1 Anti Cancer Part 1
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Neoplastic disease
Term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and are able to invade other tissues due to mutations in DNA of cells
Related terms: Cyst, Tumor, Neoplasm
Cancer
An abnormal sac or closed cavity filled with liquid or semisolid matter
CYST:
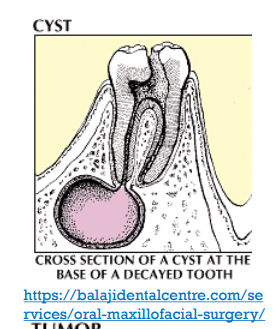
mass that is observed as a lump in the body; neoplasm
TUMOR:
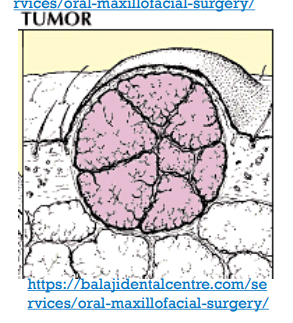
“no lump still cancer”
makes the skin on the breast look red and feel warm
affected breast may become larger or firmer, tender, or itch
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Signs & Symptoms of Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Sudden visible enlargemetn of breast
Discoloration of breast skin
Tenderness and pain in affected breast
Inward turning of nipple
does not invade surrounding tissues
Benign
invade & metastasize to all parts of the body, fatal, cancer
Malignant:
Steps of Malignant
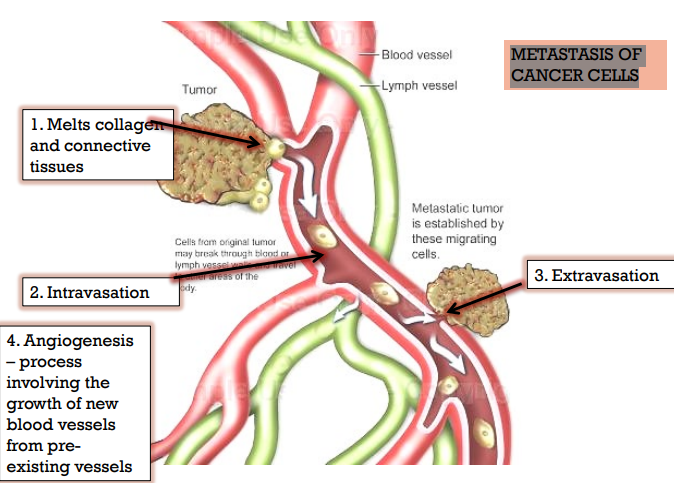
METASTASIS OF CANCER CELLS
Melts the collagen and connective tissues
Capable of intravasation
Capable of extravasation
Capable of angiogenesis
Established Cancer Treatments
Surgery
Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Hormone Therapy
Stem Cell tranplant
Treatment of cancer by using cytotoxic and other drugs
Chemotherapy
GOALS OF CHEMOTHERAPY
palliation
cure
adjuvant
neoadjuvant
alleviation of symptoms; prolong life
palliation
eradication
Cure
surgery &/or radiotherapy then chemotherapy ; done after initial treatment
adjuvant
chemotherapy then surgery &/or radiotherapy
neoadjuvant:
Drug Combination increases what and decreases what
Increases efficacy, decreases toxicity
Chemotherapy Mos common side effects
Affects all rapidly proliferating cells:
Hair loss
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhea
Bone marrow suppression
Fatigue
Chemotherapeutic Agents Types
Cell-cycle Specific Agents
Cell-cycle Non-specific Agents
Cell-cycle Specific Agents
• Phase-specific
• Phase non-specific
most active against cells that are in a specific phase of the cell cycle
Phase-specific agents:
M-phase
Vinca Alkaloids
G1 Phase
Asparaginase
Prednisone
S phase
Antimetabolites
G2 phase
bleomycin
etoposide
effective while cells are in the active cycle but do not require that the cell be in a particular phase.
Phase-Non specific agents:
Phase-Non specific agents:
Alkylating agents
Antitumor antibiotics
Cisplatin
They are effective in all phases, including G0.
Cell-cycle Non-specific Agents
Cell-cycle Non-specific Agents
Nitrosureas
Radiation
Anti-Cancer Drugs
Plant Alkaloids
2. Antibiotic Anticancer Agents
3. Hormonal Agents
4. Alkylating Agents
5. Antimetabolites
6. Miscellaneous Anticancer Drugs
Plant Alkaloids
Microtubule Damaging Agents
Topoisomerase inhibitors
Plant Alkaloids
Microtubule Damaging Agents:
Vinca Alkaloids
Taxanes
Topoisomerase Inhibitors:
Camptothecins
Podophyllotoxins
Vinca rosea (Catharanthus roseus)
Periwinkle plant
Chichirica plant
Vinca Alkaloids
Vinca alkaloids Agents
Vincristine, Vinblastine
Vindesine, Vinorelbine
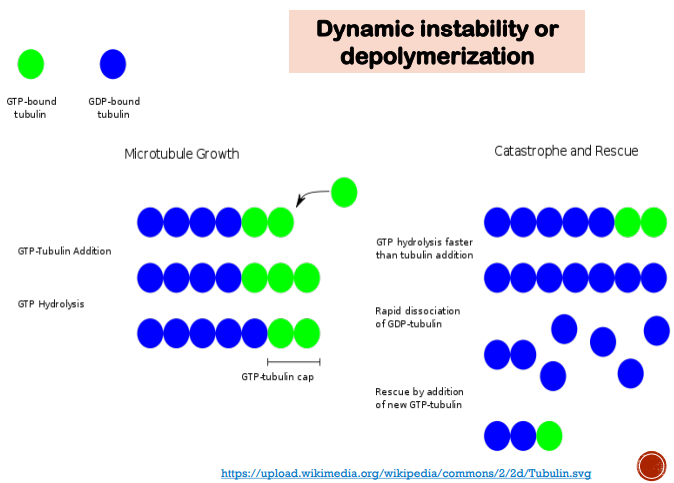
M-Phase specific
Bind to microtubules forming drug-tubulin complex
The complex terminates the formation of microtubules by promoting depolymerization (disassembly) and preventing the “rescue”of microtubules.
Disrupt formation of the mitotic spindle blocking chromosomal migration, and cell division.
Vinca Alkaloids
• Testicular cancer
• Side effects:
• Nausea and vomiting
• Alopecia
• Bone marrow suppression
Vinca Alkaloids
Vinblastine
• Hodgkin’s lymphoma Wilm’s tumor
• Side effects: Neurotoxicity or peripheral neuropathy
Vincristine
Derived from:
Western yew (Taxus brevifolia)
European yew (Taxus baccata)
Taxanes
Taxanes Agents
Docetaxel (Taxotere®)
Paclitaxel (Taxol®)
Cabazitaxel
M-phase, late G2 phase specific
Bind to and stabilize microtubules by enhancing tubulin polymerization
Blocks dynamic instability by stabilizing GDPbound tubulin in the microtubules
Forming weak polymers, clogged microtubules inhibiting cancer cell division and eventually lead to apoptosis
Taxanes
Indications:
Ovarian cancer
Advanced breast cancer
Adverse effects:
Neutropenia
Thrombocytopenia
Peripheral neuropathy
Paclitaxel
Indications:
Advanced Breast cancer
Prostate Cancer
Adverse effects:
Bone marrow suppression
Docetaxel
Extracted from the root of mayapple (Podophyllum peltatum)
Podophyllotoxins
Podophyllotoxins Agents
Etoposide - G2
Teniposidelate S, early G2
Inhibits topoisomerase II - cause double-strand DNA breaks
Podophyllotoxins
Enzymes that break, unwind and reseal tangled DNA strands which are necessary for DNA replication and RNA transcription.
Topoisomerase I: Acts on one strand only ;
Topoisomerase II: Acts on both strands ;
Topoisomerases
monocytic leukemia, testicular cancer, lung carcinoma
Podophyllotoxins
Etoposide
lymphomas
Teniposide
Podophyllotoxins
Etoposide - G2
Teniposidelate S, early G2
SIDE EFFECTS
Nausea and vomiting
Alopecia
Myelosuppression (primarily leukopenia)
Lymphoid system toxicity
Camptotheca acuminata
Camptothecins
Camptothecins Agents
Topotecan
Irinotecan
Inhibit topoisomerase I – cause single-strand DNA breaks
Camptothecins
Topotecan
Irinotecan
Metastatic ovarian cancer and cisplatinresistant neoplasms
AEs:
Neutropenia, Thrombocytopenia
Anemia, Alopecia
Myelosuppression
Nausea and vomiting
Topotecan
A prodrug ; metabolized to an active topoisomerase I inhibitor, SN-38.
Irinotecan
Indication: Colon rectal cancer
Adverse effects:
Early and Late forms of Diarrhea:
Early form occurs within the first 24 hrs of treatment due to cholinergic effect (tx: atropine)
Late or delayed form: due to SN-38 which induces direct mucosal damage with water and electrolyte malabsorption (Tx: loperamide)
Myelosuppression, Nausea and vomiting
Irinotecan
is metabolized by UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) to form an inactive metabolite
SN-38 i
Patients with abnormalities in this UDP-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 are highly susceptible to Irinotecan toxicity.
(Gilbert Syndrome)
Antibiotic Anticancer Agents
A. Anthracyclines
B. Dactinomycin
C. Plicamycin
D. Mitomycin
E. Bleomycin
Anthracyclines Agents
Daunorubicin
Doxorubicin
Idarubicin
Epirubicin
Isolated from Streptomyces peucetius var caesius
Acts on S phase
Anthracyclines
Stabilizes / inhibits topoisomerase II after it has cut and unwinded the DNA strands for replication ; prevents topoisomerase from reattaching the broken ends of DNA
Intercalation: Process by which drug slides between DNA base pairs causing additional DNA strand breaks
Anthracyclines Agents
Daunorubicin
Doxorubicin
Idarubicin
Epirubicin
Process by which drug slides between DNA base pairs causing additional DNA strand breaks
Intercalation
Anthracyclines
breast, ovarian, thyroid, lung cancers and acute leukemia
Doxorubicin
Anthracyclines
Acute leukemia
Daunorubicin & Idarubicin
Anthracyclines AEs
Cardiotoxicity
Total alopecia, Bone marrow suppression
May cause red or orange discoloration of the urine
Intercalation: Intercalates between adjacent guanine-cytosine base pairs. It inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis by blocking RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that is responsible for copying a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence
Dactinomycin
Indication: often used in pediatric cancers such as Wilm’s tumor (kidney CA)
Dactinomycin
Dactinomycin AEs
Bone marrow depression
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhea, oral ulcers
Alopecia
Causes “radiation recall”
Potent vesicant
When a person receives this drug, the skin or tissue damaged from prior radiation therapy can become red and appear damaged again.
Hyperpigmentation and thickening of the skin
Radiation Recall
Formerly Mithramycin
Isolated from Streptomyces plicatus
Indications: Testicular cancer
Plicamycin
MOA: Binds to DNA in the presence of Mg2+ or other divalent cations , where it interrupts RNA synthesis.
Adverse effects: Bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, hypocalcemia
Plicamycin
Isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus
Indications:
Second line agent for metastatic colon cancer
Cervical cancer (with Bleomycin and Vincristine)
Stomach, pancreas and lung CA (with
Doxorubicin & 5-Fluorouracil)
Mitomycin
MOA: alkylation – cross linking of DNA strands
An alkylating agent only after it has been metabolized intracellularly.
The metabolite, a bifunctional alkylating agent, binds to guanine residues which crosslinks DNA strands.
Mitomycin
Routes: Topical, intravesical (small bladder
papillomas),IV
Adverse Effects:
Severe bone marrow suppression
Nausea and vomiting
Anorexia
Renal toxicity
Interstitial pneumonitis
Mitomycin
From Streptomyces verticillus
Indications:
Testicular cancer (with vinblastine or cisplatin)
Hodgkin lymphoma
Neck, cervical carcinoma
Bleomycin
lung toxicity; also causes hyperpigmentation of the skin
Bleomycin
MOA: Causes DNA strand breaks due to oxidation of DNAbleomycin-Fe(II) complex, producing toxic free radicals which inhibits DNA synthesis
Bleomycin
drug that have estrogen receptor agonist or antagonist properties depending on the target issue
MOA: In the breast, all three agents have antiestrogen activity
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
SERMS Agents
Tamoxifen
Toremifene
Raloxifene
SERMS for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
Tamoxifen & Toremifene
SERMs – for risk reduction for women at high risk of breast cancer
Tamoxifen & Raloxifene
SERMs for osteoporosis due to its estrogenic activity in bone
Raloxifene
SERMs AEs
Hot flashes
QT prolongation (Toremifene)
SERMs Precaution
Tamoxifen has estrogenic activity in the endometrium and can increase the risk for endometrial cancer
These agents also carry the risk for thromboembolic events
MOA: Competitively binds to the estrogen receptor on tumors ; blocking the action of estrogen to inhibit tumor growth
Estrogen Receptor Antagonist
Fulvestrant
Indication: for hormone-positive breast cancer
Adverse effect:
hot flashes
Increased liver enzymes
Estrogen Receptor Antagonist
Fulvestrant
Aromatase Inhibitors
Agents:
Aminoglutethimide
Anastrozole
Letrozole
Indication: breast cancer in postmenopausal women
Aromatase Inhibitors
Aminoglutehimide
Anastrozole
Letrozole
Inhibitor of adrenal steroid synthesis at the first step which is conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone
Inhibits extra-adrenal synthesis of estrone and estradiol
Inhibits aromatase enzyme and prevent the conversion of androstenedione to estrone, and testosterone to estradiol
Overall: inhibit estrogen formation
Aromatase Inhibitors
Aminoglutehimide
Anastrozole
Letrozole
Adverse Effects: Decreased bone mineral density Hot flashes, nausea Hypercholesterolemia (Anastrozole and Letrozole)
Precautions Do not benefit premenopausal women May increase the risk for ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with pre-existing ischemic cardiac disease
Aromatase Inhibitors
Aminoglutehimide
Anastrozole
Letrozole
MOA:
Initially stimulating the release of FSH and LH, followed by inhibition of the release of these hormones reduced testicular androgen synthesis
Potent inhibitors of gonadotropin secretion
Long term administration results in the suppression of LH and FSH which leads to subsequent decrease in levels of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone and estrogen
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH Agonists)
Agents: Leuprolide, Goserelin
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH Agonists) Agents
Agents: Leuprolide, Goserelin
Responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH
is synthesized and released from hypothalamus.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH
regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation and reproductive processes of the body
FSH:
triggers production of testosterone and estrogen
LH:
Indications: advanced prostate cancer, advanced breast CA (Goserelin)
Adverse effects: hot flashes, gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction, decreased bone mineral density
Precautions: Tumor flare: initial administration of these agents before receptor desensitization occurs, may result in increased LH and FSH release, with a transitory increase in testosterone and an exacerbation of disease ; they are often administered with antiandrogens (flutamide) Tumor flare can also occur in breast CA patients due to increase in estrogen
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH Agonists)
Agents: Leuprolide, Goserelin
MOA: Blocks GnRH receptors to decrease secretion of LH and FSH resulting to a rapid androgen deprivation by decreasing testosterone production.It acts more quickly than GnRH agonists
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH) Antagonists)
Agent: Degarelix
Indication: advanced prostate cancer
Adverse effects: hot flashes, weight gain
Precaution:ADT (androgen deprivation therapy) may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease ; Does not cause tumor flare
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GNRH) Antagonists)
Agent: Degarelix
MOA:
Inhibits CYP17 (17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase) which will inhibit the formation of testosterone precursor
CYP17 is required for androgen biosynthesis
Androgen Synthesis Inhibitors
Agents: Abiraterone, Ketoconazole