Science- Unit 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
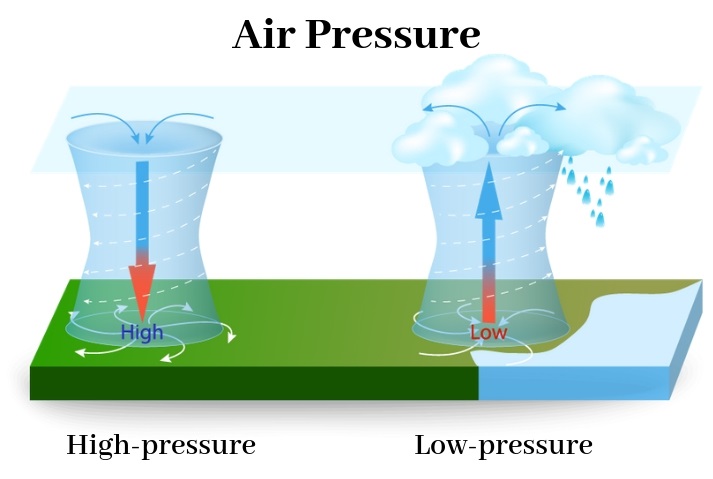
air pressure
the force exerted by the weight of a column of air above a given point
2
New cards
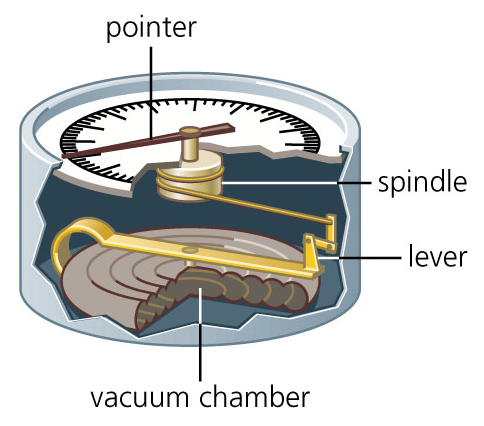
aneroid barometer
An instrument used for measuring air pressure that contains an empty metal chamber that compresses or expands as pressure changes.
3
New cards
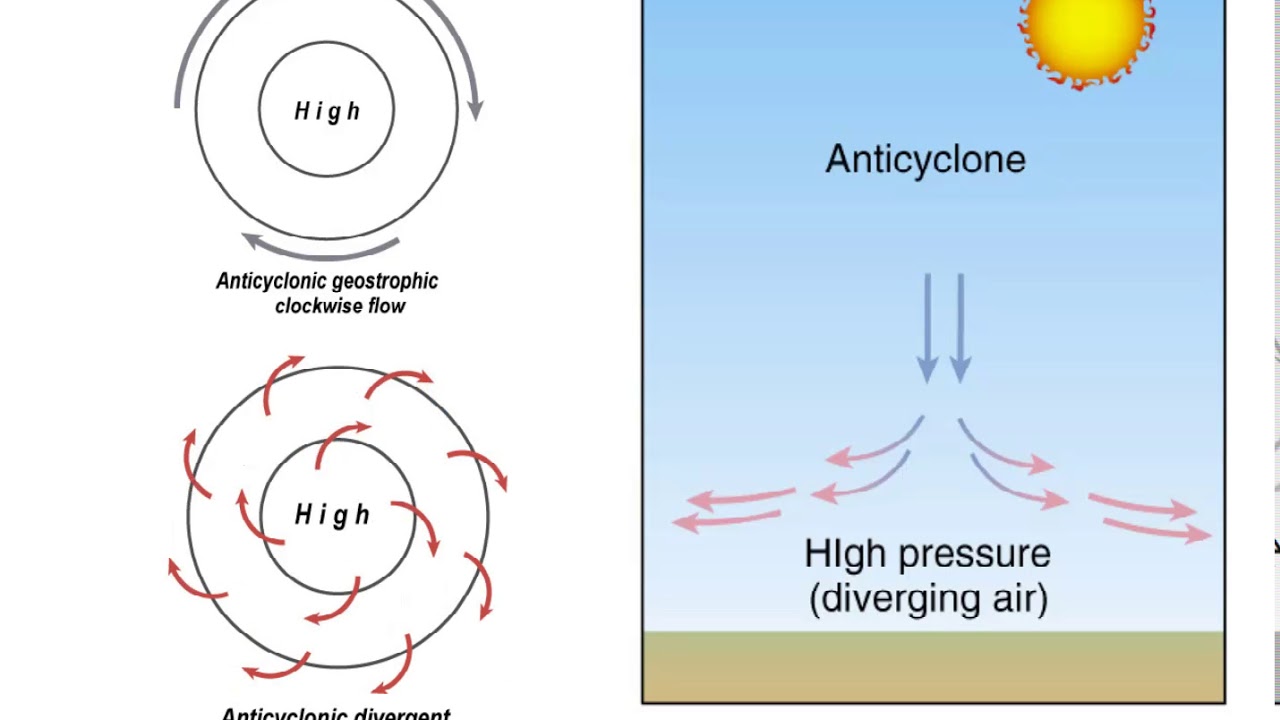
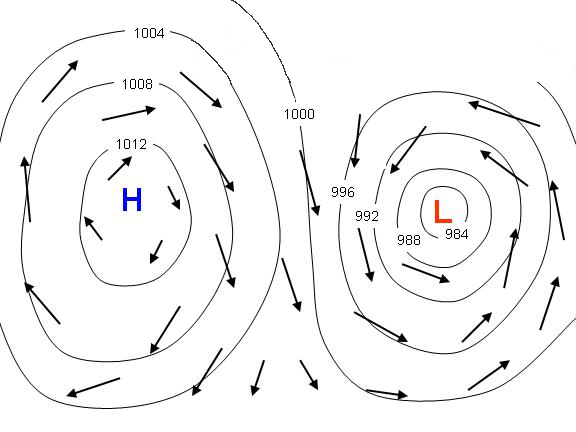
anticyclone
a high pressure system characterized by an outward, clockwise flow of air in the northern hemisphere
4
New cards
barometer
An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.
5
New cards
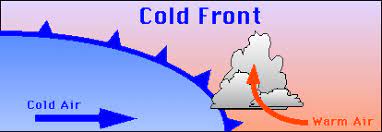
cold front
the boundary between a cold and warm air mass in which the cold air replaces the warm air at the surface and the warm air is lifted.
6
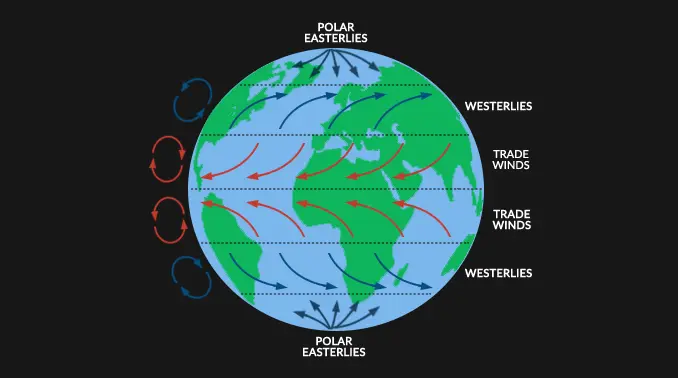
New cards
Coriolis force
the rotation of the earth causes the wind to bend to the right of its intended flow from high to low in the northern hemisphere (clockwise) and to the left in the southern hemisphere (counterclockwise).
7
New cards
cyclone
a low pressure system characterized by an inward and counterclockwise flow of air in the northern hemisphere. Tornadoes, hurricanes and mid-latitude cyclones are all types of cyclones.

8
New cards
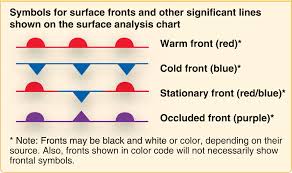
front
boundary between two different air masses
9
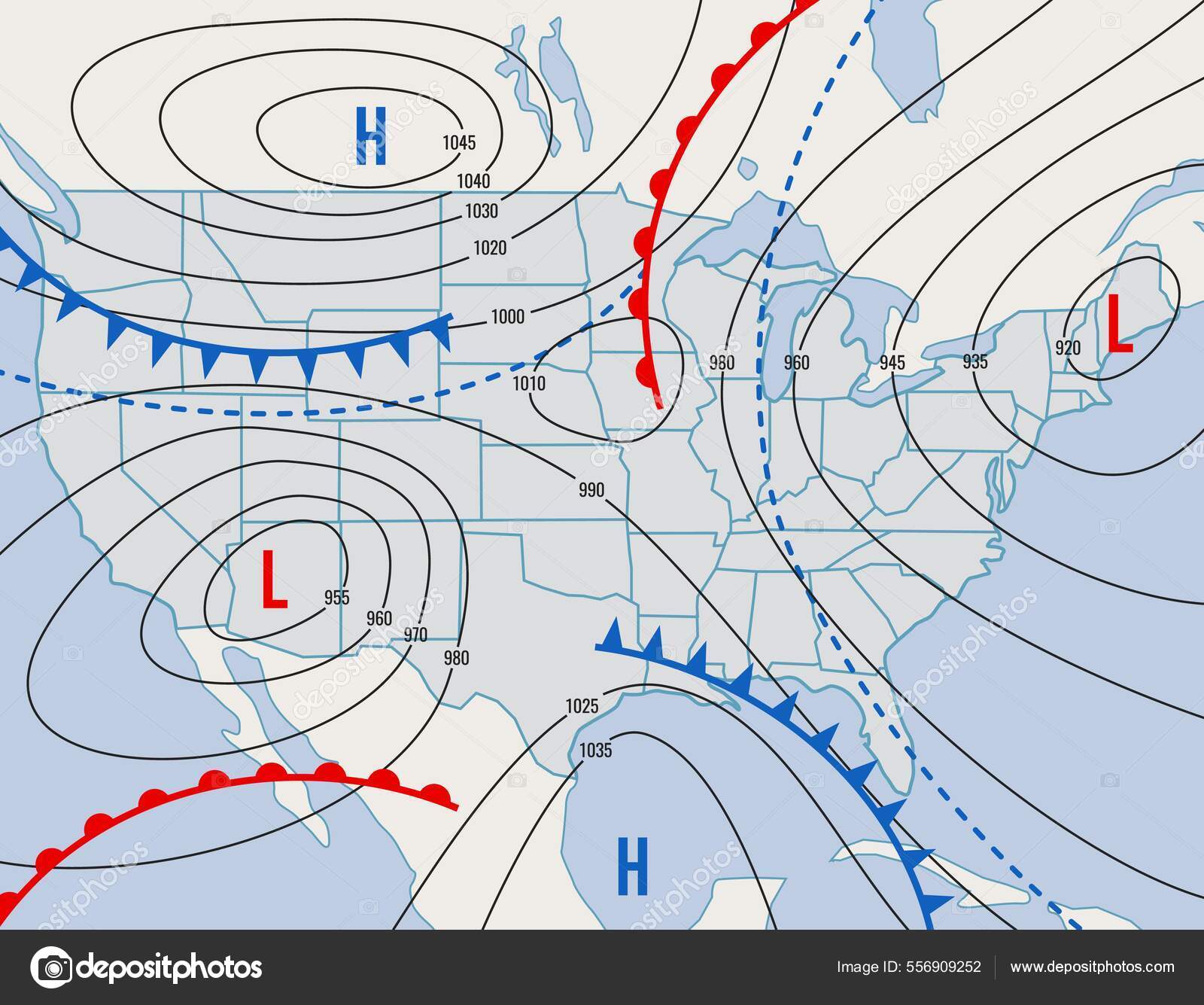
New cards
isobar
line of equal air pressure on a weather geek map
10
New cards
land breeze
local wind that comes off the land onto the water usually during the night due to differential cooling and the formation of local high and low pressures

11
New cards
mid-latitude cyclone
a large low pressure system characterized by an inward and counterclockwise flow of air and including warm and cold fronts in its middle stage ending in an occluded front- named for where air mass originates
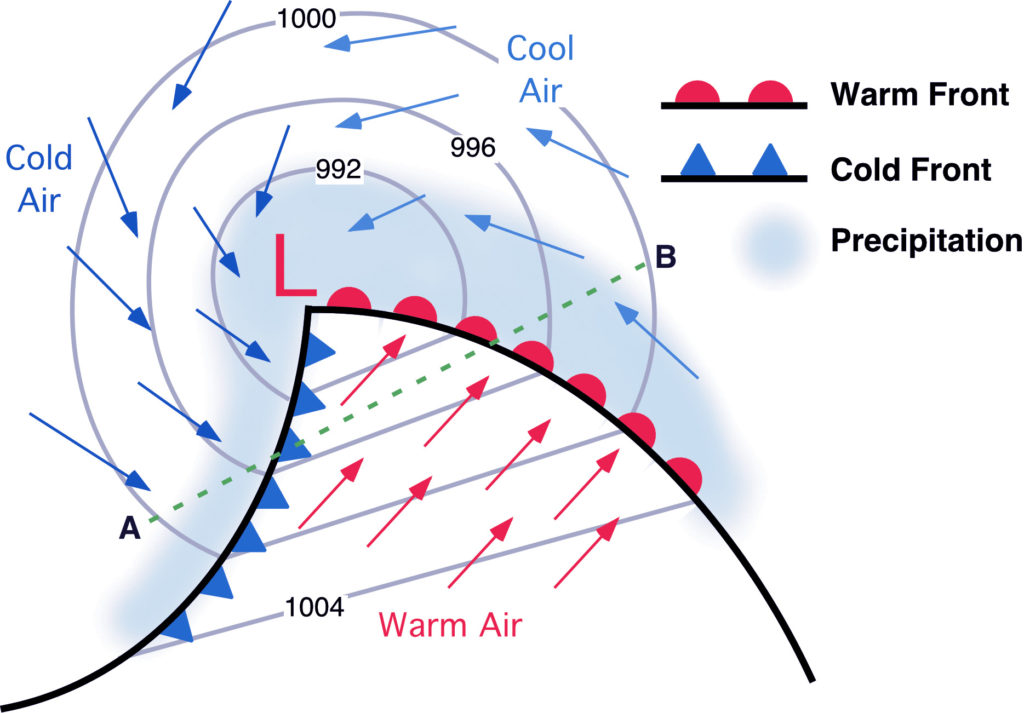
12
New cards
monsoon
A seasonal reversal of wind direction associated with large continents (especially Asia) caused by differential heating of land vs. water
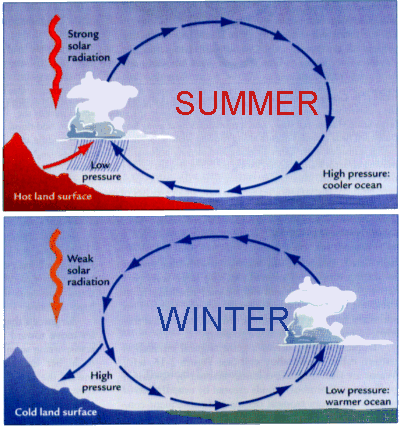
13
New cards
Occluded Front
When the warm sector between a cold and warm front is lifted above the surface as the cold front catches up to and lifts the warm front.
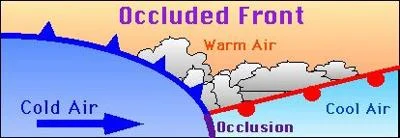
14
New cards
pressure gradient force (PGF)
difference in barometric (air) pressure between two points
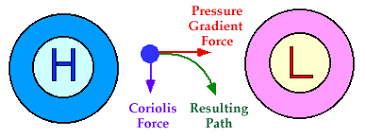
15
New cards
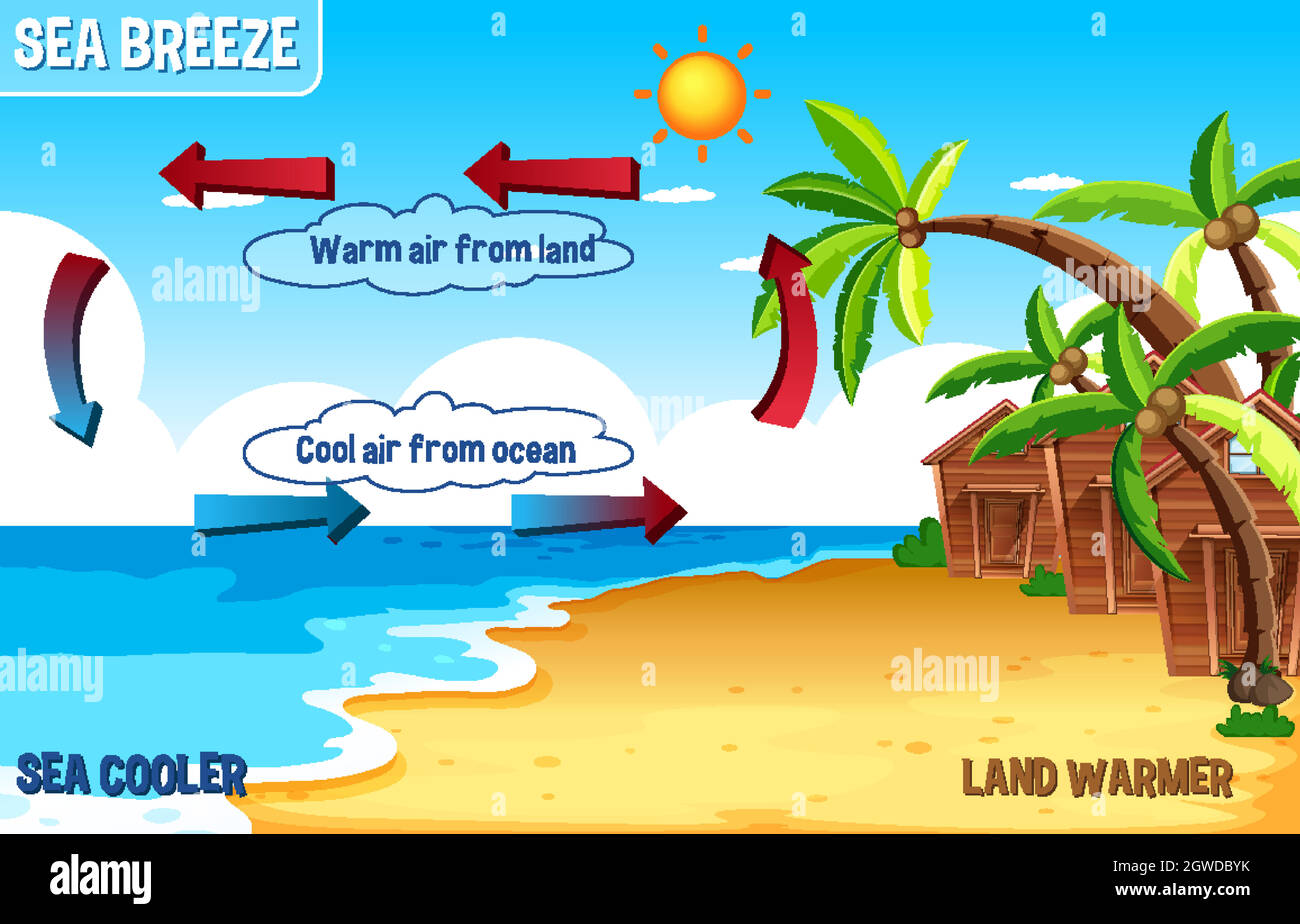
sea breeze
A local wind blowing from the ocean toward the land during the afternoon in costal areas formed due to differential heating of land vs. water and associated pressure gradient
16
New cards
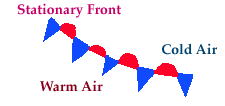
Stationary Front
A boundary between warm and cold air masses that are not moving into one another possibly causing clouds and rain for several days.
17
New cards
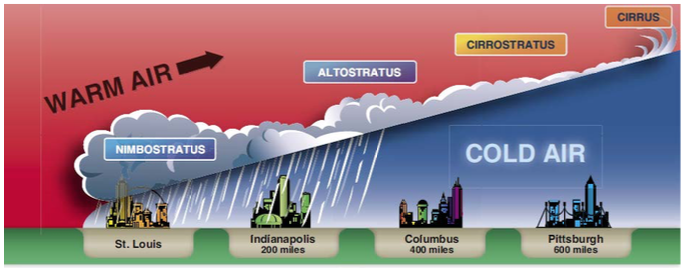
warm front
a front between a warm and cold air mass in which the warm air mass is replacing the cold at the surface. As warm air lifts in a gentle slope over cold air it brings a typical pattern of cirrus, cirrostratus/cirrocumulus, altostratus, stratus and finally nimbostratus drizzly rain followed by warm and clear weather. Sleet and freezing rain associated with this front in the winter.
18
New cards
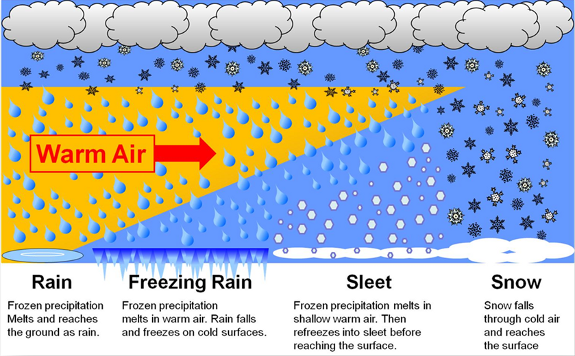
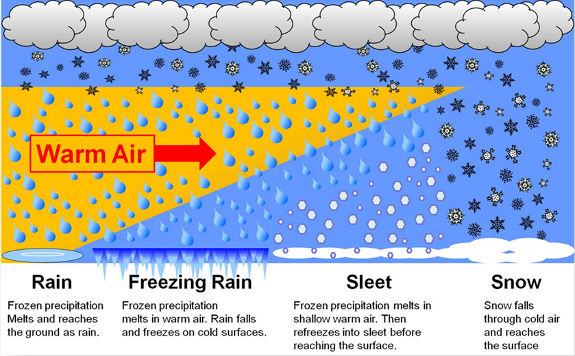
Sleet
Clear ice pellet precipitation, forms when rain falls through a thick layer of freezing air and freezes solid before hitting the ground. Associated with warm front passage in the winter
19
New cards
Hail
Clear, layered ice pellet precipitation that fall from cumulonimbus clouds after growing through multiple convection loops in cloud. Associated with Summer thunderstorms and cold fronts.
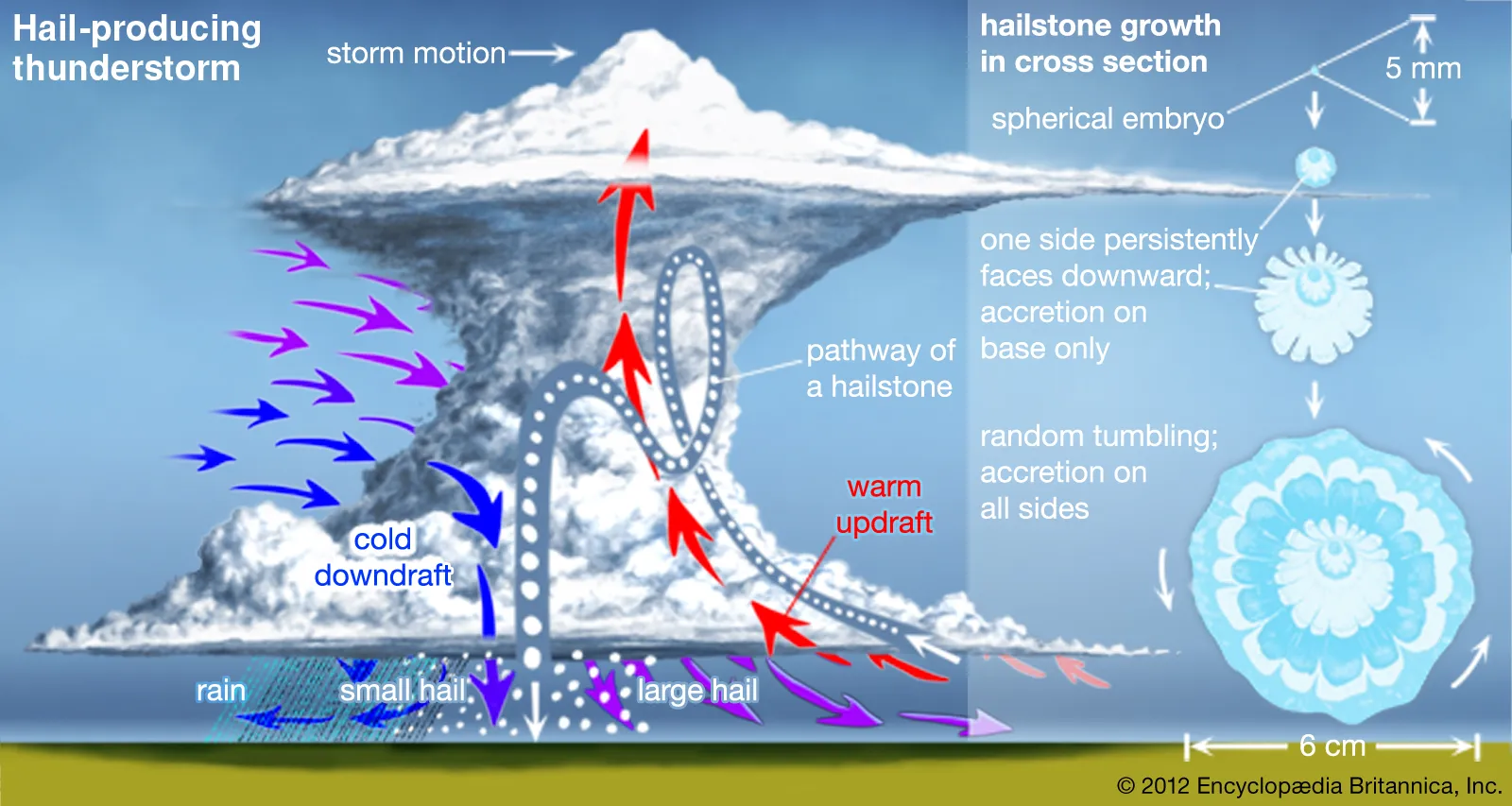
20
New cards
Freezing rain
raindrops that fall through a cold layer and cool to below freezing but don't solidify until after they hit the ground or other cold surfaces forming a dangerous ice coating. Typically forms in the winter on a warm front.
21
New cards
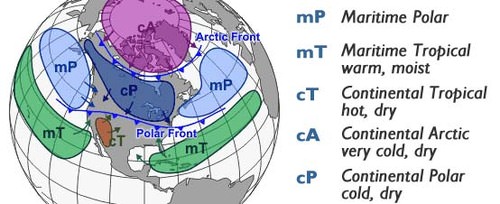
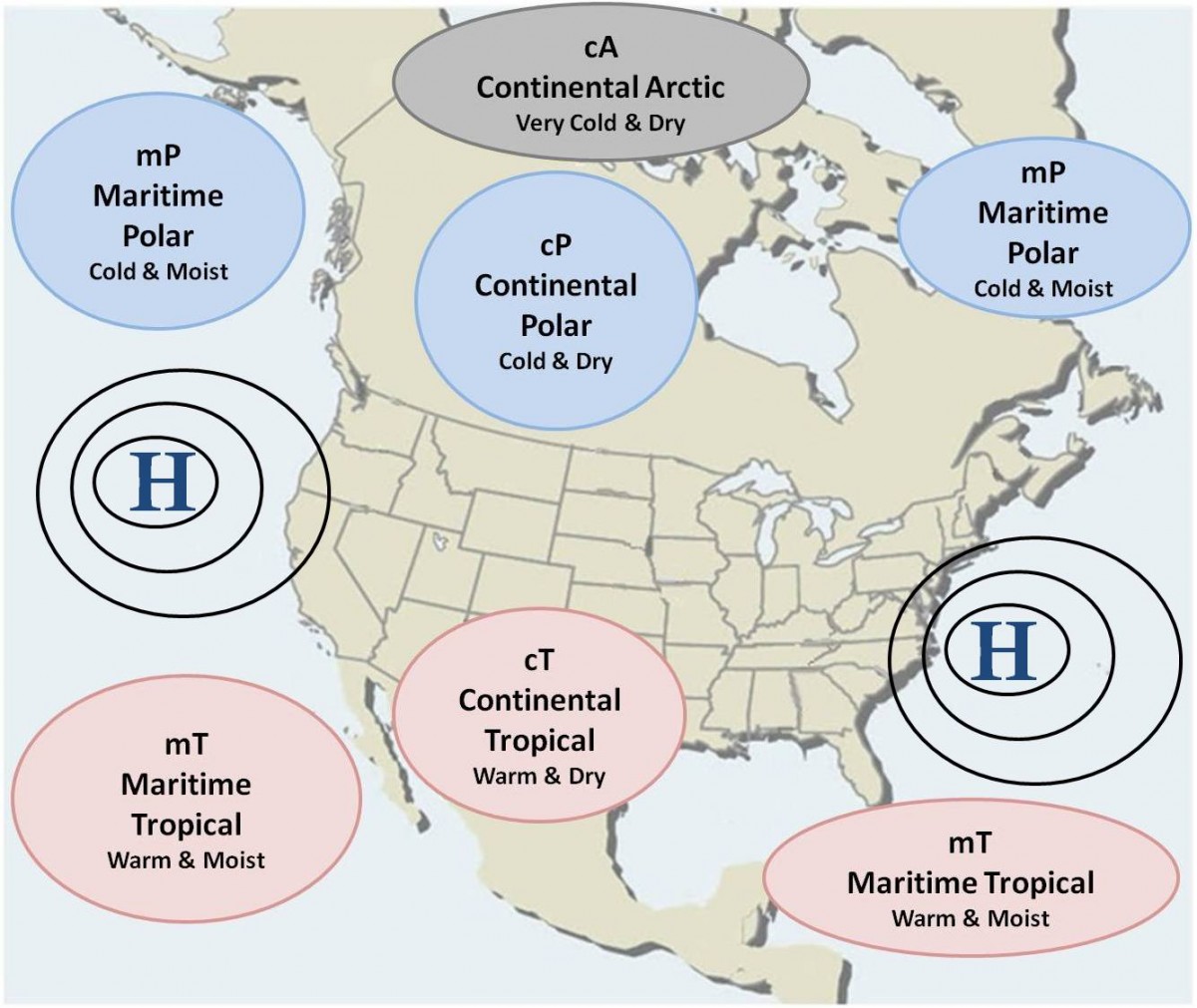
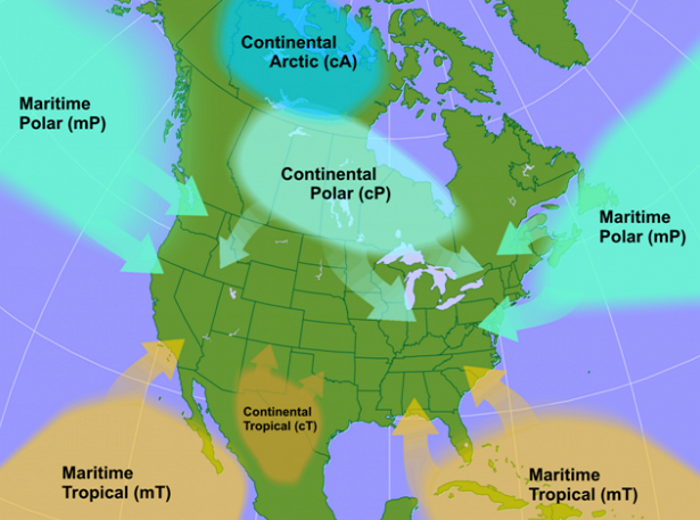
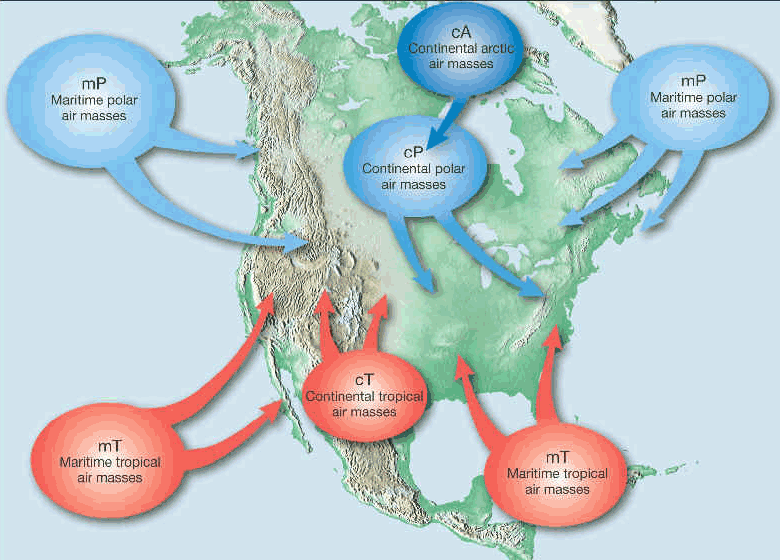
Polar
Part of air mass classification scheme that denotes an air mass that forms over cold regions in the north. Suggests the air mass will be cold. There are both maritime and continental polar air masses.
22
New cards
Tropical
Part of air mass classification scheme that denotes an air mass that forms over warm regions to our south. Suggests the air mass will be warm. There are both maritime and continental tropical air masses
23
New cards
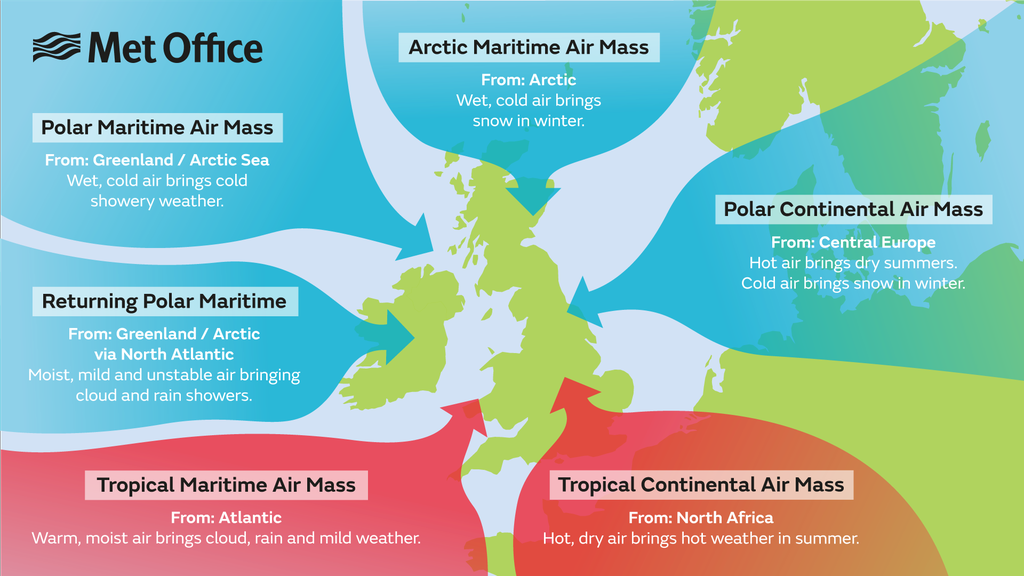
Continental
Part of air mass classification scheme that denotes an air mass that forms over land. Suggests the air mass will be dry. There are both polar and tropical continental air masses
24
New cards
Arctic
A bitterly cold air mass that forms over the frozen Arctic.
25
New cards
Maritime
Part of air mass classification scheme that denotes an air mass that forms over ocean. Suggests the air mass will be humid. There are both polar and tropical maritime air masses
26
New cards
Wind
the movement of air from high to low pressure in an attempt to equalize air pressure
27
New cards
Anemometer
An instrument used to measure wind speed
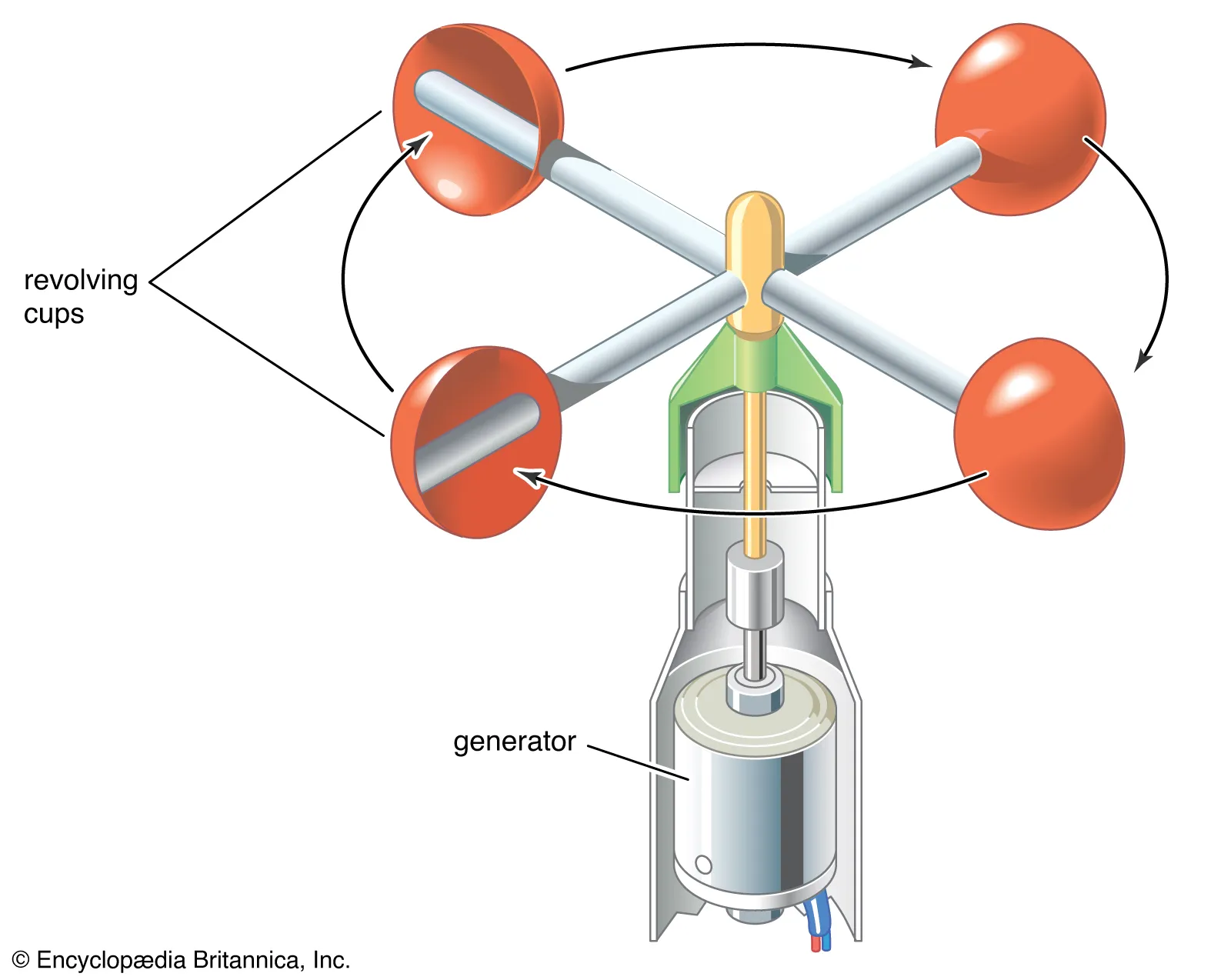
28
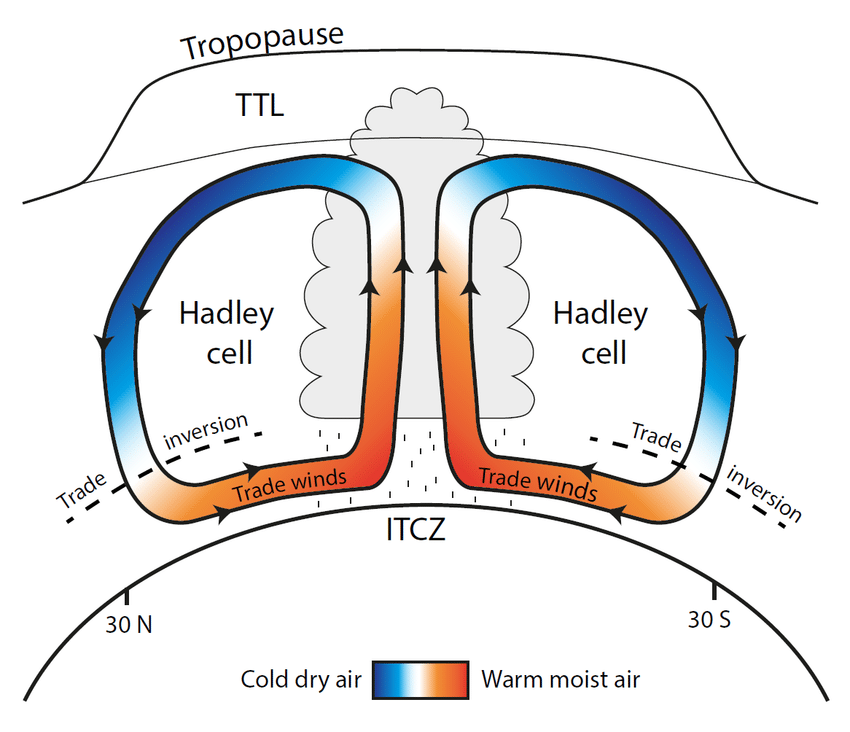
New cards
Hadley Cell
a large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south.
29
New cards
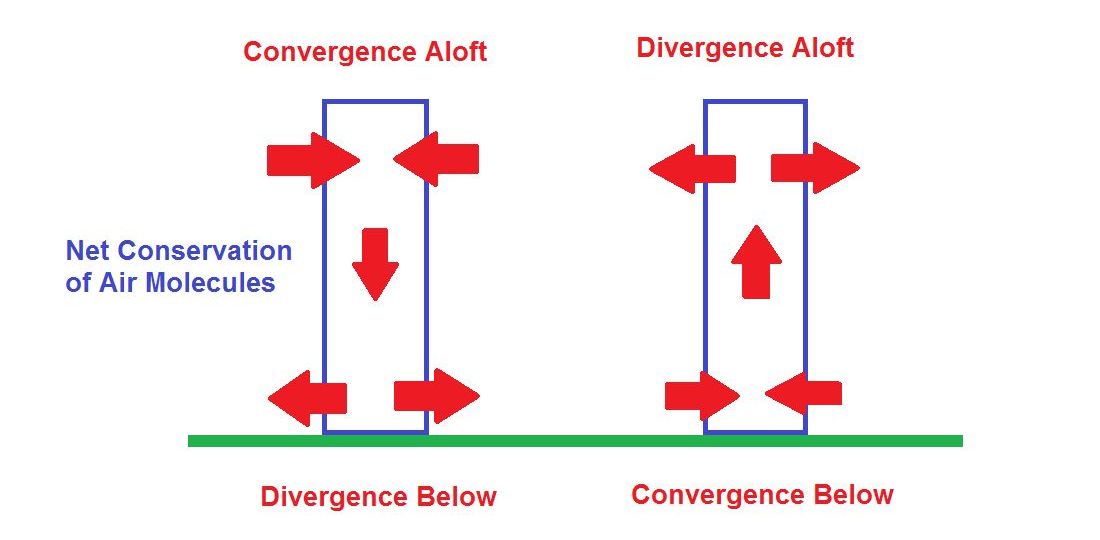
convergence aloft
The condition that exists at higher (jet stream) altitudes when the distribution of winds within a given area results in a net horizontal inflow.
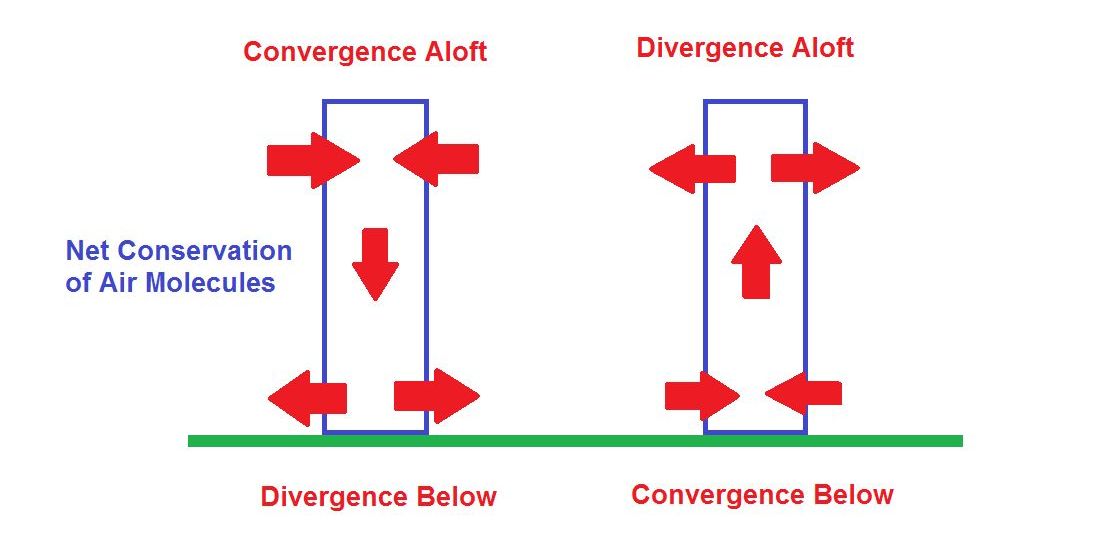
30
New cards
divergence aloft
The condition that exists at higher (jet stream) altitudes when the distribution of winds within a given area results in a net horizontal outflow.