Chapter 6- The Development of B Lymphocytes
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Immunoglobulin Repertoire
diverse set of sequences via gene rearrangement
Secondary lymphoid tissue
where B cells go to differentiate and activate
Peyer's Patches
helps foster an environment where B cells can encounter an antigen, favor isotope switching
HSC
Hematopoietic stem cell that expresses CD34, picks up more CD markers as it becomes more specialized
CD34
expressed via hematopoietic stem cell, its marker
Pro-B cell (progenitor)
when a B cell is born
early pro B cell- heavy chain rearrangement starts
late pro B cell- heavy chain rearrangement continues
Pre-B cell
large pre B cell- heavy chain is main, mu heavy chain is made
small pre B cell- light chain rearrangement starts, mu chain is in the endoplasmic reticulum
Stromal cells
(non-lymphoid) help the B cells differentiate by using adhesion molecules that maintain contact, releasing growth factors like stem cell factor and IL-7
SCF
stem cell factor, helps development of the B cells
Kit receptor
stem cell receptor, growth factor receptor
IL-7
helps the development of the B cells
IL-7 receptor
on the late pro-B cell and pre-B cell
Non-productive rearrangement
attempt to create a successful rearrangement
Apoptosis
when a cell is signaled to die
Survival signal
when a cell is signaled to survive and become a pre-B cell (only about 50% of cells)
sLC
surrogate light chain - a fake light chain that acts as a place holder for the heavy chain
pre-BCR
sLC and heavy chain form a pre B cell receptor, binding to a ligand means that the B cell will survive
Light chain rearrangement
occurs in the pre-B cell, only one recombination event required (VJ), can have multiple attempts at making a correct assembly (85% success rate), clonal expansion
B cell checkpoints
1) pre-B cell receptor- makes sure there are pre-B cell receptors (pre-BCR), if not, cell goes through apoptosis (after heavy-chain rearrangement)
2) B cell receptor- looks to see if there is a B-cell receptor, if not, cell goes through apoptosis (after light chain rearrangement)
RAG
RAG protein expression is turned on and off (2 times), once for the heavy chain, then again for light chain
Ig alpha and Ig beta
always on until the B cell turns into a plasma cell then turned off
approximate expression patterns of TdT, sLC, RAG, and growth receptors
TdT (N-nucleotide addition) - early pro-B cell phase to small pre-B cell phase
sLC- early pro B cell to immature B cell
RAG (lymphoid-specific recombinase)- early pro-B cell to large pre-B cell, small-pre B cell to mature B cell
Growth receptors:
Kit- stem cell to late pro- B cell
IL-7 receptors- stem cell to small pre-B cell
CD25- late pro B cell-small to pre-B cell
Chromosome translocation
when different chromosomes fuse together by accident
Burkitt's lymphoma
MYC proto-oncogene- the MYC gene normally controls the cell cycle but this control is disrupted with translocation leading to Burkitt's lymphoma
B-1 cells
atypical subset of B cells that are made early in embryonic development
CD5 cell surface protein is a marker
Antibodies are not diverse and tend to bind to more than one antigen
produced in bone marrow in embryo but this stops in adults
In adults- B-1 cells persist in the lymphoid tissue and can self-renew
B cell selection
1) Prepare (Repertoire assembly)
2) Weed out (Negative selection)
3) Promote (Positive selection)
4) Search (Search while recirculating)
5) Activation (Clonal expansion)
6) Attack (Differentiation)
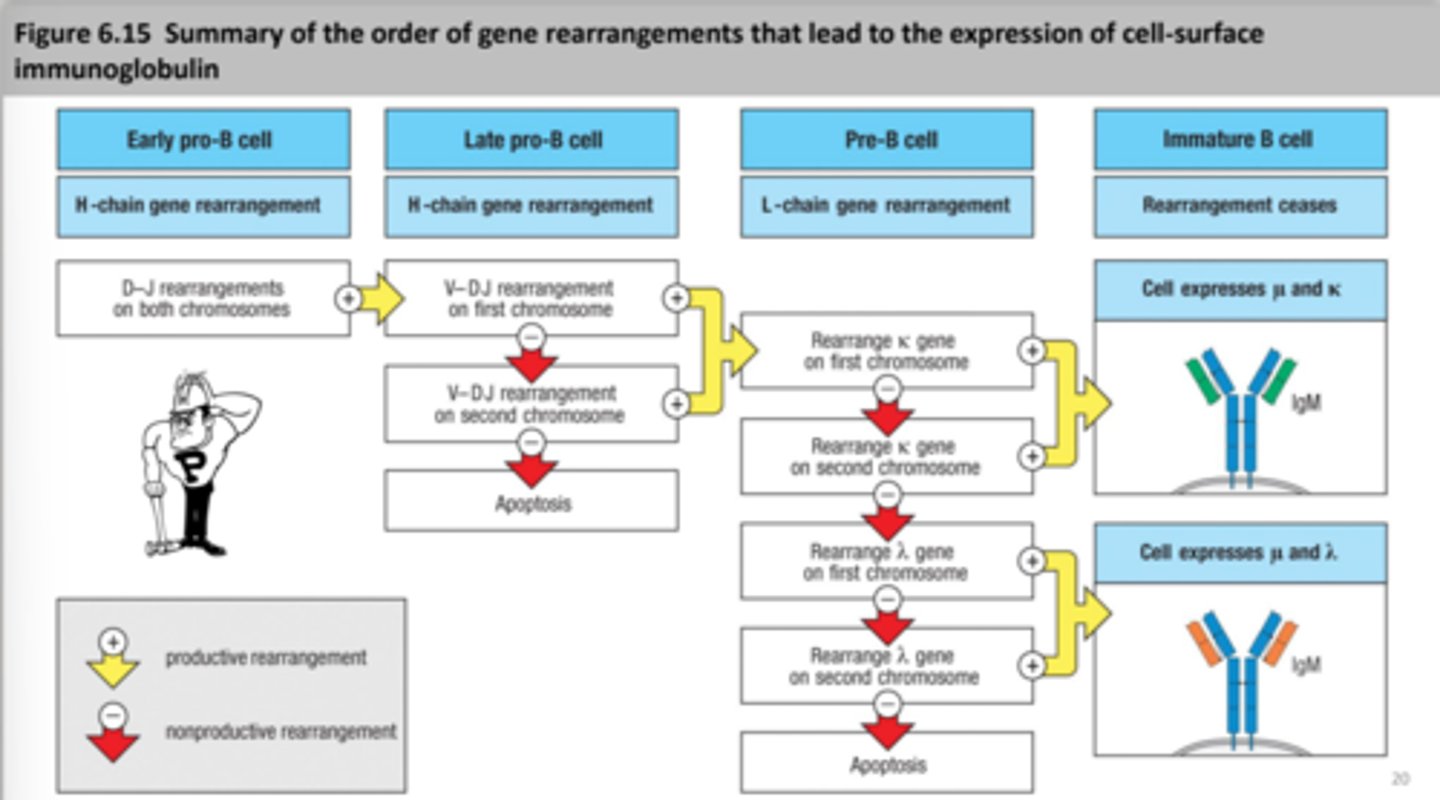
self-reactive B cells
B cells that will die or become inactive when they bind to a self-antigen in the bone marrow, stay in bone marrow to be tweaked
Immature B cells
IgM on the surface, leave bone marrow if they do not react, goes to secondary lymphoid tissue for continued development
Receptor editing
contribute to self tolerance
1) self-reactive B cells reduce IgM BCR levels and maintain expression of RAG proteins
2) light chain is rearranged again to make a new BCR. This leads to two outcomes: New BCR is NOT self-reactive- B cell will develop further, New BCR is self-reactive- rearrangement keeps going until the B cell runs out of attempts
3) Clonal deletion
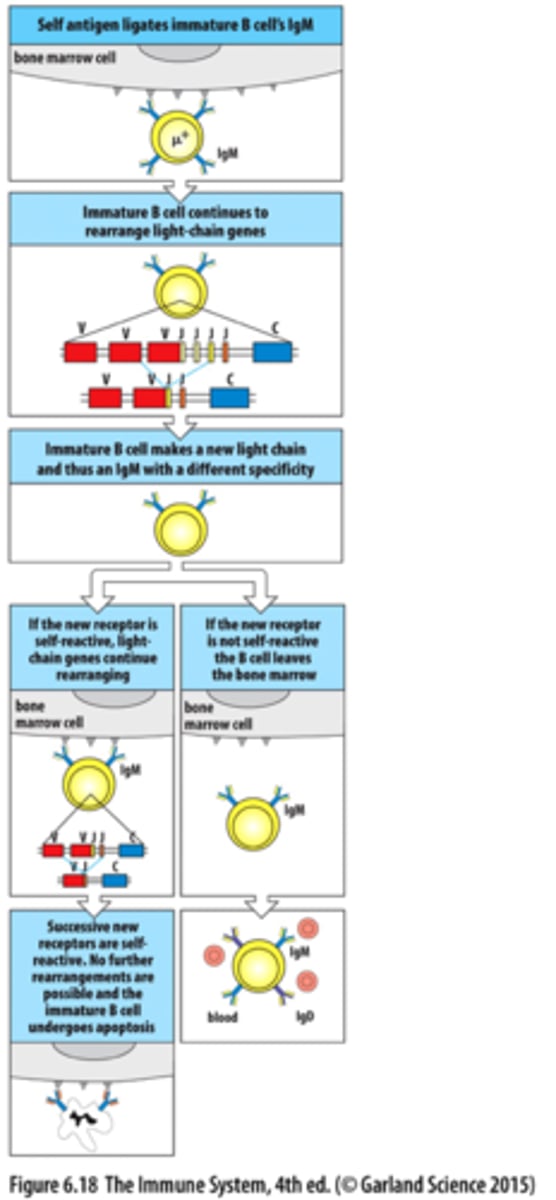
Clonal deletion
self-reactive B cells eventually die by apoptosis and are cleaned up by macrophages
Anergy
B cells that bind to monovalent and soluble self-antigens in the bone marrow
have a short lifespan (5 days)
come from self-reactive B cells
Primary lymphoid follicle
B cells congregate here from the lymph nodes, continuation of B cell maturation, when B cells enter the primary follicle it will increase their life-span, majority of immature B cells don't enter the primary follicle, Anergic B cells are stuck in the T cell area, some B cells stay in the primary lymphoid follicles
Homing
help B cells enter the lymph, similar to extravasation
-HEV
-stromal/dendritic cells
-naive B cells bind via specific receptor
HEV
high endothelial venule, part of the homing mechanism, leads them to the T cell area
Stromal cells/dendritic cells
secrete chemokines, part of the homing mechanism
Stromal cells - CCL21
Dendritic cells - CCL21, CCL19
FDCs
Follicular Dendritic Cells, in follicles, secrete CSCL13 and BAFF, found in the lymph nodes
CXCL13
secrete chemokine survival, attracts B cells into the primary follicle
BAFF
works with FDCs, differentiation signals, transforms immature B cells that enter follicle to become mature B cells
plasma cells
very specialized- protein synthesis and secretion is highly developed and they lose MHC II and BCR expression, CD4 T cells will help activate B cells directly become plasma cells (secrete IgM)
primary focus
how B cells develop to plasma cells or memory B cells
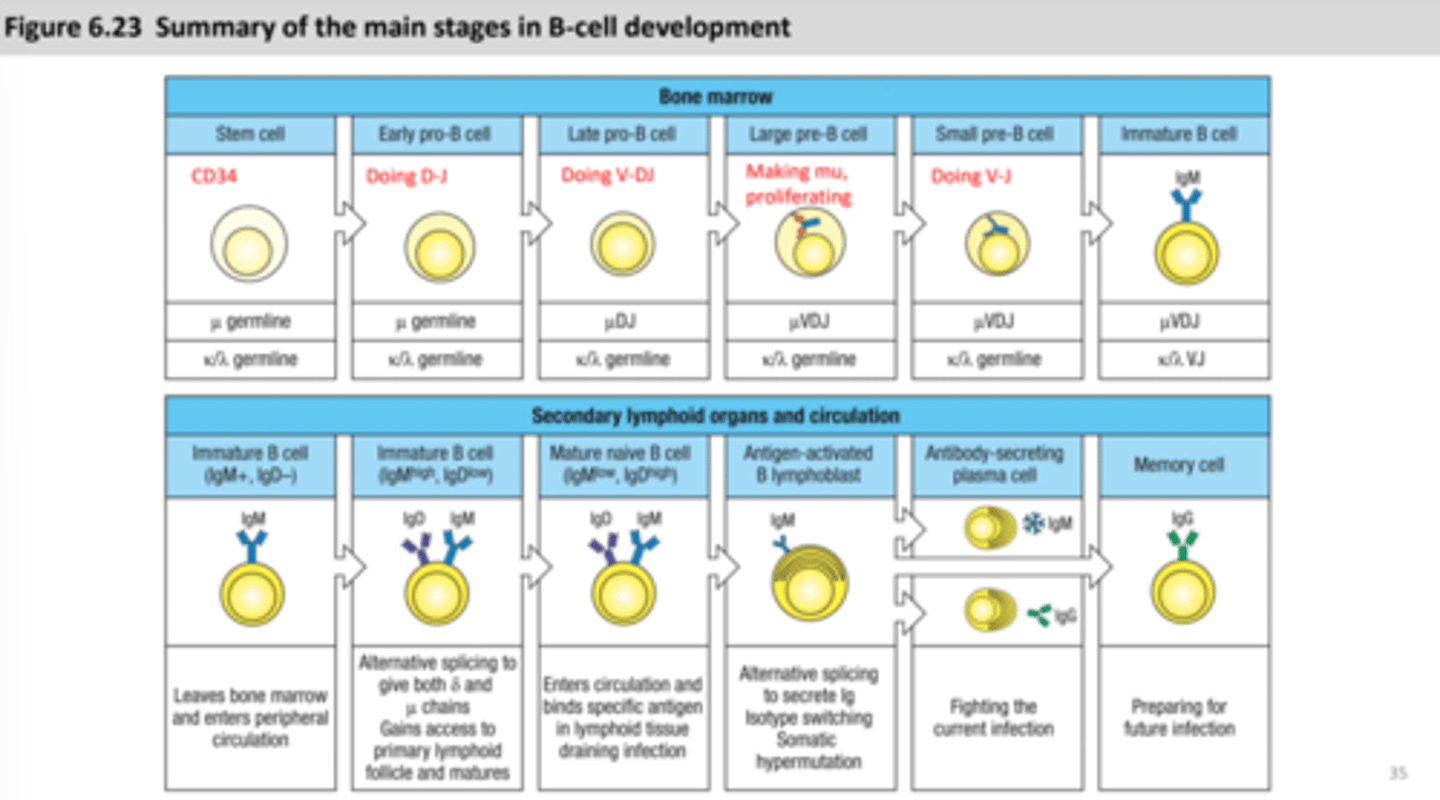
germinal center
Where B cells undergo affinity maturation and proliferation
B cells will differentiate and reside in the medullary cords, spleen, and bone marrow as plasma cells secreting high-affinity, isotype-switched antibodies; some B cells become long-lived memory B cells that recirculate and rapidly activate after recognizing their antigen
velcade
used to treat multiple myeloma
B cell tumors
many B cell tumors have chromosomal translocations involving immunoglobulin genes, has similar properties equivalent to its developmental stage like location, morphology, and surface receptors
ALL
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, lymphoid stem cell, in the bone marrow and blood, the Ig V gene is unmutated, comes from the lymphoid progenitor, treated with chemotherapy or bone marrow transplant
multiple myeloma
plasma cell origin, comes from plasma cell and various isotypes, from the bone marrow, the Ig V gene is mutated, with no variability within clone