Class 11 - Intervention Research
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
How many brand name psychotherapies are there?
> 600
When does ANXIETY developmentally emerge?
Around age 5
When do EATING DISORDERS developmentally emerge?
Late Teens
When does SCHIZOPHRENIA developmentally emerge?
Early 20s
3 Goals of Therapy Research
Efficacy
Effectiveness
Active Components
Efficacy
Does it work in controlled study settings? Can it actually improve someone’s symptoms of problems?
Effectiveness
Does it work in the real world of clinical delivery?
Active Components
What part of the therapy works?
Between-Subjects Design
every participant experiences only one condition, and you compare group differences between participants in various conditions
Within-Subjects Design
every participant experiences every condition
True or False: Randomized control trials are in between within and between designs
True
What are common control conditions?
Waitlist Control
Treatment as Usual
Waitlist Control (Intent to Treat)
Essentially no treatment, but you know it’s coming
Takes into account the phenomenon that many psychiatric symptoms often improve on their own without treatment
Treatment as Usual
Most rigorous test of a new therapy
Control treatment should be:
of long-standing use
designed to treat the problem being studied
supported by large body of evidence
Attention Control/Psychological Placebo
approaches specific v. common factor issue
deliver the same nose of interpersonal interaction (common factors) but no other intervention elements
Takes into account the many benefits of psychological attention
True or False: The control we use can change our effect estimates.
True
Response to Treatment"
at least 50% reduction in depressive symptoms
Waitlist “less effective” than No Treatment?
Participants on non-treatment and waitlist are free to seek other treatments while being monitored
waitlisters more likely to wait for active treatment, while non-treatment may be more likely to seek help somewhere else
waitlist can also increase state of helplessness during the waiting period, while increasing expectations for upcoming intervention
What is the weakest control condition?
waitlsit
What are other designs that exist to determine components of psychotherapies?
Dismantling Design
Additive Design
Dismantling Design
Break the treatment into all its components and give them individually (separately)
help identify active components/streamline therapies
Additive Design
Break the treatment into all its components and give them individually (one on top of the other)
help identify active components/streamline therapies
Why is it important to identify active components and streamline therapies?
We tend to build therapies to “get the job done,” meaning we throw everything we can at the problem.
True or False: Shorter therapies are more accessible, more tolerable, and can reach more people.
True
Is therapy effective?
Since the 1970s, yes!
How effective is therapy?
1977 - Smith & Glass Meta-Analysis of 400 treatment studies
“The average person who receives psychotherapy is better off than 80& of untreated individuals”
effect size of 0.85 SD; big shift to the right
How can we check if therapy is effective?
Client Satisfaction Surveys - non-random, post-treatment clients asked to rate helpfulness of their therapy ~90% say that it helped them, regardless of type of treatment
Is therapy well tolerated?
Clients often drop out of therapy!
What is the average drop-out rate?
30% (high-income countries)
45% (low/middle income)
When is dropout more likely?
In general medical (60%) rather than in specialist settings (20%)
For mild and moderate, rather than for severe presentations
When do most drop-outs occur?
Within the first 2 sessions
Clients are more likely to drop out with:
lower education levels
lower income
poor social support
True or False: You can expect around 1 in 5 of your patients to drop out
True
Meta-Analysis Findings suggest…
Estimate of therapy effectiveness range from medium to highly effective
Generally behavioral and cognitive-behavioral therapies do the best
What is the gold standard/most effective treatment (regardless of disorder)?
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Empirically-Supported Treatments
APA has determined whether specific treatments are efficacious for certain disorders based on the empirical evidence (meta-analyses of RCTs)
Terms that are used Synonymously
Empirical-validated treatments
Evidence-based treatments
Empirically-supported treatments
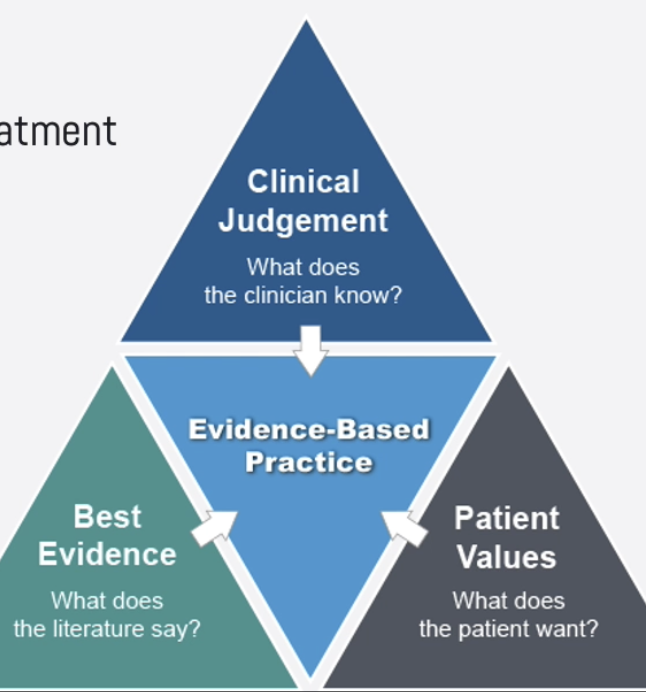
Evidence-based practice (EBP)
delivers an empirically supported treatment (EST) selected via evidence, clinical judgement, and patient values