Equine med & Surg
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Veterinary client patient relationship
Basis for interaction among veterinarians, their clients and their patients
Critical to the health of the animal
Can only be established when a veterinarian examines the animal and meets the owner in person.
T/F: A VCPR cannot be established solely on the telephone, but you can use other electronic means
False - must be in person
Veterinary client patient relationship steps
Veterinarian has assumed the responsibility for making critical judgements regarding the health of the patient
The client has agreed to follow the veterinarian’s instructions
The veterinarian has sufficient knowledge of the patient to initiate a general diagnosis
Veterinarian is readily available for follow-up care
Veterinarian provides oversight of treatment, compliance and outcome.
Patient records are maintained
Establishing a contract or agent: Decision makers
owners
riders
trainers
barn managers
Establishing a contact or agent: A priori agreements
Who makes decisions on what and when?
What if the owner is unavailable?
Is an insurance company involved?
Initial History: Signalment
age
breed
gender
Initial history: Ownership history
previous owners
length of ownership
reason for sale
initial history: previous or current medical history
preventative care
conditions
lameness
medications
Initial History: reproductive history
foals
castration
Initial history: Herd health
new horses
previous health concerns
Initial history: atheletic history
pets vs athletes
variety of use
Knowledge of sport helps narrow down the importance of presenting complaint.
Immediate HIstory steps:
onset
duration
behavior of the horse
appetite
appearance of the lesion
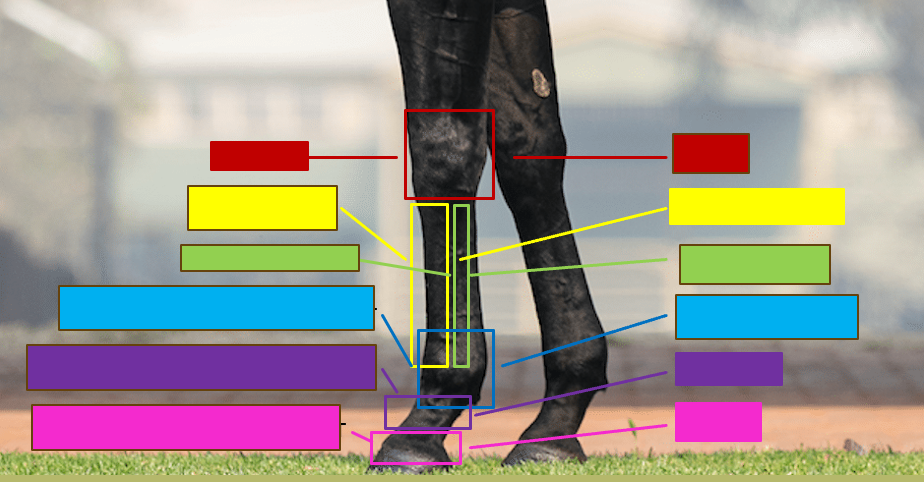
Give the professional and common name for the red box
Carpus - Knee
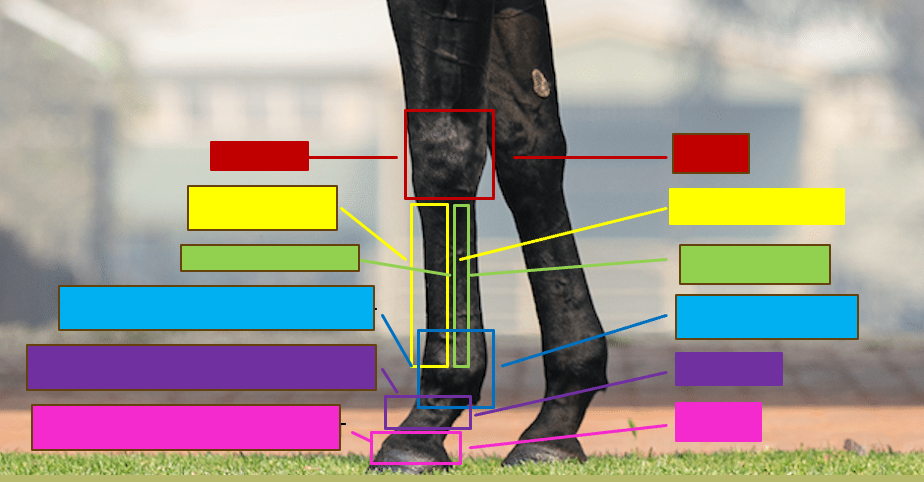
Give the professional and the common name for the yellow box
Metacarpal III - Cannon bone
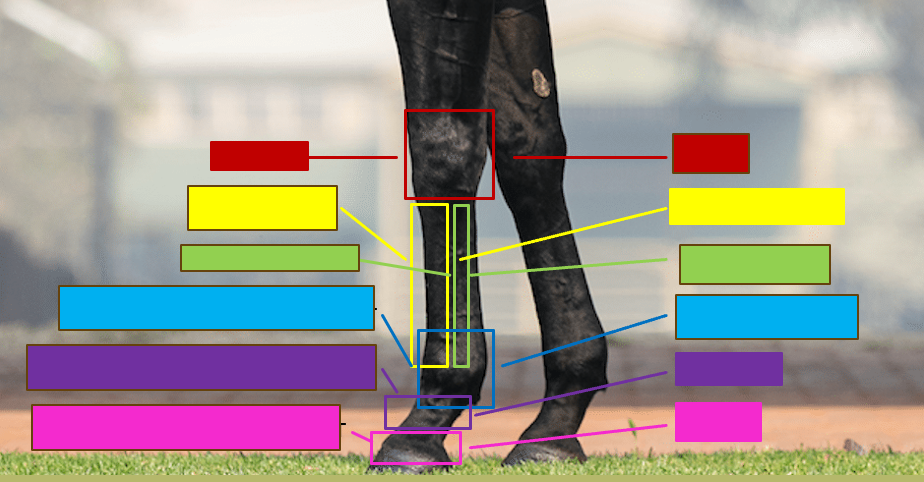
Give the professional and the common name for the green box
Metacarpal II/IV - Splint bone
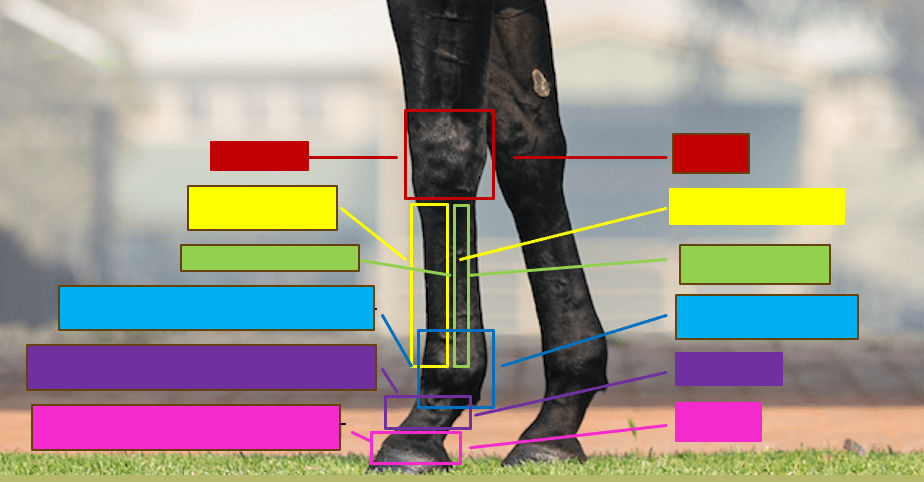
Give the professional and the common name for the blue box
Metacarpophalangeal joint - Fetlock/ankle
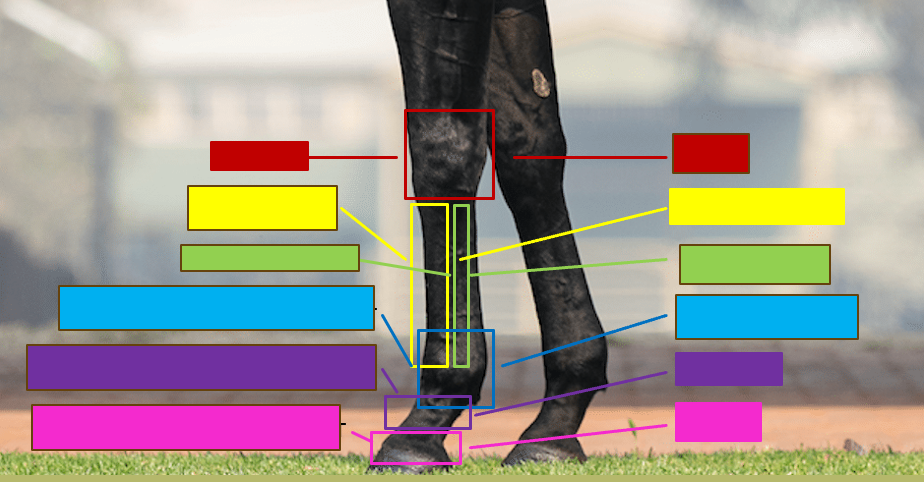
Give the professional and the common name for the purple box
Proximal interphalangeal joint - Pastern
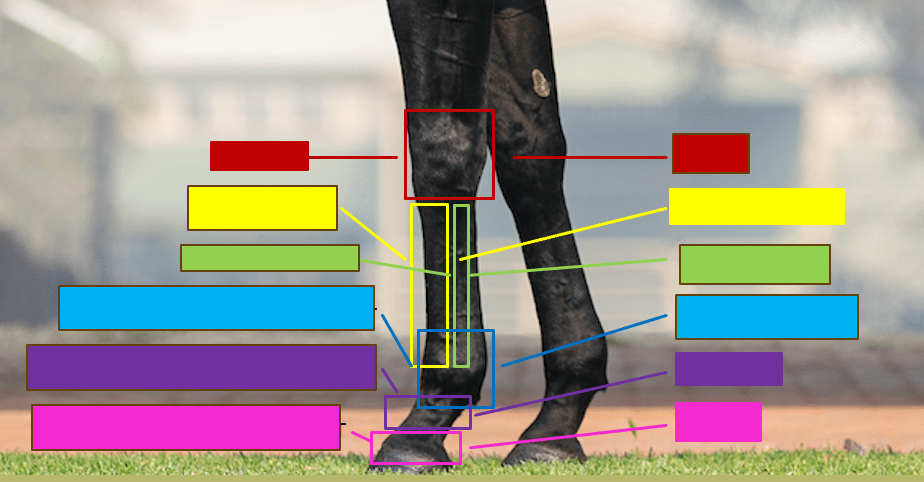
Give the profesisonal and the common name for the pink box
Distal interphalangeal joint - coffin
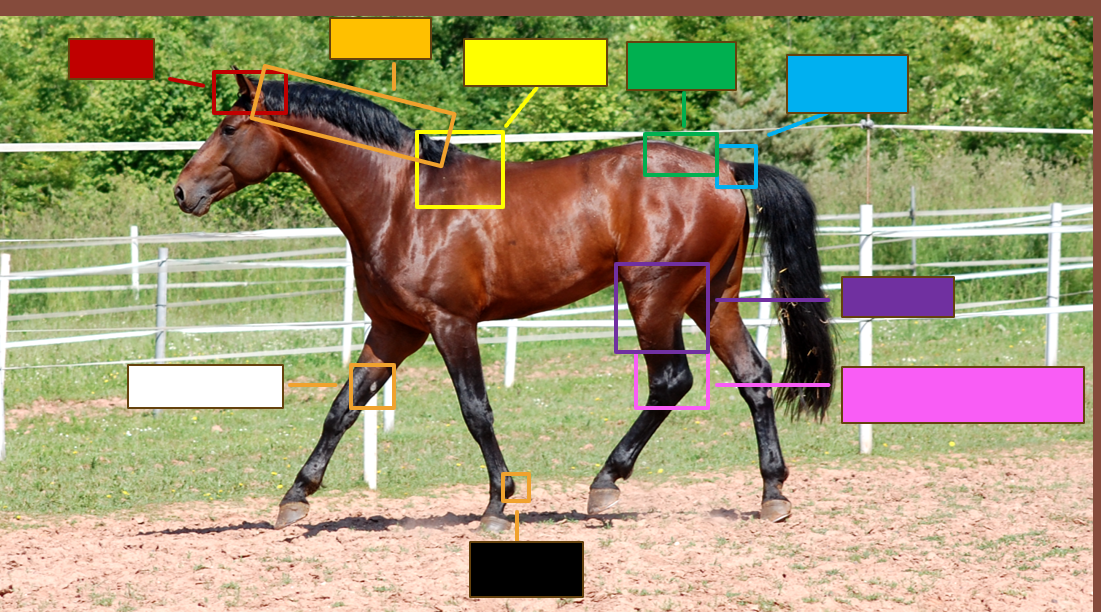
Label the red square
Poll
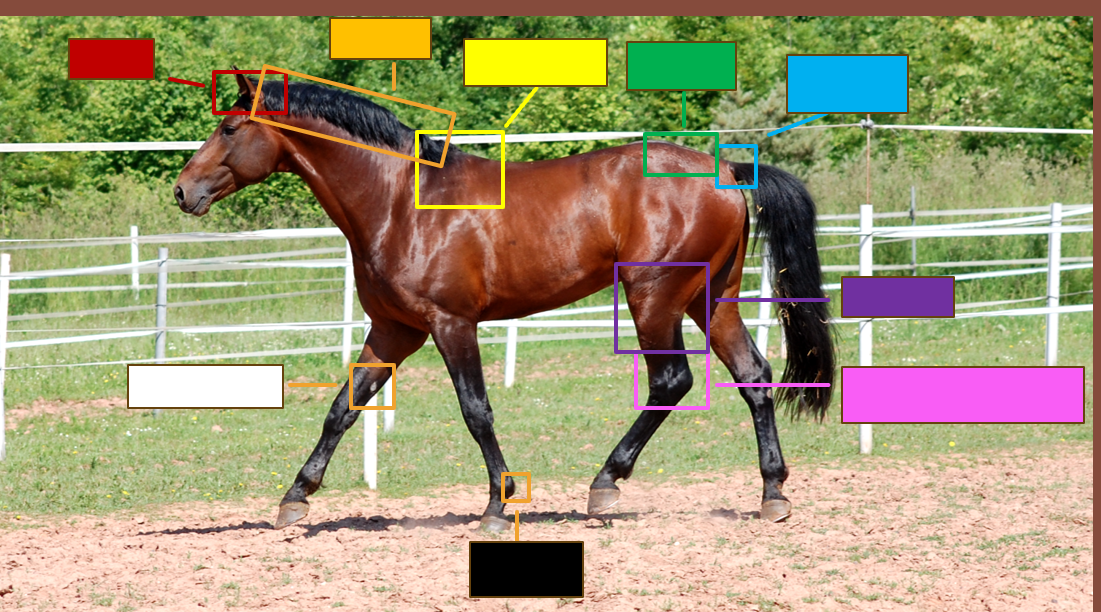
Label the orange square
Crest
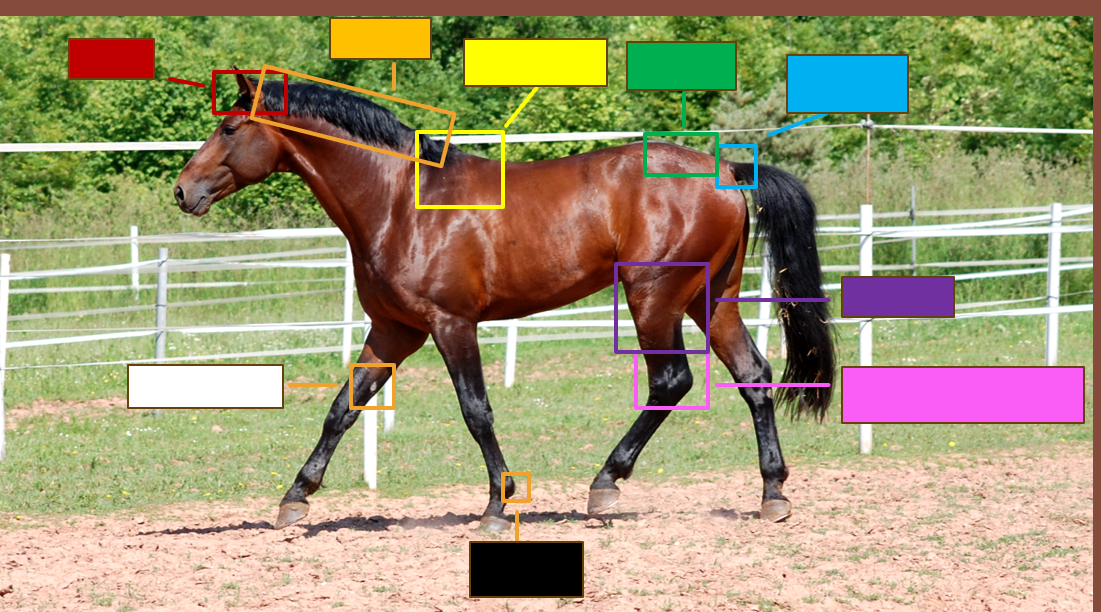
Label the yellow square
withers
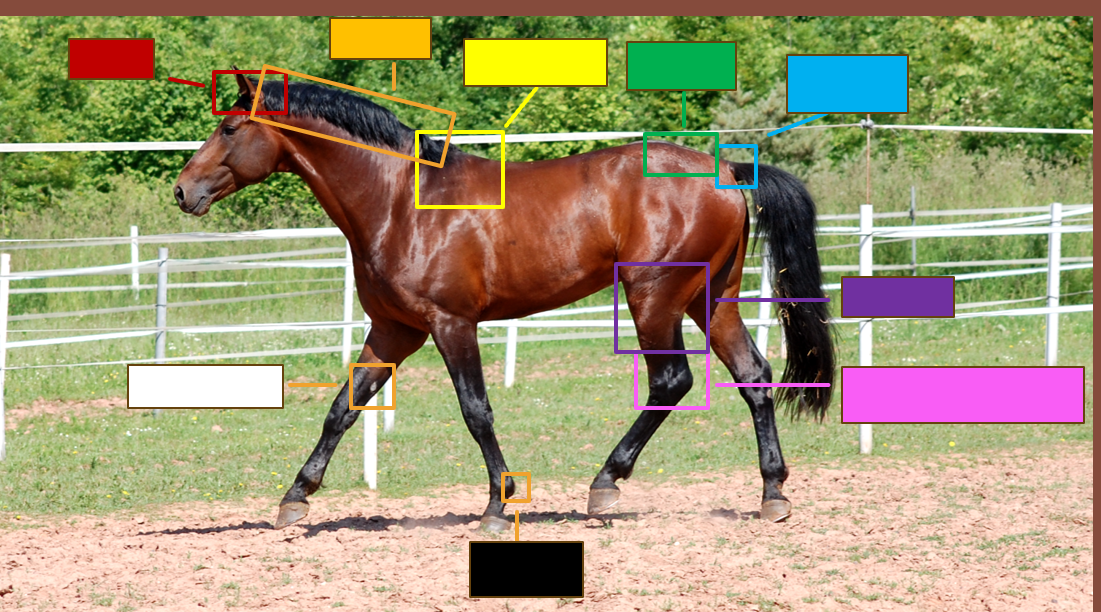
Label the green square
croup
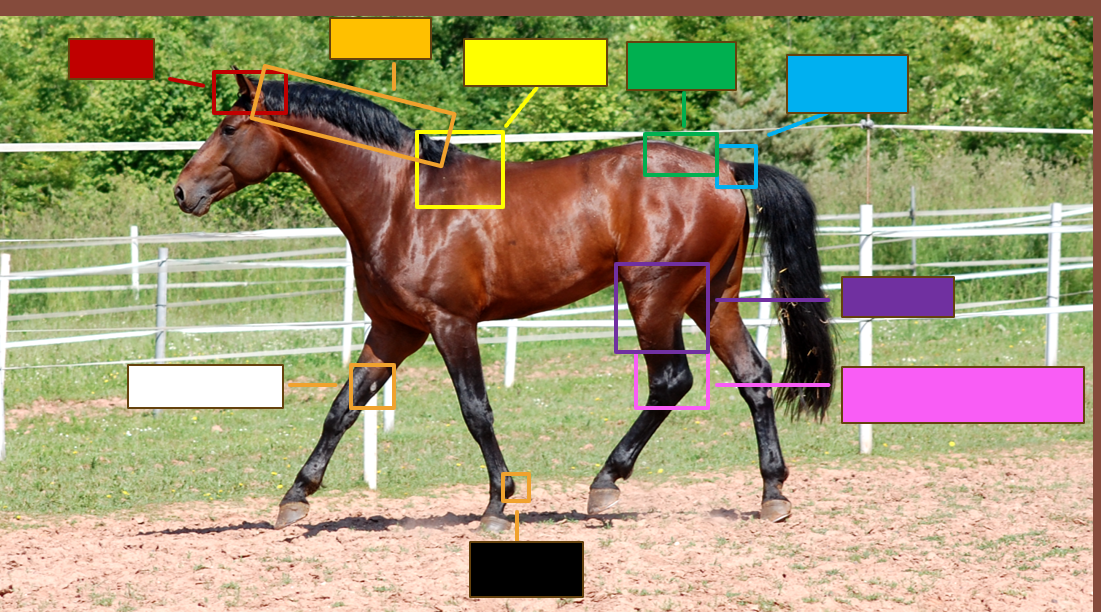
Label the blue square
Dock
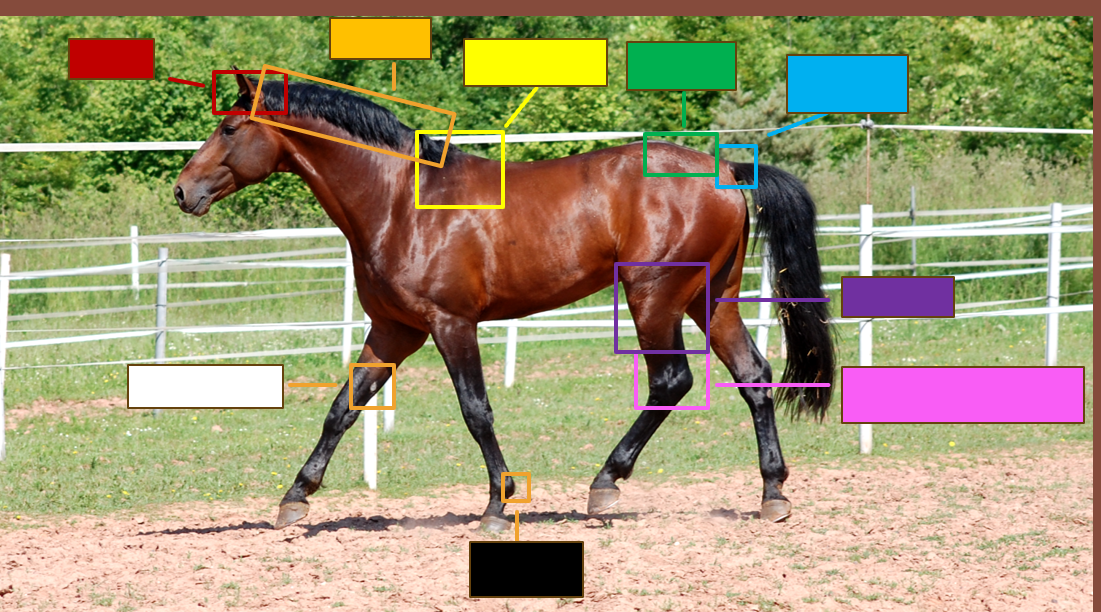
Label the purple square
Gaskin
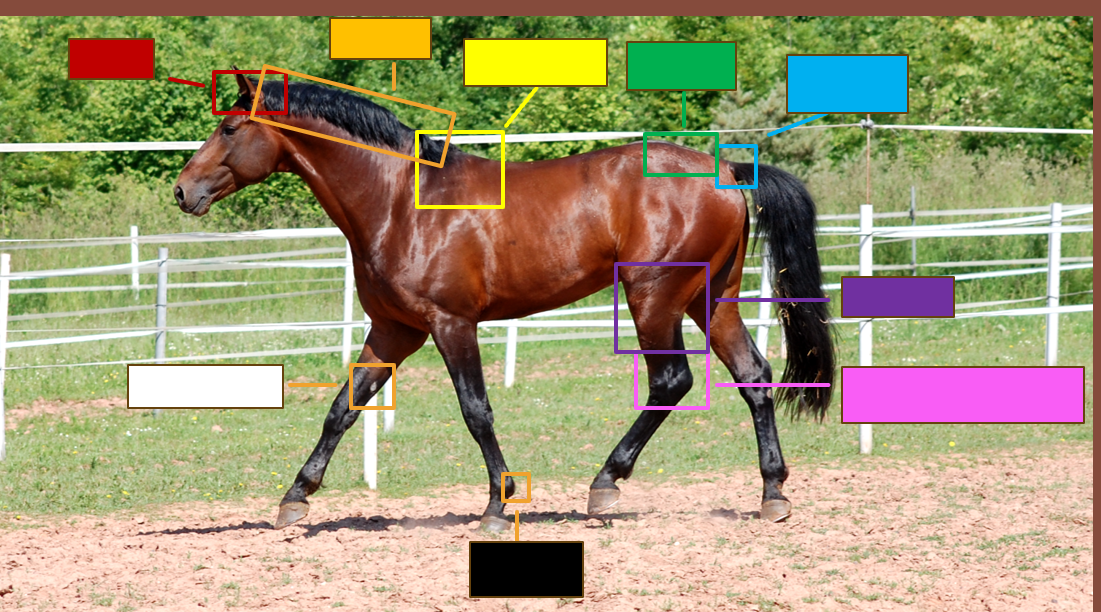
Label the pink square
Tarsus/Hock
Label the black square
Ergot
Label the white square
chestnut
Visual observation during PE: Ease of handling
stallion vs gelding vs mare
foal vs adult
feral vs broke
Visual observation during PE: Ground manners
pawing
moving
neighing
Visual observation: vices
headshaking
weaving
biting
cribbing
Behavior: Horses are prey animals
strong flight instinct
predators are everywhere
Behavior: Perceptive and sensitive
near instantaneous response time
desensitized to stimuli over time.
Behavior: Ocular
Developed different ocular anatomy due to being prey
nearly 360 degree field of vision
Have a combination of monocular and binocular vision
Poor 3D vision except directly in front of the horse
creates blind spots that can increase risk of injury to animal and human

Mentation of this horse?
Bright, alert, responsive

Mentation of this horse?
Quite, alert, responsive
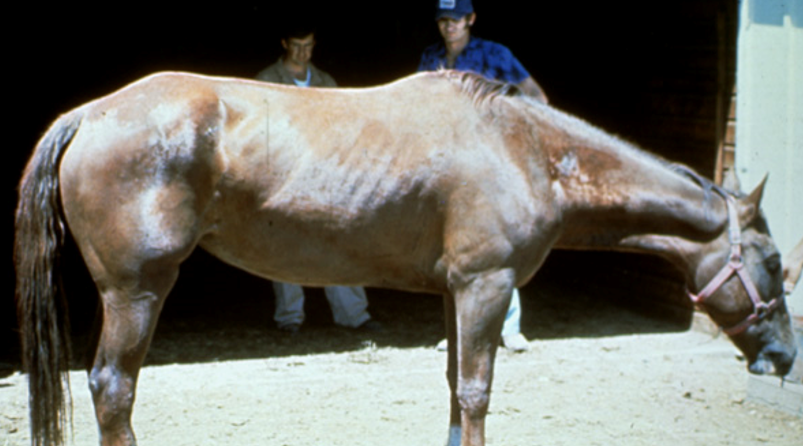

Mentation of this horse?
lethargic, dull

Mentation of these horses?
unresponsive, obtunded
What to look at to score the body condition on a horse?
Neck
withers
down the crease of the back
tailhead
ribs
behind the shoulder at the girth
Normal temperature for a horse
99 - 101.5 F
Normal Heart rate for a horse
24 bpm - 48 bpm
Normal respiratory rate for a horse
8 brpm - 24 brpm
Cardiovascular exam: Auscultation of the heart
both sides of the heart
Pre- and post- exercise
cardiovascular exam: common abnormalities
tachycardia
2nd degree AV block
murmurs - aortic and mitral regurgitation
Cardiovascular exam: Pulses
palpate pulses
digital pulses
mandibular pulse
evaluate strength
weak vs bounding
T/F: a weak pulse under the mandible is fine
False bad
T/F: strong digital pulses are good
False BAD
Cardiovascular exam: Mucous membranes
color
normal: pale pink in horses
bad: brick red, toxic line
capillary refill time
<2 seconds
Cardiovascular exam: Potential issues
peripheral vasculature
waterhammer jugular pulse
Edema
peripheral edema
limb edema
Respiratory exam:
upper and lower airway
rebreathing bag
Pre-and post-exercise
Respiratory exam: Nostrils
airflow
discharge
epistaxis
Respiratory exam: sinuses
percussion
Respiratory exam: Larynx
palpation

What is the pink labeled?
Frontal sinus

What is the purple labeled?
caudal maxillary sinus

Name the light blue label
rostral maxillary sinus

Label the red sinus
ventral conchal sinus

Label the dark blue sinus
Dorsal conchal sinus

Label the green sinus
palatine sinus
Gastrointestinal exam:
Auscultate for gastrointestinal sounds
Borborygmi
Normal
constant gurgle
Abnormal
Hypo- or hypermotile
gas pings
In a GI exam, what are you listening to in the left dorsal compartment?
small intestine
In a GI exam, what are you listenting to left ventral?
large colon (left dorsal/ventral colon, pelvic flexure)
In a GI exam, what is located right dorsally?
cecum
In a GI exam, what is located right ventrally?
cecum and large colon (right dorsal/ventral colon)
Gastrointestinal exam: examine feces
under tail head, rear end, and hind limbs
consistency
parasites
Gastrointestinal exam: transrectal palpation
under certain circumstances
Examinaiton of the heat:
supraorbital fossa
Nostrils
muzzle
ears
poll
temporal muscles
Temporo-mandibular joint
Masseter muscles
Lymph nodes
Mandible
Maxilla
Facial crest
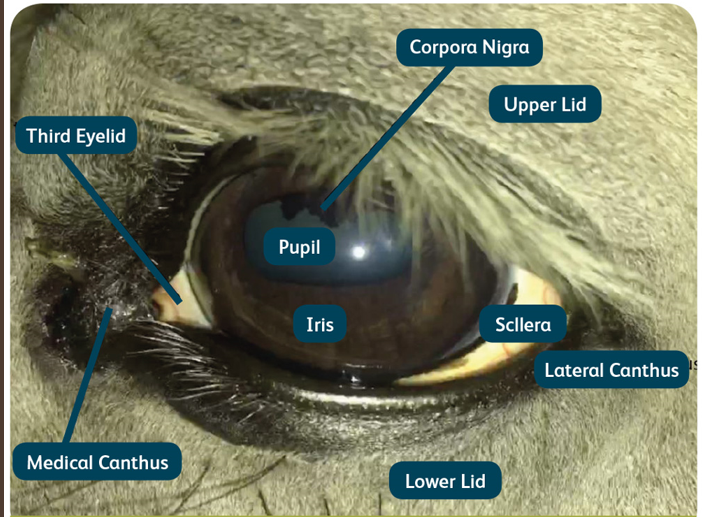
Opthalmic examination
normal features
work from the outside in
important to evaluate front and back of the eye
Opthalamic examination:
vision
comfort
scars
neoplasia
discharge
Oral examination
routine care recommended annually
performed additionally if
drooling
dropping feed/weight
odor from mouth
health certificates
Oral examination requirements:
sedation
light
speculum
head restraint
Oral examination: look for
hooks and points
ulcerative lesions
missing teeth
incisor wear
Oral examination: aging
eruption
size of incisors
Galvayne’s groove
stars and cups on incisors
Musculoskeletal exam:
looking at conformation and symmetry
Musculoskeletal exam: angular deformaties
varus
valgus
musculoskeletal exam: Flexural deformities
contracture
laxity
Musculoskeletal examination: evaluation and palpation
hoof
bones
joints
tendons
visual examination
palpation
range of motion
passive flexion
hoof testers
Lameness examination:
at the walk - straight line and circling
at the trot - hard and soft surfaces
athletic evaluation - on a lunge line, under saddle.
Flexion tests - place stresses on joints, can exacerbate lameness and localize pain
Peripheral nerve blocks - further localization of pain (separating distal structures, etc).
Neurologic examination:
cranial nerves
conscious proprioception
weakness
ataxia
Reproductive exam
External exam
conformation
neoplasia
Ultrasonography
semen evaluation
Special focus
abnormalities
presenting signs
owner’s concerns
welfare concerns.