W4 - Heckscher-Ohlin Model
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Heckscher Ohlin model argues for
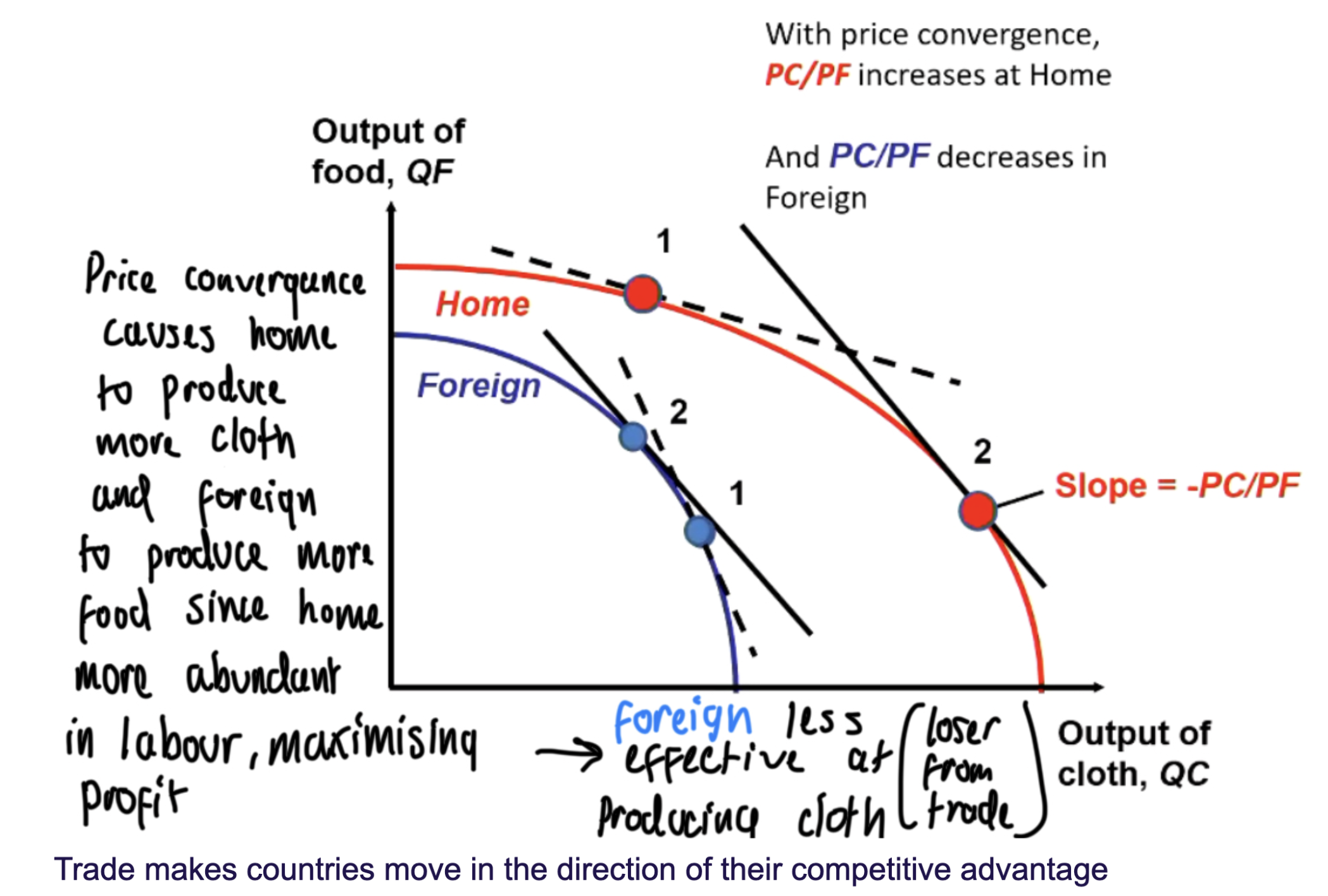
a ealistic view of trade must allow for differences in factors of production such as land, capital, and natural resources
relative factor abundance
what countries have alot of
relative factor insensity
what goods use intensivley
what influences comparitive advantage
relative factor abundance and intensity
a good that requires 4 units of labour and 2 units of capital is
labour intensive
a country that has 200 labour and 300 capital is
capital abundant
aKC
unit of capital used to produce one unit of cloth
aLF
unit of labour used to produce one unit of food
how might inputs to production differ (give example)
countries can choose combination depending on endowments or intensity e.g. 1 machine vs 10 workers
capital to labour intensity ratio
aKF/aLF
how might model influence specialisation
country moves toward specialization in the good that uses its abundant factor
amount of labour hours or machines used cannot exceed
machine or labour supply
express the following formulaically: amount of labour hours or machines used cannot exceed machine or labour supply
aKC x Qc + aKF x Qc > K
aLC X Qc + aLF x Qc > L
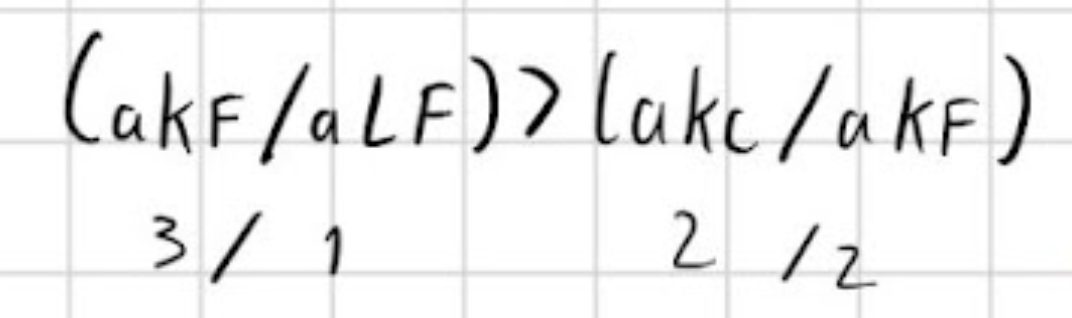
Which is capital and labour intensive based on this calculation (second term should say aKC/aLC)
food capital intensive
cloth labour intensive
HO y and x axes
quantity of cloth and food
what curves included in HO graph and what do they show
labour constraint and capital constraint and PPF
PPF is intersection
combinations at which labour and capital is exhausted
input mix depends on
costs of production and abundance
draw a graph showing how trade might cause specialisation in HO model