Bonding
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Draw a diagram to show the shape of the BF4- ion. State its shape. (2 marks)
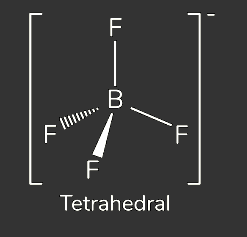
Name the type of bond formed in the reaction between BF3 and F- to form BF4-.
Explain how this bond is formed in terms of electrons involved. (2 marks)
co-ordinate bond
lone pair of electrons on F- donated to B(F3)
The boiling point of pentan-2-ol is 119 °C. The boiling point of pent-1-ene is 30 °C. Explain why pentan-2-ol has a higher boiling point than pent-1-ene. (3 marks)
Pent-2-ol has stronger intermolecular forces
As pent-1-ene has van der Waals’ forces only
Pent-2-ol also has hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen peroxide dissolves in water.
State the strongest type of interaction that occurs between molecules of hydrogen peroxide and water. (1 mark)
Hydrogen bonding
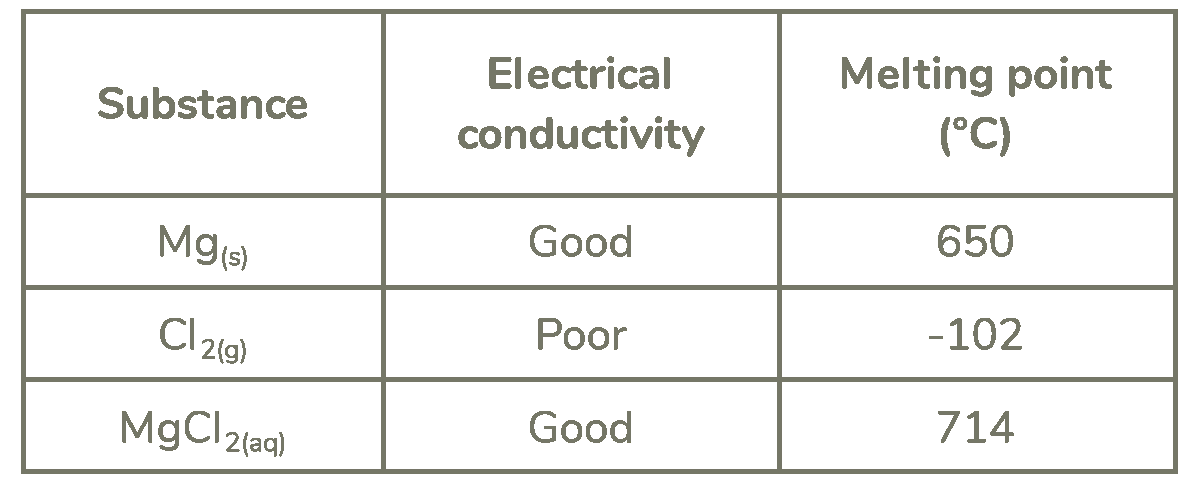
This question is about elements in period 3 of the periodic table. The table shows some properties of magnesium, chlorine and magnesium chloride.
Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain the electrical conductivity and melting point of the three substances in the table. (6 marks)
Structure and bonding:
Mg: metallic bonding
Cl2: simple covalent bonding
MgCl2: ionic bonding
Conductivity:
Mg: delocalised electrons can carry electrical charge
Cl2: no mobile charge carriers
MgCl2: mobile ions can carry electrical charge
Melting point:
Mg: metallic bonds are strong AND metallic bonds require large amounts of energy to break
Cl2: intermolecular forces are weak AND intermolecular forces require little energy to overcome
MgCl2: ionic bonds are strong AND ionic bonds require large amounts of energy to break
Name the type of bond formed between N and Al in H3NAlCl3. (1 mark)
Coordinate bond
Explain how the value of the Cl-Al-Cl bond angle in AlCl3 changes, if at all, on formation of the compound H3NAlCl3. (2 marks)
Cl-Al-Cl bond angle decreases to 109.5°
Because Al is tetrahedral
The Si-Cl bond is polar.
Explain why SiCl4 is not a polar molecule.
The molecule is tetrahedral OR there is an even distribution of electron density
The dipoles cancel out
Explain how induced dipole-dipole forces arise in a sample of SiCl4. (3 marks)
Electron movement in first SiCl4 molecule results in a temporary dipole in first SiCl4 molecule
Induces a dipole in a second SiCl4 molecule
Attraction between adjacent molecules
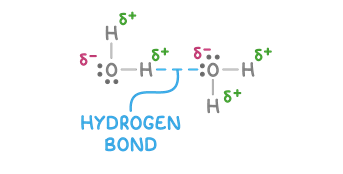
Draw a diagram of hydrogen bonding between water molecules.
Why are boiling points of group 4 hydrides lower than hydrides of groups 5,6 and 7? (3 marks)
Group 4 hydrides are non polar and so only have van der Waals forces between molecules
Hydrides of group 5,6 and 7 are polar and so have dipole-dipole attraction between molecules
Stronger than van der Waals forces
Suggest, in terms of intermolecular forces, why SiCl4 has a higher boiling point than SiHCl3. (4 marks)
SiCl4 has van der Waal forces between molecules
SiHCl3 has van der Waal forces AND SiHCl3 has permanent dipole-dipole forces
The intermolecular forces in SiCl4 are stronger than the intermolecular forces in SiHCl3
Because SiCl4 has more electrons (than SiHCl3)
allow a larger mass or a larger electron cloud
Why is the melting temperature of sodium lower than the melting temperature of magnesium?
The number of delocalised electrons per atom is fewer in sodium than in magnesium
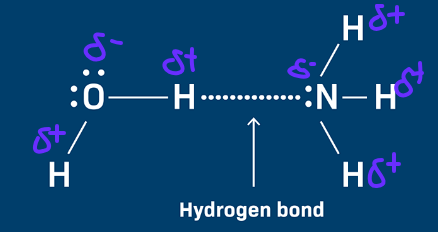
Draw a diagram to show the strongest type of interaction between a molecule of ammonia and a molecule of water.
Include all lone pairs and partial charges in your diagram. (3 marks)
Q8. Which molecule has a permanent dipole? (1 mark)
A BF3
B NH3
C SiCl4
D SO3
B NH3
Which polymer has hydrogen bonding between the polymer chains?
A Kevlar
B PVC
C poly(phenylethene)
D Terylene
A Kevlar
Sodium fluoride contains sodium ions (Na+) and fluoride ions (F-). Na+ and F- have the same electron configuration.
Explain why a fluoride ion is larger than a sodium ion. (2 marks)
Fluoride ion has (two) fewer protons/lower nuclear charge
Weaker attraction between nucleus and (outer) electrons
The melting point of XeF4 is higher than the melting point of PF3.
Explain why the melting points of these two compounds are different.
In your answer you should give the shape of each molecule, explain why each molecule has that shape and how the shape influences the forces that affect the melting point. (6 marks)
Stage 1 electron pairs:
XeF4 4bp and 2lp around Xe
PF3 3bp and 1lp around P
Stage 2 explanation of shapes:
XeF4 is square planar
PF3 is pyramidal
Electron pairs repel as far as possible or Lone pair repels more than bonding pairs
Stage 3 IMF:
XeF4 has vdw forces and PF3 has dipole-dipole forces (and vdw)
Stronger/more intermolecular forces in XeF4
Due to more electrons or larger molecules
Which compound has the highest boiling point? (1 mark)
A CH3CH2CH2Br
B CH3CH2CH2F
C CH3CH2CHO
D CH3CH2COOH
D CH3CH2COOH
Draw a diagram to show the strongest type of interaction between two molecules of ethanol (C2H5OH) in the liquid phase. Include all lone pairs and partial charges in your diagram. (3 marks)
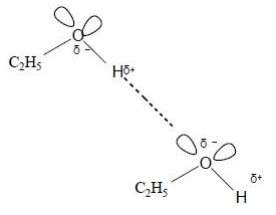
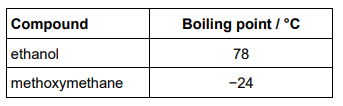
Methoxymethane (CH3OCH3) is an isomer of ethanol. The table shows the boiling points of ethanol and methoxymethane.
In terms of the intermolecular forces involved, explain the difference in boiling points. (3 marks)
Hydrogen bonds between ethanol molecules
Dipole-dipole OR van der Waals force between methoxymethane molecules
Hydrogen bonds are a stronger intermolecular force
Which is not responsible for conduction of electricity? (1 mark)
A The sodium ions in molten sodium chloride
B The electrons between layers of carbon atoms in graphite
C The bonding electrons in a metal
D The lone pair electrons on water molecules
D The lone pair electrons on water molecules
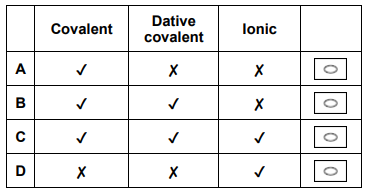
Which row shows the bonding in ammonium chloride? (1 mark)
C (Covalent, Dative covalent, and Ionic)
Silicon tetrafluoride (SiF4) is a tetrahedral molecule.
Deduce the type of intermolecular forces in SiF4. Explain how this type of intermolecular force arises and why no other type of intermolecular force exists in a sample of SiF4. (3 marks)
Van der Waals forces
Uneven distribution of electrons in one molecule induces dipole in neighbouring molecule
Symmetrical molecule / dipoles cancel so no dipole-dipole attraction
Deduce why the bonding in nitrogen oxide is covalent rather than ionic. (1 mark)
Small electronegativity difference
Suggest the type of crystal shown by OF2 (1 mark)
Simple molecular