosome who are short, often sterile, and have difficulty calculating.
Klinefelter's syndrome
Males with XXY sex chromosomes.
Down syndrome
Usually with three copies of chromosome 21 in their cells, individuals typically have intellectual disability and have a round head, flat nasal bridge, protruding tongue, small round ears, a fold in the eyelid, and poor muscle tone and coordination.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an individual.
Phenotype
The expression of the genes.
Homozygous
The condition when both genes for a trait are the same.
Heterozygous
Also called hybrid; the condition when the genes for a trait are different.
Dominant gene
The gene expressed when the genes for a trait are different.
Recessive gene
The gene that is hidden or not expressed when the genes for a trait are different.
Tay-Sachs syndrome
Recessive trait that produces progressive loss of nervous function and death in a baby.
Albinism
Recessive trait that produces lack of pigment and involves quivering eyes and inability to perceive depth with both eyes.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Recessive trait that results in severe, irreversible brain damage unless the baby is fed a special diet low in phenylalanine.
Huntington's disease
Dominant gene defect that involves degeneration of the nervous system, characterized by tremors, jerky motions, blindness, and death.
Sex-linked traits
Recessive genes located on the X chromosome with no corresponding gene on the Y chromosome, which result in expression of recessive trait, more frequently in males.
Color blindness
Sex-linked trait with which individual cannot see certain colors, most often red and green.
Consciousness
Our awareness of the outside world and of ourselves, including our own mental processes, thoughts, feelings, and perceptions.
Preconscious
Level of consciousness that is outside of awareness but contains feelings and memories that can easily be brought to conscious awareness.
Unconscious (subconscious)
Level of consciousness that includes often unacceptable feelings, wishes, and thoughts not directly available to conscious awareness.