FC03-CRB1-Exam_Gloria-02-Notes
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Question:
To avoid Legionella, to what temperature should domestic hot water be heated regularly?
Answer:
60°C (can be from 60–80°C)
What is the efficiency of polycrystalline photovoltaic under usual condition?
Answer: 17%
Note: The 17% value is at the upper end of typical commercial efficiency. The average for standard polycrystalline (multicrystalline) PV modules is usually around 15–17% under standard test conditions (STC).
Question:
An office building in Munich is fully glazed on the east and west façade. Which statement is correct?
Essential for the performance in summer are SHGC-values of glazing and not orientation.
Choosing this orientation is reasonable compared to south orientation, because solar gain in summer are higher.
With solar heat gain only 200 W/m² in summer, the chosen orientation is best for an office building in Munich.
Due to 800 W/m² of solar gain in summer, overheating would be a huge problem with this orientation in summer.
Answer:
Due to 800 W/m² of solar gain in summer, overheating would be a huge problem with this orientation in summer.
Note:
This is correct. East and West façades are more problematic than the South in summer due to lower solar altitude angles during mornings and afternoons, leading to higher incident radiation and less shading effectiveness. This makes overheating more likely in such orientations—especially with full glazing—making them critical from a summer thermal comfort perspective.
Question:
The PMV index tells us about the thermal comfort and is directly related to the PPD. What number is 3 for the PMV index?
Answer:
Hot
Note:
The PMV (Predicted Mean Vote) index ranges from -3 (cold) to +3 (hot). A PMV of +3 corresponds to the sensation of “hot” on the thermal comfort scale, while 0 represents “neutral.” Therefore, this answer is correct. PMV is used together with PPD (Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied) to assess comfort levels in indoor environments.
What is the typical depth of a borehole?
• a) 500 m
• b) 100 m
• c) 200 m
• d) 50 m
Answer: 100 m
Explanation:
A typical geothermal borehole for heat exchange (e.g., for heat pumps) is usually drilled to a depth of 80–150 meters, depending on soil conditions and the thermal demand. Thus, 100 meters is a realistic and commonly encountered average value in moderate climates like Germany.
Question:
The PMV index tells us about how people feel in a room in terms of thermal comfort and is directly connected to the PPD (Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied).
What is the typical range for the PPD axis?
Correct Answer:
d) 5–80%
Explanation Note:
The PPD (Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied) indicates the expected percentage of people dissatisfied with the thermal environment at a given PMV value. Even in ideal thermal conditions (PMV = 0), some people will still feel discomfort. This is why the minimum PPD is 5%, meaning 5% of people will always be uncomfortable, no matter the conditions.
The upper limit of 80% corresponds to extreme discomfort on the PMV scale.
Question (Plain English):
What does the COP (Coefficient of Performance) tell us? —- what information does it give us?
Correct Answer:
c) Thermal Output / Power Input
Explanation:
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a measure of the efficiency of a heating or cooling system. It is calculated by dividing the amount of useful thermal energy (heat) output by the electrical energy (power) input.
A higher COP means the system is more efficient, as it provides more heating or cooling for the same amount of input power.
For example, a COP of 4 means the system produces 4 units of heat for every 1 unit of electricity consumed.
Order the cooling systems below by their flow temperatures, from the lowest to the highest:
Thermoactive floor slab
Air conditioning
Cooling panels
Correct Order (from lowest to highest):
Thermoactive floor slab → ~20°C
Cooling panels → ~10–14°C
Air conditioning → ~5–10°C
Explanation:
Thermoactive floor slabs use chilled water at relatively high temperatures (~18–20°C) to avoid condensation and use the thermal mass of concrete to cool spaces slowly and efficiently.
Cooling panels operate with cooler water but must avoid surface condensation, so they usually run at 10–14°C.
Air conditioning systems, particularly direct expansion (DX) types, operate with the coldest air or coolant, typically between 5–10°C, to allow quick temperature drops.
Question:
Which component of the heat pump requires electric power?
Options:
a) Evaporator
b) Expansion valve
c) Condenser
d) Compressor
Correct Answer:
d) Compressor
Explanation:
The compressor is the primary component in a heat pump that requires electric energy. It compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature before it releases heat in the condenser. This mechanical work is where most of the electrical input for a heat pump is consumed.
The evaporator, expansion valve, and condenser mainly facilitate heat transfer processes but do not themselves consume significant electric power.
Translated Question:
Which of the following heat transfer systems cannot be used both for heating and cooling?
Options:
a) Radiator
b) Thermoactive floor slab
c) Air conditioning
d) Radiant ceiling panels
Correct Answer:
a) Radiator
Explanation:
Radiators are typically designed only for heating. They operate using hot water or steam and cannot effectively be used to cool a space. In contrast:
Thermoactive floor slabs, air conditioning systems, and radiant ceiling panels can all function as both heating and cooling systems when properly designed.
Cooling with radiators is not feasible because radiators would condense moisture from the air (due to dew point), which they are not built to handle.
Question: What is the main difference between a solar thermal system and a photovoltaic system?
Answer:
A solar thermal system uses the sun’s energy directly to heat a fluid, which is then circulated for space or water heating in a building.
A photovoltaic system (PV), on the other hand, converts sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight excites electrons in a semiconductor material, generating electric current.
Note:
Solar thermal = heat generation
Photovoltaic = electricity generation
Mark the parameter that influences -among others - the PMV Index.
a) Supply Air
b) Air Velocity
c) C02 concentration
d) Air change rate
b) Air velocity.
Among the listed options, air velocity is the only one that is part of the standard PMV model (defined by ISO 7730). It affects how the body perceives temperature by enhancing or reducing convective heat loss.
Which energy use is not a part of the phases A1–A5 in LCA?
a) Transport to Construction Site
b) Raw Material Supply
c) Operational Energy Use
d) Installation Process
c) Operational Energy Use
Here’s what A1–A5 include:
A1 – Raw Material Supply
A2 – Transport to manufacturer
A3 – Manufacturing
A4 – Transport to construction site
A5 – Construction/installation process
Question:
Which of the following does not influence the PMV (Predicted Mean Vote) index?
Options:
a) Clothing factor
b) Metabolic rate
c) Humidity
d) Evaporation
Correct Answer:
d) Evaporation
Question:
Which water temperature can be achieved in flat plate collectors?
a) up to 60°C
b) up to 130°C
c) up to 90°C
d) up to 160°C
Correct answer: c) up to 90°C
Question 16
Which of the following is not counted as local thermal discomfort in a room?
a) Large horizontal air temperature difference
b) Heat or cold feet, caused by uncomfortable floor temperature
c) Cooling or heating of parts of the body by radiation
d) Local convective cooling of the body caused by draught
Correct answer: a)
Large horizontal air temperature difference is not typically classified as local thermal discomfort. Local discomfort factors usually include vertical air temperature differences, draught, radiant asymmetry, and floor surface temperature. Horizontal differences are not a standard criterion.
Question:
Mark the parameter that influences — among others — the PMV index.
Options:
a) Outside Air Temperature
b) Radiation of the occupants
c) Air Temperature
d) Ceiling Temperature
Correct Answer: c) Air Temperature
Explanation:
The PMV (Predicted Mean Vote) index depends on environmental and personal variables that affect thermal comfort. One of the key environmental factors is the air temperature, which directly impacts heat exchange between the body and the environment.
Notes:
Outside air temperature (option a) is not directly relevant to indoor thermal comfort if the building envelope is well-insulated.
Radiation of the occupants (option b) is not a scientifically valid term — it is the mean radiant temperature that matters.
Ceiling temperature (option d) may affect radiant temperature but is not typically an input to PMV.
Question 17
Cooling a room means:
a) Leading coldness into a room
b) Extract heat from the room
c) Supply heat to the room at a very low temp level
d) Supply coldness into a room through a system
Correct Answer: b) Extract heat from the room
Explanation:
Cooling a room is not about “adding cold,” but about removing heat. Heat naturally flows from warmer to cooler areas, so cooling systems work by extracting thermal energy (heat) from the indoor space and releasing it elsewhere, such as outside.
Question 20:
What is the current primary energy factor of power?
a) 1.8
b) 1.1
c) 0.2
d) 2.4
a) 1.8 is correct
The primary energy factor (PEF) for electricity indicates how much primary energy (e.g., fossil fuel) is needed to deliver one unit of final energy (electricity) to the user. The value can vary between countries and regulations, but in many European contexts, the commonly used default PEF is 1.8, especially after updates in standards aiming to reflect increased renewable shares in the grid mix.
The value 2.4 was used in older standards, but 1.8 is now considered current and widely accepted (e.g., in German EnEV / GEG context)
Question 21
Which of the following energy consumers has the lowest CO₂ equivalent per kWh end energy?
a) Gas boiler
b) Heat pump
c) Auxiliary energy
d) Lighting
Correct answer: b) Heat pump
Heat pumps have the lowest CO₂ emissions per kWh of delivered energy because they transfer existing thermal energy rather than generating heat through combustion or resistance. This high efficiency results in less primary energy use and therefore lower CO₂ emissions.
Question 22:
Which of the following measures does not reduce heating demand?
a) High standard of insulation of the building skin
b) Using low temperature heat transfer system like underfloor heating in combination with heat pump
c) Heat recovery of the ventilation system
d) Increasing internal gain, e.g., bigger window on south façade
Correct answer: d) Increasing internal gain, e.g., bigger window on south façade
Explanation: While larger south-facing windows can contribute to solar gains (potentially reducing heating demand under certain conditions), internal gains generally refer to heat from occupants, lighting, or equipment, and are not typically a design strategy to reduce heating demand. In contrast, options a, b, and c are well-established energy efficiency strategies for reducing heating loads.
Question 23: Which factor indicates a humid climate?
a) Little temperature difference between summer and winter
b) Little temperature difference between day and night
c) Large temperature difference between summer and winter
d) Large temperature difference between day and night
Correct answer: b) Little temperature difference between day and night
Note:
In humid climates, due to the high moisture content in the air, the temperature tends to remain more stable over a 24-hour period, which results in a small difference between day and night temperatures.
Question 24
What is the function of a cooling tower?
a) To store liquid of district cooling
b) To precool the supply air for ventilation system
c) To dissipate heat from the refrigerant
d) To cool the surrounding and increase outdoor comfort nearby the tower
Marked Answer: c) To dissipate heat from the refrigerant
That is correct — the main function of a cooling tower is to reject heat from a building’s HVAC or industrial process system, typically by dissipating heat from the refrigerant or water used in heat exchange.
What is the range of PMV?
-3 to +3
Question 26
Which of the following passive strategies would improve thermal comfort most in a building located in a tropical climate zone?
a) High thermal mass with minimal ventilation
b) Light construction and increased air flow
c) Fully glazed façade with external shading only
d) High insulation levels with sealed envelope
e) Thermal mass and night cooling
b) Light construction and increased air flow
Question 27) Which option is not correct regarding PV.
a) PV modules increase their power generation when they are placed at the optimal angle to the sun.
b) When PV-module get too hot the efficiency goes down.
c) It is more economical to use the power by yourself, than to feed into the grid.
d) With an overcast sky there is no generation of power.
d) With an overcast sky there is no generation of power. —— wrong.
Question 28) Which factor do you not get out of climate data?
a) Rainfall
b) Insolation
c) Wind
d) Heat Island Coefficient
d) Heat Island Coefficient is correct.
This factor is not typically included in standard climate datasets, which focus on measurable atmospheric parameters like rainfall, solar radiation (insolation), wind speed/direction, temperature, and humidity. The Heat Island effect is a localized urban phenomenon and must be assessed through specialized urban climatology studies.
Which form of energy plays the biggest tile in the building sector
a) heat
b) Coldness
c) Electricity
d) Mechanical Energy
HEAT
Which of the following heat sources is not applicabble for co-generation?
a) Gas
b) Biomass
c) WasteWater Utilisation
d) Deep Geothermal energy
d) Deep Geothermal energy
Heat production = _______________
Heat production = Heat loss
“Heat Production = Heat Loss” is correct in the context of thermal comfort under steady-state conditions. It refers to the human body’s heat balance: to maintain a stable core temperature, the metabolic heat produced by the body must be equal to the total heat lost to the environment through mechanisms like conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation.
If this balance is disrupted, thermal discomfort occurs (e.g., if heat production exceeds loss, one feels hot).
Question 33) Which statement is correct regarding heat emission of a human body?
a) The higher the air temperature, the higher the percentage of heat emission by conduction.
b) The lower the air temperature, the lower the percentage of heat emission by evaporation.
c) The higher the air temperature, the higher the percentage of heat emission by convection.
d) The lower the air temperature, the lower the percentage of heat emission by radiation.
a) Incorrect: Conduction plays a very minor role overall and is not significantly affected by air temperature.
b) Incorrect: When air temperature is low, evaporation (sweating) becomes more important, not less.
c) Correct: As the air heats up, convection increases its relative contribution to heat loss.
d) Incorrect: At lower temperatures, radiation is a major form of heat loss — it increases, not decreases.
Question 34) Which of the following technology solutions should result in the best COP value for the heat pump?
a) Groundwater well with floor heating
b) Ambient air with radiator
c) Ground collector with air heating
d) Geothermal borehole with convector
Correct answer: a) Groundwater well with floor heating
This setup provides the most favorable temperature levels for efficient heat exchange and low-temperature heat distribution, maximizing the coefficient of performance (COP).
Which option is correct?
Answer Mean r___________ is taken into account when calculating the operative temperature.
Answer Mean radiant temperature is taken into account when calculating the operative temperature.
Question 34) What is the highest monthly insolation on a horizontal surface in Munich in summer?
Correct answer: 160 kWh/m²/month
The value of 710 kWh/m²/month is far too high for Munich. For central European cities like Munich, the highest monthly global horizontal irradiation in summer (typically in June or July) is around 160 to 180 kWh/m²/month, based on reliable climate databases like PVGIS.
Question 30) Which statement is not correct regarding a low temperature district heating network?
a) Heat losses are negligible compared to a high temperature network.
b) There is no need of heat transfer station in every connected building.
c) You never have an additional heat source for the peak load.
d) Each connected building needs to have an own heat pump.
d) Each connected building needs to have an own heat pump.
Question
Which Geothermal system does not require a heat pump to provide sufficient temperature for heating?
Answer) Deep Geothermal Energy.
What is the definition of weather and climate?
Weather refers to the short-term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place, including temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity.
Climate is the average weather conditions in a region over a long period, typically 30 years or more.
Q2) What are the different scales of climate data used in building simulation tools, and how are they defined by spatial extent?
Microclimate (mm to ~100 m),
Mesoclimate (100 m to 100 km),
Macroclimate (100 km to >1000 km, including zone/global types).
You want to run a simulation for a building in downtown LA - what could be the problem with the climate data?
Urban Heat Island
The yearly insulation in Munich on a horizontal surface is about?:
1100 kWh/m²a
Yes, the value of 1100 kWh/m²a is approximately correct. This is a realistic estimate for the annual global horizontal irradiance (GHI) in Munich, which typically ranges between 1000 to 1200 kWh/m² per year, depending on specific weather patterns and measurement years.
Which factor indicates a humid climate?
Little temperature difference between day and night.
In a humid climate with low wind speed. the thermal comfort is to be optimzed with creating air flow. Which orientation is best for long rectangular building.
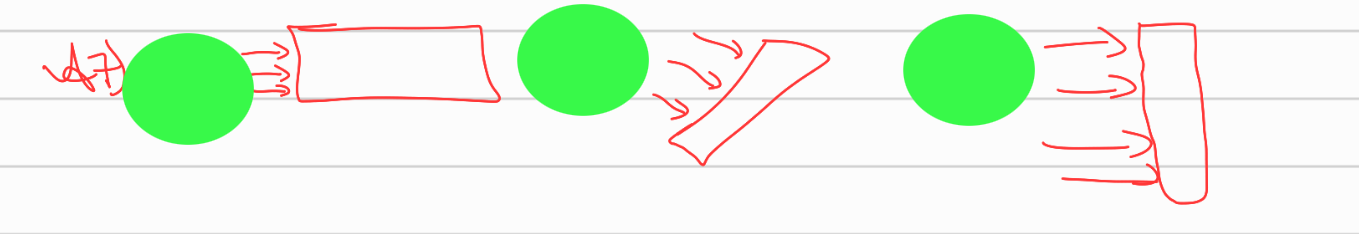
C) last image - due to the low speed of the wind.
high speed = a is correct.
Draw the comfort zone according to DIN 1946 in Psychometric chart.
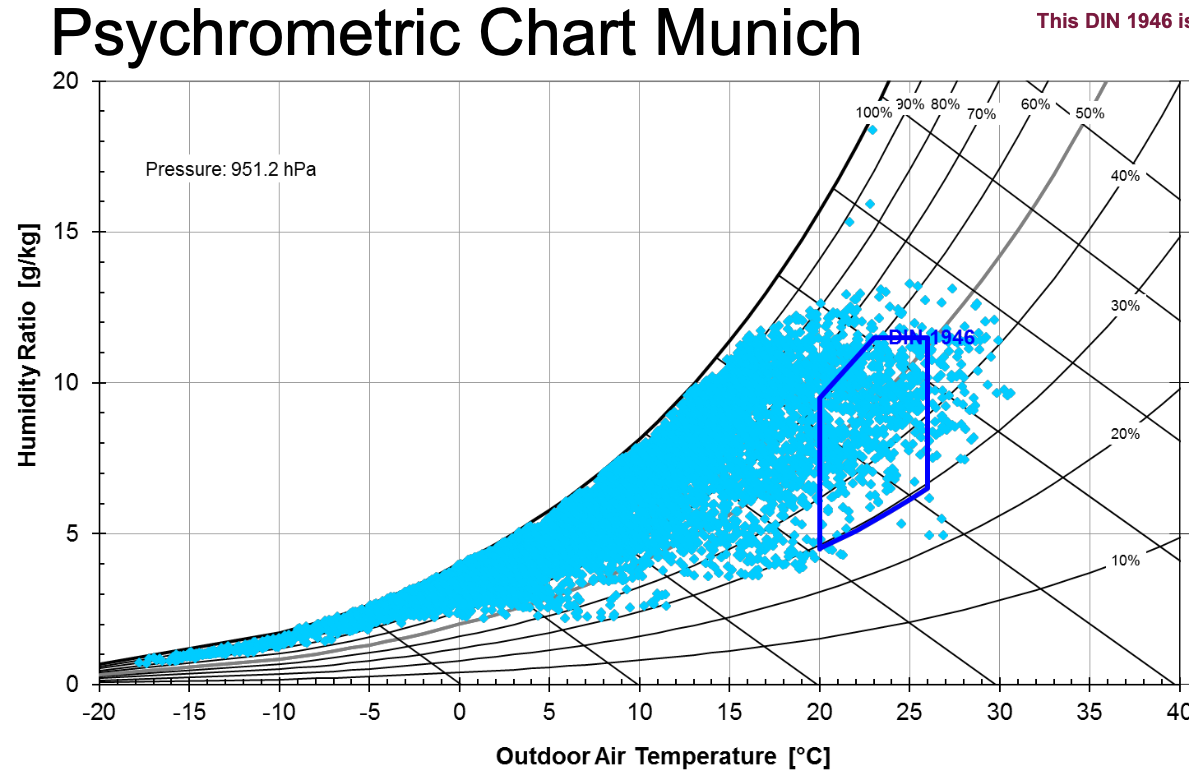
Draw - on the chart the dark blue part.
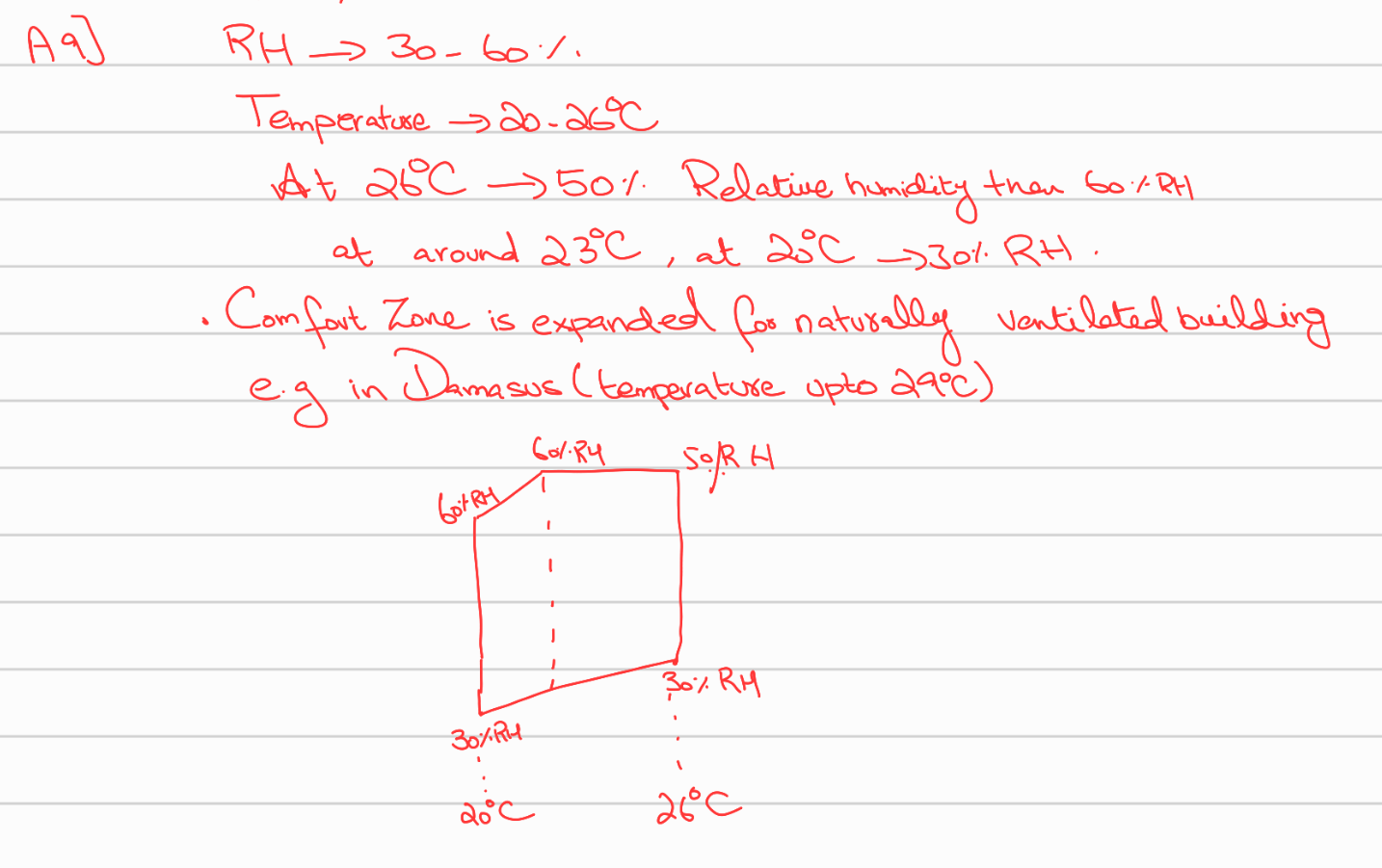
The comfort zone in the psychrometric chart according to DIN 1946 is defined by specific conditions of temperature and humidity where most people feel thermally comfortable. - main conditions:
Temperature range: Roughly between 20 °C and 26 °C (dry bulb temperature).
Relative humidity: Between 30% and 70%.
No draft: Air velocity must remain low to avoid discomfort from moving air.
Moderate clothing and activity level: Defined for people doing light work with typical indoor clothing (~1.0 clo).
Operative temperature: A balance between air temperature and radiant temperature.
(read-out) of the psychometric chart.
Name 5 indicators for thermal comfort in a room?
1) Air Temperature
2) Humidity
3) Clothing
4) Air Velocity
5) Surface Temperature.
What does PPD Stands for and what does it say?
PPD (Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied) indicates the percentage of people likely to feel thermally uncomfortable in a given environment, even if the average thermal sensation (PMV) is within the comfort range.
PPD is based on PMV (Predicted Mean Vote).
Even at the best possible comfort level (PMV = 0), at least 5% of people are still predicted to be dissatisfied. So the minimum PPD is 5%.
Name three reasons for local discomfort in a room?
Stating one for each type of heat transfer:
1) Draft (Convection)
2) Large Vertical Temperature difference (due to radiant heat transfer)
3) Warm and cold feet due to higher floor temperature. (conduction)
Which statement is not correct regarding the adaptive Comfort Model?
It can only be applied in naturally ventilated buildings.
The DIN EN 15251 defines four categories with different threshold.
Varying the air speed has no effect on the threshold of the comfort zone.
The past thermal history has no influence on the occupant expectation.
The past thermal history has no influence on the occupant expectation.
Describe the urban heat problem and what effect it ahs on a citys climate and how to reduce them?
Urban Heat Problem – Explanation and Solutions
EXAM Style:
Urban heat islands occur when cities become significantly warmer than surrounding areas due to materials like concrete and asphalt storing heat, removal of vegetation, and heat from traffic and buildings. This intensifies heatwaves and worsens air quality. To reduce it, cities can add vegetation for shade and cooling, promote cycling to reduce emissions, and use permeable surfaces to support natural cooling through evaporation.
LONG:
Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) are areas within cities that experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. This phenomenon occurs because cities are densely built with materials like asphalt and concrete that absorb and retain heat. On hot days, a 30°C temperature can feel like 35–38°C due to UHI effects.
Key contributors to UHIs include:
Paved surfaces and buildings that store heat and re-emit it.
Lack of vegetation, which would otherwise cool the air through shading and evapotranspiration.
Traffic congestion and combustion engine emissions that generate heat.
Dense urban structures that reduce airflow and trap warm air.
Impacts:
Increased energy demand for cooling.
Higher air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Negative health impacts, especially for vulnerable populations.
Local climate alteration and reduced nighttime cooling.
Reduction Strategies:
Promote cycling and public transport to reduce traffic-related emissions and heat.
Increase urban greenery: trees, green roofs, and parks can provide shading and improve air quality.
Use reflective or light-colored materials for pavements and buildings (cool roofs).
Allow permeable ground surfaces that can absorb rainwater and release moisture into the air.
Encourage urban planning that considers wind flow and reduces heat trapping.
Q16) In a logistic centre, there is a defined working area: 20% of the area has to be heated to provide thermal comfort for the worker in winter. The rest of the area is to store the goods, which have no specific requirement regarding temperature.
Which heating system would you suggest to the client?
A thermactive slab, because it is most efficient due to a very low supply temperature and works best with the light building structure of a logistic center.
Under-floor convector, because air heating system works best for big halls and they can be placed right under the working area.
Radiant ceiling panel, because they can heat a restricted area over a great height.
An air heating system, because air has high specific heat capacity and heat recovery is possible.
Radiant ceiling panel, because they can heat a restricted area over a great height.
This one is correct
Q17) Which statement is not correct regarding the underfloor heating system?
It operates with low temp so it’s very efficient with low ex system and a heat pump.
It provides high comfort because it reacts very fast to occupant’s temperature changes.
It is a system that works primarily by radiation.
The heating load is limited to 80 W/m² so it could be insufficient in old buildings without insulation.
Correct answer: 2)
That is the false statement. Underfloor heating systems do not react very fast to temperature changes—they have high thermal inertia, meaning they take longer to heat up or cool down.
Q18) Which statement is not correct concerning the use of solar power systems?
The higher the temperature, the more effective is PV system.
Using solar thermal system in housing should include a buffer storage.
A PV system produces electricity both as diffuse and direct radiation, but much more at direct radiation.
The total output of a PV roof is higher when it’s completely vertical covered than with an optimized angle of 35° and only 40% coverage of the roof area.
1) is not correct:
WRONG:
The higher the temperature, the more effective is PV system.
Name the main climate type for climate classification
1) Equitorial
2) Arid
3) Warm temperature
4) Snow
5) Polar
Name the main precipitation types of climate classification
1) Desert
2) Steppe (Area with trees & low rainfall
3) Fully humid
4)Summer Dry
5) Winter Dry
6) Monsoonal
Name the main temperature type for climate classification?
1) Hot arid
2) Cold arid
3) Hot Summer
4) Warm Summer
5) Cool Summer
6) Extremly Continental
7) Polar frost.
8) . Polar tundra
What is latent heat?
Heat absorbed or released by an object without change in temperature
Name 4 attributes of thermal Comfort
Air Temperature
Radiation
Wind
Relative Humidity
Q24: Why is the regulation of dew point important?
A24: To avoid condensation → Can lead to damage and discomfort.
Name the AXIS - what are they?
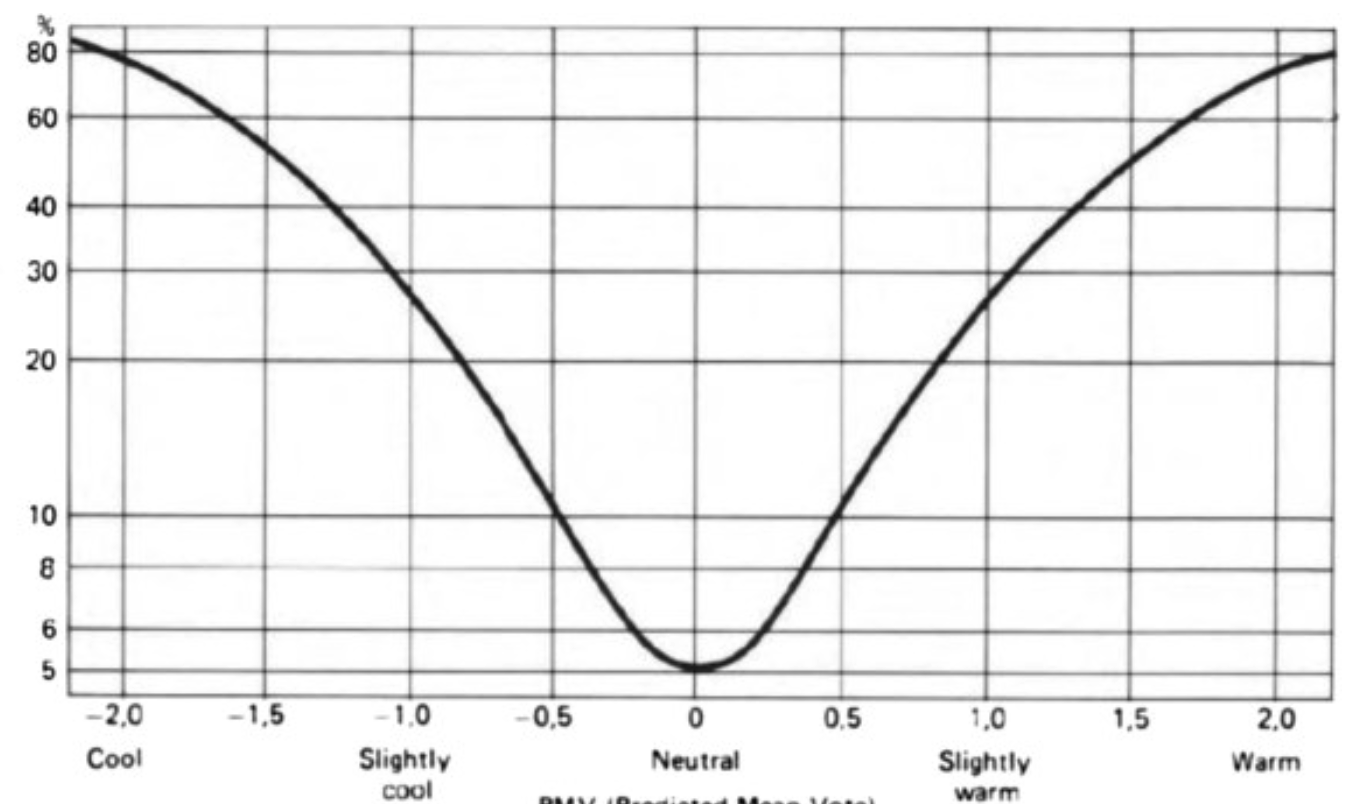
PPD / PMV
Predicted Percentage of dissatisfied
Predicted Main Vote
Y axis = PPD
X axis = PMV
What means SCOP?
Seasonal Coefficient of Performance
= Annual Emitted Heating power / Absorbed operating power.
What is COP
Coefficient of Performance = Thermal output/ Input power or Useable Heat output / Inserted power.
Q30) About Singapore
A30)
In which climate zone?
Which indicators for thermal comfort are out of the diagram?
Name meaningful passive and active systems for Singapore:
Do the same for other cities!
In which climate zone?
→ Tropical Climate Zone
Which indicators for thermal comfort are out of the diagram?
a) Too humid
b) Too hot
Name meaningful passive and active systems for Singapore:
a) Passive: Use of ambient air
b) Active cooling system: Air conditioning, radiant panels, chilled beam
Q31.
Compare the heat load that can be switched off in the following building types:
a) Old building
b) EnEV standard building
c) Passive house
Answer (based on the image):
Old building: 28 W/m²
EnEV: 12 W/m²
Passive house: 3 W/m²
Relate the following typical specific cooling outputs to the corresponding systems:
80–120 W/m²
50 W/m²
30–40 W/m²
60–100 W/m²
Cooling Ceiling
Thermoactive Floor Slab
Fan Coil / Coil Cooling
Induction Unit, Downflow Cooling
Regulation Air Unit / Air Conditioning
Cooling Ceiling → 80–120 W/m²
Thermoactive Floor Slab → 50 W/m²
Fan Coil / Coil Cooling → 30–40 W/m²
Induction Unit, Downflow Cooling → 60–100 W/m²
Regulation Air Unit / Air Conditioning → 80–120 W/m²
You’re instructed to plan an office building in a warm and humid climate. You decide to use radiant panels with a dew point control to cool the offices and a mechanical ventilation system with dehumidification.
Explain the cooling system and what problem could occur due to user misbehavior.
Radiant panels in form of cooling fins in suspended ceiling
Very good controllability
Restricted design freedoms for façade
Problem: If users open windows and humid air enters, the dew point can be exceeded, causing condensation on the panels → leads to discomfort and possible malfunction of the system.
At which depth below ground level do the thermal conditions remain nearly constant throughout the year?
a) 0.5 m
b) 0.8 m
c) 1.5 m
d) 5 m
e) 20 m
20m