Mod 3 (Geometrical Optics, Mirrors) – Homework Answers
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
geometrical optics
study of light propagation in terms of rays,
rectilinear propagation of light
In a homogeneous medium, light travels in straight lines
law of reflection
The angle of incidence (θ₁) = angle of reflection (θ₂),
The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane
angle of incidence (θ₁) is measured where
between the incident ray and the normal to the
surface
angle of reflection (θ₂) is measured where
between the reflected ray and the
normal
how does law of reflection determine the behavior of light on a reflective surface
governs how mirrors and other reflective surfaces form images.
refraction
change in direction of a wave (such as light) when it
moves from one medium to another
Light going from a higher refractive index to lower
It travels faster and bends away from normal
Light going from a lower refractive index to higher
travels slower and bends toward normal
Snell’s Law equation
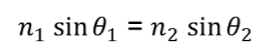
Snell’s Law
allows us to calculate how much light bends between media due to the differences in index
of refraction
How do optical fibers utilize the principle of total internal reflection
guide light through continuous internal reflections, preventing signal loss
while transmitting data efficiently over long distances
characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror
virtual, upright, laterally inverted, and the same size as the object. The image appears behind the mirror at the same distance as the object is in front
Characteristics concave mirror
curves inward and can produce both real and virtual images.
Characteristics Convex mirror
always forms virtual, upright, and reduced images
focal point (F) of a spherical mirror
where parallel rays converge after reflection
Focal Point location
half the distance between the mirror’s vertex and its center of curvature
If magnification is negative
the image is inverted
If magnification is positive
The image is upright
How does the image formed by a concave mirror change as the object distance approaches
the focal length
the image becomes larger and farther away
Image at focal length of concave
No image
Why do convex mirrors always produce virtual, upright, and reduced images
reflected rays always diverge, appearing to originate from behind the mirror,
making the image virtual and smaller
Why does a real image appear inverted
forms where actual light rays converge
Why does a virtual image appear upright
forms from apparent ray extensions
If a concave mirror produces a real and inverted image, where is the object located relative
to the focal point
beyond the focal point.
why no image is formed when an object is placed exactly at the focal point of a
concave mirror
reflected rays become parallel, meaning they never converge
How does increasing the curvature of a spherical mirror affect its focal length
decreases the radius of curvature, making the focal length shorter.