Greek Religion (OCR A-Level): Religious Sanctuaries
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
Since the 16th century...
...the Acropolis had been the religious heart of Athens.
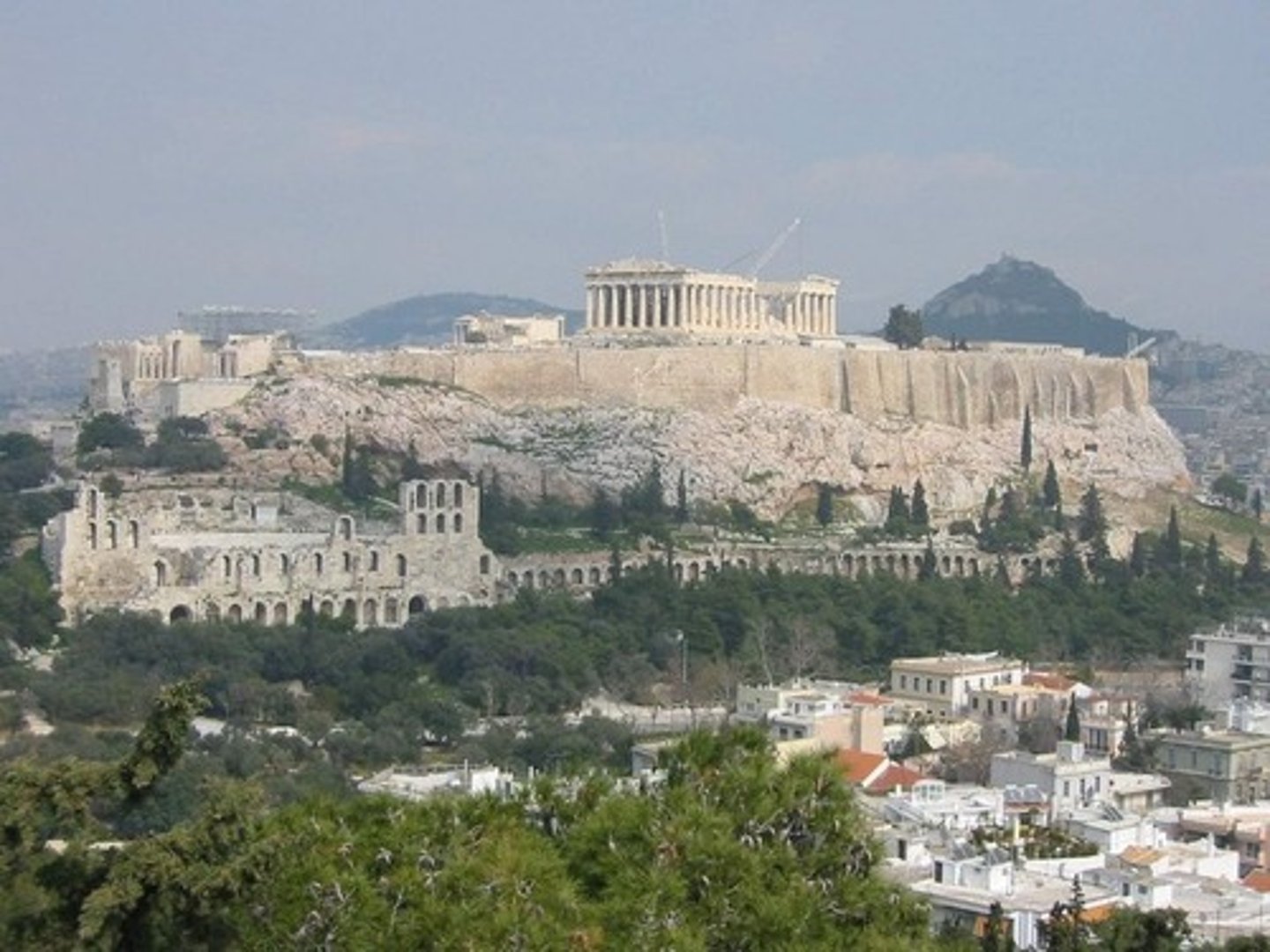

What has been found dating to 6th Century BC?
Votive offerings, mainly to Athena.
An early temple was destroyed by who and when?
The Persian Empire in 480 BC.
Name the 4 main buildings on the Acropolis.
- The Temple of Athena Nike.
- The Parthenon.
- The Propylaia.
- The Erechtheion.
Between what years was the Parthenon built?
447 - 432 BC.
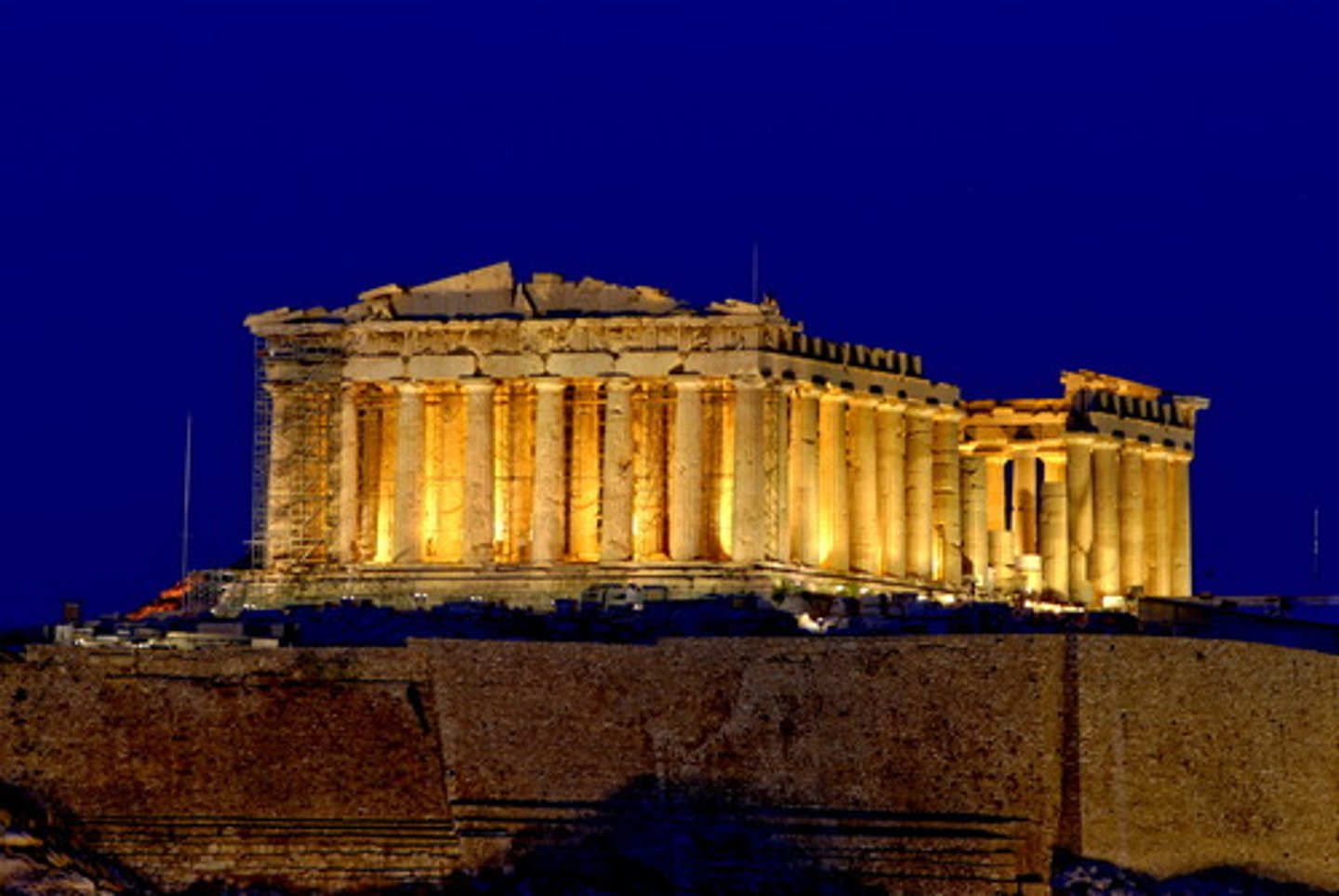

What was the Parthenon made of?
Marble.
What was housed inside the Parthenon?
A gold and ivory (chryselephantine) statue of Athena by Pheidias (a skilled sculpter).

Why do people challenge the idea that the Parthenon is a religious building?
- No altar found with it.
- No record of any dedicated priests/priestesses decades after construction.
- Backroom is unusually big.
- Contained large amounts of gold and silver.

How many columns were on the Parthenon?
8 x 17 columns.
What style was the Parthenon built in?
A mixture of styles, both doric and ionic.
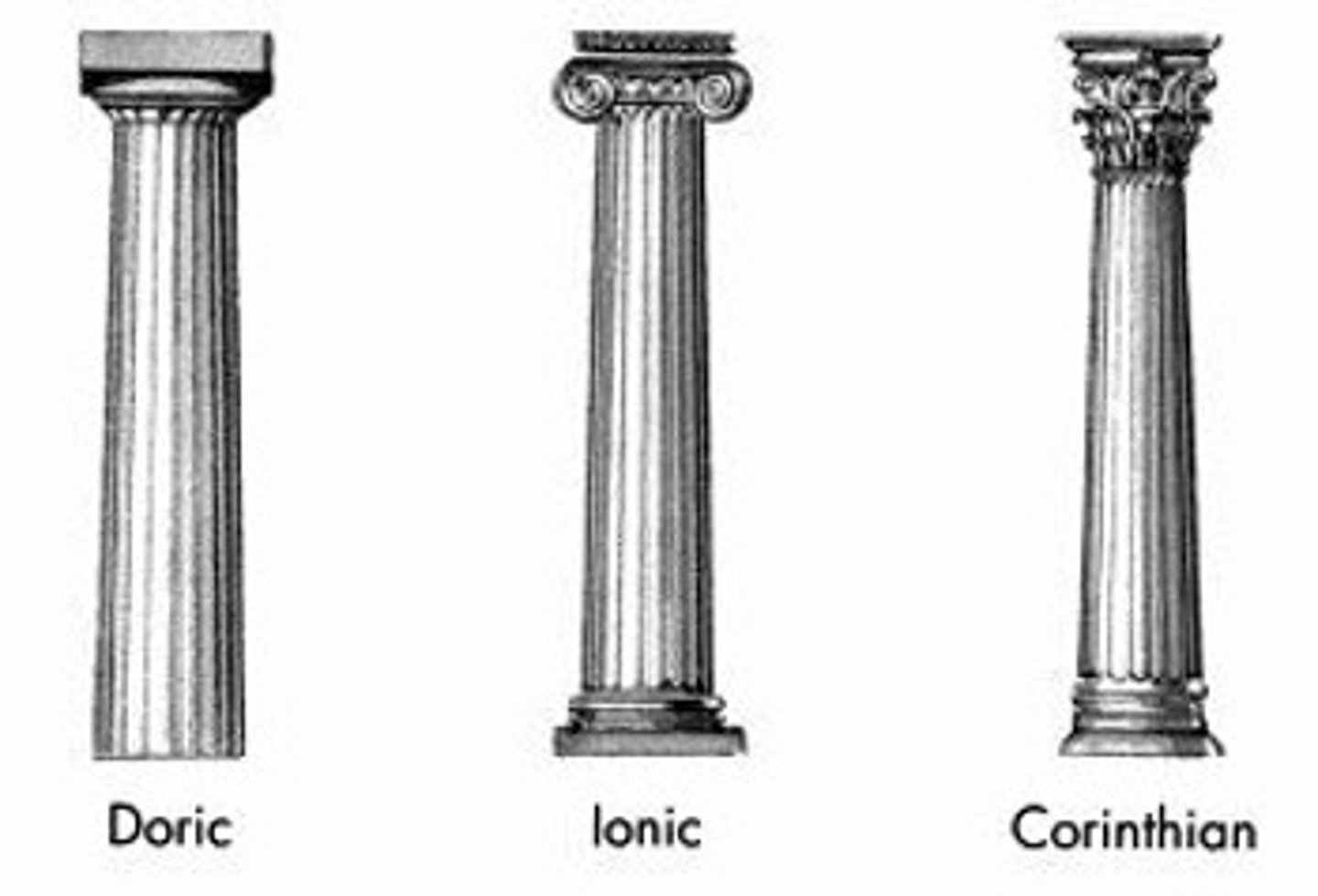
What ratio were things built in?
9:4 ratio (length/width, distance between the columns/diameter of the columns, width/height of the front rectangle).
How did the Greeks counter the illusion that the columns looked wider at the top?
Columns taper upwards.
How did the Greeks counter the illusion that the columns looked like they were falling towards you?
Columns lean slightly inwards.
How did the Greeks counter the illusion that the floor dips?
Floor curves slightly upwards.
The Parthenon would've been brightly...
...painted.

What does the East pediment show?
The Birth of Athena.

Describe the East pediment.
- Armour pinned on.
-Designed carefully (so scene fits in).
- Athena in centre.
- All other Gods present.
- Born from Zeus' head fully armed.
What does the West pediment show?
Contest between Athena and Poseidon.
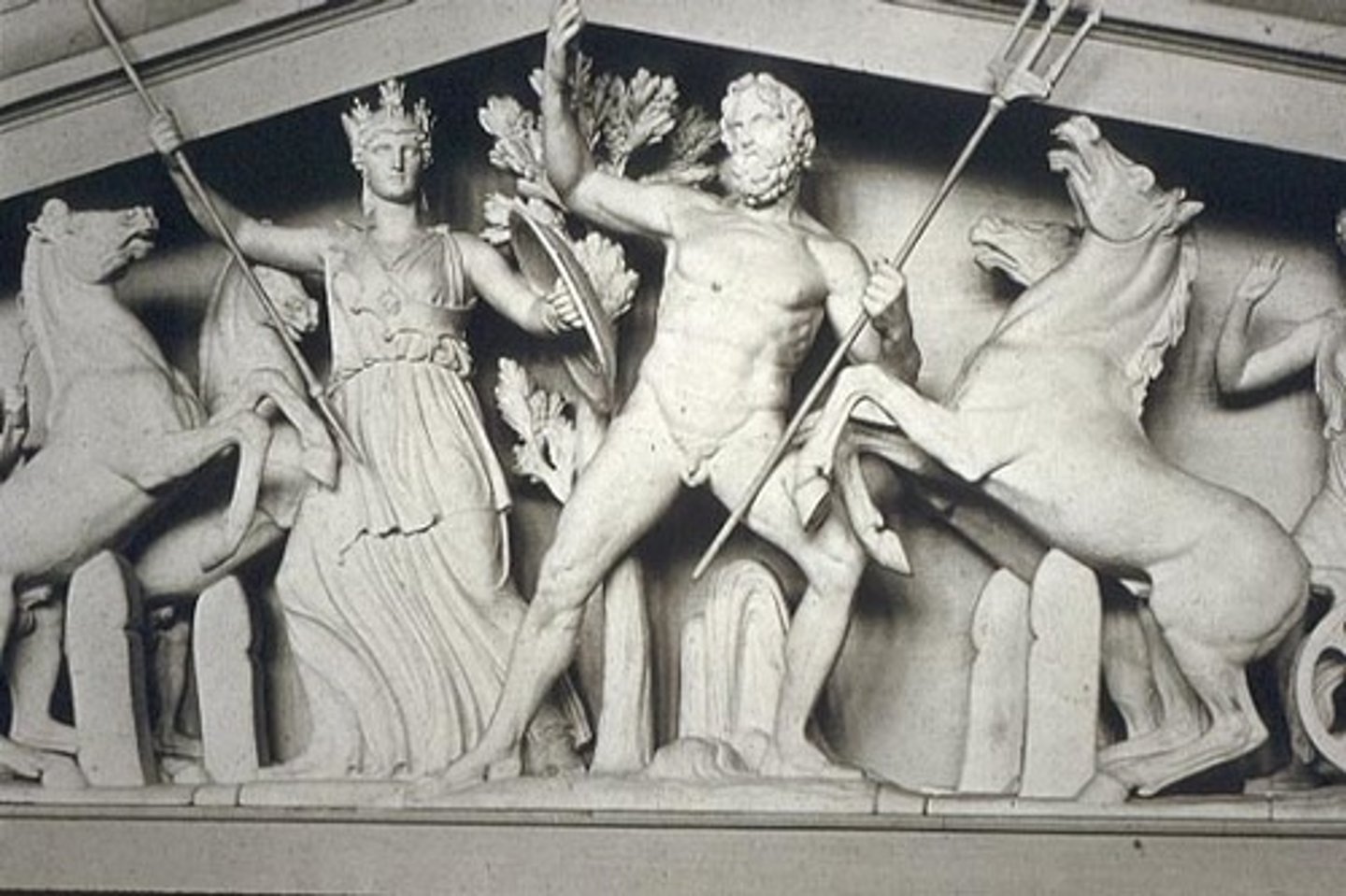

Describe the West pediment.
- Athena (becomes patron through gift of an olive tree).
- Poseidon still important (navy/gift of salt water).
How many metopes are on the Parthenon?
14 x 32 metopes.
What is shown on the East metopes?
Gigantomachy (Gods vs Titans).
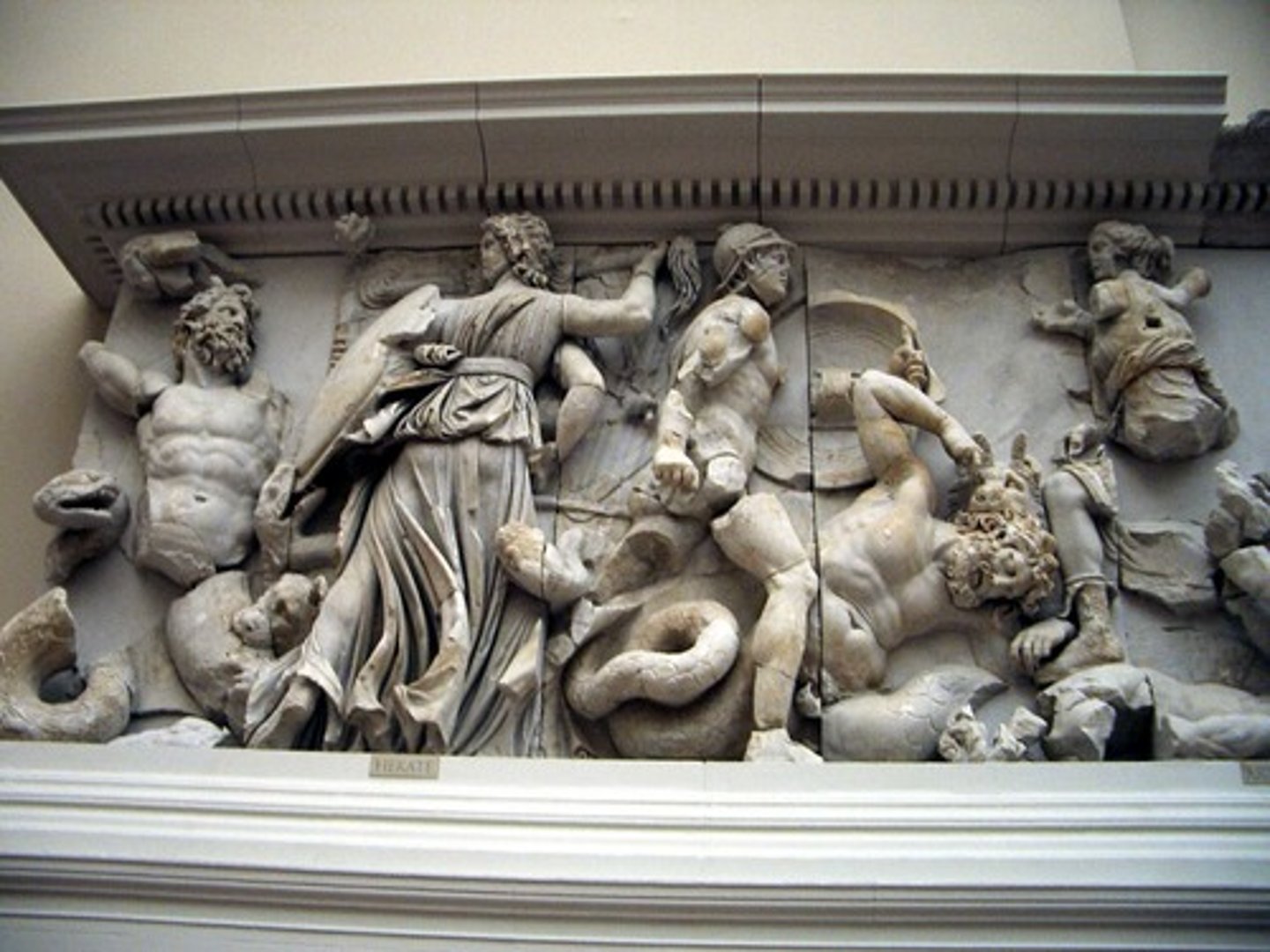

What is shown on the West metopes?
Amazonomachy (Men vs Amazonian women).

What is shown on the North metopes?
Sack of Troy (Greeks vs Trojans).
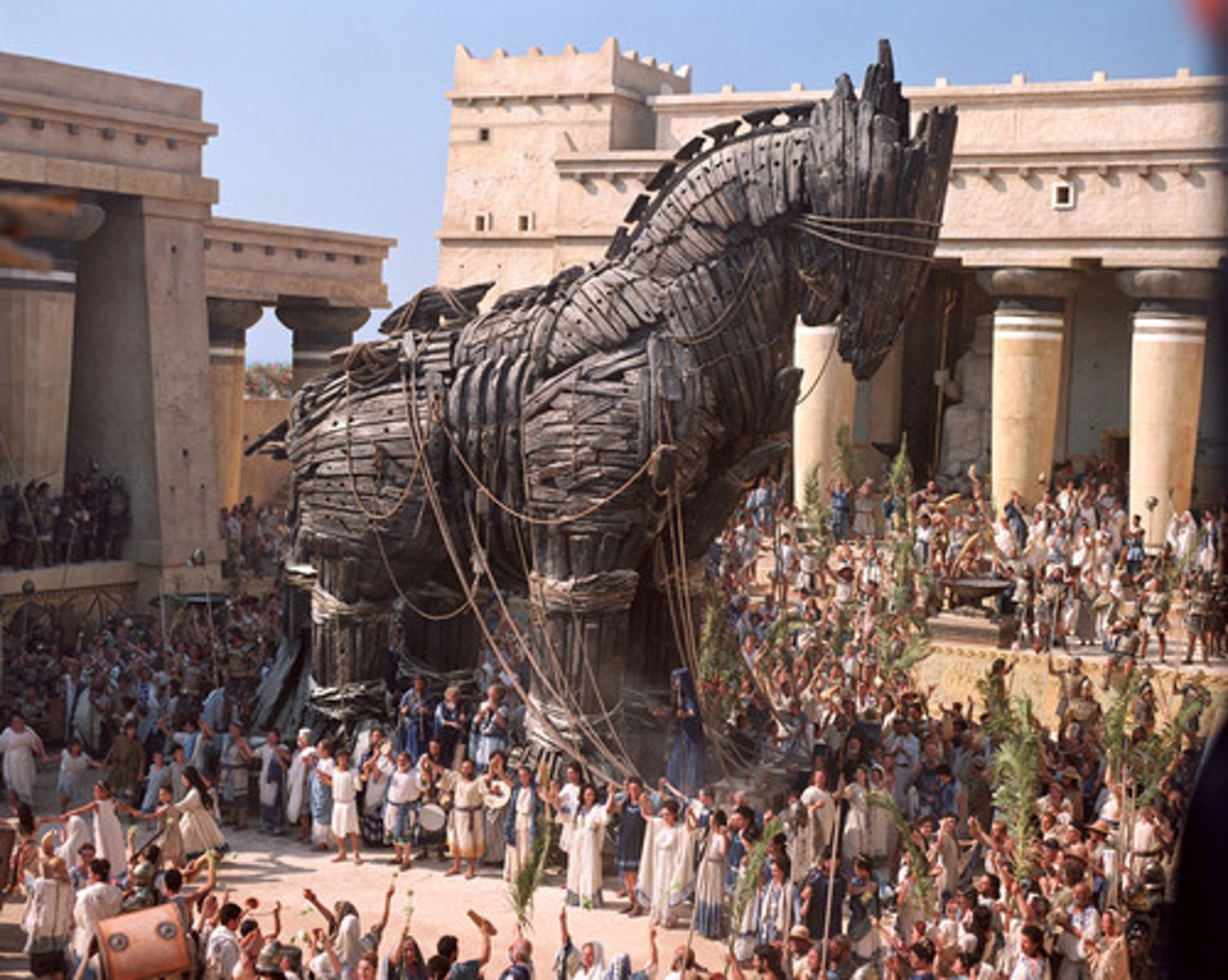

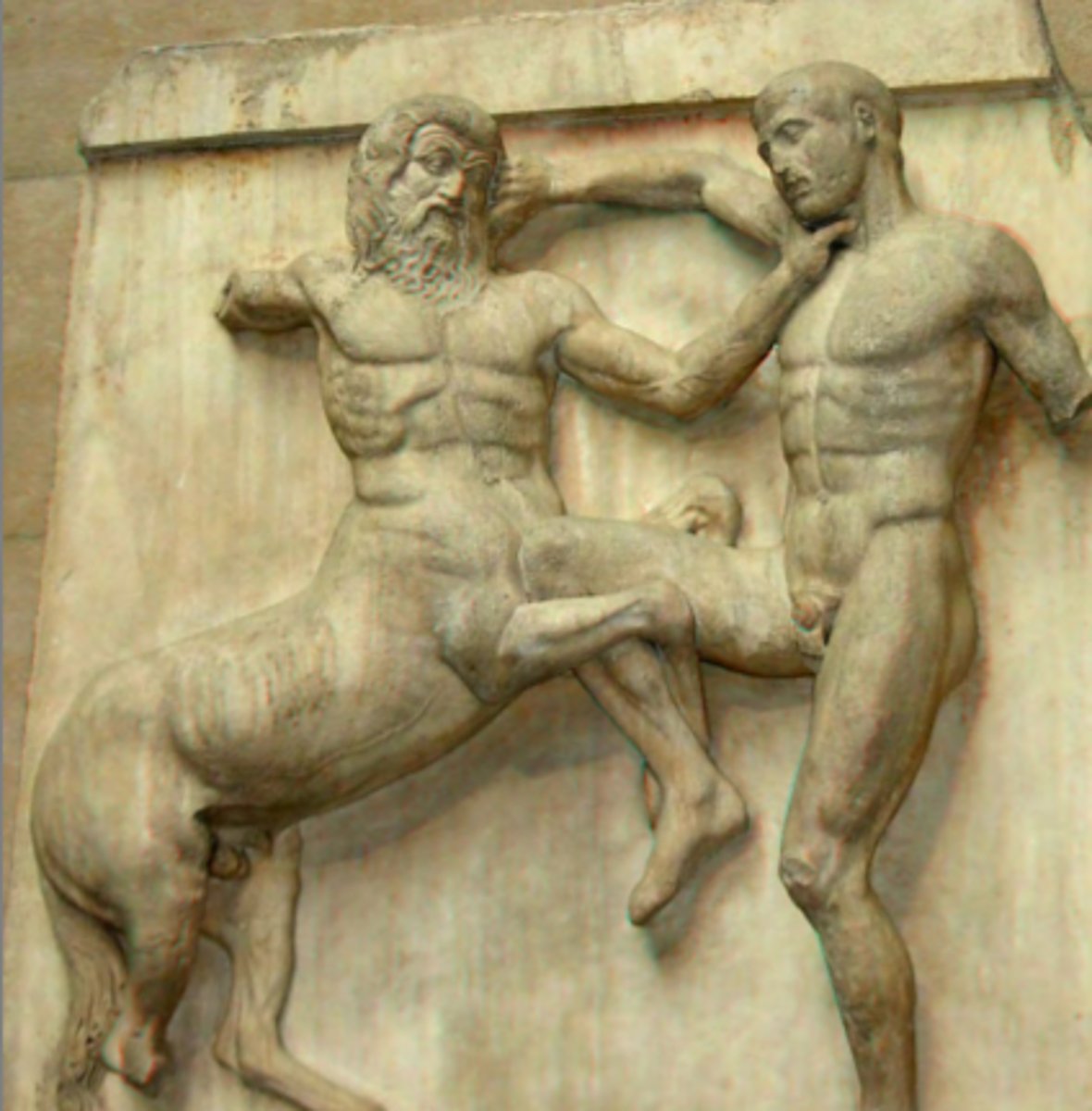
What is shown on the South metopes?
Centauromachy (Centaurs vs Lapiths).

What festival does the frieze show?
The Panathenaea.
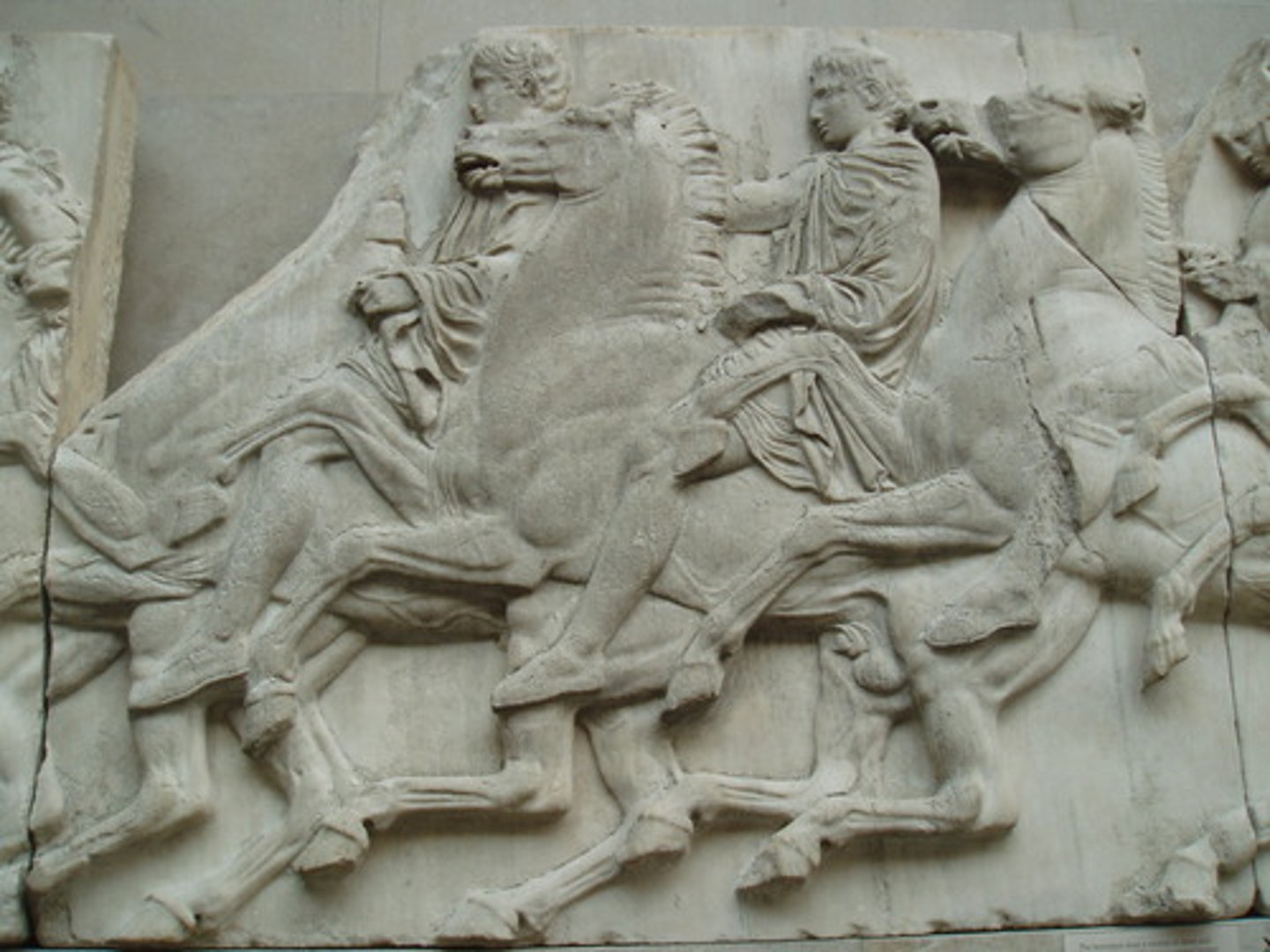

What does the East side of the frieze show?
Girls with offering bowls either side with the gods and the handing over of the peplos in the middle.
What does the West side of the frieze show?
Horsemen preparing for the procession.
What does the North side of the frieze show?
Gods and mortals celebrating Athens and Athena.
What does the South side of the frieze show?
Similar to the North but includes musicians.
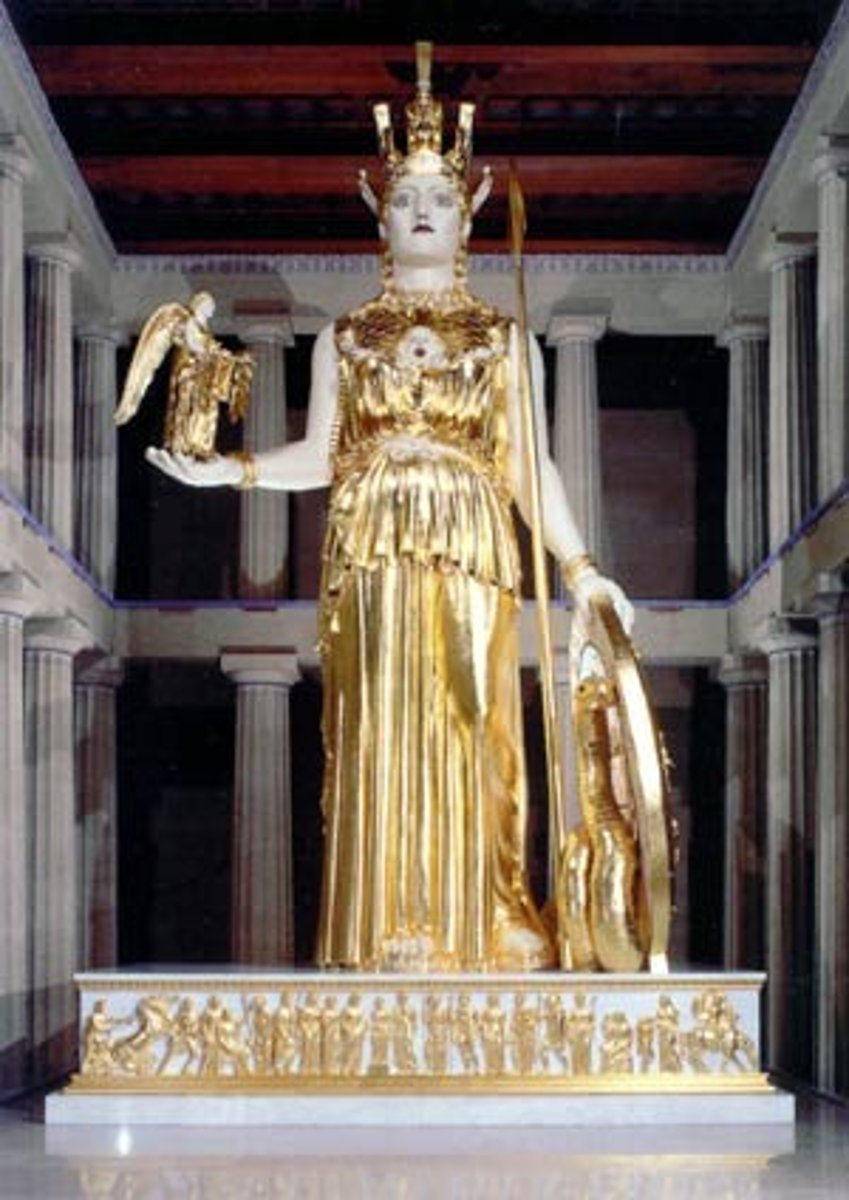
What is the statue inside of the Parthenon called?
The Statue of Athena Parthenos.
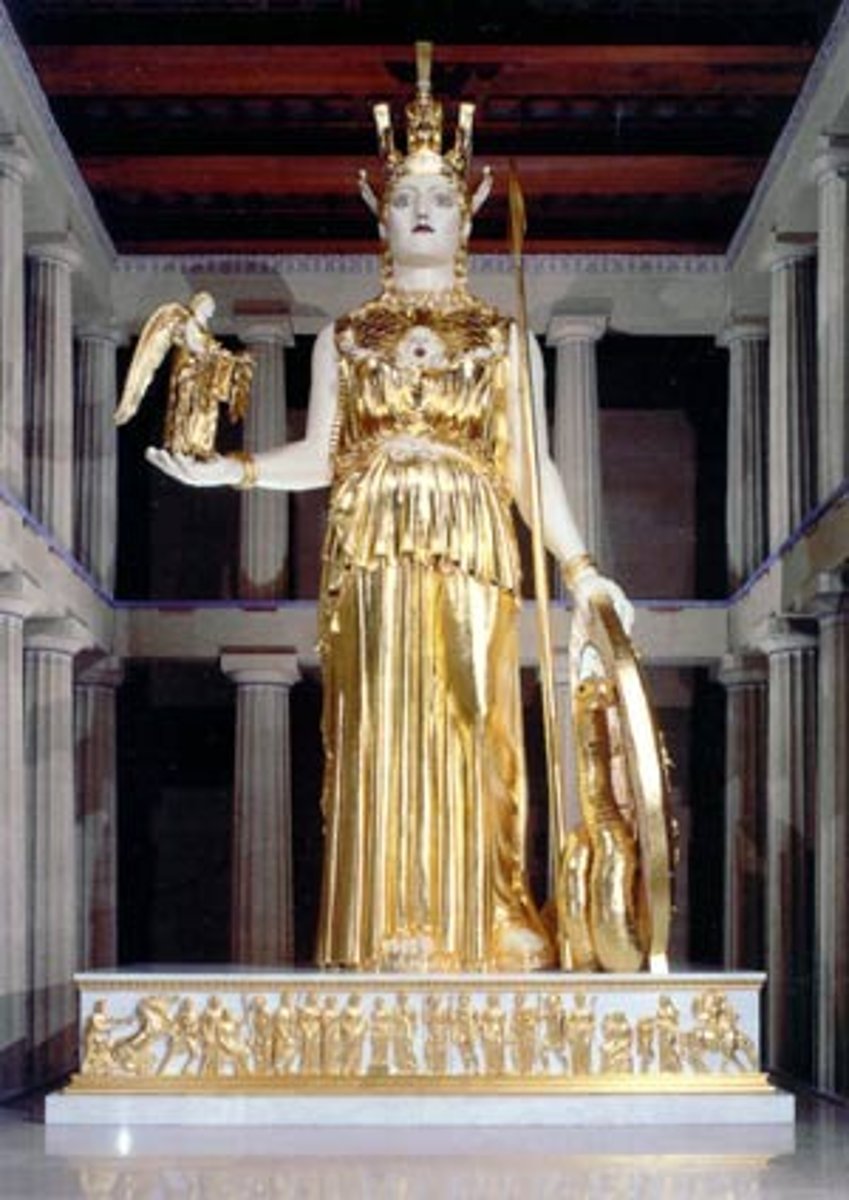

How do we know about the statue?
A man called Pausanius wrote about it. It was destroyed by hordes.

What was the statue made of?
Gold and ivory (chryselephantine).

How tall was the statue?
About 10 metres tall.
What is the statue holding in it's right hand?
Nike.

What does the shield depict?
Amazonomachy and Gigantomachy.
What do the sandals depict?
Centauromachy.
The Erechtheion was the most...
...sacred spot on the Acropolis (Poseidon and Athena fought for patronage).
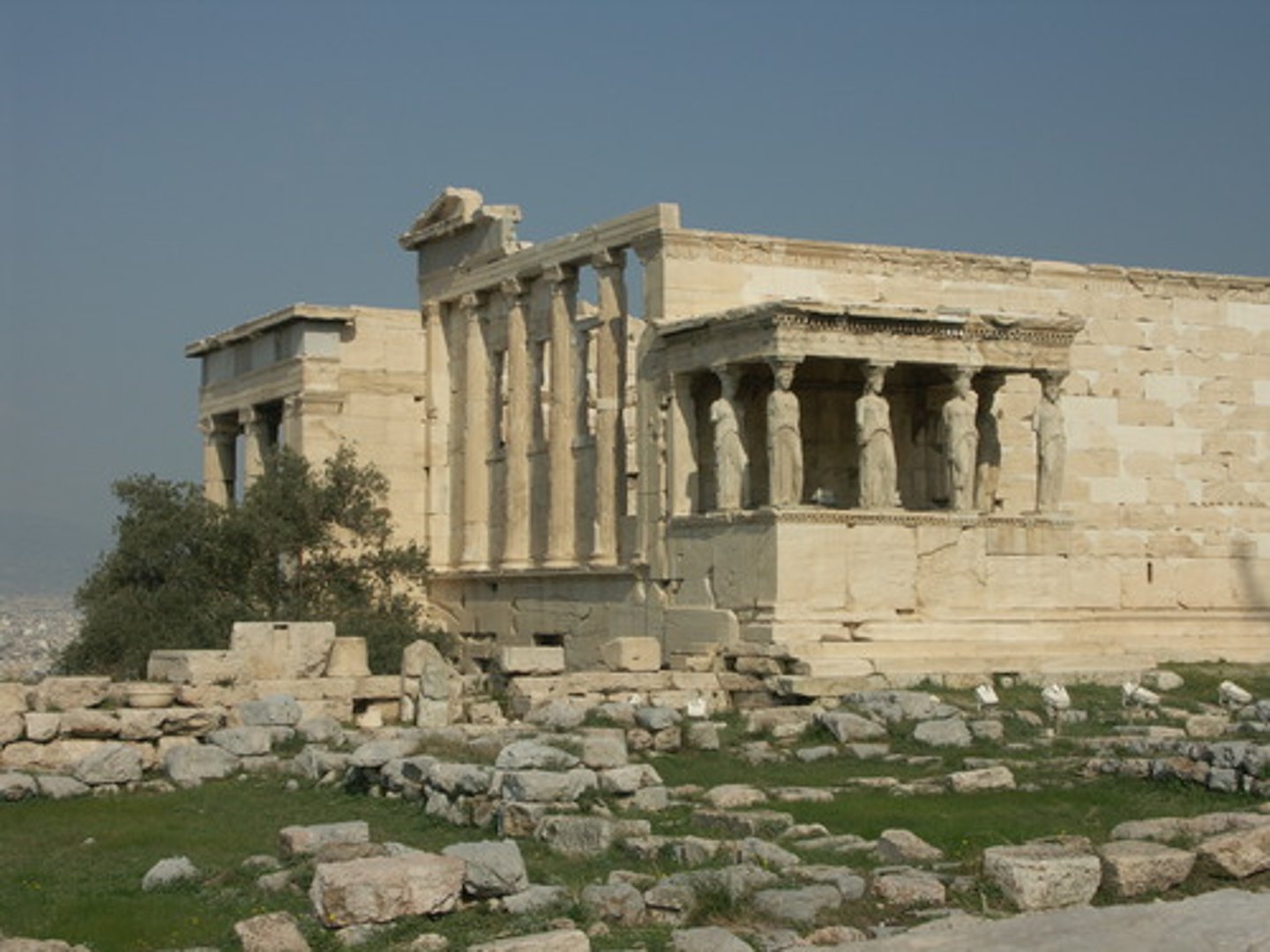

Who was it dedicated to?
Erechtheios.
It housed the grave of...
...the mythical King Kekrops.

Why is the North porch important?
- Where Poseidon's gift of salt water is.
- Mark of Zeus' thunderbolt sent to kill Erechtheios under the floor.

Why is the Cella of Athena Polias important?
It's where the Polias cult statue is presented with the peplos.

Why is the Pandroseum important?
Where Athena's gift of an olive tree is.

Who was the Pandroseum dedicated to?
Pandrosus (one of the three daughters of Kekrops and the only one to not open the chest that Athena gave them).
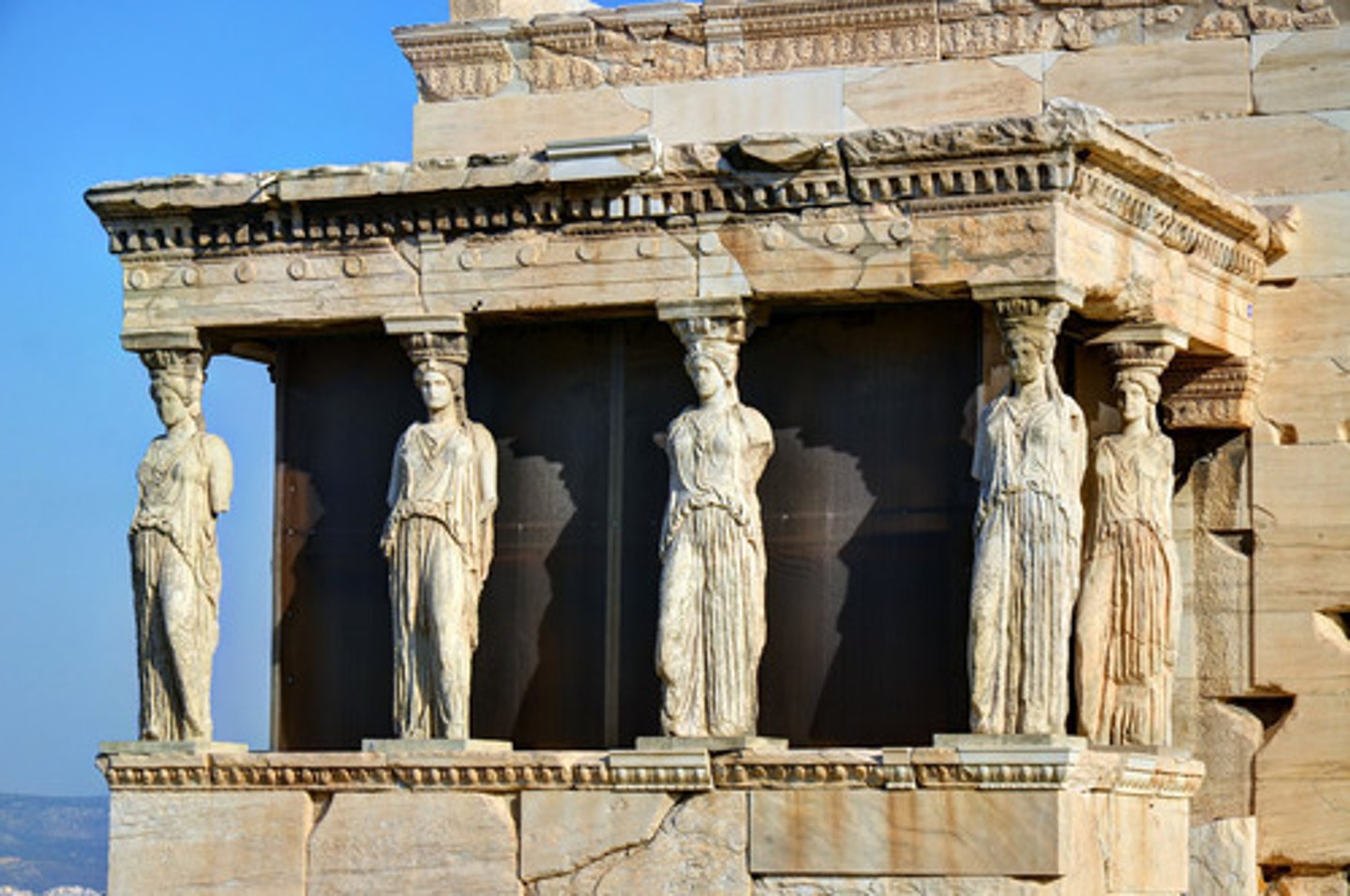
Why is the Porch of the Caryatids important?
It has 6 statues of maidens known as the caryatids as pillars.

What is the myth of Erechtheios?
Athena went to get weapons from Hephaestus, who then attempted to rape her. She resisted but he ejaculated on her leg, and when Athena wiped it off, Ge (mother Earth) was impregnated. Erechtheios was then born from the ground. Athenians claim descent from him so they are connected to Athena, who was part of the conception.
What are the three interpretations of the caryatids?
- They are carrying the baskets in the Panathenaea and are in procession.
- They are mourners because the stand over Kekrops tomb.
- They are the enslaved women of Carya, a city accused of treason during the Persian war (according the the Roman Vetruvius).
What was the Plynteria and when was it celebrated?
An annual festival taking place on the 22nd of Thargelion, was an honouring break in the name of Athena.
First the ___ is surrounded by ___ to ___ as the ___
First the Temple of Athena is surrounded by rope to preclude all communication as the statue is tripped of the peplos.
Where is there a procession to?
Sea, several miles away.

What do the women in front do?
Carry baskets of figs, which were believed to cleanse the salt water.

What were the mounted young men known as?
Epheboi.
What did the mounted young men do?
Took the cult statue into the water and back out.
What were the girls who bathed the statue known as?
Lautrides.
What was the priestesses sole responsibility?
Cleansing the peplos, only she was allowed to do this.
What then happened in the evening?
There was a torch-lit procession back to the Erechtheion and the statue was redressed by special women.
What were these women known as?
The proxiergidia.
How do we know about the Plynteria?
Plutarch's life of Alcibiades.
In what ways is the procession of the Panathanaea related to the Acropolis?
- Frieze shows evidence of it.
- Brought people together and allowed them to admire Athens.
- Procession began in Kerameikos and moved south to the Acropolis.
What did the Athenian Civic Decree of 335/334 BC state?
The Hecatomb (sacrafice of 100 cattle) had to occur at the altar of Athena on the Acropolis.

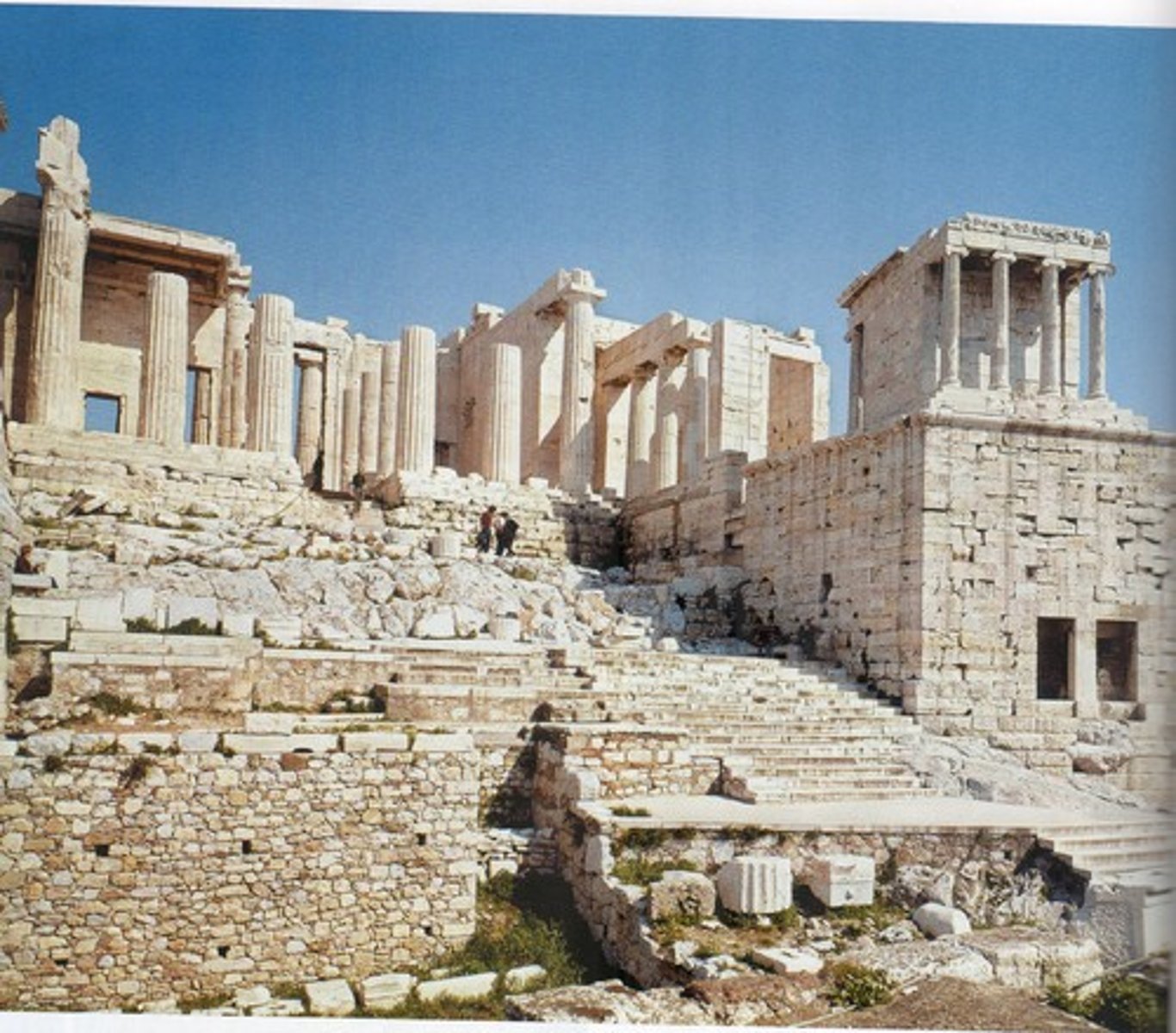
How were prizes of the Panathanaea linked to the Acropolis?
- Winner of the Eundrian (male beauty contest) led the procession.
- Victors named engraved on the Acropolis.
- Boat race in honour of Athena and Poseidon.
- Torch race from Piraeis (harbour) to Acropolis.
- Panathenaic Amphorae contained sacred olive oil (links to patronage story).
When was the Propylaia built?
437 - 432 BC.

What style was it built in?
Mostly Doric other than 2 rows of Ionic columns.
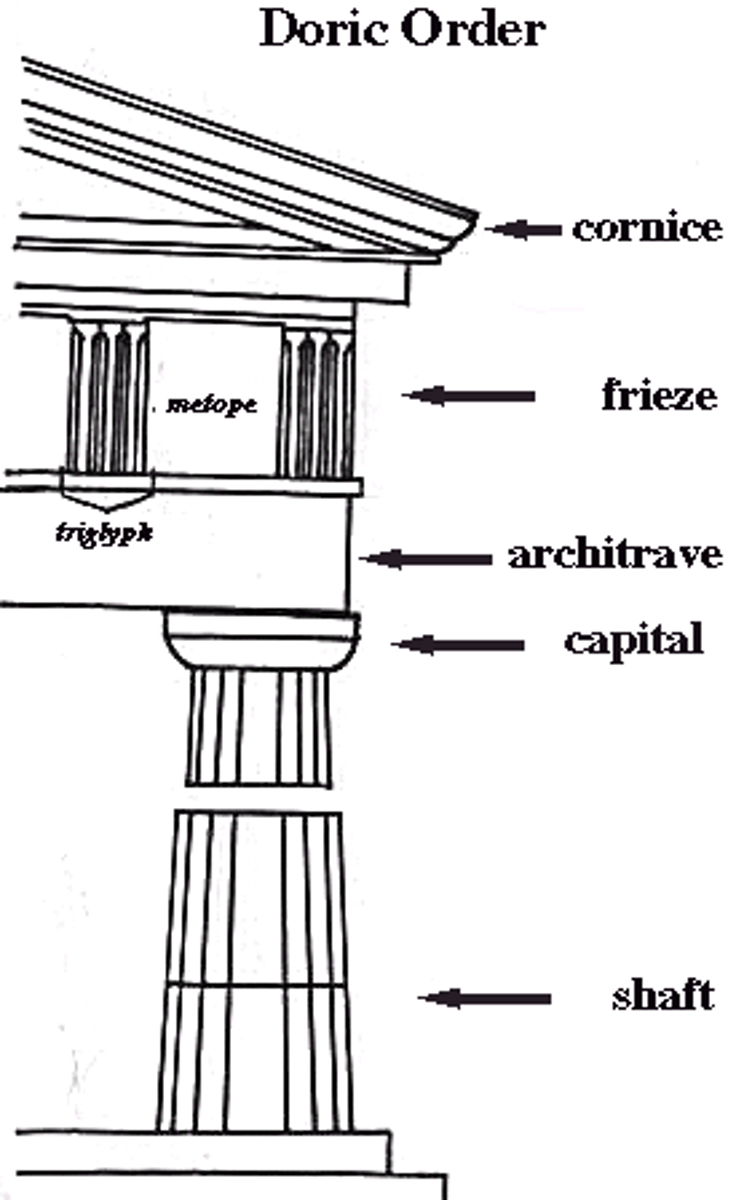
What was it made of?
Pentellic marble.
Why was it built so wide?
- Acted as the gateway to the Acropolis.
- Could allow crowds and chariots to fit through.
When was the Temple of Athena Nike finished?
420 BC.
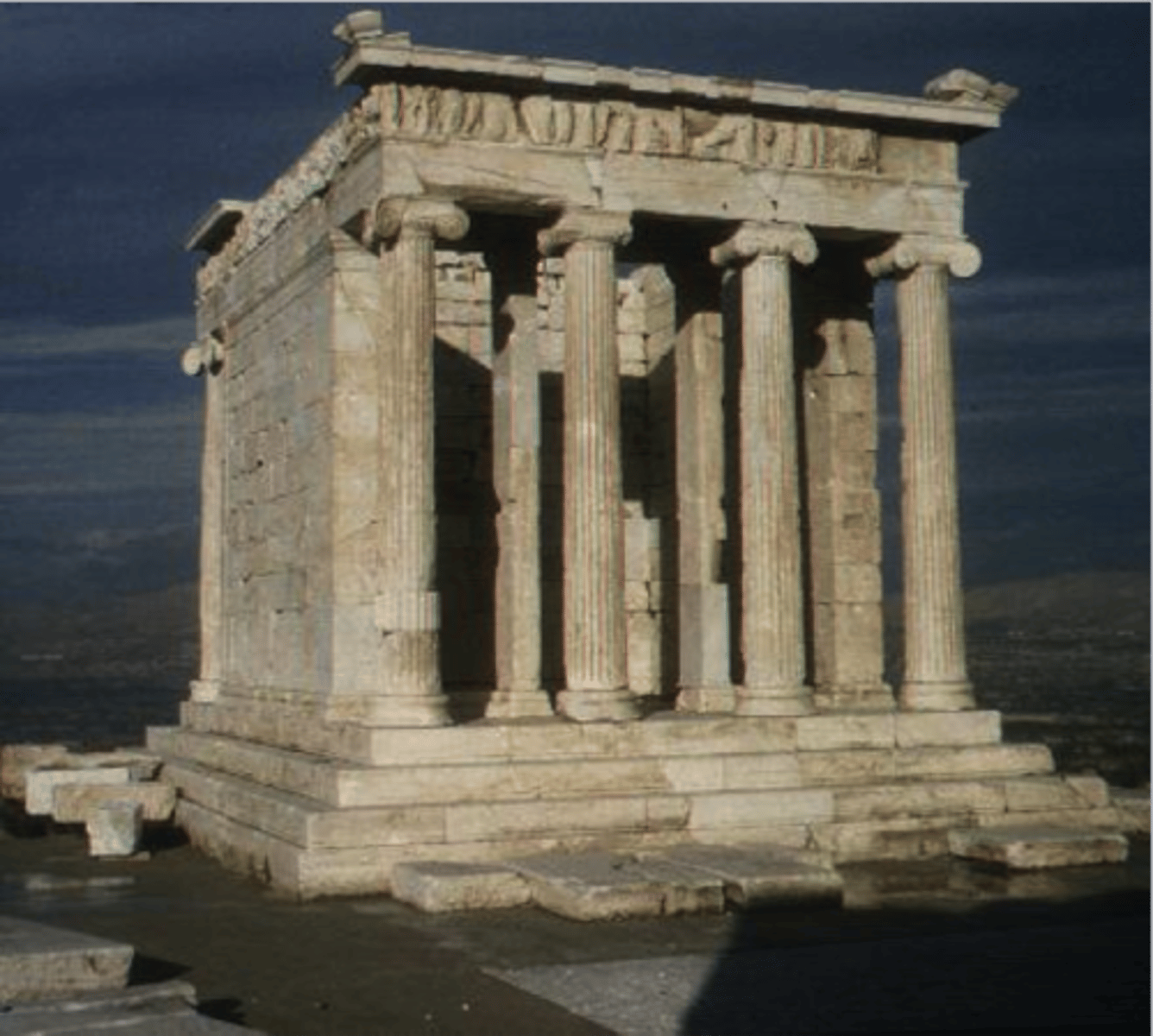

What did this indicate?
The use of war starved funds.
How long and tall was it?
26 x 18 feet long and 23 feet tall.
What was it made of?
Pentellic marble.
What ratio was it built in?
7:1.
What did its North frieze depict?
A battle between Greeks and entailing cavalry.
What did its South frieze depict?
Victory over the Persians at Plateae (479 BC).
What did it's East frieze depict?
Assembly of Athena, Zeus and Poseidon.
Where is the sanctuary of Olympia located?
Central-western Peloponnese.
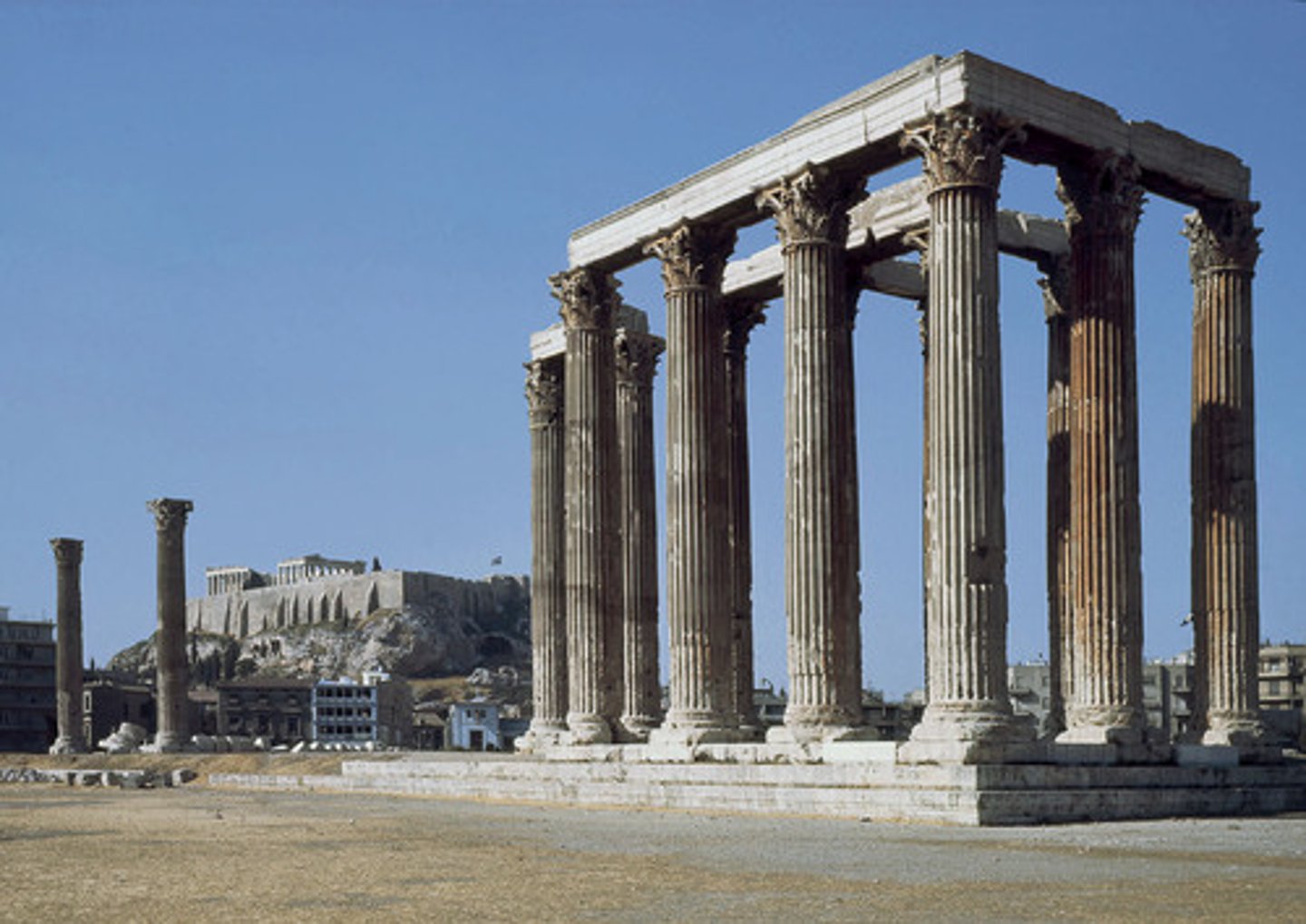

Whose cult was it linked with?
Zeus'.

What city was it under the authority of?
Elis. It provided all priests and there was a procession from there before the Olympics.
What was the Temenos renamed?
The Altis.
When was the Temple of Zeus built?
Built before 456 BC.
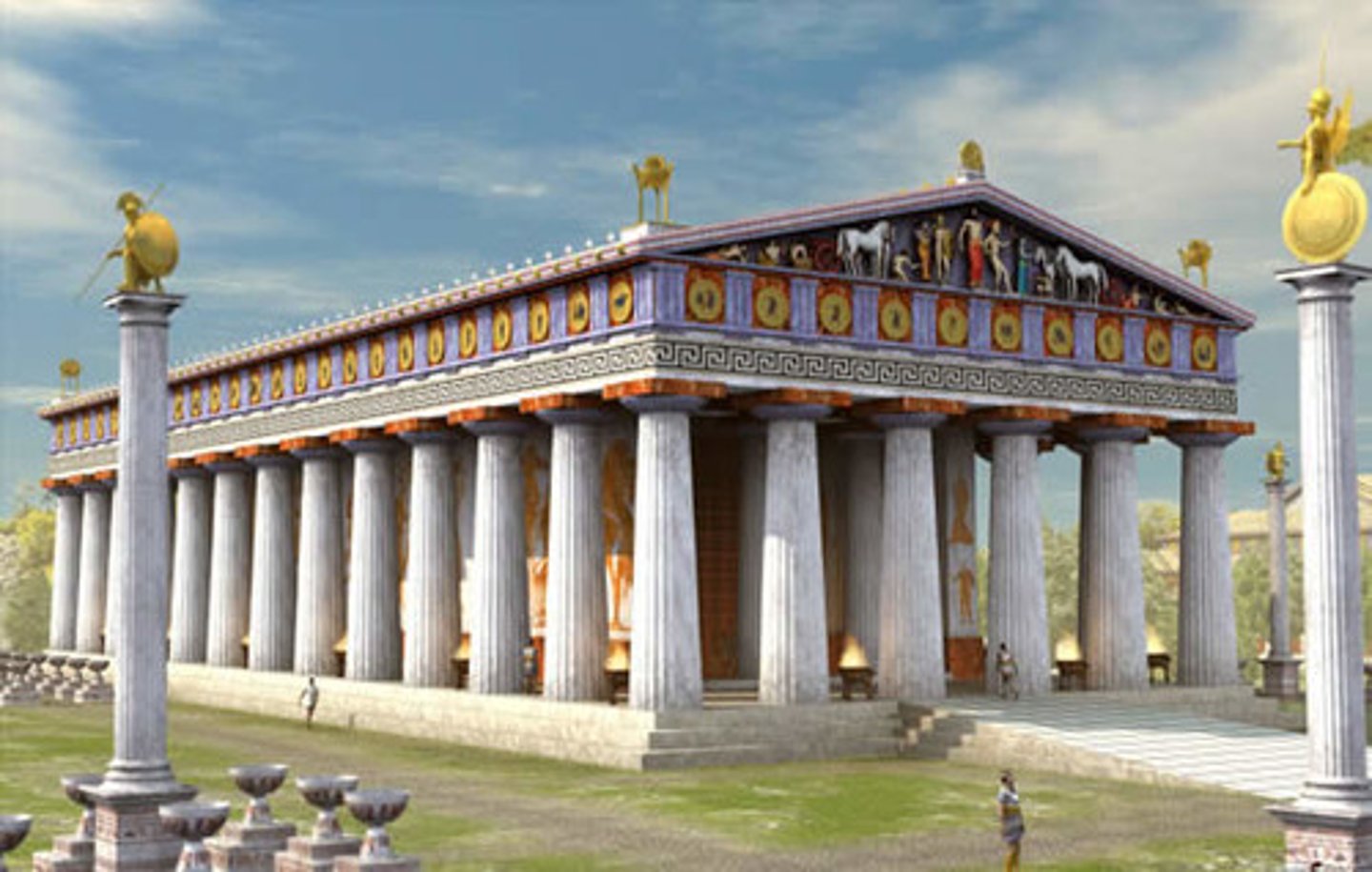

What style was it built in?
Doric.
How many columns were there?
6 x 13 columns.
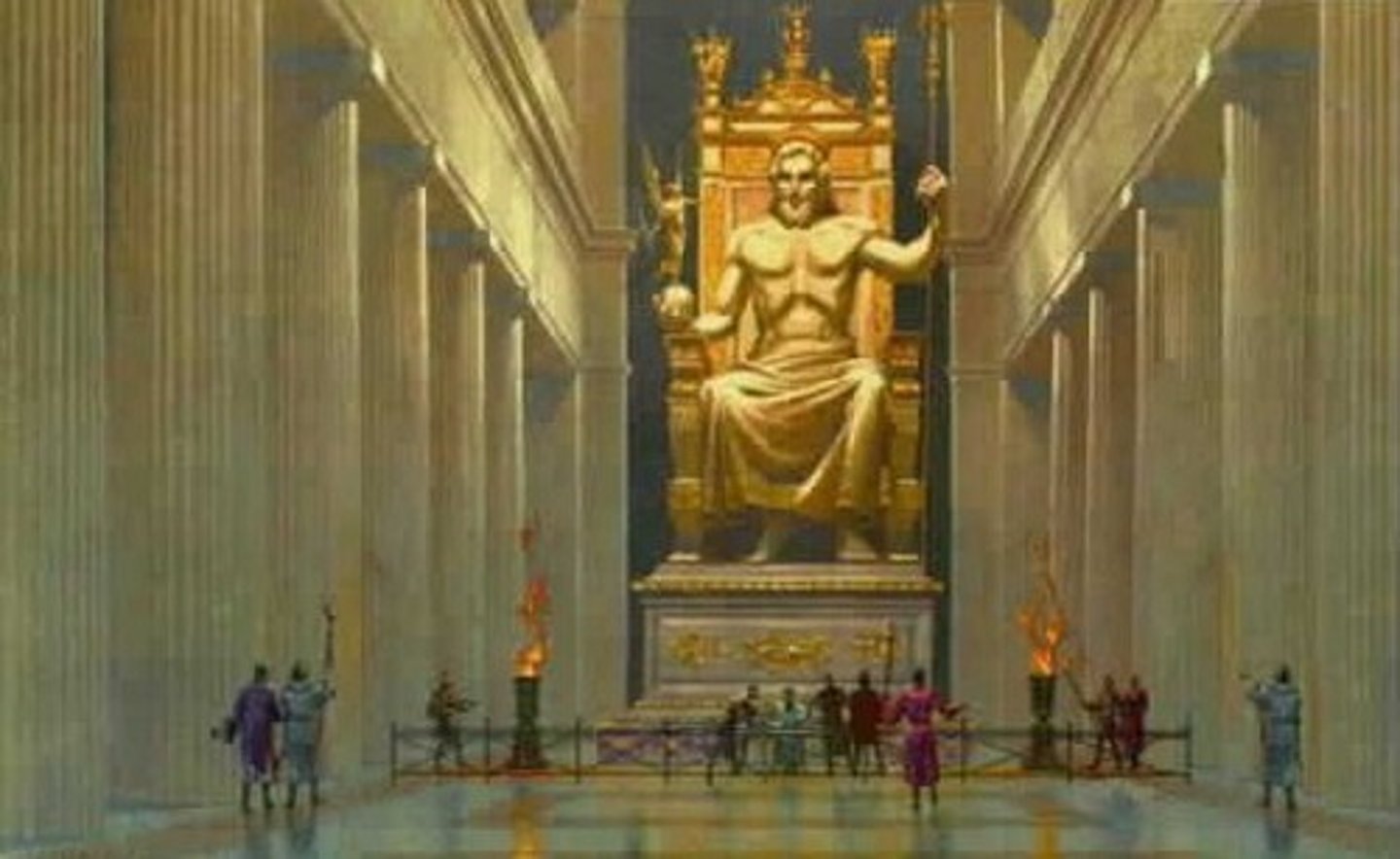
What did it contain?
A chryselephantine statue of Zeus seated (one of the 7 wonders of the world).

What does the East pediment show?
The chariot race between Pelops and Oinomaus.
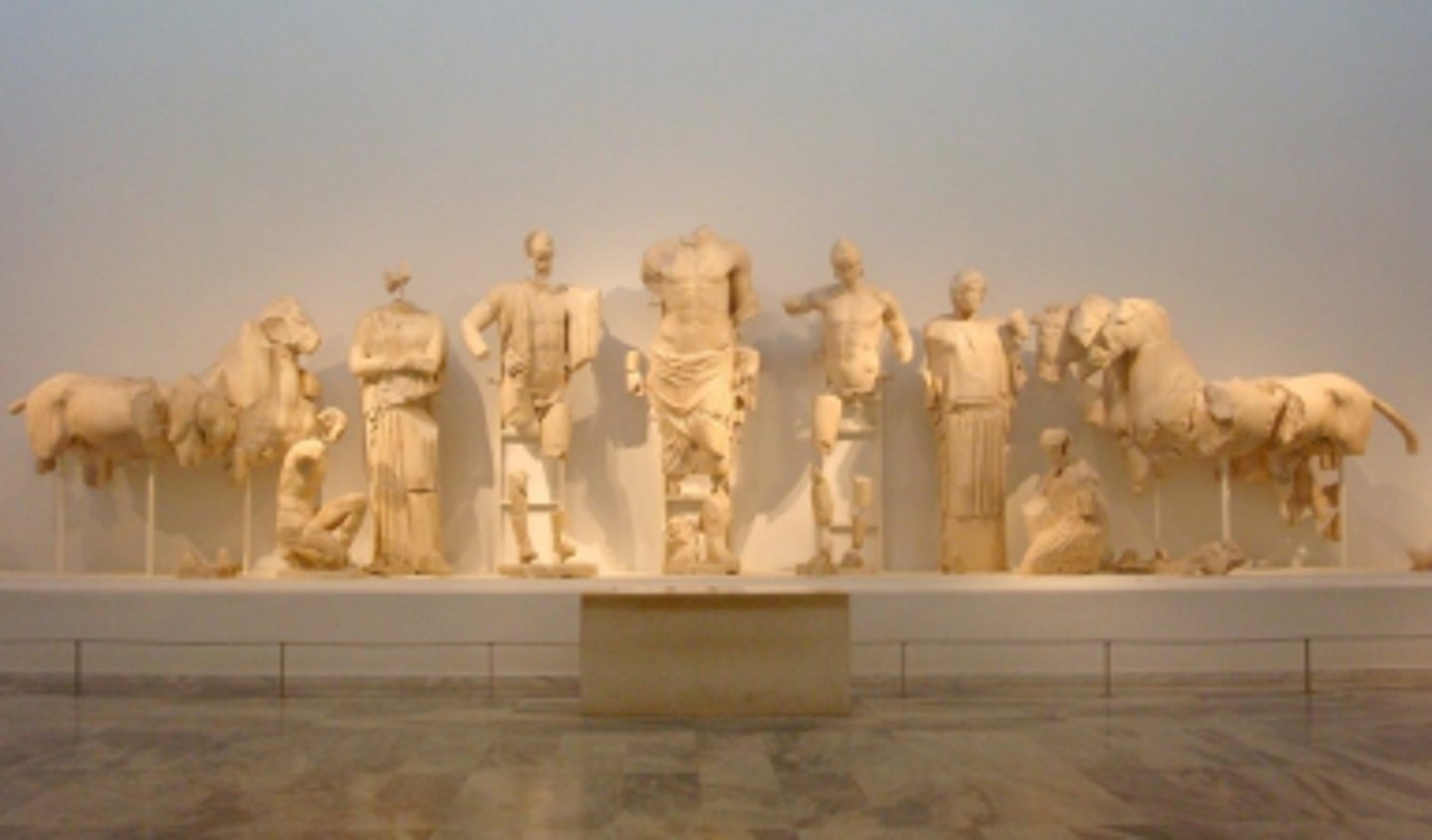

What did the two men in the corners represent?
The rivers of Olympia (Kladeios and Alpheios).
What different figures were on it?
Hippodamia (Oinomaus' daughter) --> Pelops (Zeus' grandson) --> Zeus <-- Oinomaus (a King) <-- Sterope.
What is the myth of Oinomaus and the chariot race with Pelops?
He said anyone who could beat him in a Chariot race would win his daughter, but if you lost you would be killed (13 already killed). His Chariot was a gift from his father, Ares. Pelops decided to challenge him as his chariot was a gift from Poseidon. He convinced Oinomaus' charioteer to replace his wheel pins with wax, meaning Pelops won.
What does the west pediment show?
Centauromachy.
Which figures are depicted on it?
Deidameia (assaulted by Centaur) --> Penithous (King of Lapiths) --> Apollo <-- Theseus (slaying Centaurs).
What is the myth of Centauromachy?
The Centaurs were invited to the wedding feast of Perithous but unused to wine their wild nature took over. Eurytion attempted to abduct Deidameia (the bride), and the rest of the Centaurs began to assault the women. The Lapiths and Centaurs began fighting, Theseus helping the Lapiths. The Centaurs were then expelled from Thessaly to the north-west.
How many metopes were on the Temple of Zeus?
6 on the front and 6 on the back.
What did they depict?
The 12 labours of Heracles.
How did this relate to Olympia?
It related to his strength as the son of Zeus and reinforced the idea of justice (punishment for killing his children).
What do some myths suggest Heracles founded?
The Olympic Games.
What were the 12 labours of Heracles?
- Capturing the Cretan Bull.
- Capturing the man-eating horses of Diomedes.
- Fetching the golden girdle of Hippolyte.
- Capturing the oxen of Geryon.
- Fetching the golden apples of the Hesperides.
- Bringing back Cerberus from Hades.
- Washing out the stables of King Augeias.
- Capturing the Erymanthian Boar.
- Capturing the Keryritan Hind.
- Killing the Hydra.
- Killing the Nemean lion.
Who described the statue and in what work?
Pausanius in "Guide to Greece".
What materials was the Statue of Zeus made of?
Chryselephantine and the throne was adorned with jewels and robes were embroidered.
What does he hold in his right hand?
Nike.
What is Zeus depicted as doing in the statue?
Sitting on a throne holding a sceptre with an eagle on top.
What do the rods between his feet depict?
Thebans ravished by Sphinxes and Pantarcles who won wrestling at the 68th festival etc.
When was access to the statue probably allowed?
Every 4 years during the Olympics.
Who sculpted the statue?
Pheidias.
When were the Olympics founded?
776 BC.