MTE2201 Module 6 - Copolymers and Network formation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Number avg molecular weight for anionic polymerisation
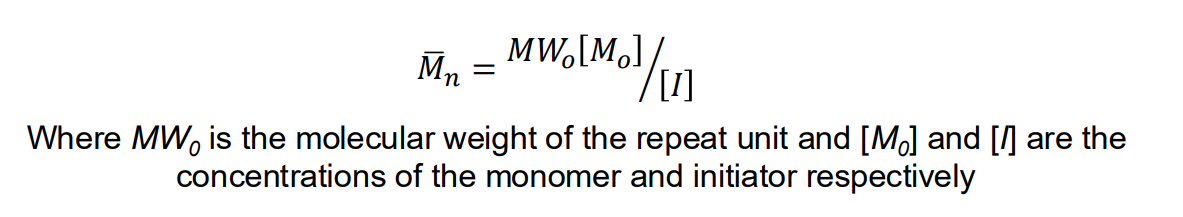
Features of anionic polymersiation
Reactions are very sensitive to reagent purity and solvent used
▪ In careful control of conditions, theres few termination reactions,so chains can be indefinitely active
All chains are initiated at about the same time, thus the reaction can be carried out in a controlled manner
This leads to low polymer dispersity values as well as uniform polymer structure
Conditions needed to form “living” polymers through anionic polymerisation
The solvent cannot be one that can give a "killer" positive charge to the growing chain.
-Absence of O2 , CO2 , water, other impurities
Why is relationship linear between conversion and molecular weight in anionic polymerisation
Termination and chain transfer are absent, therefore the overall concentration of chains remains constant during he reaction. (reaction is first order)
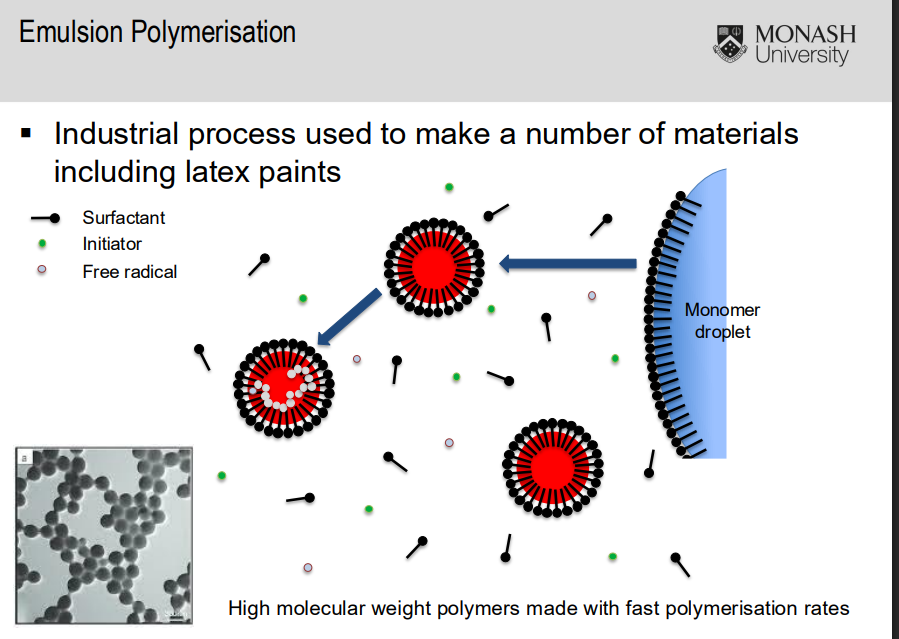
Emulsion polymerisation
Industrial process used to make materials including latex paints. Creates high molecular weight polymers with fast polymerisation rates
Steps of emulsion polymerisation
Emulsification of the monomer in the aqueous phase which contains a surfactant using agitation (stirring/mixing) → stable emulsion
▪ Heat to the relevant reaction temperature
▪ Add the initiator solution to start the polymerization
▪ Continue the agitation until the end of the polymerisation reaction
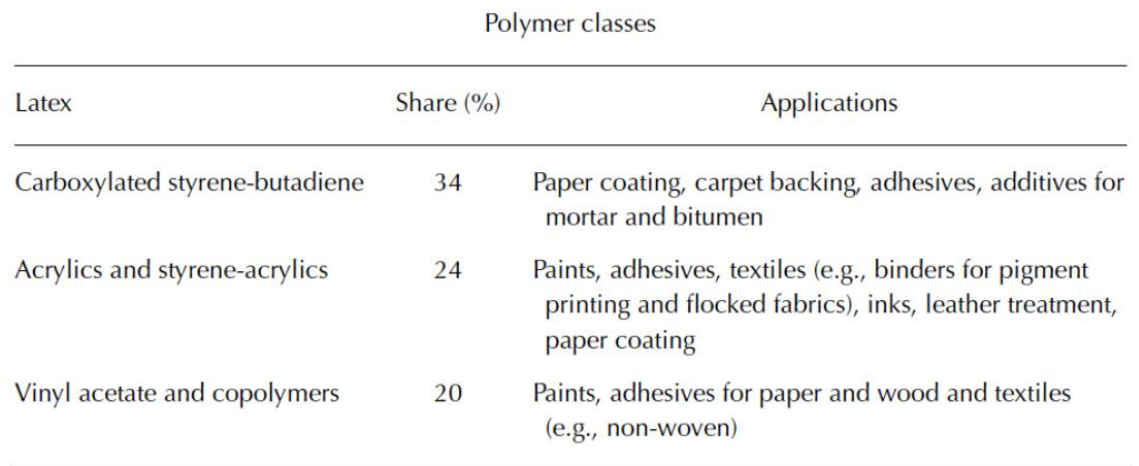
Latex types and applications
Networks are either formed by covalent bonds or physical bonds such as…
– Van der Waals interactions – Hydrogen bonding – Electrostatic interactions – Hydrophobic interactions
Networks Formed in Chain Polymerisation
Vulcanisation with sulfur using a polymer formed by chain growth
or
hydrogel - Polyacrylamide Network Gel
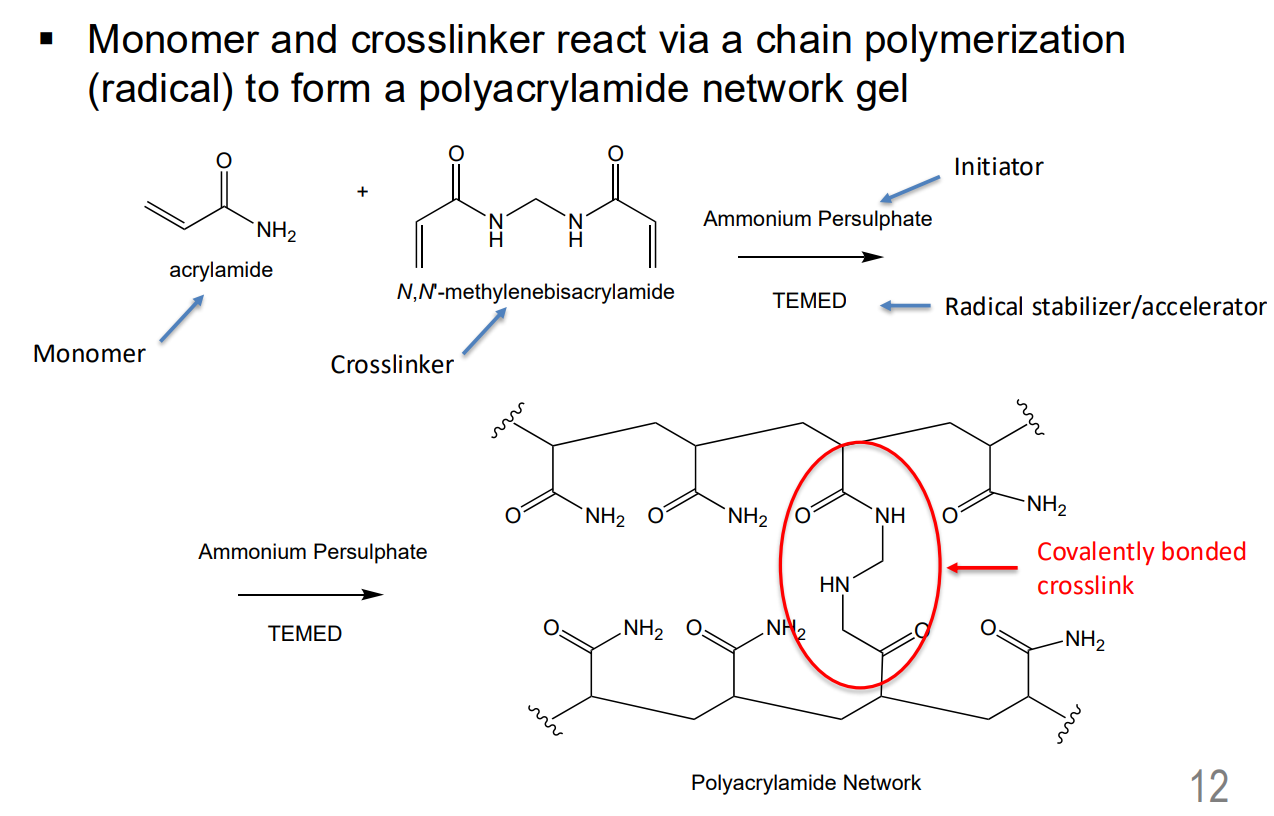
Networks formed in step growth
epoxide resins (epoxide group is a triangle with 2 carbon atoms and an oxygen) with diamine crosslinker
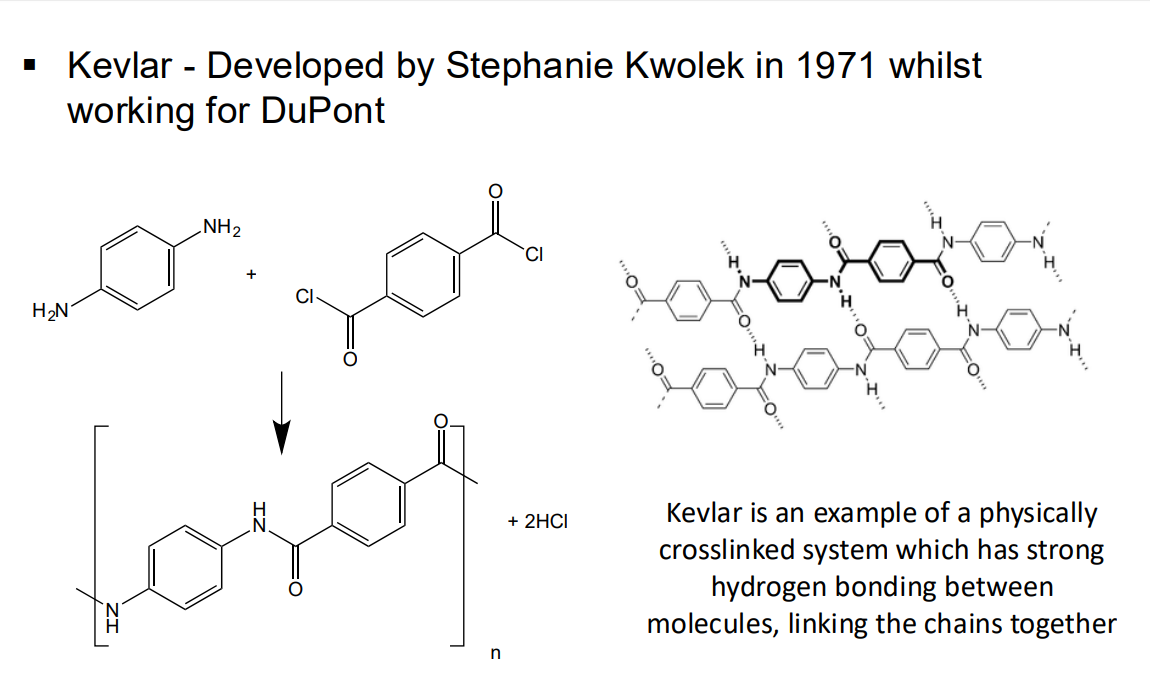
or kevlar
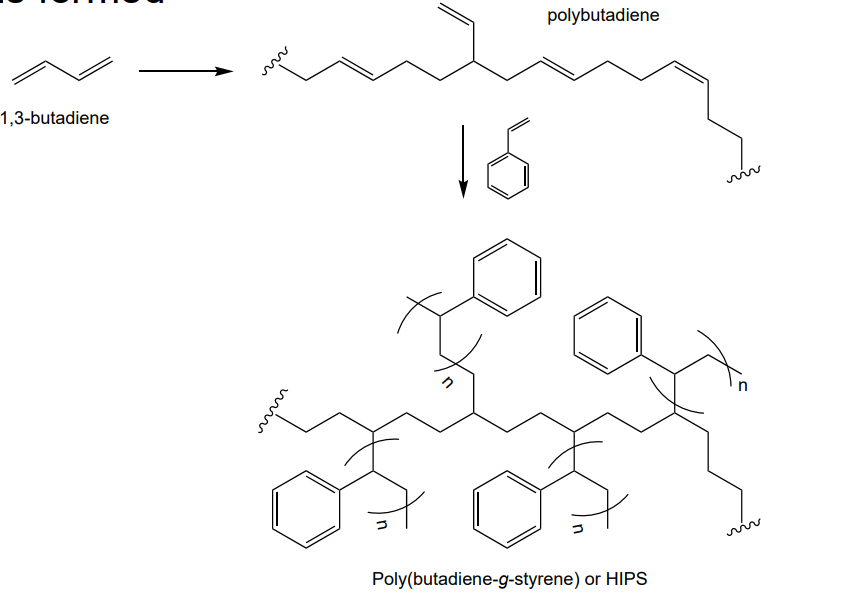
graft copolymer - high impact polystyrene (HIPS)
thanks to grafting, inclusion of the polybutadiene changes the impact resistance properties dramatically compared to normal PS. like PS, its used in food packaging, healthcare and houseware applications
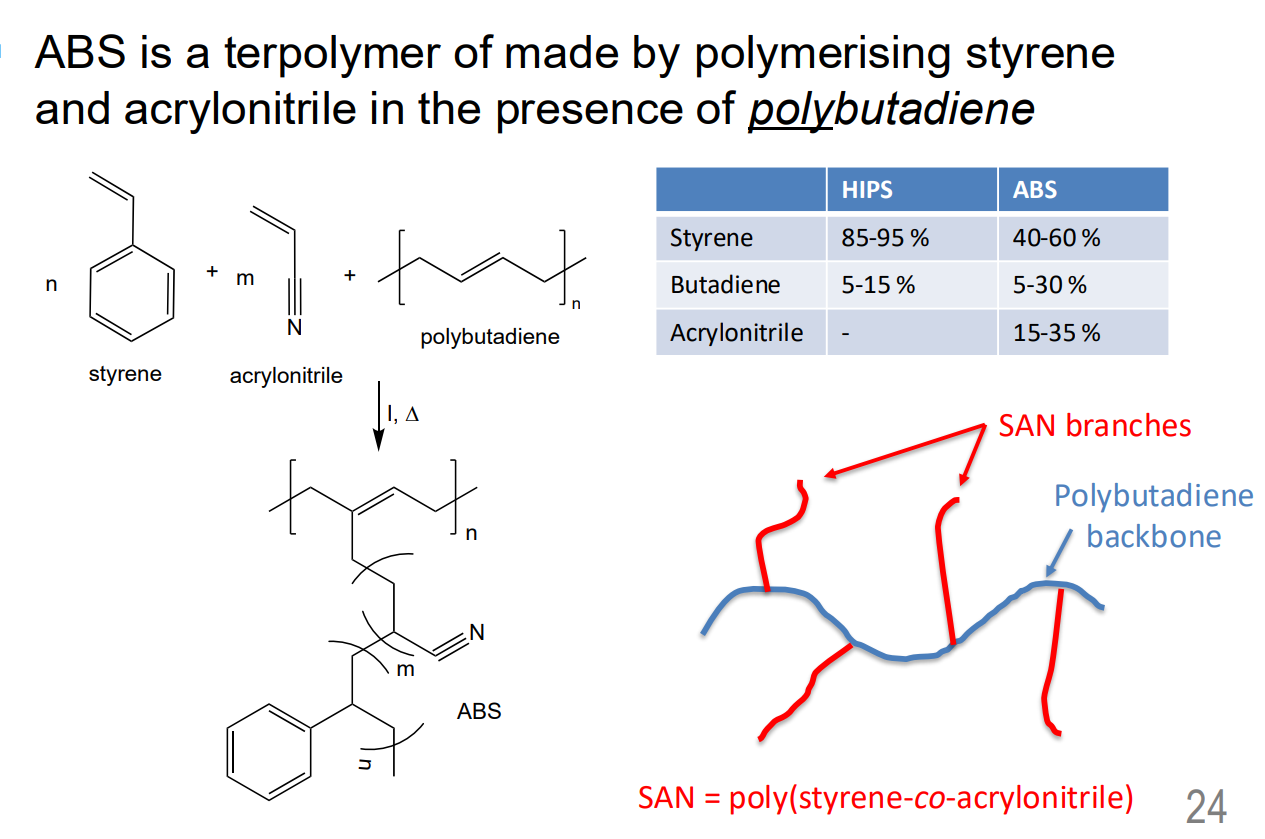
Graft Copolymer – poly(acrylonitrile-co-butadiene-costyrene) (ABS)
Like HIPS, ABS is also rubber-toughened grade of polystyreneABS are essentially rubber-toughened grades of polystyrene