Unit 3
Force - a push or pull one thing exerts on another
examples of force - gravity, magnetism, air, friction
Friction - the resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another
Fnet - the sum of all forces that act on an object
inertia - the momentum that is resistant to change in an object
equilibrium - where all forces acting on an object are balanced, resulting in no net force
mass vs. weight - mass is determined by the amount of matter an object has, and weight is determined by the amount of matter and the force of gravity acting upon it
Formulas
1 Newton = 1 kg x 1 m/s2
First Law of Motion - Fnet = 0
Second Law of Motion - Fnet= m x ā
weight of an object - Fg = mg
Newton’s Laws of Motion
if fnet=0, then the object is at rest or moving with a constant velocity and is at equilibrium
net force and acceleration are directly related
-
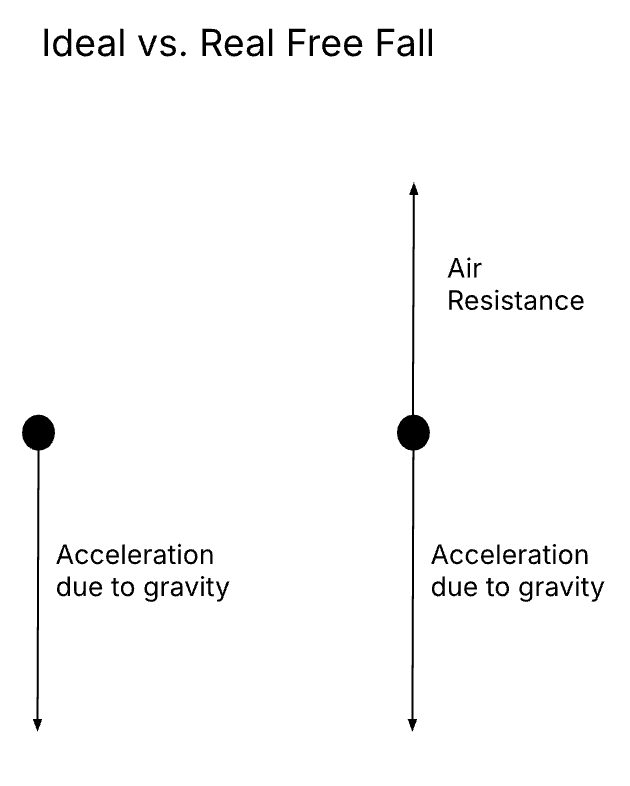
Acceleration
acceleration is positive at all times during calculations
when acceleration is pointing downwards - Fr < Fg
when acceleration is pointing downwards - Fr > Fg
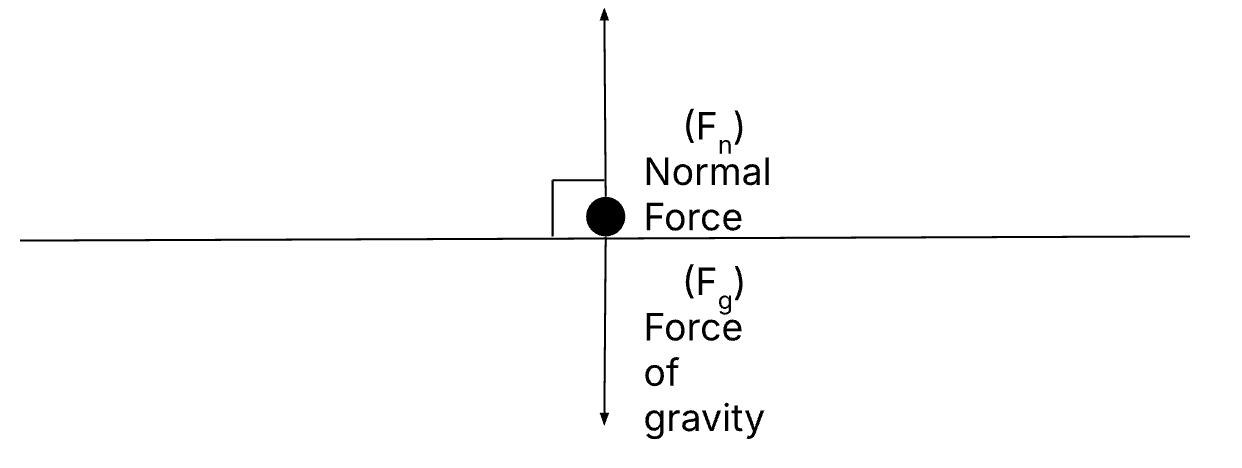
Normal Force
Normal force - a force exerted by the surface an object is on that is perpendicular to the surface
Normal force and the force of gravity cancel each other
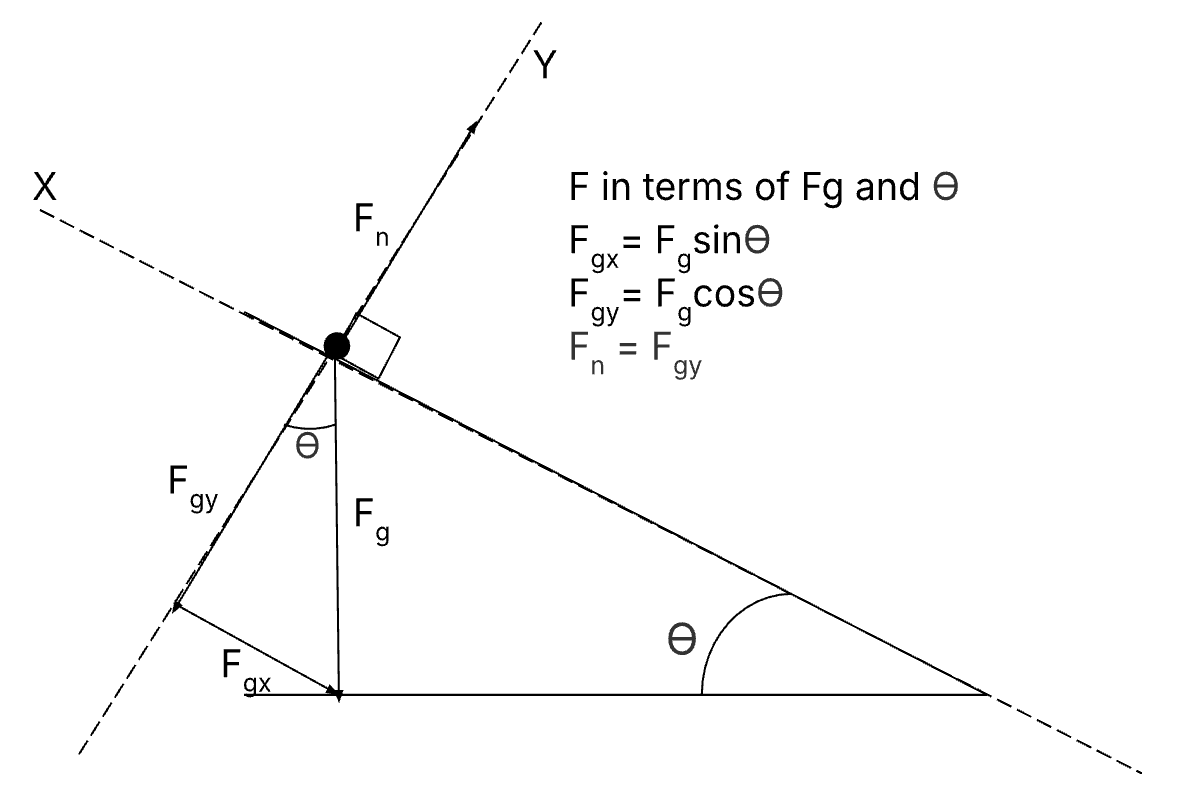
Movement at an Incline
Youtube Videos
