BIO 200 Lecture 6 (What Mendel Didn't Know: Genetics)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA and proteins that carry genetic information
implications of paired chromosomes
chromosomes come in homologous pairs (one from each parent), allowing for recombination and independent assortment
human chromosome counts
23 pairs, 46 chromosomes
karyotypes
picture/map of all chromosomes in a cell, arranged in homologous pairs
chromatids
identical copies of a duplicated chromosome, joined at the centromere
sister chromatids
the two identical chromatids of a duplicated chromosome
centromere
the region where sister chromatids are joined
spindle fibers attach here during division
homologous pair
two chromosomes (one maternal, one paternal) with the same genes but possibly different alleles
basics of mitosis and meiosis
mitosis: produces identical cells for growth and repair
meiosis: produces gametes (sperm/egg) with half the chromosome number
cell outcomes of mitosis and meiosis
mitosis: 2 identical diploid cells
meiosis: 4 unique haploid cells
basic differences between mitosis and meiosis
mitosis: one division, no crossing over, identical cells
meiosis: two divisions, crossing over, genetic variation
ploidy
number of copies of chromosomes:
haploid (1N)
diploid (2N)
polyploid (>2N)
sex chromosomes
chromosomes that determine sec (X and Y in humans)
crossing over/recombination
exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, increasing variation
how chromosomes explain gene linkage
genes close together on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together
how recombination eliminates gene linkage
crossing over can separate linked genes, creating new allele combinations
basics of DNA structure
DNA is a double helix with a sugar-phosphate backbone and paired bases (A-T, C-G)
nucleotides
DNA building blocks: sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base (A, T, C, G)
Adanine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
how does DNA replicate
semi-conservative process: each new DNA molecule has one old strand and one new strand, guided by DNA polymerase
the central dogma
flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → protein
transcription and translation
transcription: DNA → RNA (in nucleus)
translation: RNA → protein (at ribosome)
how are proteins formed?
chains of amino acids assembled by ribosomes according to RNA instructions
can you go from DNA sequence to protein?
not directly from DNA to protein, but DNA codes for RNA, and RNA codons direct amino acid sequence
codons and using the amino acid table
a codon = 3 nucleotides coding for 1 amino acid. The amino acid table helps decode RNA sequences
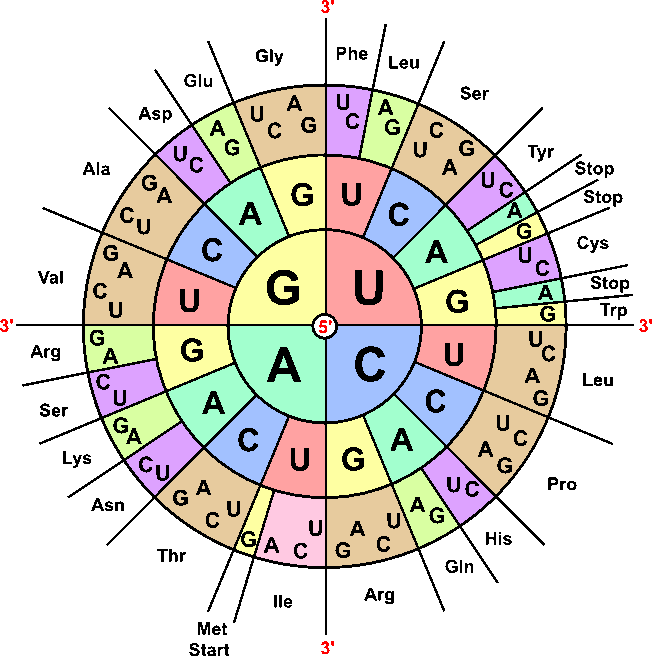
what do comparisons of protein sequences or DNA tell us about organism relatedness?
species with more similar DNA/protein sequences are more closely related evolutionarily
Watson and Crick
scientists who described the double-helix structure of DNA in 1953