Unit 3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Force
a push or pull one thing exerts on another
examples of force
gravity, magnetism, air, friction
friction
the resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another
Fnet
the sum of al forces that act on an object
inertia
the momentum that is resistant to change in an object
equilibrium
where all forces acting on an object are balanced, resulting in no net force
mass vs. weight
mass is determined by the amount of matter an object has, while weight is also determined by the force of gravity acting upon it
Newton’s First Law of Motion (law of inertia)
if net force is equal to zero, then the object is at rest or moving with a constant velocity
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
net force and acceleration are directly related
1 Newton
1 kg x 1 m/s2
Fnet
m x ā
Formula for Fnet according to the first law of motion
0
Formula for Fnet according to the second law of motion
mā
the formula for the weight of an object
Fg = mg
when acceleration is pointing downwards
Fr < Fg
when acceleration is pointing downwards
Fr > Fg
Normal force
a force exerted by the surface an object is on that is perpendicular to the surface
what cancels out normal force?
the force of gravity
Fgx
Fgsinϴ
Fgy
Fgcosϴ
Fn is equal too…
Fgy
what is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line?
inertia
a satellite is in orbit around the earth. what object feels the greater force?
both feel the same force because of Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion
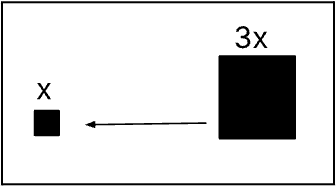
If these two objects with frictionless wheels move when the larger object pushes on the other, what is the speed of the smaller object?
Since the objects are moving away from each other, the smaller object’s speed is equal to the mass of the larger one due to the conservation of movement and the principle of action and reaction.

an object with m mass rests on a flat table, and the earth pulls on this object with a magnitude mg. what is the reaction force to this pull?
the object pulling upward on the earth with a magnitude of mg
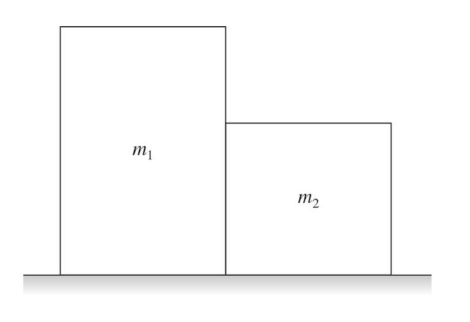
m1>m2 is on a frictionless surface and a force F can be applied on either object. Is the force's magnitude zero newtons in either case, the same, or larger when the force is applied to the left or right?
larger if F is applied to the right
a rock is thrown straight up from the earth's surface. what is true about the direction of the net force at the top of its path?
The direction of the net force changes from up to down
a block of mass m sits at rest on a rough inclined ramp that makes an angle with the horizontal. what does the force of static friction equal in mathematical terms?
f = mg(sinϴ)
A block of mass m sits at rest on a rough inclined ramp that makes an angle with the horizontal. what does the normal force equal in mathematical terms?
f = mg(cosϴ)
A brick slides on a horizontal surface. what increases the friction, increasing or decreasing the surface of contact, or increasing or decreasing the mass, and why?
increasing the mass because the force of gravity increases, then the normal force, and then the force of kinetic friction
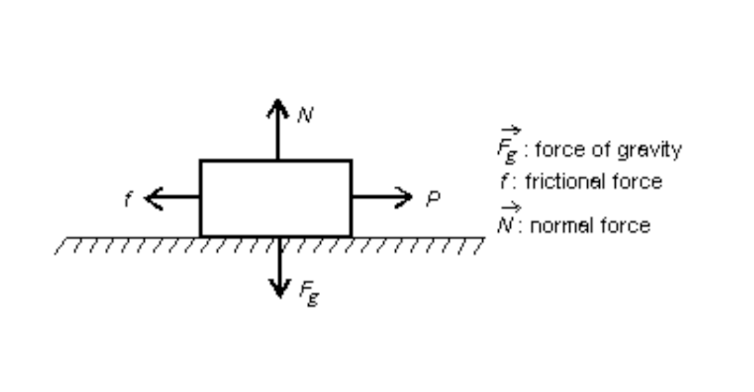
A boy pulls a wooden box along a rough horizontal floor at a constant speed through a force P as shown. In the diagram f is the magnitude of the force of friction, N is the magnitude of the normal force, and Fg is the magnitude of the force of gravity. is P greater than or equal to f? is the normal force greater than, less than, or equal to Fg? Why?
P = f and N = Fg because velocity is constant so net force is zero
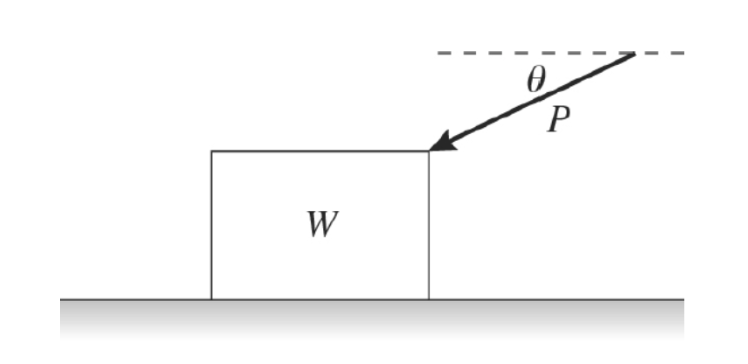
A push of magnitude P acts on a box of weight W as shown in the figure. The push is directed at an angle e below the horizontal, and the box remains a rest. The box rests on a horizontal surface that has some friction with the box. The friction force on the box due to the floor is equal to what?
P(cosϴ)
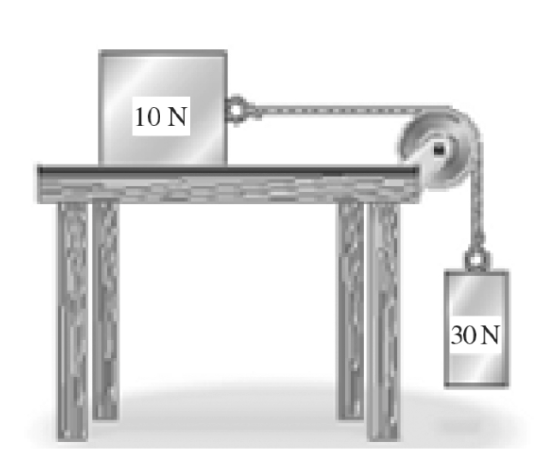
Two boxes are connected by a string as shown in the figure. The 10-N box slides without friction on the horizontal table surface. The pulley is ideal and the string has negligible mass. What is true about the magnitude of the tension T in the string and why?
T < 30 N because since acceleration is going down tension is less than 30
A car traveling at 100 km/hr strikes an unfortunate bug and splatters it. Is the force of impact equal on each object or greater on one and why?
the same because of Newton’s 3rd Law
A player hits a ball with a bat. The action force is the impact of the bat against the ball. Is the reaction to this force the weight of one of the objects, the air resistance on the ball, the grip of the player’s hand on the ball, or the force the ball exerts on the bat?
the force the bat exerts on the ball