BIOL 1030 / Topic 9b: Plant Diversity - Bryophyta and Monilophyta
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psalm 104:24 (NIV): "How many are your works, Lord! In wisdom you made them all; the earth is full of your creatures."
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
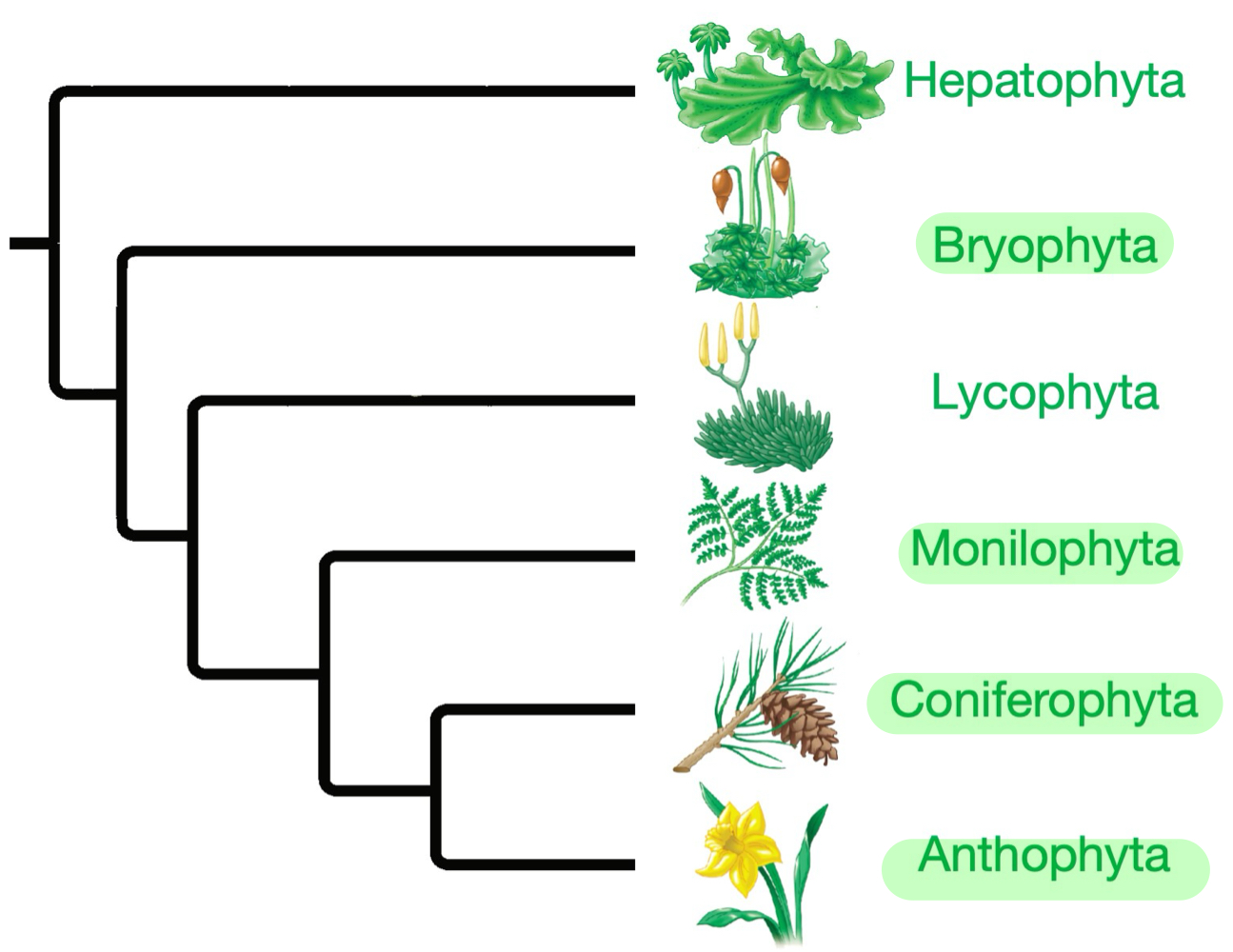
What are the three major “clades” of land plants?
Nonvascular plants (a.k.a. bryophytes), seedless vascular, seeded vascular.
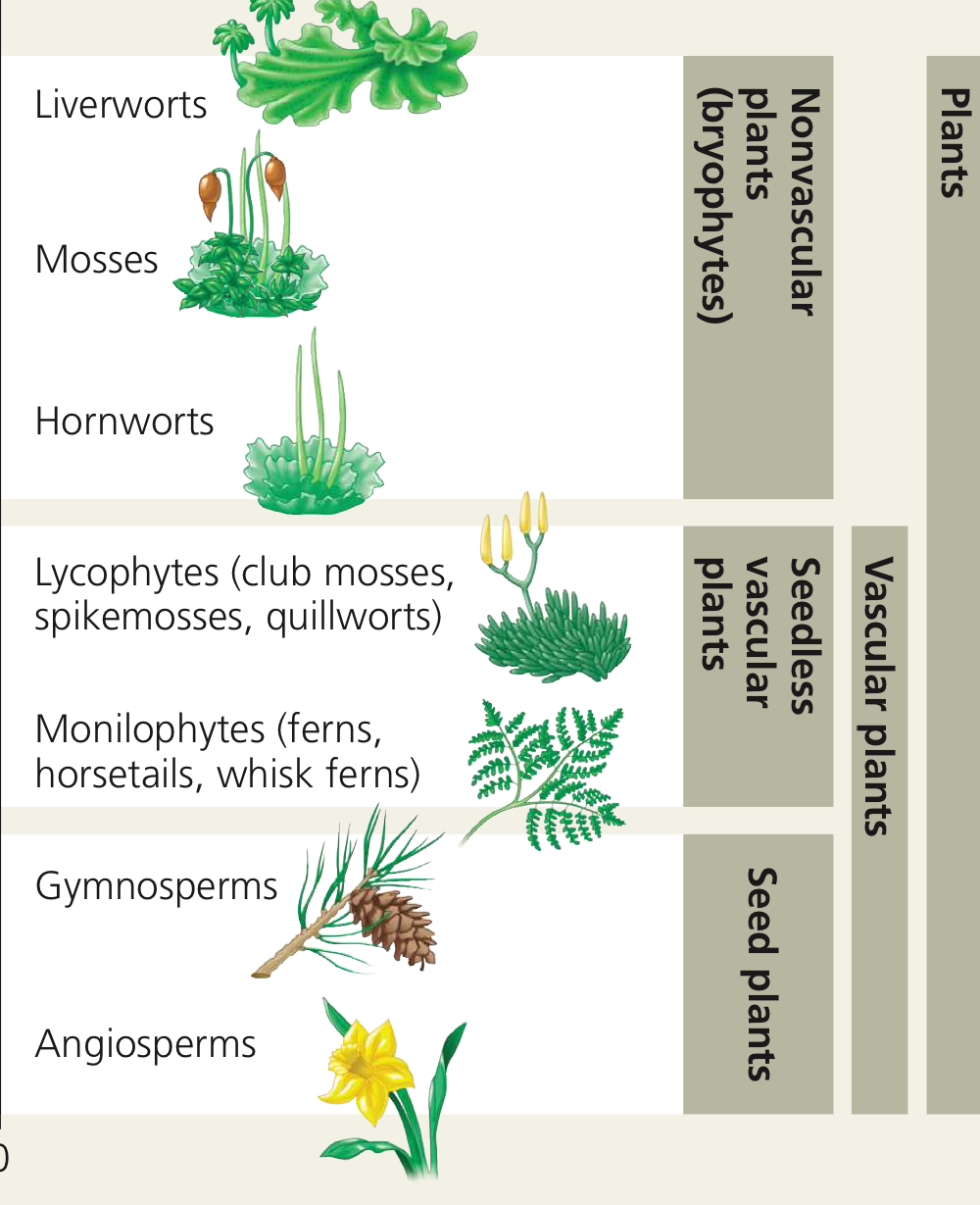
In our course together, from each “clade,” what phyla/um are we going to be discussing?
From the nonvascular plants, the phylum Bryophyta.
From the seedless vascular plants, the phylum Monilophyta.
From the seeded vascular plants, the phyla Coniferophyta and Anthophyta.
Root
Organ absorbing water and nutrients from soil.
Stem
Organ conducting water, minerals, and nutrients throughout vascular plant.
Leaves
Organ serving as photosynthetic organ of vascular plant.
What does a dominant body plan mean?
A dominant body plan is typically the larger and longer-living body out of the two body plans.
Homosporous plant
A plant producing spores of the same size.
Heterosporous plant
A plant producing spores of different sizes.
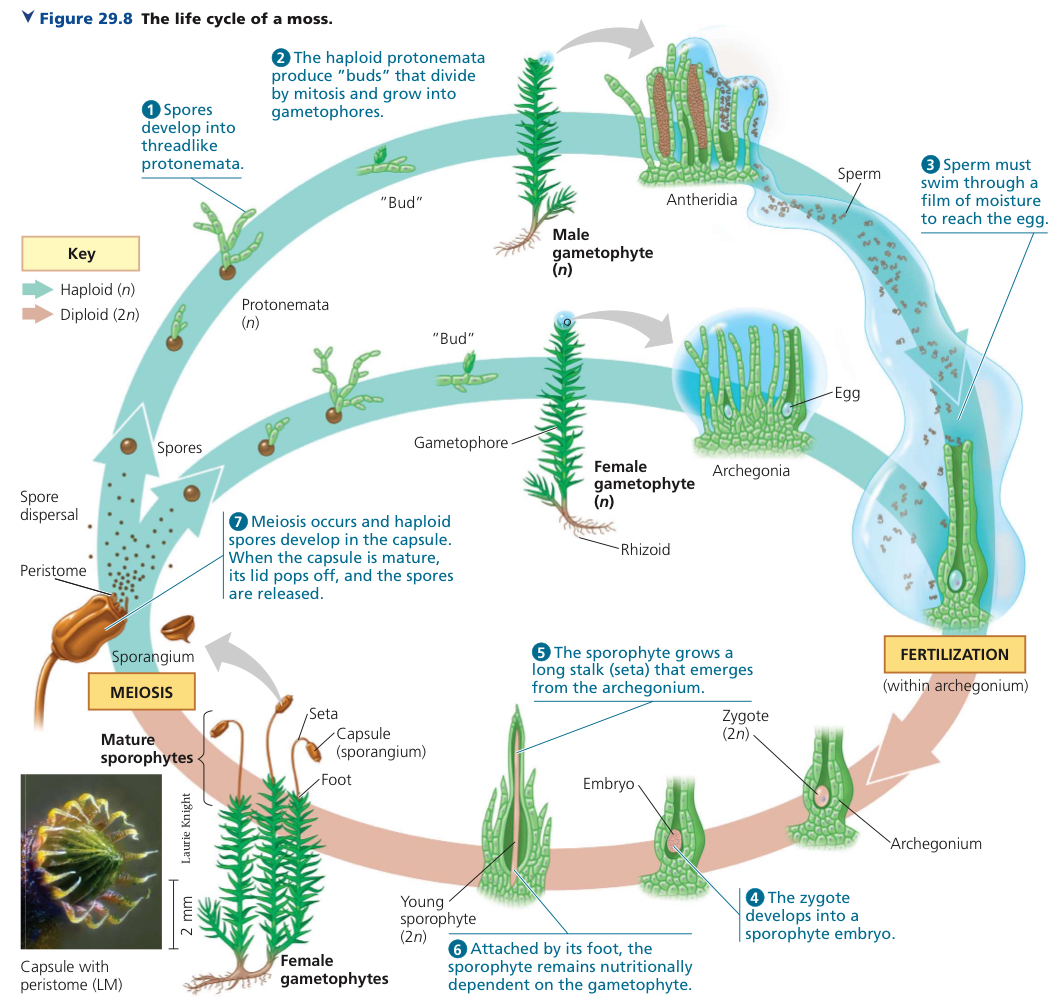
Phylum Bryophyta
Non-vascular plants that include mosses.
What is the dominant generation of Bryophyta?
Gametophyte.
What is the gametophyte structure like in Bryophyta?
In a thallus level of organization, relatively large in size, nutritionally independent, and dioecious.
How is gamete transfer done in Bryophyta?
Through a thin film of water.
What is the sporophyte structure like in Bryophyta?
Nutritionally dependent, relatively small in size.
Is Bryophyta homosporous or heterosporous?
Homosporous.
For Bryophyta, does it have organs? Does it have vascular tissue? Does it have seeds? Does it undergo pollination?
No, it doesn’t have organs.
No, it doesn’t have vascular tissue.
No, it doesn’t have seeds.
No, it doesn’t undergo pollination.
What are the two major parts on the moss gametophyte?
Protonema and gametophores.
Protonema
A mass of green, branched, one-cell-thick filaments, having a large surface area that enhances absorption of water and minerals.
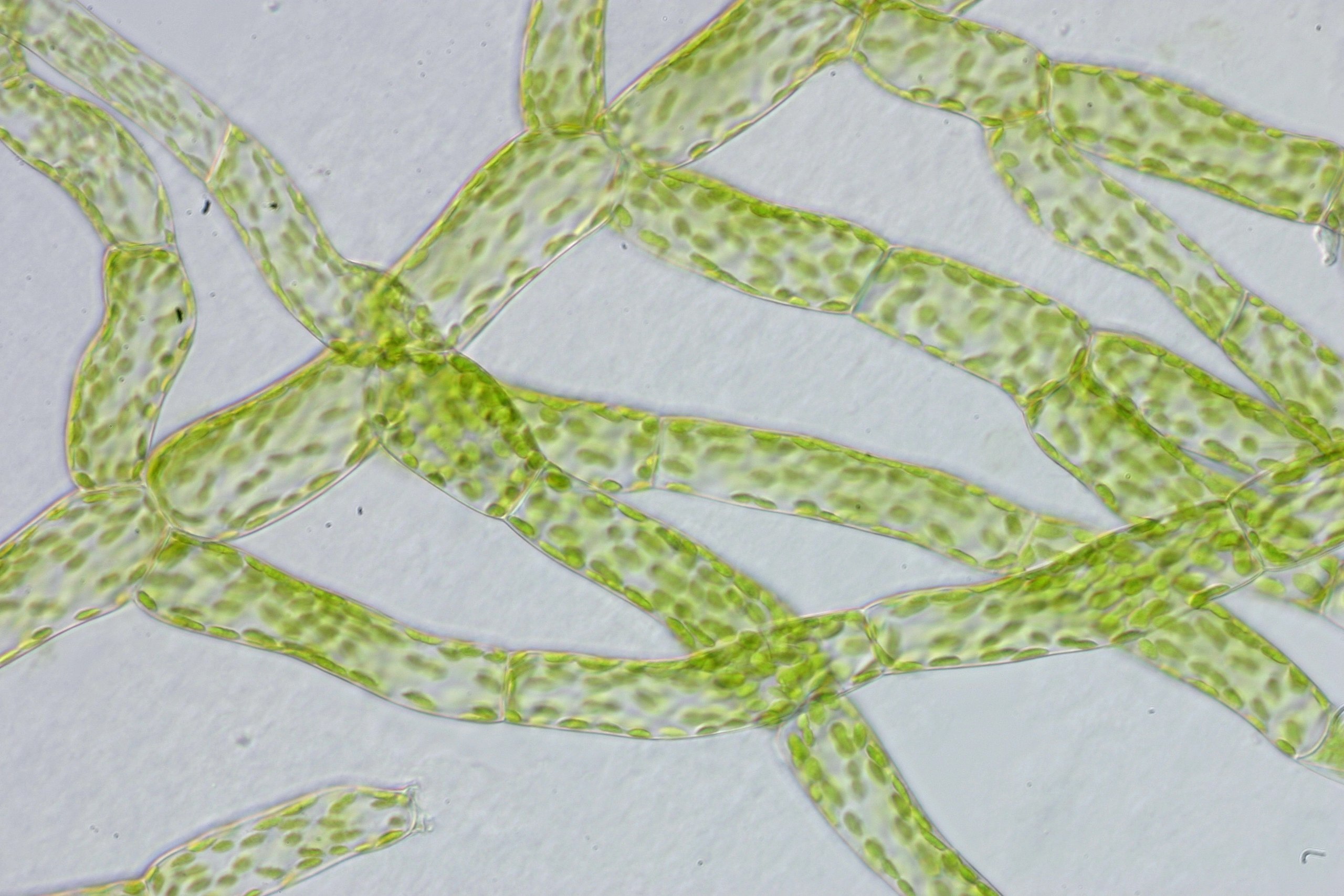
When does the protonema grow?
When bryophyte spores germinate.
What does a protonema produce?
Bud-like structures.
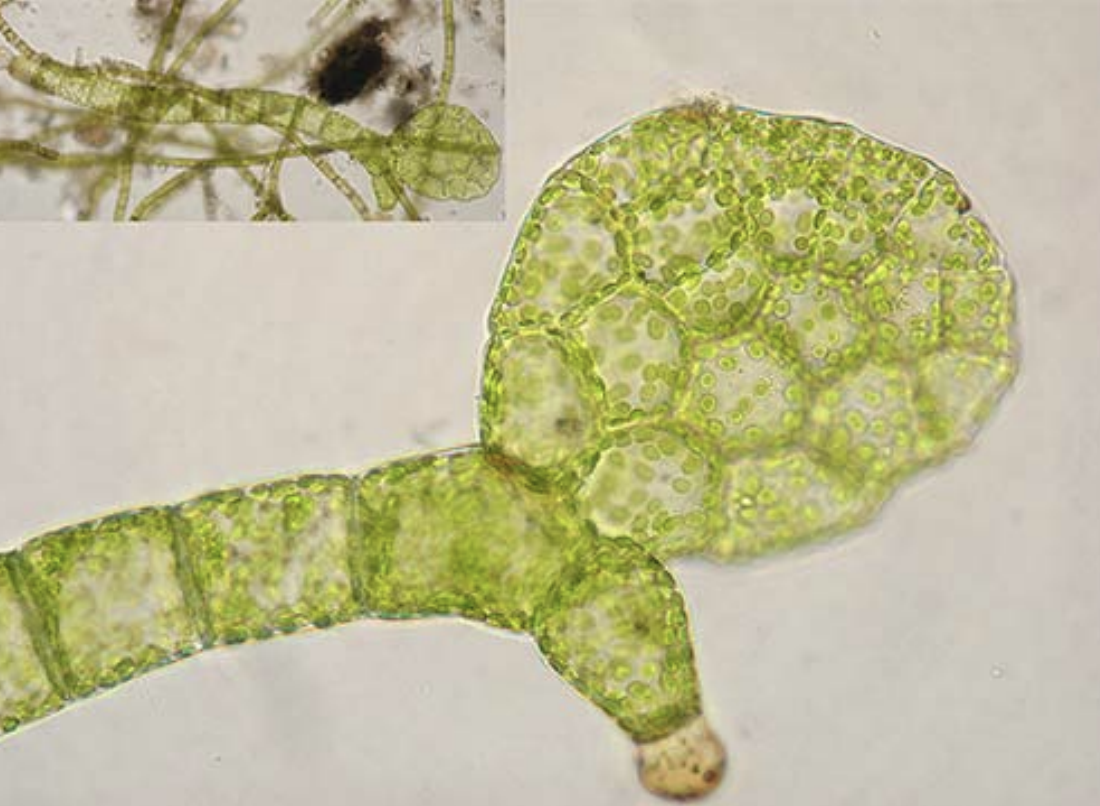

What is the role of bud-like structures in Bryophyta?
Each of these bud-like structures produce a structure housing the gametangia, called the gametophore.
Rhizoids
Filaments of cells anchoring moss gametophyte to the ground, acting like roots.
Where would you usually find moss gametophytes, and why?
In moist habitats, because sperm requires film of water to reach eggs.
Embedded in the archegonium of the moss gametophyte, what are the three major parts of the moss sporophyte?
The foot, the seta, and the capsule.
Moss foot
The structure absorbing nutrients from the gametophyte.
Moss setae
Also called the stalks, they conduct nutrients to the sporangium.
Moss capsule
The sporangium of the moss sporophyte.
Enumerate ‘n’ explain the life cycle of mosses.
Spore germination into dioecious gametophyte.
Gametogenesis.
Gamete transfer and fertilization.
Zygote development.
Sporophyte development.
Sporogenesis. When the capsule is mature, its lid pops off, and the spores are released.
What are the two specific adaptations that allowed plant evolution and movement into land?
Epidermal secretions, i.e. dermal tissue and waxy cuticle.
Transport tissue, i.e. vascular tissue.
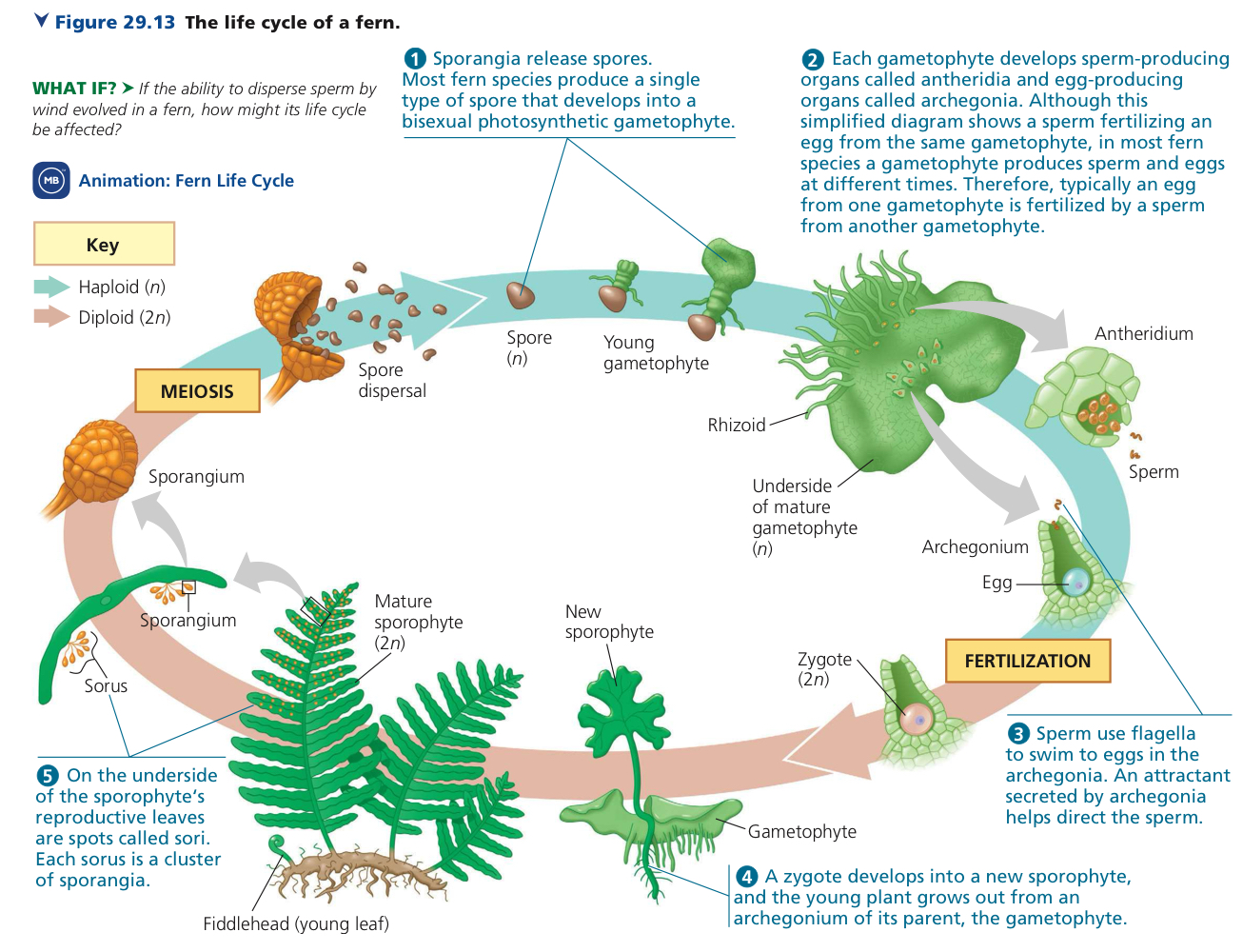
Phylum Monilophyta
Seedless vascular plants including the ferns, whisk ferns, and horsetails.
What is the dominant generation of Monilophyta?
Sporophyte.
What is the gametophyte structure like in Monilophyta?
It has a thallus level of organization, relatively small in size, and mostly hermaphroditic, with males in some species.
What is the sporophyte structure like in Monilophyta?
TBA.
How is gamete transfer done in Monilophyta?
Through thin film of water.
What is the sporophyte structure like in Monilophyta?
TBA.
Is Monilophyta homosporous or heterosporous?
Homosporous.
For Monilophyta, does it have organs? Does it have vascular tissue? Does it have seeds? Does it undergo pollination?
TBA on organs.
Yes, it has vascular tissue.
No, it doesn’t have seeds.
No, it doesn’t undergo pollination.
Rhizome
Underground stem of a fern.
Fronds
Mature, fully expanded leaf of a fern.
Fiddlehead
Young, tightly coiled frond of a fern.
Sporophyll
Modified fronds that have sporangia.
Annulus
Specialized ring of cells on the wall of an individual sporangium.
Sori
Clusters of sporangia.
Indusium
Protective covering over sori.
Enumerate ‘n’ explain the life cycle of ferns.
Spore germination into monoecious gametophyte.
Gametogenesis.
Gamete transfer and fertilization.
Zygote development.
Sporophyte development.
Sporogenesis.