Rheumatic Fever
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
(Modified) Centor Criteria
What criteria is this?

strep throat
What is the centor criteria used to assess?
1, 2-3, 4-5
Centor Criteria Scoring
< _ → no antibiotic or further testing recommended
_-_ → rapid strep testing and/or culture
Tx if rapid antigen detection or throat cx (+)
_-_ → Rapid strep testing and/or culture
Empiric tx is okay w/o testing
immune, streptococcal, 5-15, 2-3, 5
Acute Rheumatic Fever
Systemic ______ process that is a sequela of beta-hemolytic __________ infection of the pharynx
More common in developing countries
Peak incidence in ages _-__
Rare before 4 and after 40
Signs usually being _-_ weeks after throat infection
But may begin as early as 1 week or as late as _ weeks after infection
genetic, injury, cross-reactive, proteins, mitral,
Acute Rheumatic Fever Pathophysiology
Not completely understood
_______ susceptibility may be present
Tissue ______ is thought to be caused by an autoimmune process generated by cross-reactive antibodies and T cells between group A strep (GAS) antigens and human ________
Affects the valves:
_______ valve in 75-80% of cases
Aortic valve in 30%
Tricuspid and pulmonary valves in <5%
rheumatic fever, cusps, chordae tendineae, regurgitation, mitral, aortic, mitral
Chronic Rheumatic Heart Disease
A complication of Acute Rheumatic Fever
Results from a single or repeated attacks of ________ _____
Causes rigidity and deformity of the valve _____ and shortening and fusion of the ______ _________ → results in valvular stenosis and/or ____________
Affects the ______ valve alone in 50-60% of cases
Combined lesions of the ______ and ______ valves occur in 20%
Jones Criteria
What criteria is used to diagnose rheumatic fever?
2, 1, 2
Jones Criteria
The presence of _ major criteria OR _ major and _ minor criteria establishes the diagnosis
carditis, marginatum, subcutaneous, Sydenham, polyarthritis
Jones Criteria - Major Criteria
________
Pericarditis, cardiomegaly, heart failure, mitral or aortic regurgitation murmurs
Occurs most often in children and adolescents
Erythema __________
Rapidly enlarging macules → annular or crescent shaped
Trunk and proximal extrimities
“migrates”
__________ Nodules
Small (<2cm), firm, and nontender
days-weeks and are recurrent
Uncommon except in children
_______ Chorea (“Saint Vitus Dance”)
Disorder of CNS: sudden, purposeless, irregular, involuntary movements
face, tongue, upper extremities
MC in children (Females > males)
____________
Acute migratory and asymmetrical → involves the large joints
Carey-Coombs murmur
short mid-diastolic mitral murmur may be present due to inflammation of the mitral valve
Erythema Marginatum
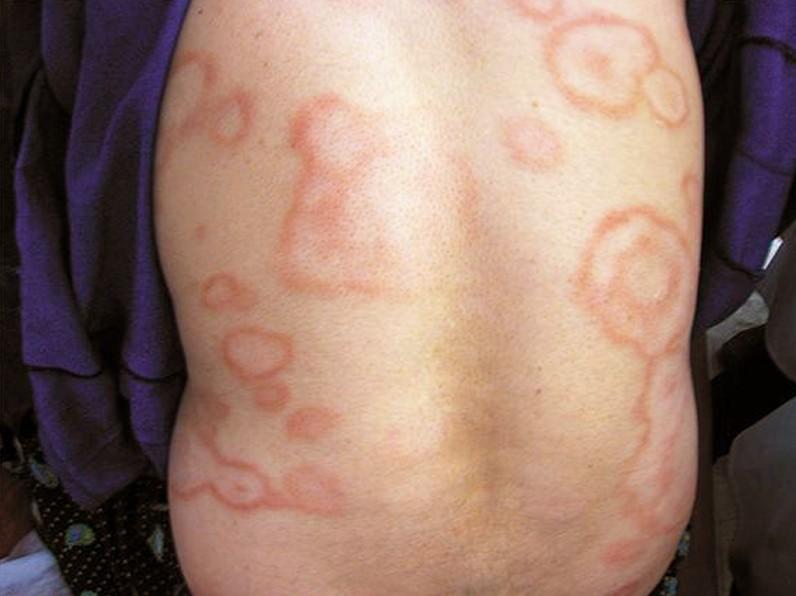
Subcutaneous Nodules
Small, firm, and nontender
Attached to fascia or tendon sheaths over bony prominences
Indistinguishable from rheumatoid nodules
Fever, algia, PR, elevated, streptococcal
Jones Criteria - Minor Criteria
_____
Polyarthr_____
Prolonged __ interval
________ ESR or CRP
Evidence of preceding __________ infection
bed rest, antipyretic, baseline, penicillin
Rheumatic Fever Treatment
Strict ___ ____ until:
Temp returns to normal without the use of __________ medications
ESR, resting pulse rate, and ECG have all returned to ________
Medications
Salicylates
__________
Corticosteroids
fever, aspirin, lower, NSAID, 8
Salicylates
Markedly reduces _____ and joint pain/swelling
_______ 4 to 8 g/day in 4-5 doses
Children are treated with _____ doses or ______
Continue treatment until symptoms resolve (typically 1-2 weeks, possibly up to _ weeks)
benzathine, erythromycin
Penicillin
_________ penicillin, 1.2 million units IM once
___________ may be substituted (40mg/kg/day)
Other penicillins, cephalosporins, and macrolides may also be used
salicylates, prednisone, cardiac
Corticosteroids
Indicated when response to _________ has been inadequate
_________, 40-60 mg orally daily with tapering over 2 weeks
No proof of preventing or minimizing _______ damage
prevented, carditis, children, severe, recurrent, penicillin G benzathine
Prevention of Recurrent Rheumatic Fever
The initial episode of rheumatic fever can usually be _________ by early treatment of strep throat
recurrences are most common in:
Patients who had ________ during their initial episode
________
Rheumatic heart disease becomes more _______ with each recurrent episode
Therefore, the most effective method to limit progression of RHD severity is prevention of ________ GAS strep throat
Preferred prophylaxis
__________ _ _______ 1.2 million units IM every 4 weeks
21, 5, 21, 10, 40, 10
Prevention of Recurrent Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic Fever without carditis
Continue prophylaxis until age __ or _ years after last episode (whichever is longer)
Rheumatic fever with carditis but no residual heart disease
Age __ or __ years after last episode (whichever is longer)
Rheumatic fever with carditis and residual heart disease
Age __ or __ years after last episode (whichever is longer)
1-2, poor, 10, valvular, single
Rheumatic Fever Prognosis
Immediate mortality rate is _-_%
Persistent rheumatic carditis with cardiomegaly, HF, and pericarditis implies a ____ prognosis
30% of children affected die within __ years after the initial attach
After 10 years, 2/3 of patients with RF will have detectable ________ abnormalities
Usually thickened valves with limited mobility
Significant symptomatic valvular heart disease or persistent cardiomyopathy occurs in <10% of patients with a _____ episode