Microscopy and the Cell Quiz study
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microscope quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
magnification
the amount the image is enlarged
revolving power
the extent to which object detail in an image is preserved during magnification
light microscope
use visible light rays that are magnified and focused by means of lenses
the binocular dissecting microscope (stereomicroscope)
designed to study entire objects in three dimensions at low magnification
compound light microscope
used for examining small or thinly sliced selections of objects under higher magnification
transmission electron microscope
the object is ultra-thinly sliced and treated with heavy metal salts to provide contrast
scanning electron microscope
gives an image of the surface and dimensions of an object
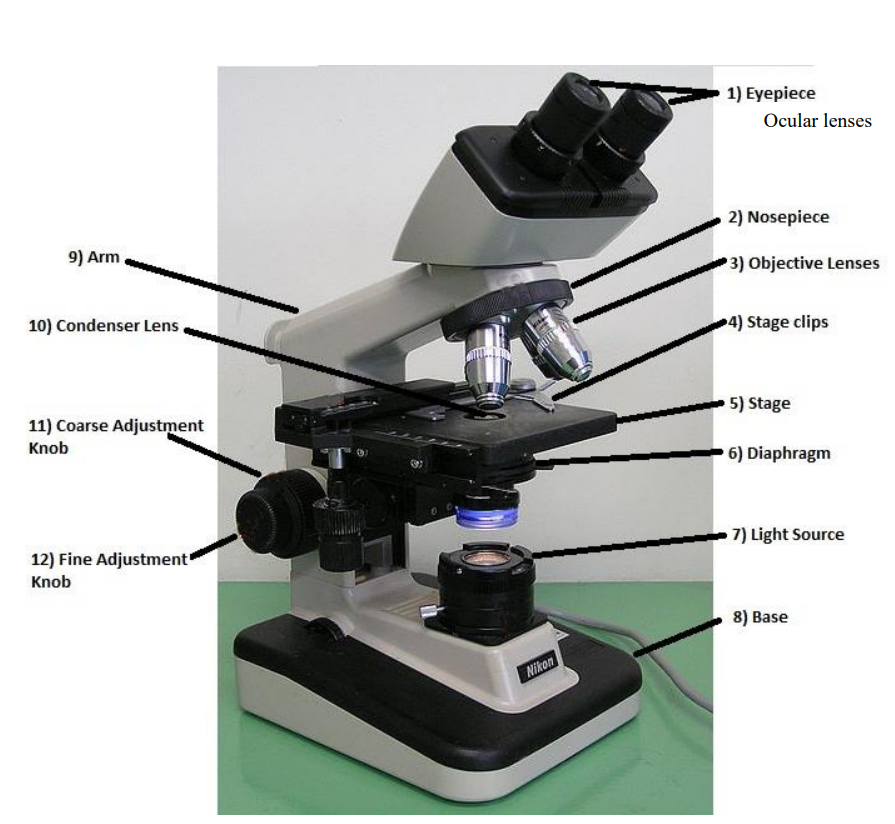
ocular/eyepiece lens
the lens at the top that you look through. usually 10x power
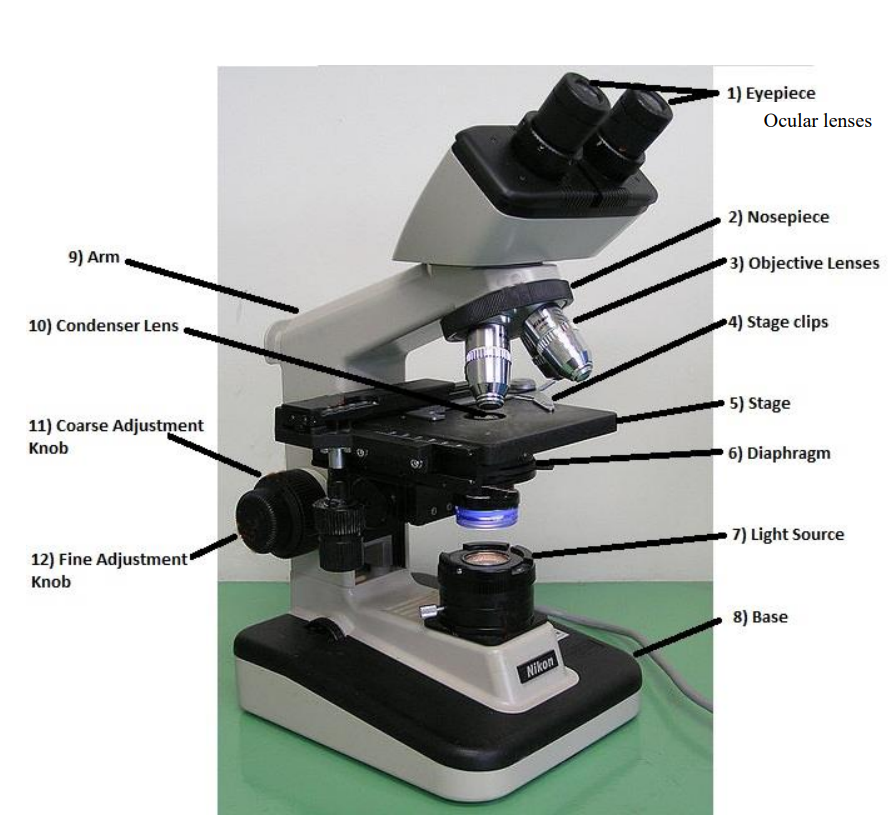
tube
connects the eyepiece to the objective lens
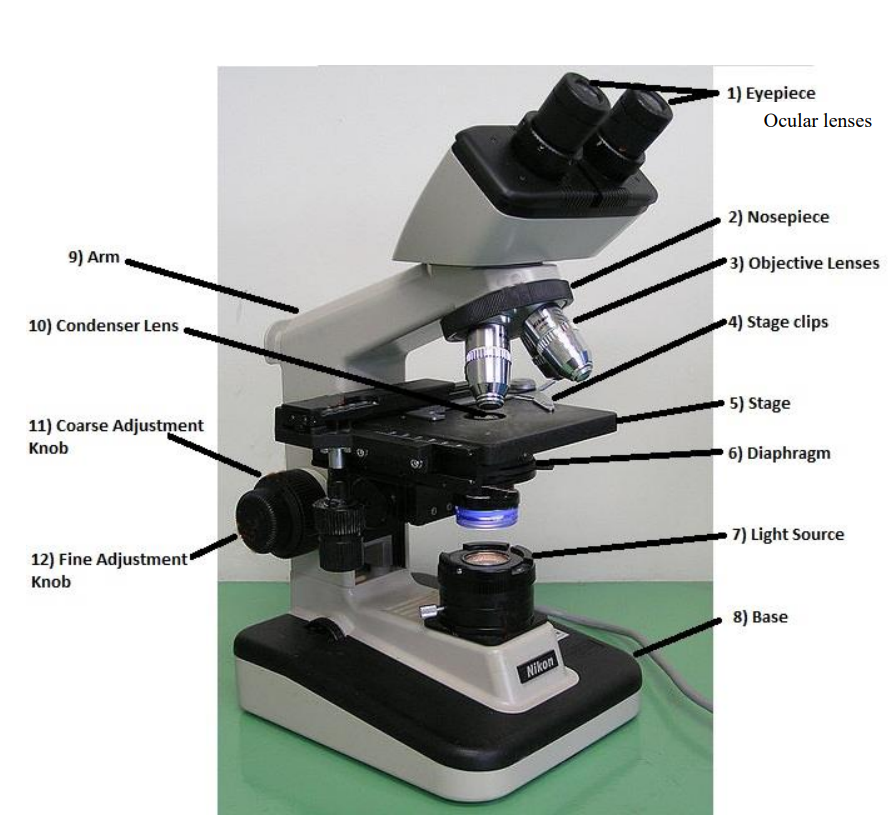
arm
supports the tube and connects it to the base
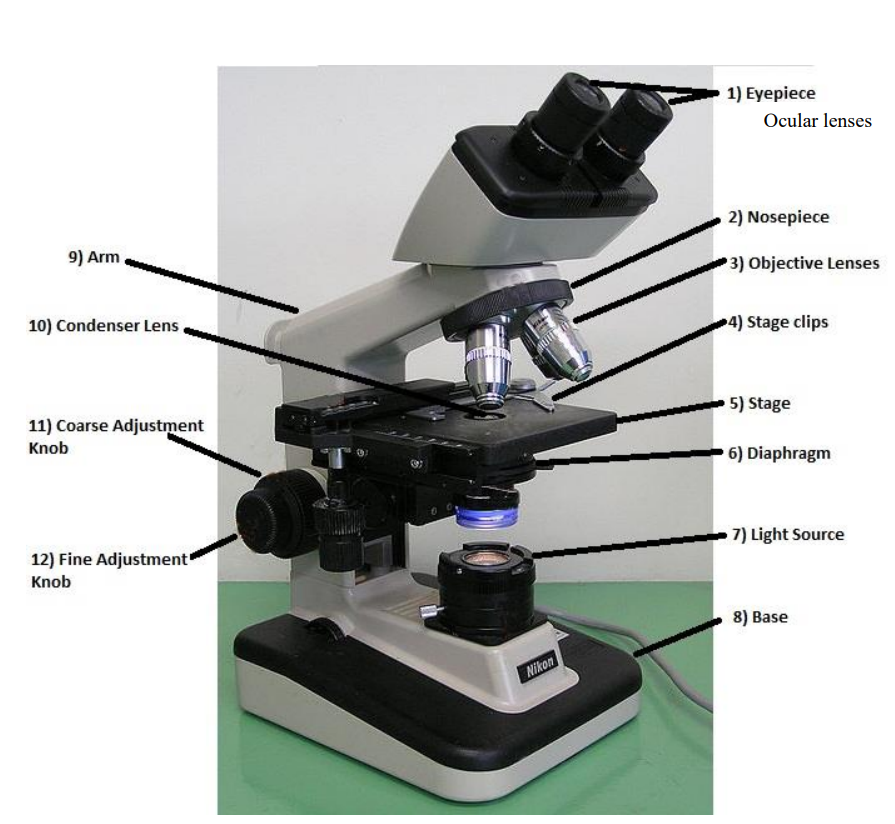
base
the bottom of the microscope, used for support
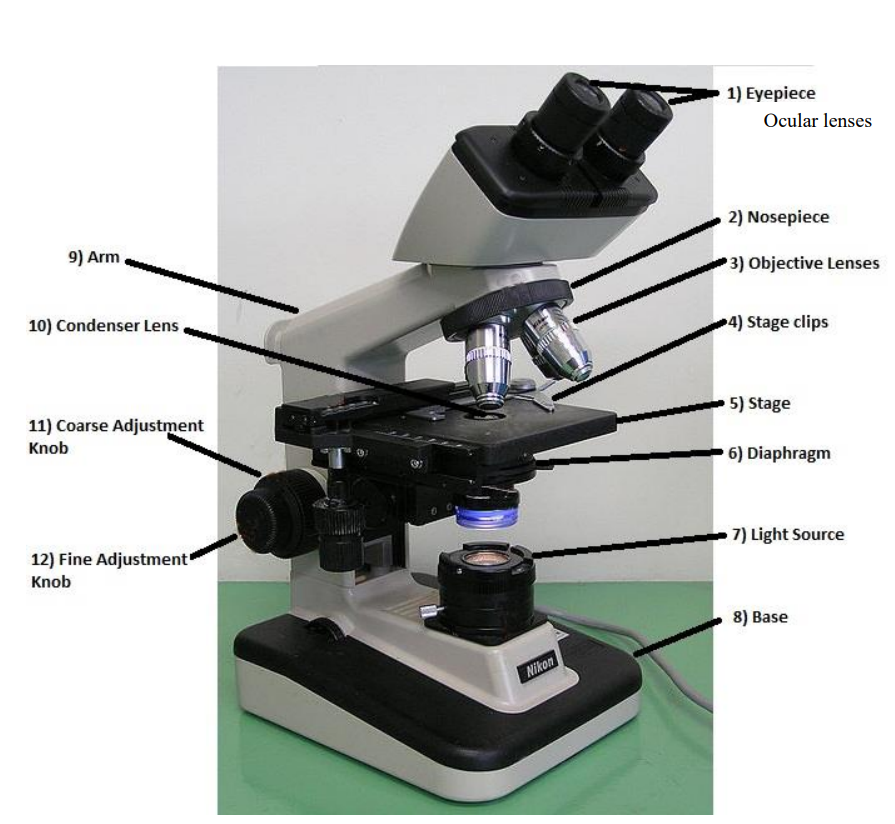
illuminator
a steady light source(110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If the microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
stage
the flat platform where you place your slides
stage clips
holds the slide in place
mechanical stage
moveable stage that aids in accurate positioning of the slide
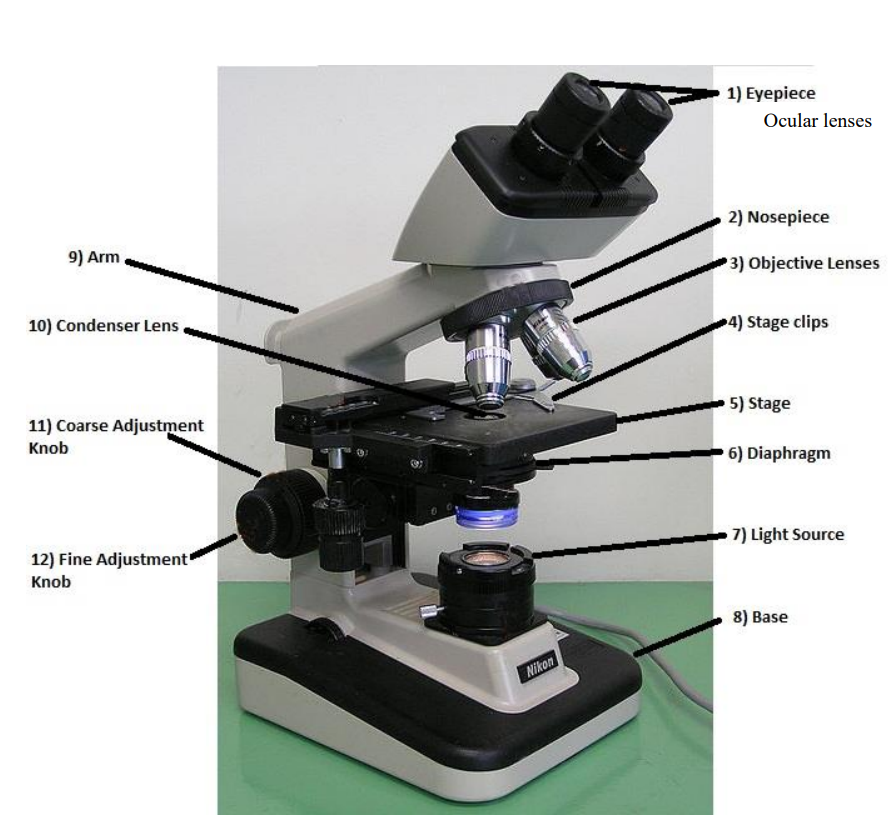
mechanical stage control knobs
two knobs that control the mechanical stage; one moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down
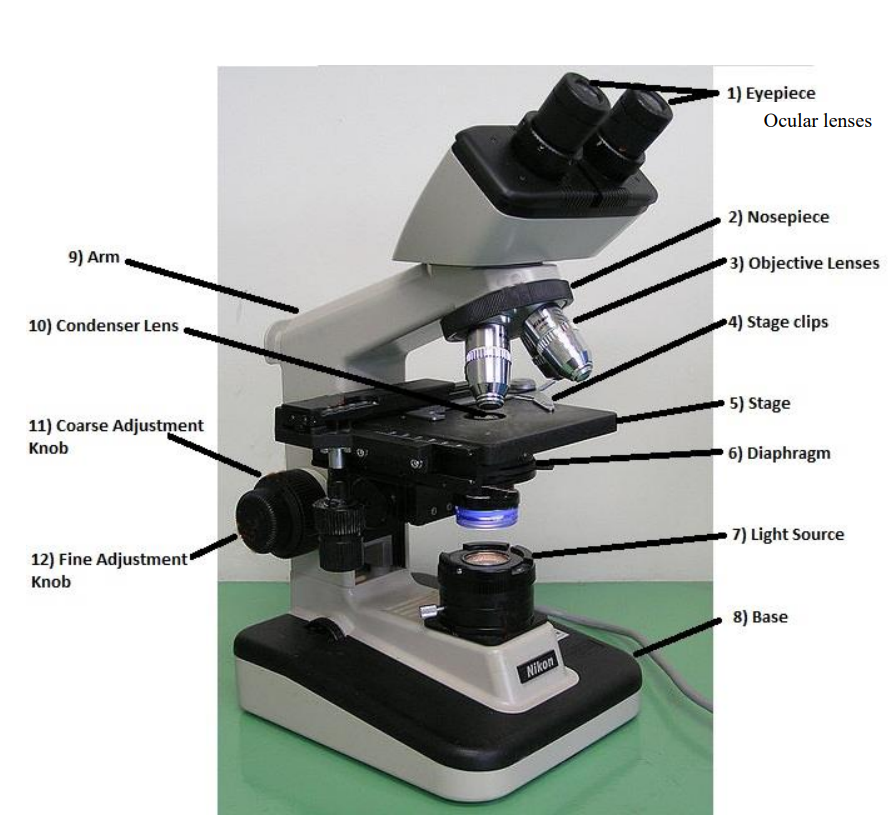
revolving nosepiece or turret
holds two or more objective lenses and can be roteated to easily change power
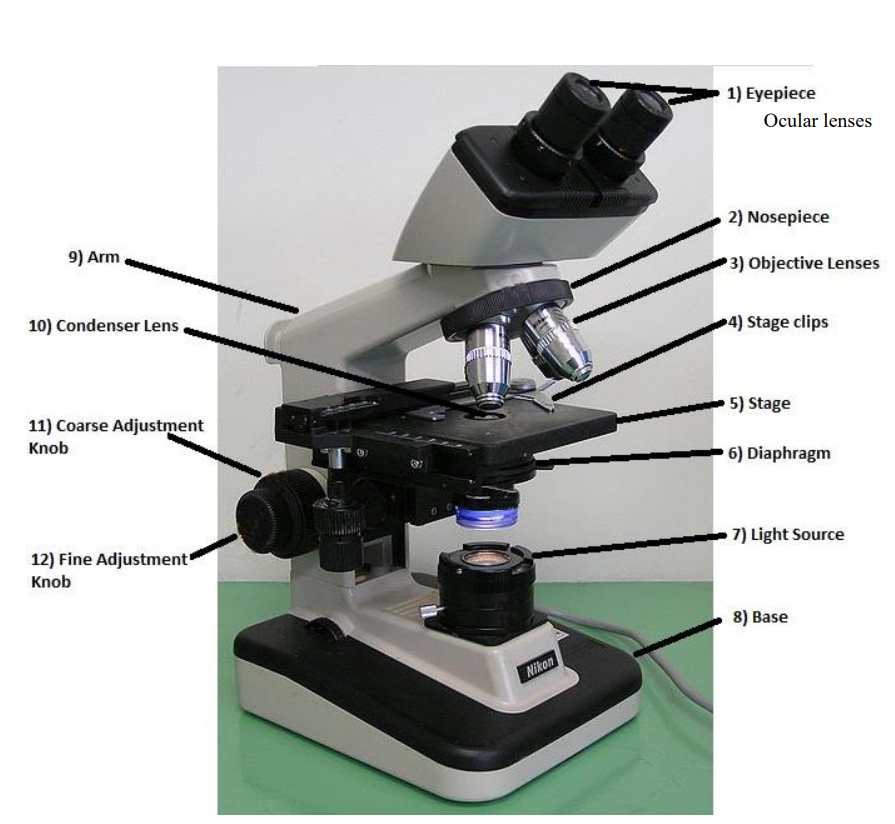
objective lenses
3-4 lenses on a microscope
the shortest lens is the lowest power, the longest one is the lens with the greatest power. All quality microscopes have achromatic, par centered, parfocal lenses.
scanning lens
4x
(4x * 10x eyepiece lens = 40x magnification)
low power lens
10x
high-dry lens
40x
high oil (oil is needed)
100x
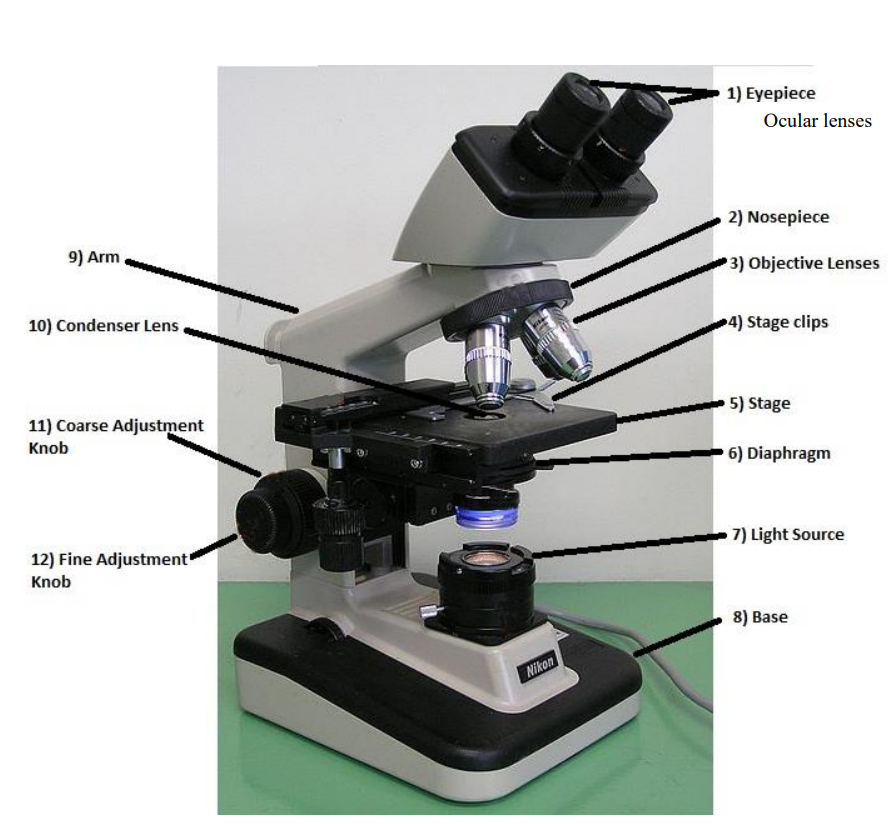
condenser lens
focuses the light onto the specimen
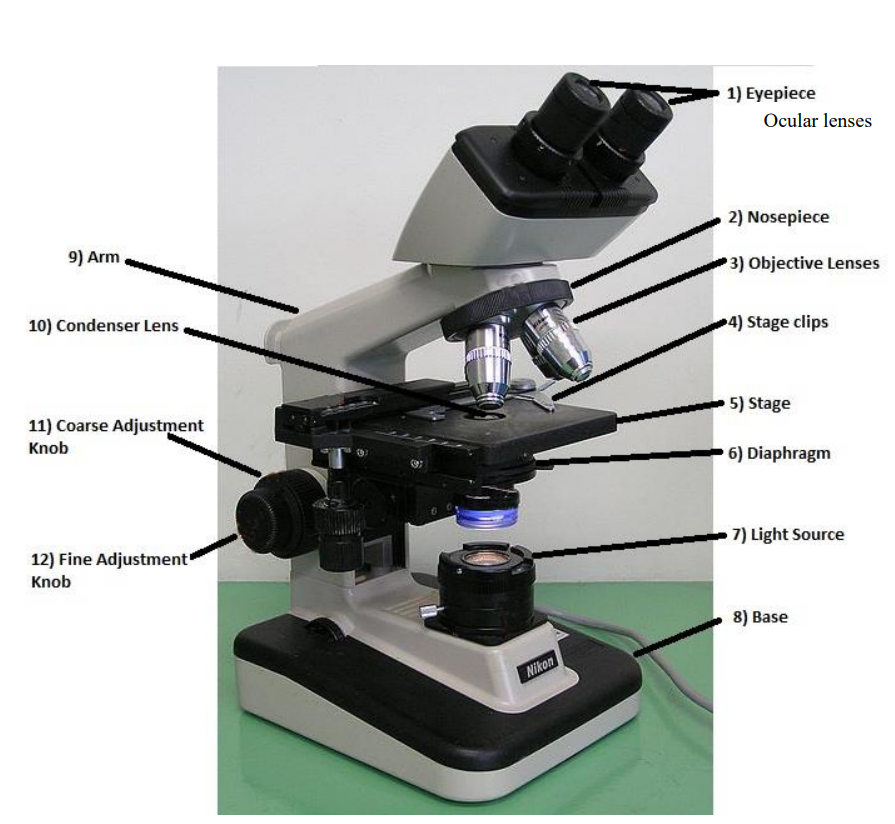
diaphragm/iris
many microscopes have a rotating disk under the stage. This diaphragm has different sized holes and is used to vary the intensity and size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide.
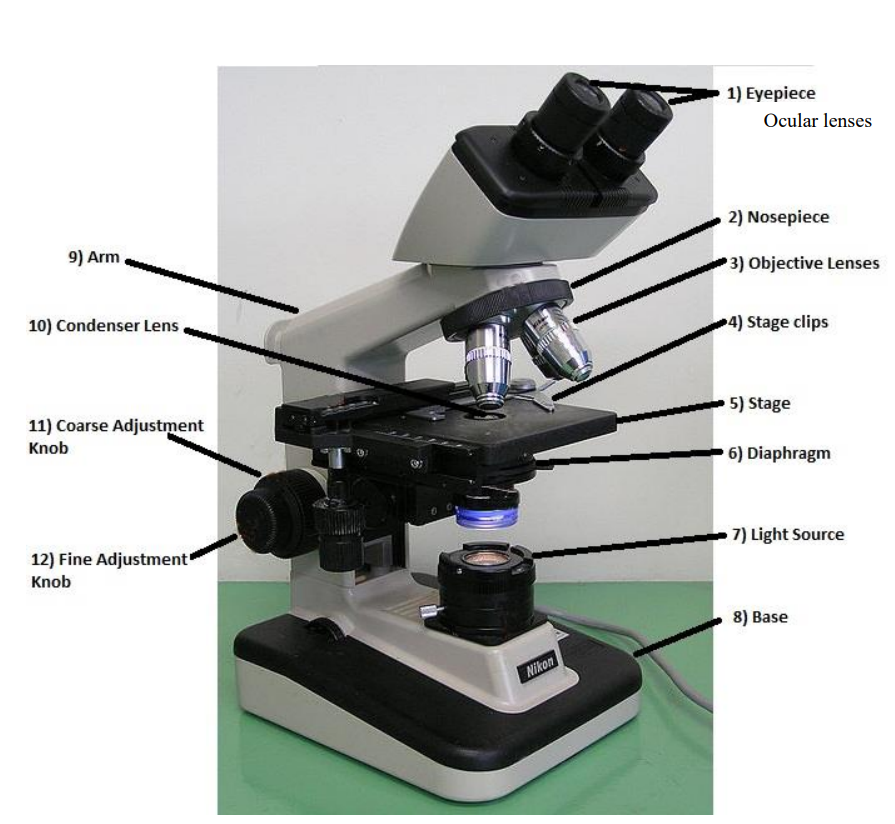
coarse focuse knob
used to bring object into approximate focus
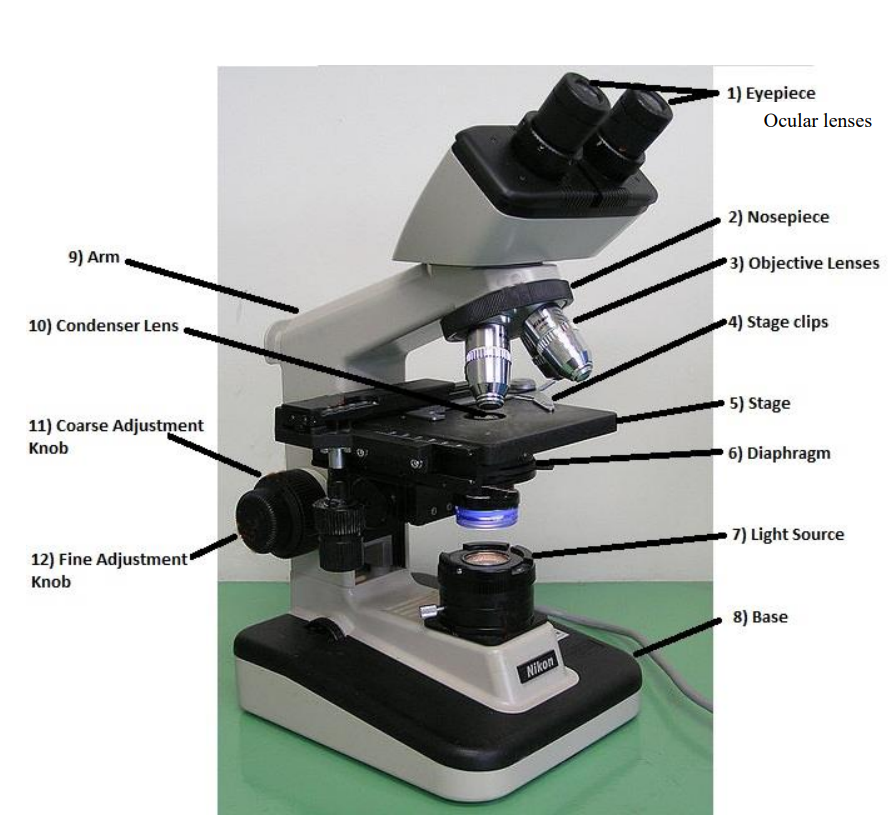
fine focus knob
used for critical focusing and used with higher power objective to bring the object into final focus
parcentral
it stays in the center
parfocal
mostly in focus
depth of field
the distance through which you can move the specimen and still have it remain in focus
working distance
space between the objective lens and the coverslip. It decreases with increasing magnifying power
cell
the basic unit of life
cell theory
states that all living things are compsoed of one or more cells
plasma membrane
defines the boundary of the living material
DNA
stores genetic information
cytoplasm
everything inside the plasma membrane that is not part of the DNA region
prokaryotic
no nucleus
eukaryotic
nucleus
nucleus
stores genetic info/synthesis of DNA and RNA
ribosomes
protein synthesis
rough ER
synthesis/modification and transport of proteins
smooth ER
lipid synthesis
Golgi appratus
processing, sorting and distribution of proteins, lipids
microtubule
shape of cell and movement of its parts
cytoplasm
contains fluid and organelles
chloroplasts
photosynthesis (plants only)
flagella/cilia
cell movement
vacuole and vesicle
storage of cellular substances
centriole
microtubule organization ( humans only)
plasma membrane
definition of cell boundary; regulation of a molecular passage
mitochondria
cellular respiration
nuclear pore
regulation of material in and out of the nucleus
nucleolus
ribosomal formation
cell wall
support and protection ( plant only)
prokaryotic cells are typically…
bacteria, cyanobacteria, and archaea. They’re believed to be similar to the earliest cellular life. no membrane bound organelles
eukaryotic cells are usually…
found in protists, fungi, plants, and animals. They contain membrane bound organelles.