Med Term TEST REVIEW (Ch. 1 and Ch.2)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
acr/o
extremities
ankyl/o
crooked; bent; stiff; fused together
arthr/o
joint
cardi/o
heart
caud/o
tail
cephal/o
head
cervic/o
neck; cervix (neck of uterus)
col/o, colon/o
large intestine; colon
cost/o
rib
enter/o
intestines (usually the small intestine)
gastr/o
stomach
glyc/o
sugar; glucose
hepat/o
liver
lip/o
fat
log/o
study
medi/o
middle
my/o
muscle
neur/o
nerve
pod/o
foot
pyret/o
fever
rachi/o
spine; vertebra
rheumat/o
watery flow
sarc/o
flesh; connective tissue
super/o
above
thorac/o
chest
ventr/o
belly side of body; ventral aspect
viscer/o
internal organs
Long bones
found in the extremities
Short bones
located in the hands and feet, cube-shaped, and composed of spongy bones which allows for flexible movement
Flat bones
protects vital organs, and provides a broad surface area for muscle attachment
Sesamoid bones
Resemble large sesame seeds, embedded within tendons, facilitate joint movement and are found in the patella, hands, wrists, and feet
Irregular bones
Have an unusual or complex shape, and cannot be characterized as long, short, or flat. Provides support and protection, yet allows flexible movement
Cortical bones
Compact Bone, is very dense, hard, and strong. Lies under the periosteum (or the outer membrane of bone).
Cancellous bone
Trabecular Bone, is much more porous and much less dense than compact bone. Spongy bone.
Histology
the study of the structure and function of tissues
Bone density test
X-ray test that determines loss of, or changes in, bone density. The test uses X-rays to measure how many grams of calcium and other bone minerals are packed into a segment of bone. The higher your bone mineral content, the denser your bones are.
CT Scan
Process in which radiographic images of a specific section of the body are taken from multiple angles and then analyzed by a computer to identify bone injury or disease.
MRI
A noninvasive scanning test that involves use of an electromagnetic field and radio waves to visualize soft-tissue structures.
X-ray
Radiographic image used to diagnose skeletal changes in the body.
-algia
pain
-cyte
cell
-ectomy
surgical removal; excision
-emia
blood condition
-itis
inflammation
-oma
tumor; mass
-osis
abnormal condition
-stomy
surgical opening
Cell
basic structural unit of the body
Tissue
combination of similar cells
Organ
collection of tissues working together to preform a particular function
Body System
group of organs that work together to preform a specific function
Organism
life form made up of interdependent parts (cell, tissue, organ, body system), all of which work together to maintain life
ante-
before
anti-
against
hyper-
above; above normal; excessive
hypo-
below; below normal; deficient
inter-
between
intra-
within; into
endo-
in; within
exo-
outside; exterior
Endemic
A disease that is ongoing and restricted to a specific population, group, or area of land.
Endogenous
An injury or condition that originates within the body
Epidemic
A sudden, widespread outbreak of a disease within a population, group, or area of land.
Exogenous
An injury or condition that originates outside the body
Iatrogenic
An infection or disease that arises as a complication of medical or surgical intervention.
EX: chemotherapy- hair loss
Idiopathic
A disease that has an unknown etiology (cause)
Infectious
Capable of causing an infection
Nosocomial
An infection acquired in a hospital setting that was not present upon admission.
Opportunistic
A pathogen that does not normally cause a disease unless the immune system is in a weakened state
Auscultation
Use of a stethoscope to listen to sounds within body cavities.
Palpation
Application of light or firm pressure on the skin above internal organs or structures to check for abnormalities
Percussion
Tapping areas on the surface of the body to produce a vibrating sound. The nature of the sound indicates the size of the organ, whether it is filled with air or fluid, and so on.
Olfaction
Use of the sense of smell to detect abnormalities.
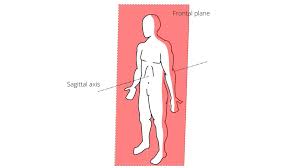
Frontal Plane
Coronal Plane, is a vertical plane that divides the body into front and back sections
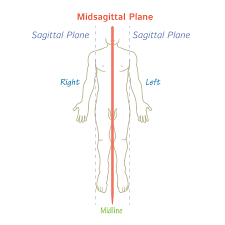
Mid-sagittal Plane
Vertical Plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves.
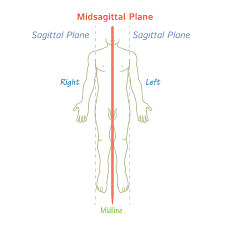
Sagittal Plane
When the mid-sagittal plane is visualized on any other part other than the center
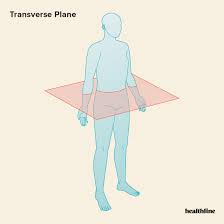
Transverse Plane
Horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower sections. Cross section plane.
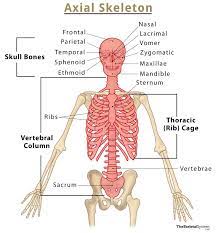
Axis Skeleton
Consists of the bones along the axis, or central line, of the human body. (facial bones, sternum, skull)
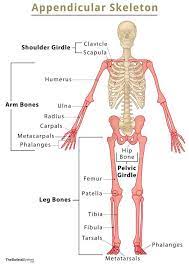
Appendicular Skeleton
Contains the bones in the appendages of the body, as well as the structures that connect the appendages to the axial skeleton (arm, wrist, hand bones; leg, ankle, foot bones)
Anterior
“Head end” of the body
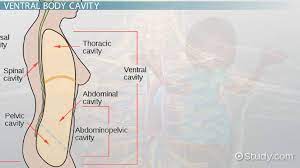
Ventral
“Belly side” of the body
Posterior
Tail end, or rear, of body
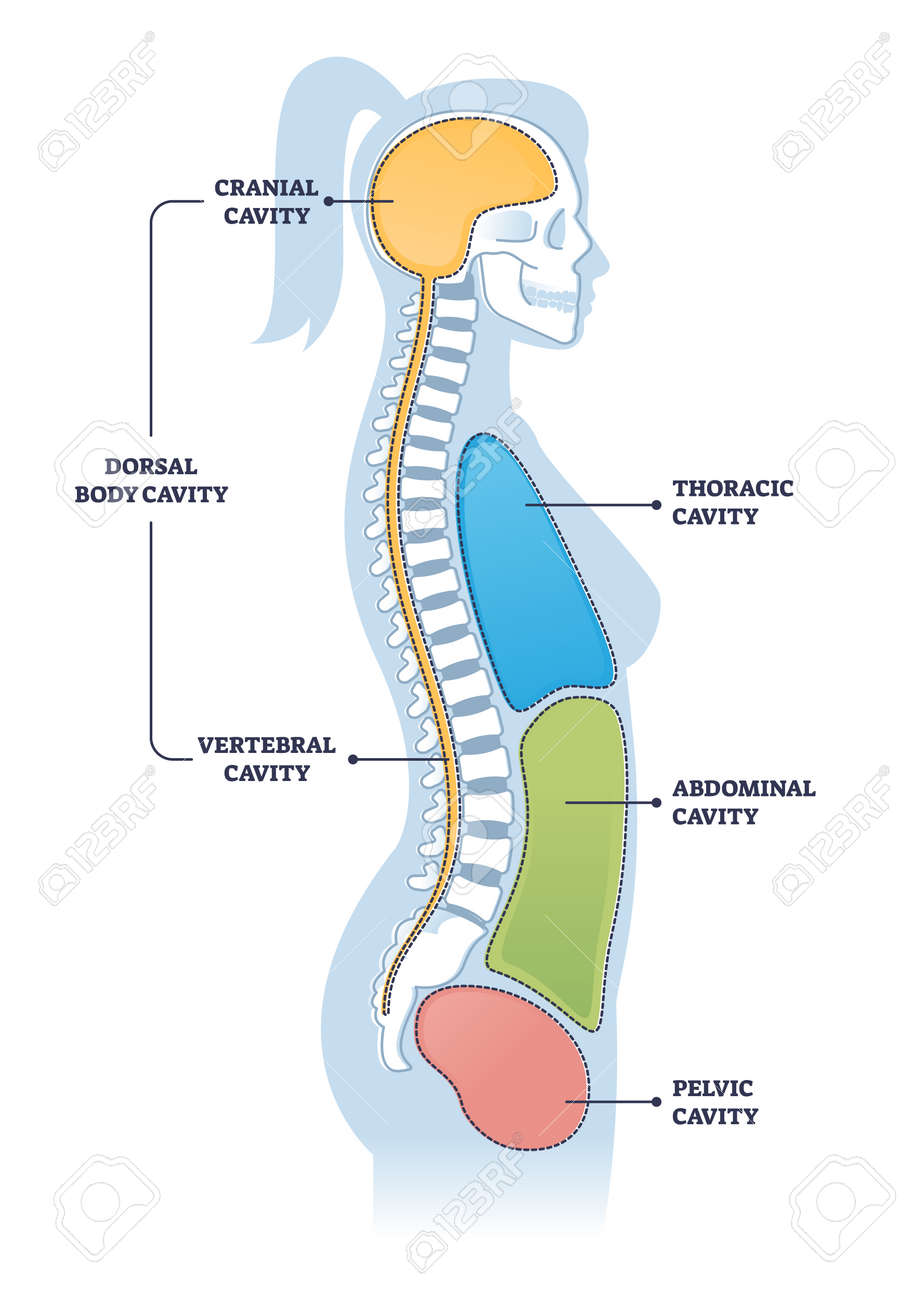
Dorsal
Back of the body, or spinal column