FAD - Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is Biopharmaceutics and why is it important for pharmaceutical science?
- Biopharmaceutics studies the relationship of physicochemical properties of a drug and the biological performance of the drug product
- Biopharmaceutics is important for producing an optimum formulation, route of administration and determining effects of the drug product
What is Bioavailability and why is it important for pharmaceutical science?
- Bioavailability is the description and indication of the rate and extent of API that becomes therapeutically available at the site of action (rate of uptake + amount of uptake)
- Bioavailability acts as a key indicator of performance and efficiency of a formulation (eg. drug release is slower than intended, its a poor formulation)
What is Pharmacokinetics?
- Pharmacokinetic describes the effect the body has on an API, and a PK profile is displayed as a graph of plasma-concentration against time
- The graph can give information on all, if not most, PK factors (ADME)
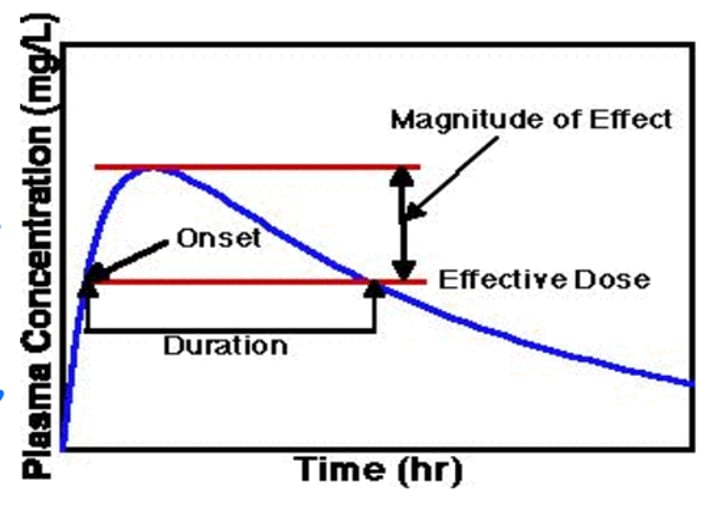
What information can a Pharmacokinetic study provide clinically?
- A PK profile can be used to determine the MSC (Maximum safe concentration) and MEC (Minimum effective concentration)
- The above can then be used to determine a dosing regimen (via the therapeutic window), effects of accumulation (systemic, active site and metabolite) and bioavailability
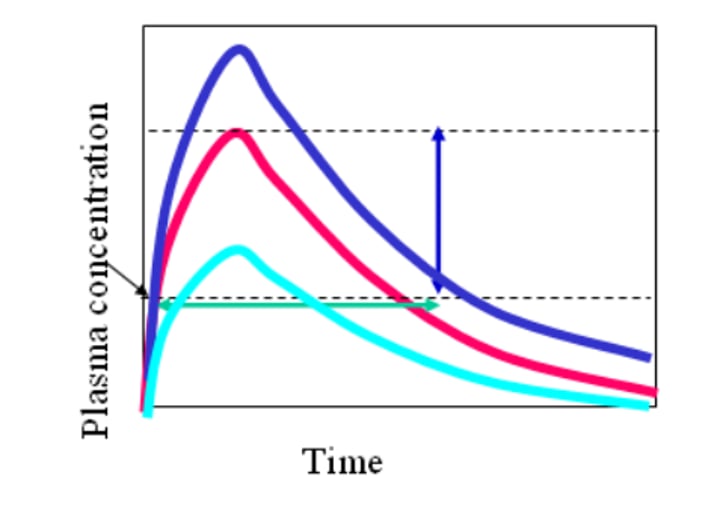
How is Bioavailability quantified?
- Cpmax (max plasma concentration) and Tmax (time to reach max) are used to determine the rate, for the absorption phase in non IV drugs
- AUC (area under curve) is used to determine the extent, for the total amount of drug in the body
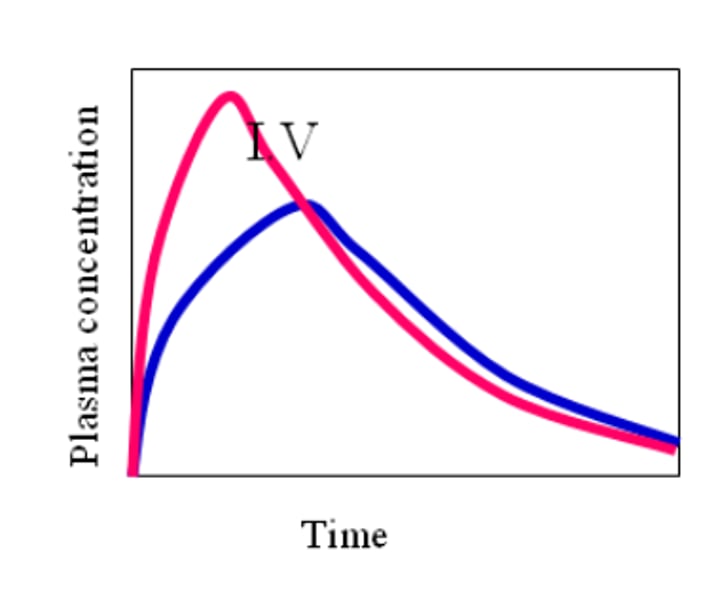
What is Absolute and Relative Bioavailability?
- Absolute bioavailability is a fraction of the administered dose that reaches systemic circulation (usually compared to IV as IV has 100% bioavailability)
- F = AUCev / AUCiv or F = (AUCev/DOSEev) / (AUCiv/DOSEiv)
- Relative bioavailability is a fraction of the administered dose reaching systemic circulation, compared to another formulation of the same drug
What factors affect Bioavailability in patients?
- Age, sex and weight
- Diseases or medical conditions
- Gastrointestinal properties like emptying rate, pH variations, motility, etc
- Food, Fluids and other drugs
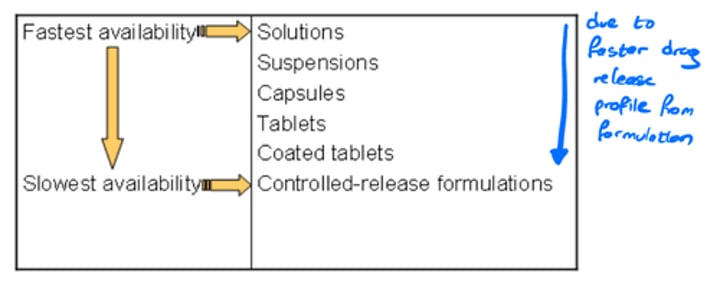
What factors affect Bioavailability in formulations?
- Formulations where drug is most available has the fastest availability (eg. solutions, while lowest availability has the slowest availability (eg. controlled-release)
- Excipient and drug properties that improve the drug release profile or reduce drug release impedance have greater bioavailability
What is Bioequivalence?
- Bioequivalence is when two drug products (same API + formulation) have similar bioavailability (not significantly different) when given the same molar dose and studied in similar conditions (eg. generic vs branded API)
- To be determined bioequivalent, the PK profiles need to be similar, but can't match exactly, and AUC/Cmax needs to be within 80-125%
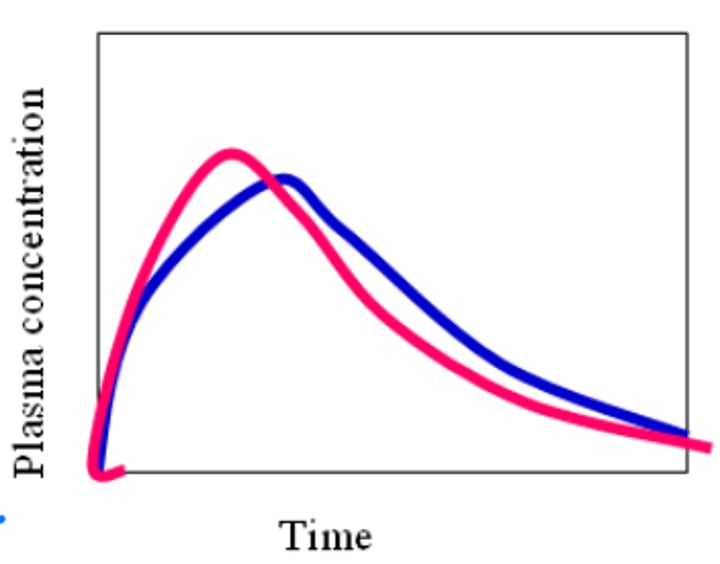
How is Bioequivalence determined?
- Bioequivalence can be determined by directly using an In-Vivo test on PK in humans, or correlating one to the below
- In-vitro test (with or without a known IVIVC (In-vivo-in-vitro-correlation))
- In-vivo test on animals
- in-vivo test on human urinary metabolites