The Circulatory System
Functions of blood
- %%Transport%%
- Carries oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells
- Carries waste back from them
- Water
- CO2
- %%Defence%%
- Destroys bacteria
- Destroys blood clots
- %%Controls body temperature%%
- 37 degree
Composition of blood
%%Plasma%%
- Liquid of blood
- Transports and carries
%%Red blood cells%%
- Red: haemoglobin
- Carries oxygen
- no nucleus
%%Platelets%%
- Clots blood
- no nucleus
%%White blood cells%%
- Fights infections
- Makes anti-bodies or engulfs the infection
- Nucleus
Blood vessels
%%Artery%%: carries blood away from the heart
- Thick wall
- Small lumen
- High pressure
- No valves
- Goes away from heart
- High in O2
%%Veins%%: carries blood to the heart
- Thin wall
- Big lumen
- Low pressure
- Valves
- Goes to heart
- Low in O2
%%Capilaries%%: links arteries to veins
- Very tiny wall
- Tiny lumen
- Low pressure
- No valves
- Artery to vein
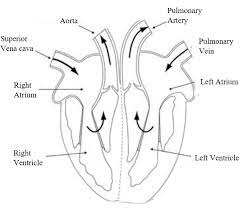
Heart
The heart is a pump
Cardiac: to do with heart
Pulse
- Pressure of blood in arteries
- %%72 bpm%%
Can be effected by:
- %%Age%%
- %%Diet%%
- %%Gender%%
- %%Stress%%
- %%Exersise%%
Why does the pulse increase with exercise
- Exercise needs energy
- More respiration
- More toxic Co2 made
- Pump blood faster to get rid of the Co2
- More O2 and food is brought to the cells for respiration