Pathology of rheumatic fever-
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what ages does rheumatic fever affect
ages 5-15
Pathogensis of RF
GAS infection (Streptococcus pyogenes) triggers the immune system, leading to antibody formation against bacterial antigens such as:
M-protein (a key virulence factor that resists phagocytosis)
N-acetylglucosamine (a component of the bacterial cell wall)
Due to molecular mimicry, these antibodies cross-react with host tissues because of structural similarity to human proteins, leading to autoimmune inflammation.
Rheumatic fever is considered a Type II hypersensitivity reaction (antibody-mediated).
Migratory arthritis
-Migratory arthritis, moving from one joint to another
-Polyarthritis, affecting mainly the large joints (with large blood flow)
-antibodies attack proteins in synovial joints due to molecular mimickery
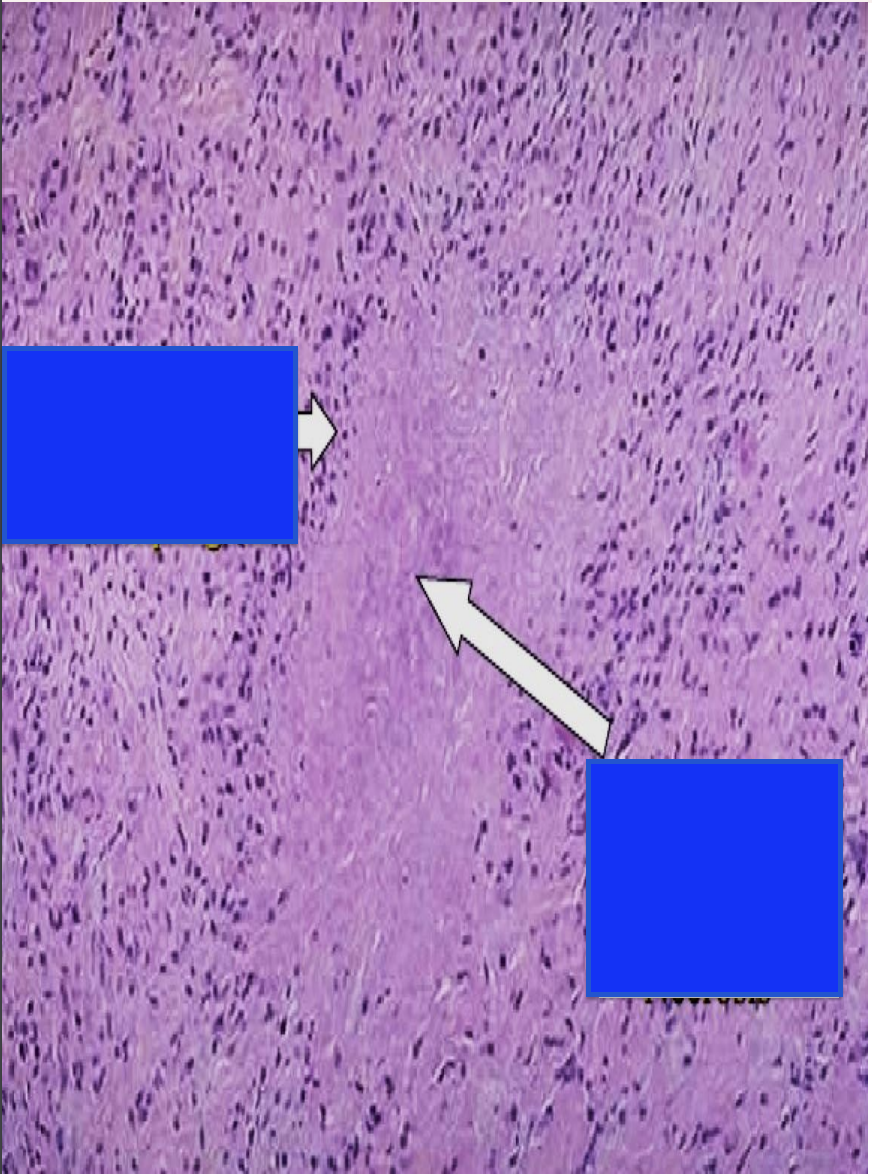
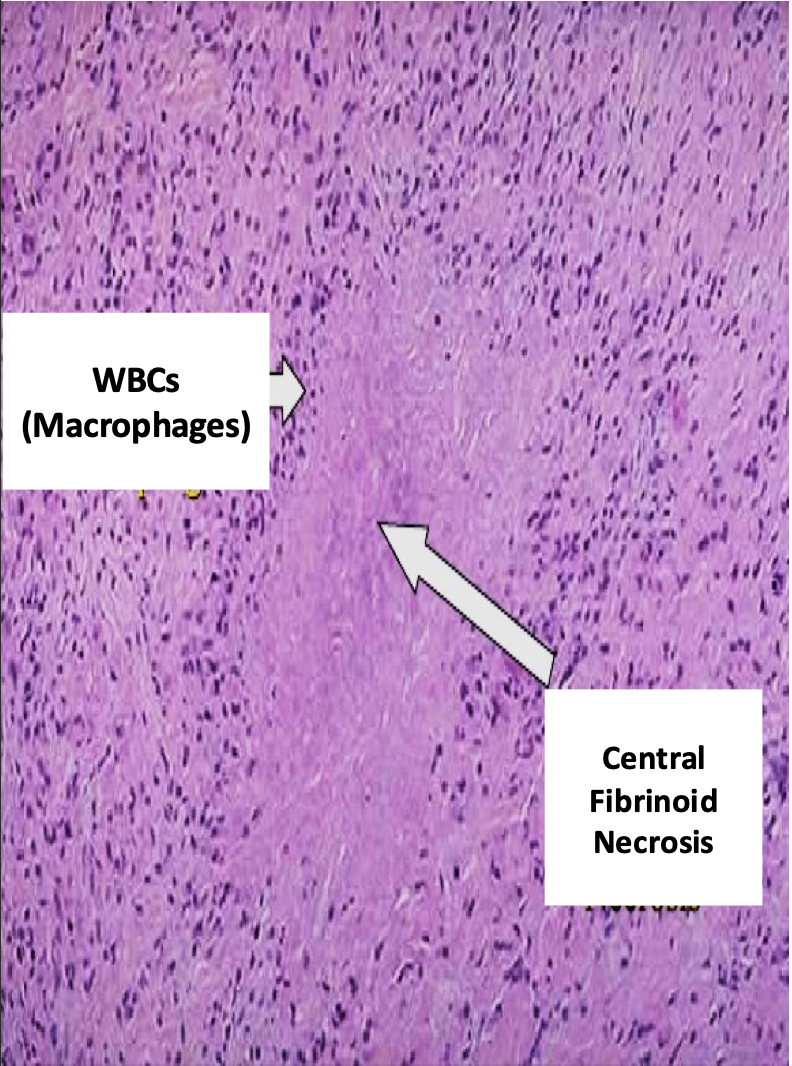
seen in subcutaneous nodules
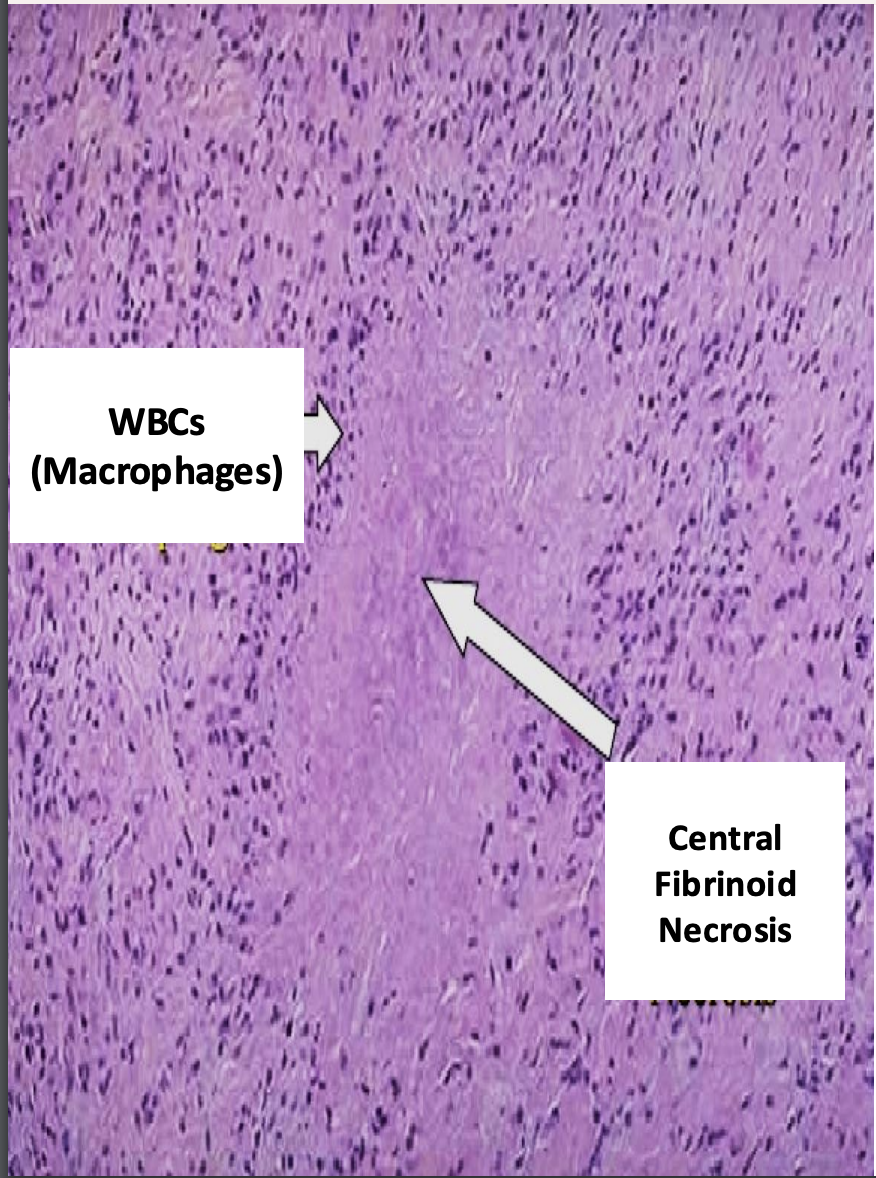
skin has CT with molecules similar to bacterial molecules so are attacked by antibodies and initiate inflammation, with central fibrinoid necrosis and macrophages forming subcutaneous nodules
-seen near elbow, which is a joint with large blood flow to it
what are nodules
elevation more than 0.5 cm
histology of subcutaneous nodule
fibrinoid necrosis because it is close to blood vessels
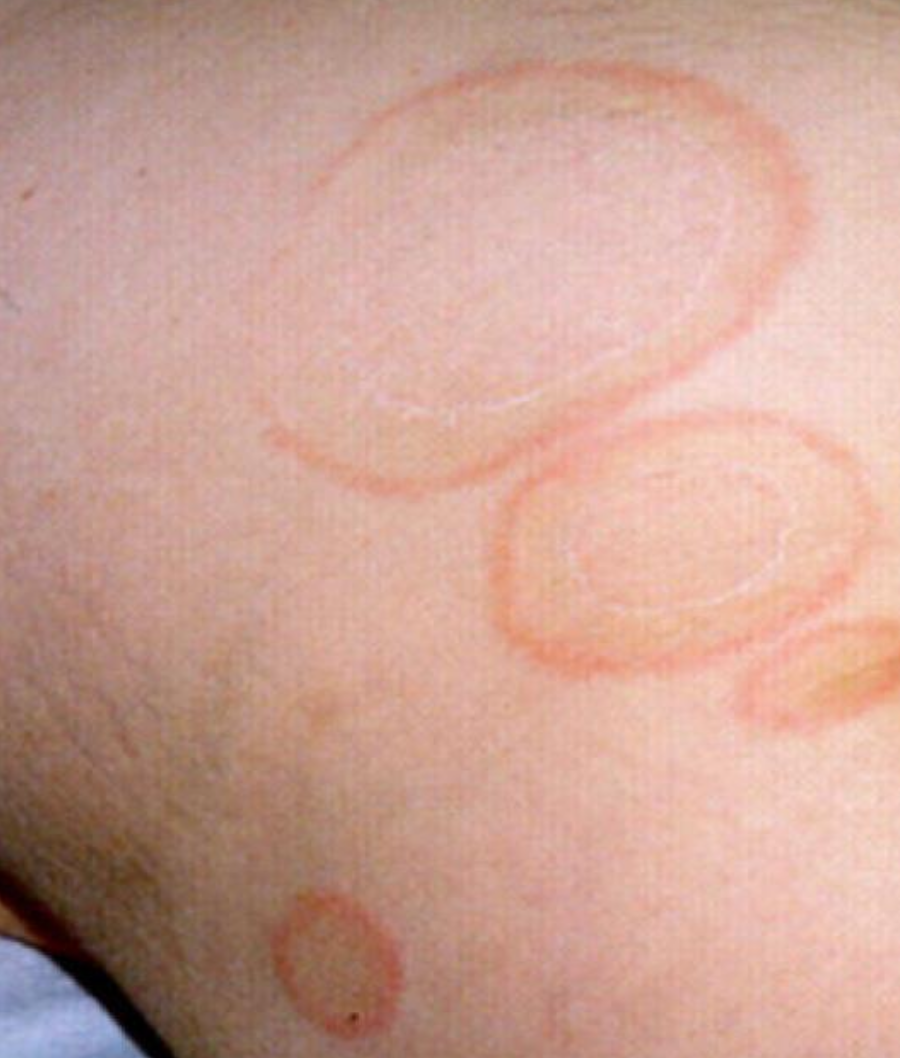
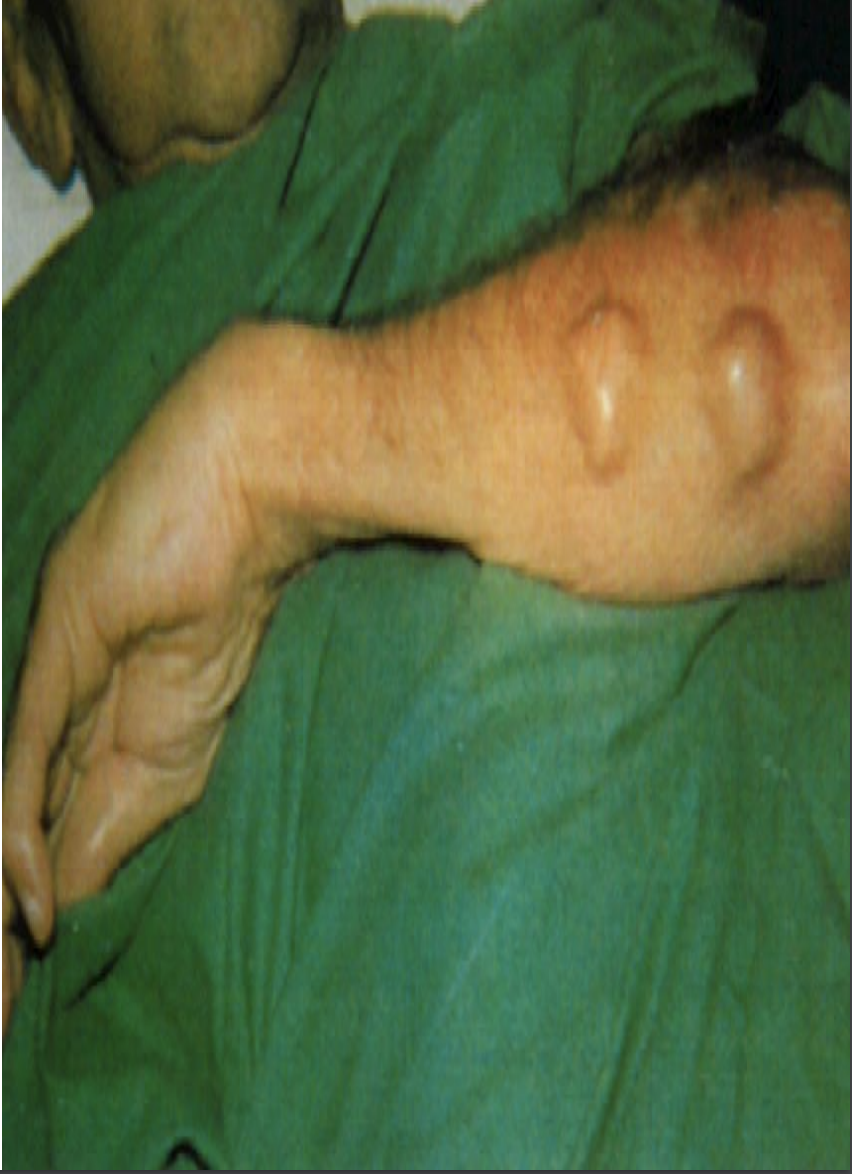
what is this
Erythema = Redness
Marginitum = Margin
• The red area is slightly
elevated and the
center is flat and clear.
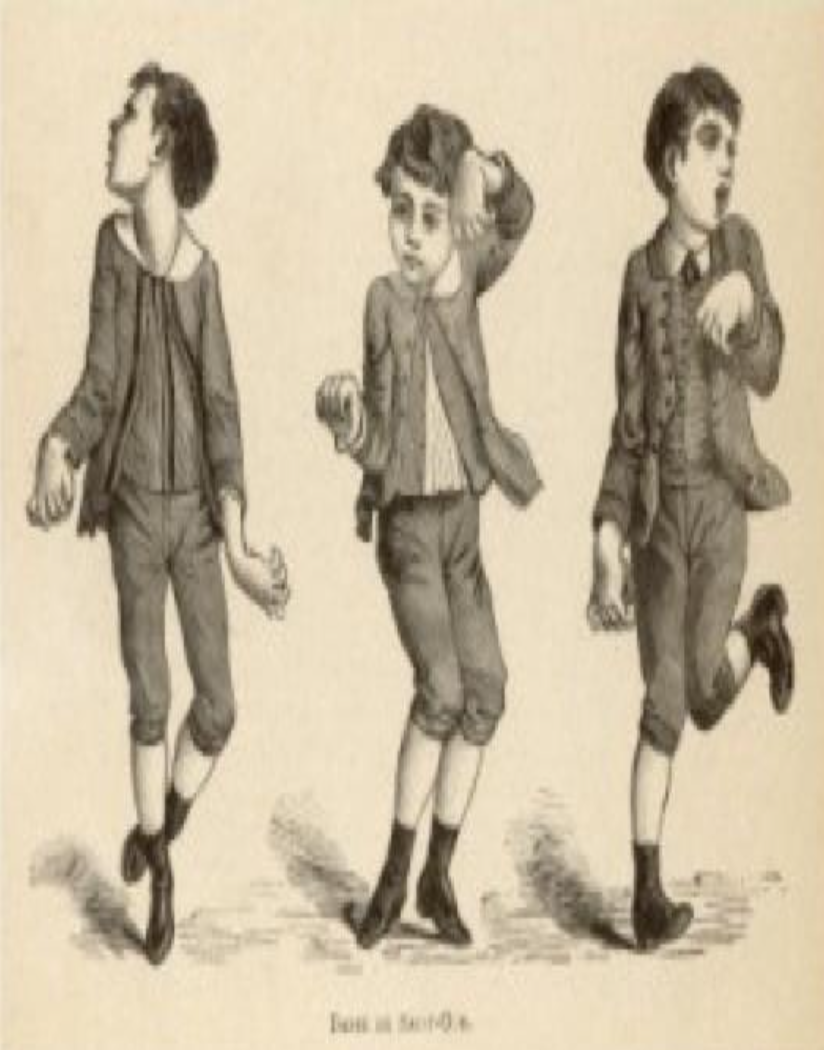

what is this
Sydenham Chorea- when CT in brain is affected
Sydenham Chorea
Occur in 5-10% of cases
• Saint Vitus Dance
• Uncoordinated jerking movements (face, hands and feet)
• Deterioration of handwriting, emotional liability or grimacing of face
• Pronator sign (), milking sign of hands, tongue fasciculations (Bag of worms)
if affects myocardium
myocarditis occurs
if affects pericardium
pericarditis
if affects endocardium
endocarditis and formation of vegetations
if all 3 layers are affected
pancarditis
pathogenesis of heart problems
-strep pharyngitis attacks tonsils, causing sore throat
-immune system produces igG and igM leads to molecular mimickery of heart features leading to valvulitis and myocarditis, pericarditis
-if inflammation is repeated or prolonged this leads to chronic inflammation which affects the mitral valve
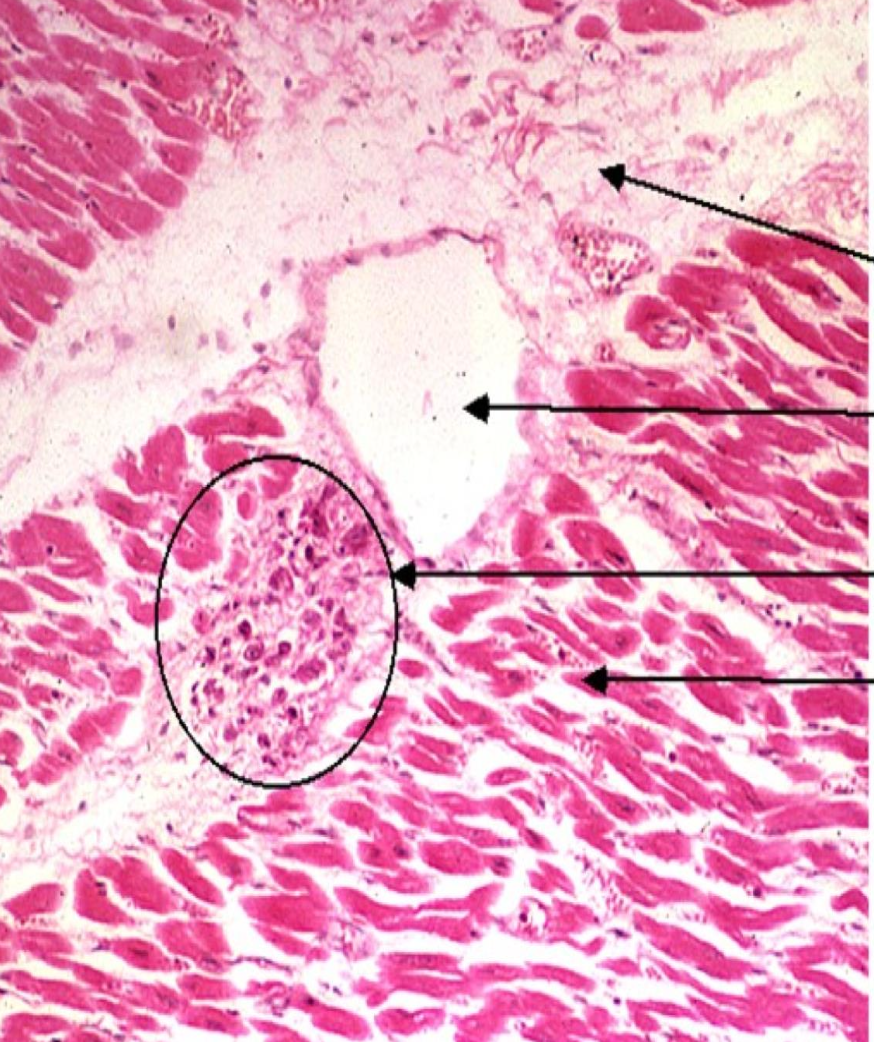
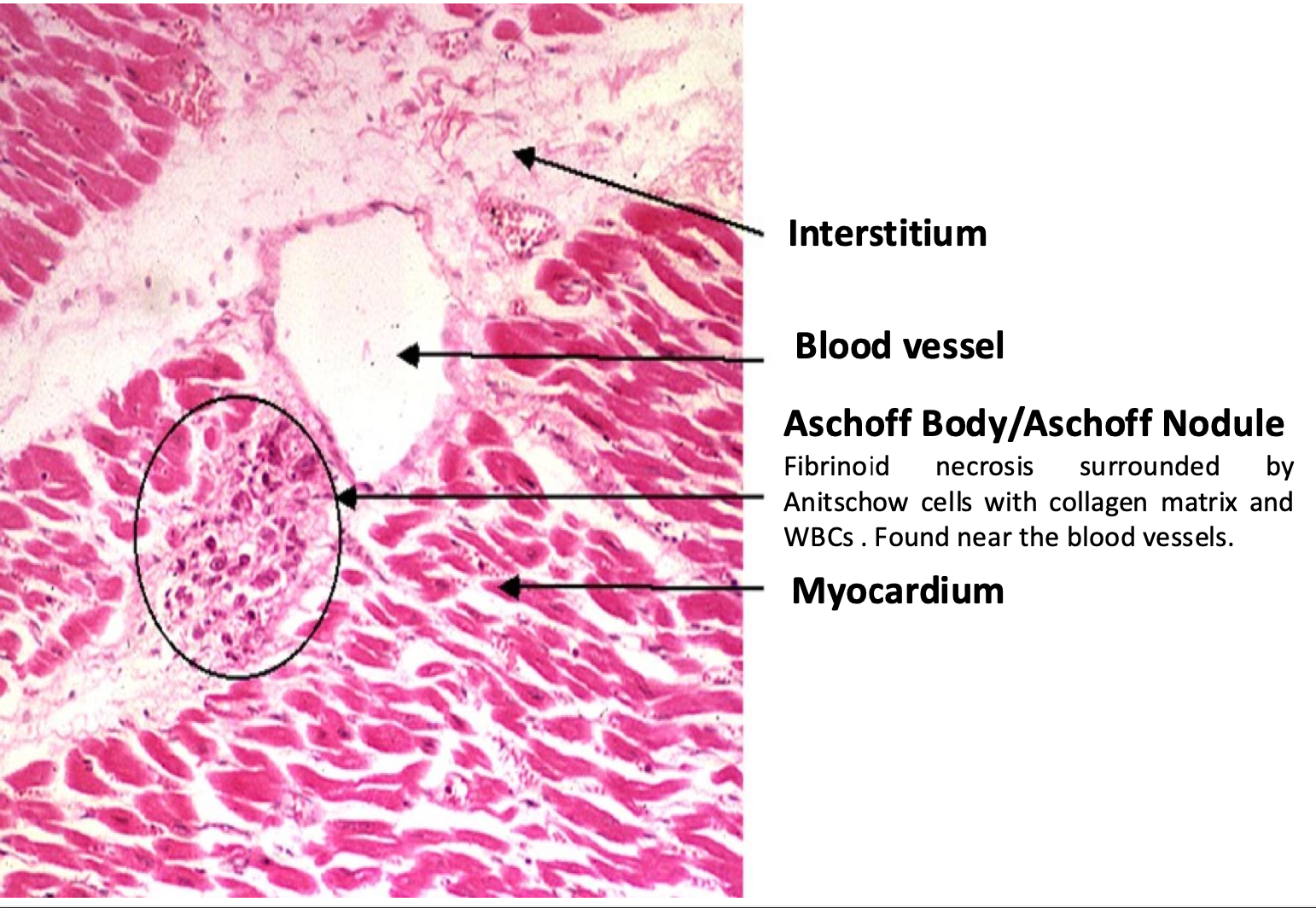
-Aschoff body/nodule
Fibrinoid necrosis surrounded by Anitschow cells with collagen matrix and WBCs . Found near the blood vessels
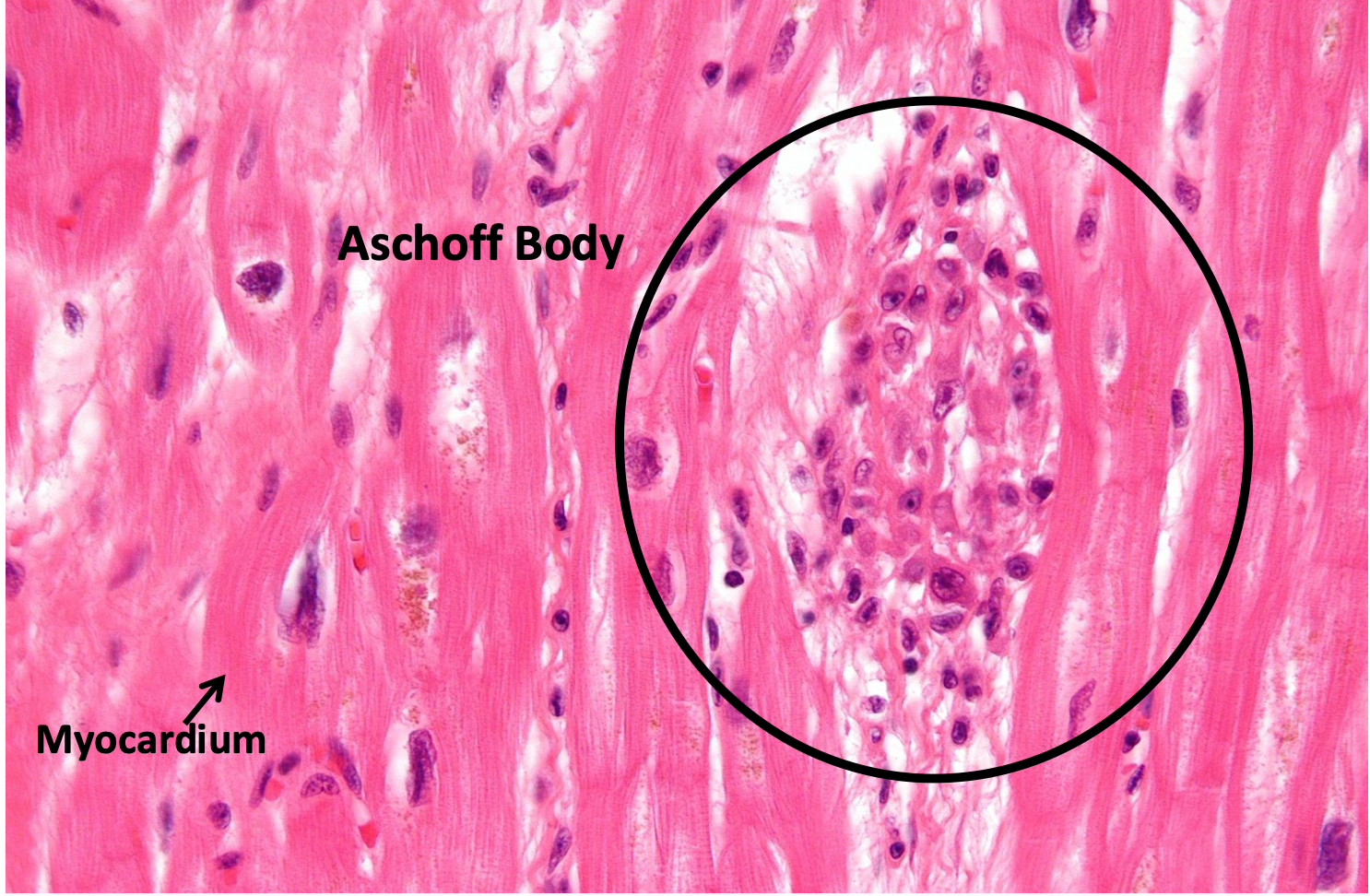
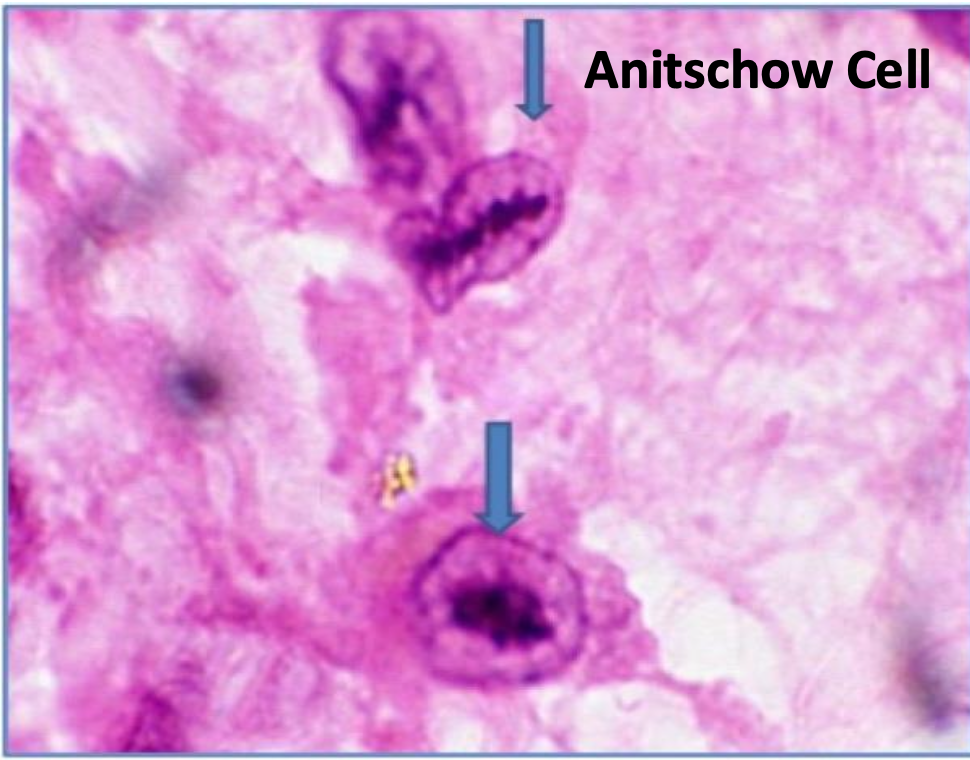
what is an anitschow cell
• Anitschow cells are within the Aschoff body
• Activated large macrophages
• In longitudinal section, the chromatin bands of the nucleus looks like a caterpillar (or owls eye in a transverse section)
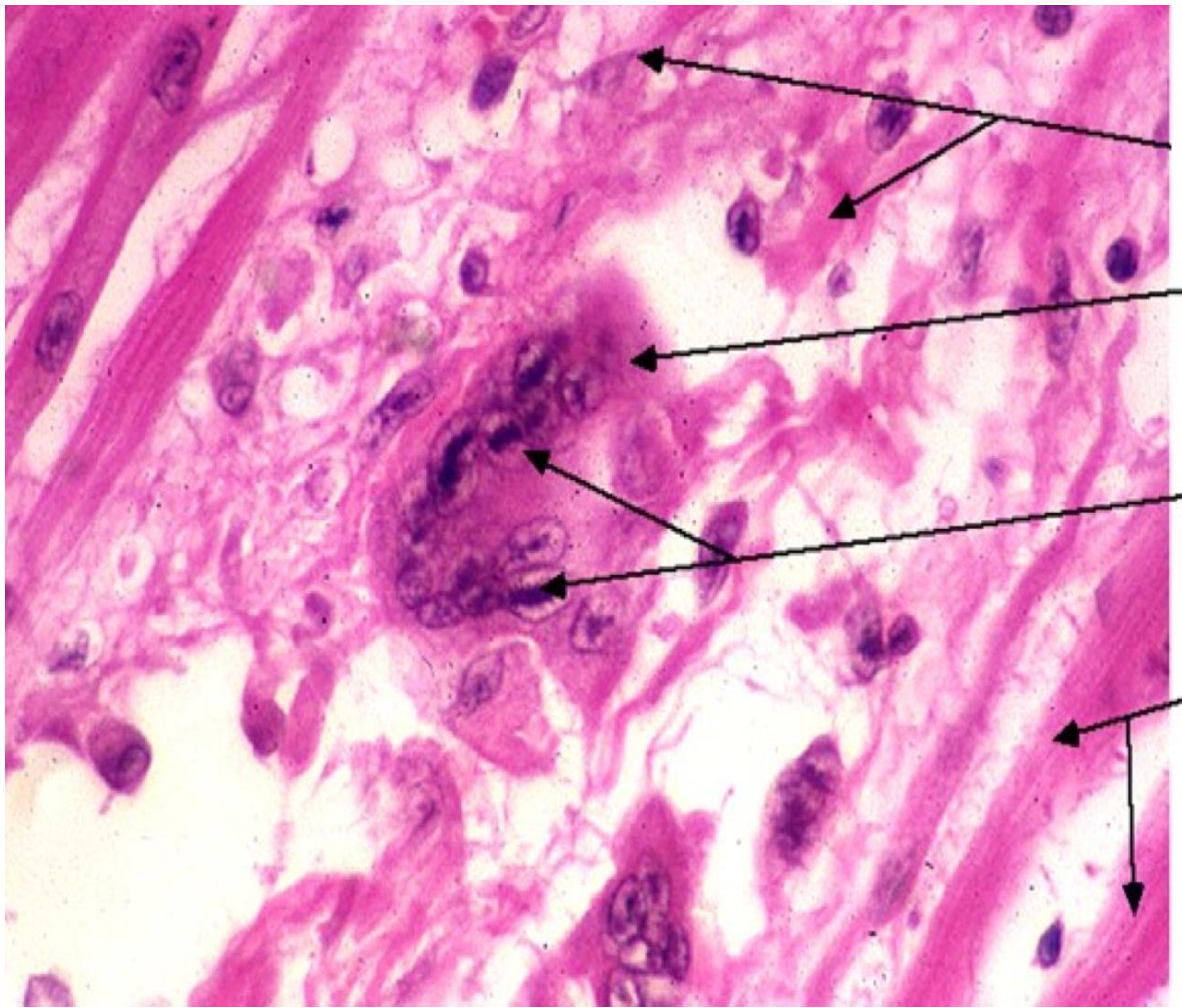
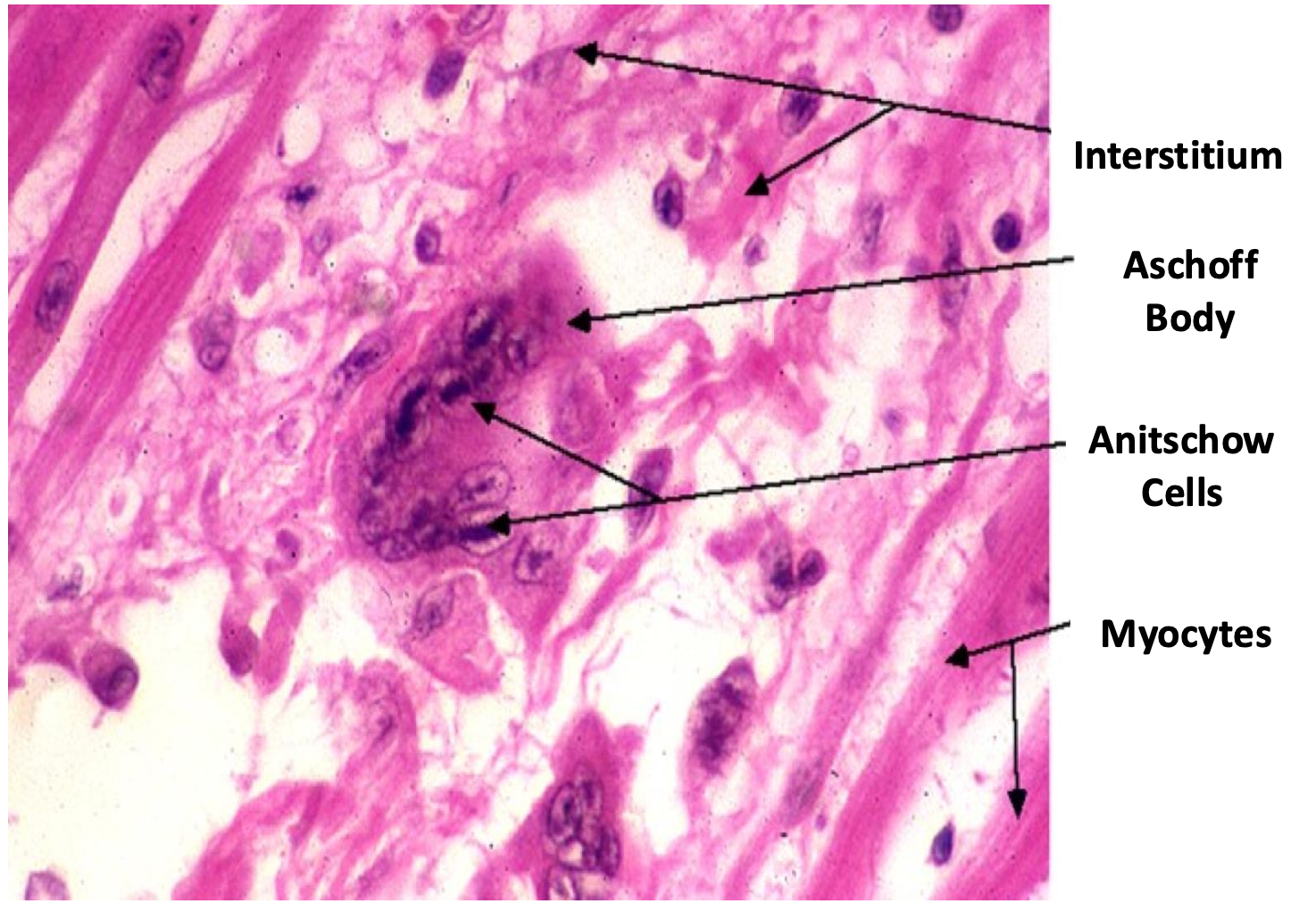
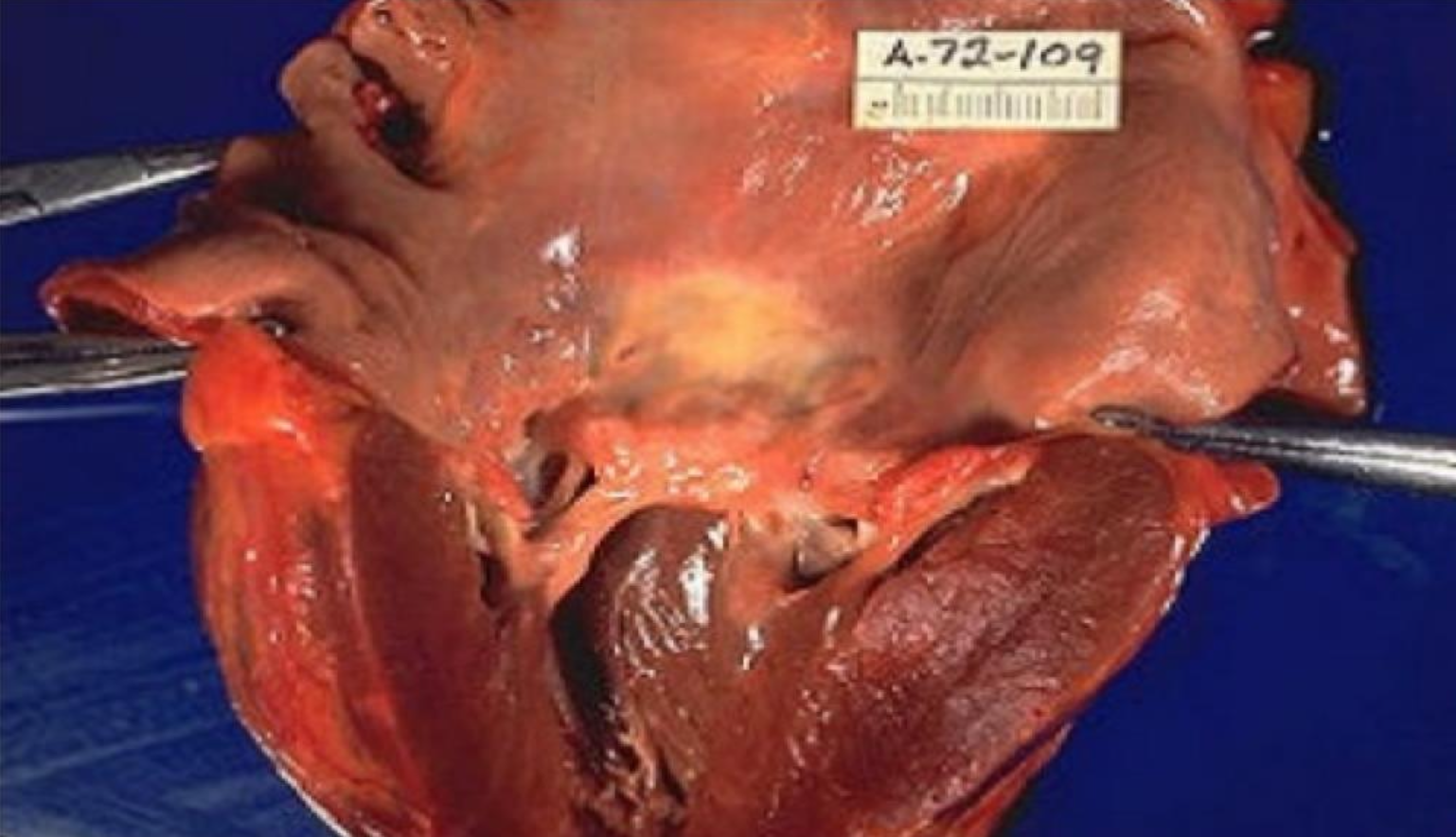
aschoff cells aggregate usually in left atrium inducing fibrosis and thickening called MacCallum Plaque and can contribute to heart failure
Pericarditis
in pericardial cavity with serous fluid becomes viscous due to Irregular deposits of fibrin found on both visceral and
parietal surfaces of pericardium
●Increased Vascular Permeability & Fibrin Exudation
•Inflammation causes leakage of fibrinogen-rich exudate into the pericardial space.
•Coagulation cascade activation converts fibrinogen to fibrin, forming "bread and butter" fibrinous deposits.
●Fibrinous Pericarditis (Early Stage)
•The rough, inflamed pericardial surfaces rub together → friction rub on auscultation and chest pain
pericarditis in physical exam
On physical examination can be recognized by a friction rub on auscultation + chest pain
Endocarditis
- Mainly mitral and aortic valves are affected because the left side has more stress because they pump blood to the body?
●formation of Sterile Vegetations on valves (Verrucous Endocarditis) at commisures
• Endocardial tissue damaged followed by platelets-fibrin (Vegetation) as a result of inflammation/healing process making this area prone to infection by bacteria (keep pt on antibiotics for prophylaxis)
-prolonged inflammation leads to mitral regurgitation
jones criteria for diagnosis of RF
chronic heart disease
-●Acute rheumatic fever (ARF) usually resolves, but in some cases, it can progress to chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD), particularly with recurrent or untreated infections.
-infection or prolonged infection of the heart leads to chronic heart disease where Mitral valve is the most common and aortic valve is the 2nd most affected
• Valvular disease characterized by irregular thickening and
calcification of the leaflets, often with fusion of the
commissures and chordea tendineae
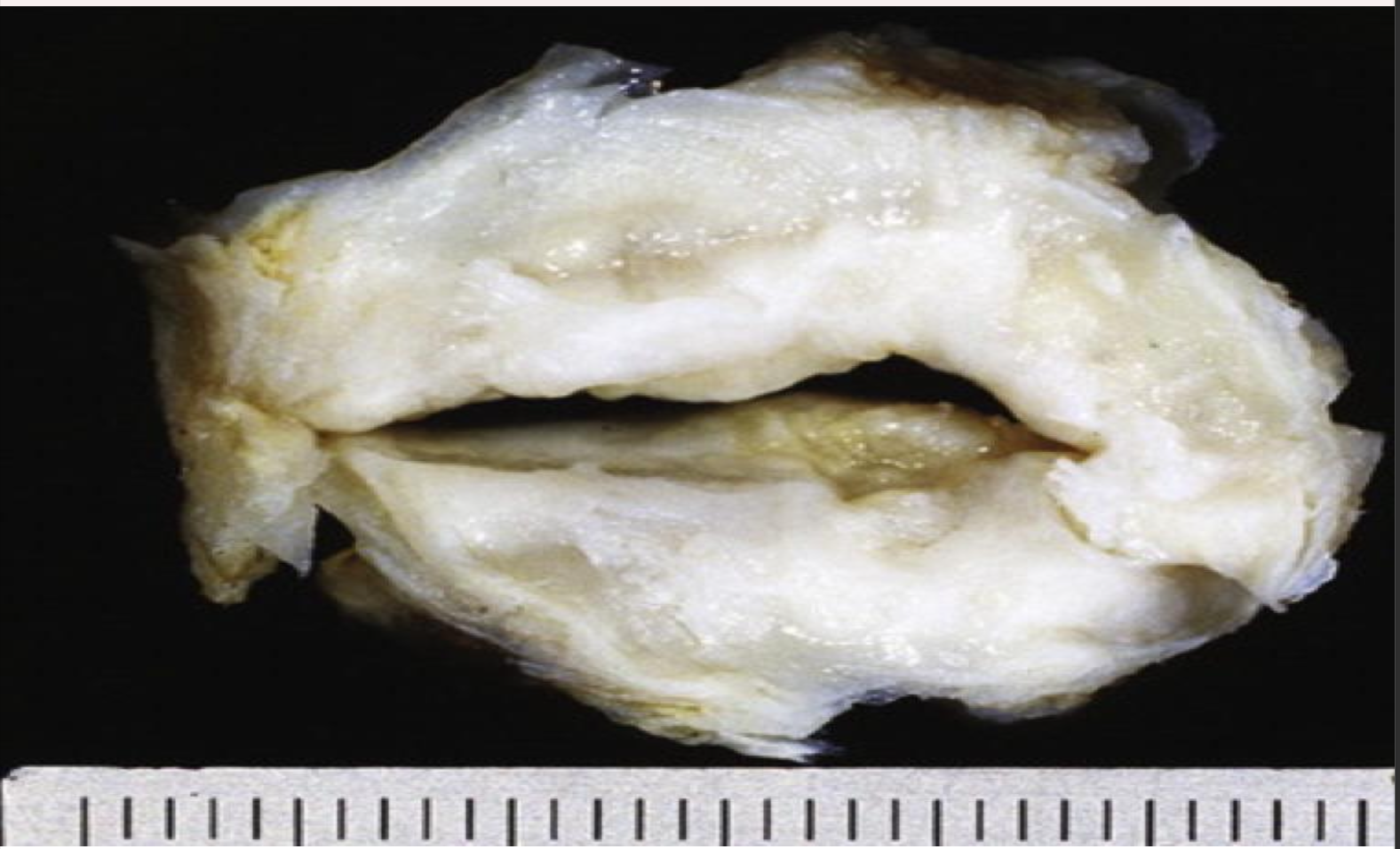
Aortic valve stenosis shows fused commissures and thickening of the cusps. Aortic valvulitis has a characteristic shape of “Teardrop”.
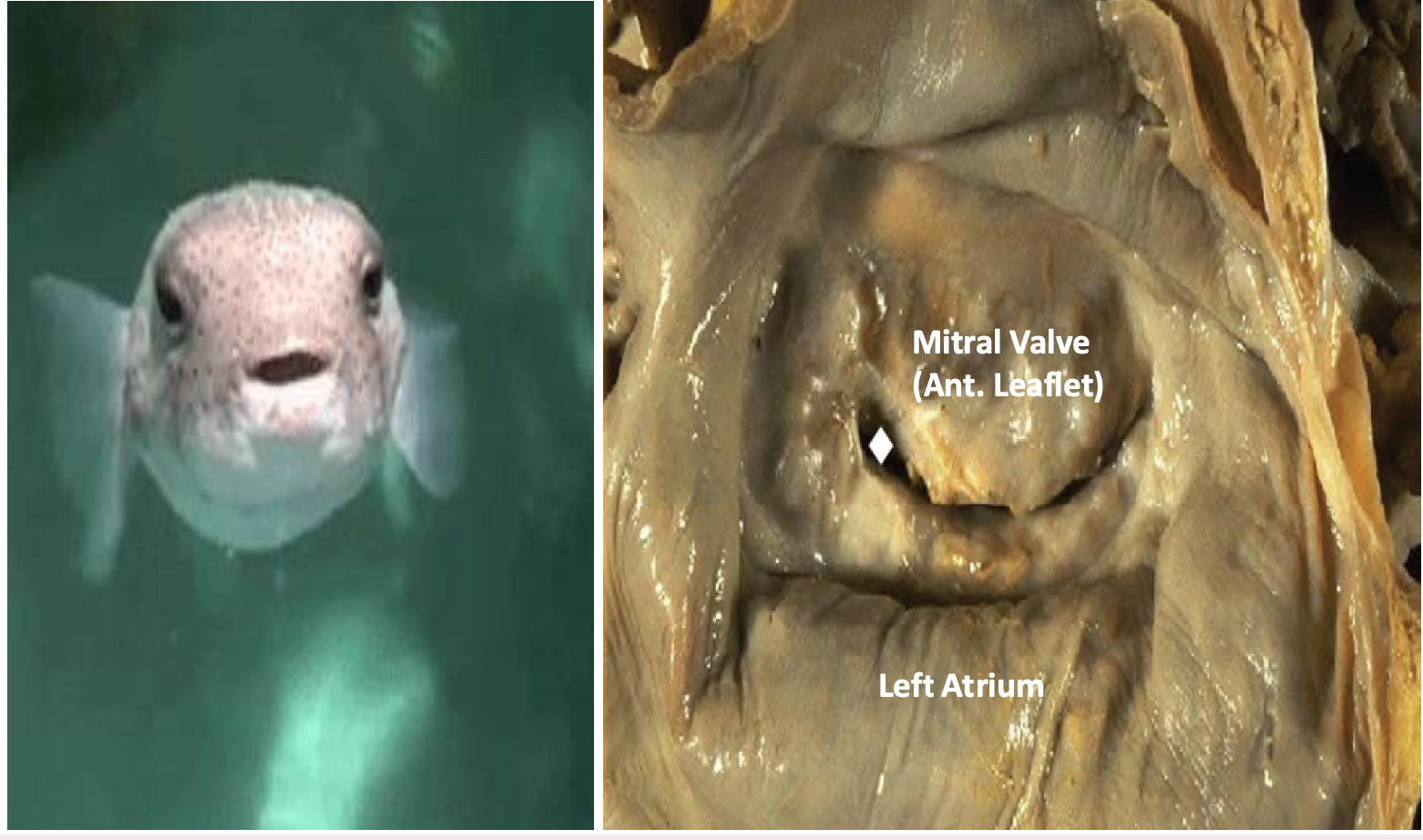
Mitral valve insufficiency + stenosis viewed from left atrial aspect, valve has a narrowed
orifice looks like “Fish mouth”
-affects blood flow on left side of heart
Complications of CHD
Infective Endocarditis
Mural Thrombi
Adhesive Pericarditis
Congestive Heart Failure
Infective Endocarditis
diseased valve with vegetation atrracts Staphylococcus aureus infections derived from I.V drug abuse, dental or surgical procedures
dukes criteria: Major and minor
Major:
Blood culture positive (Major)
Typical microorganisms in two separate blood cultures:
Staphylococcus aureus, Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus gallolyticus (bovis), HACEK organisms, Enterococci
Persistent bacteremia (≥2 positive cultures drawn >12 hours apart)
Echo findings (Major)
Vegetation (mobile echodense mass on a valve)
Abscess
New valvular regurgitation (not pre-existing murmur)
Minor
Predisposing condition (e.g., prosthetic valve, IV drug use, congenital heart disease)
🔹 Fever ≥ 38°C (100.4°F)
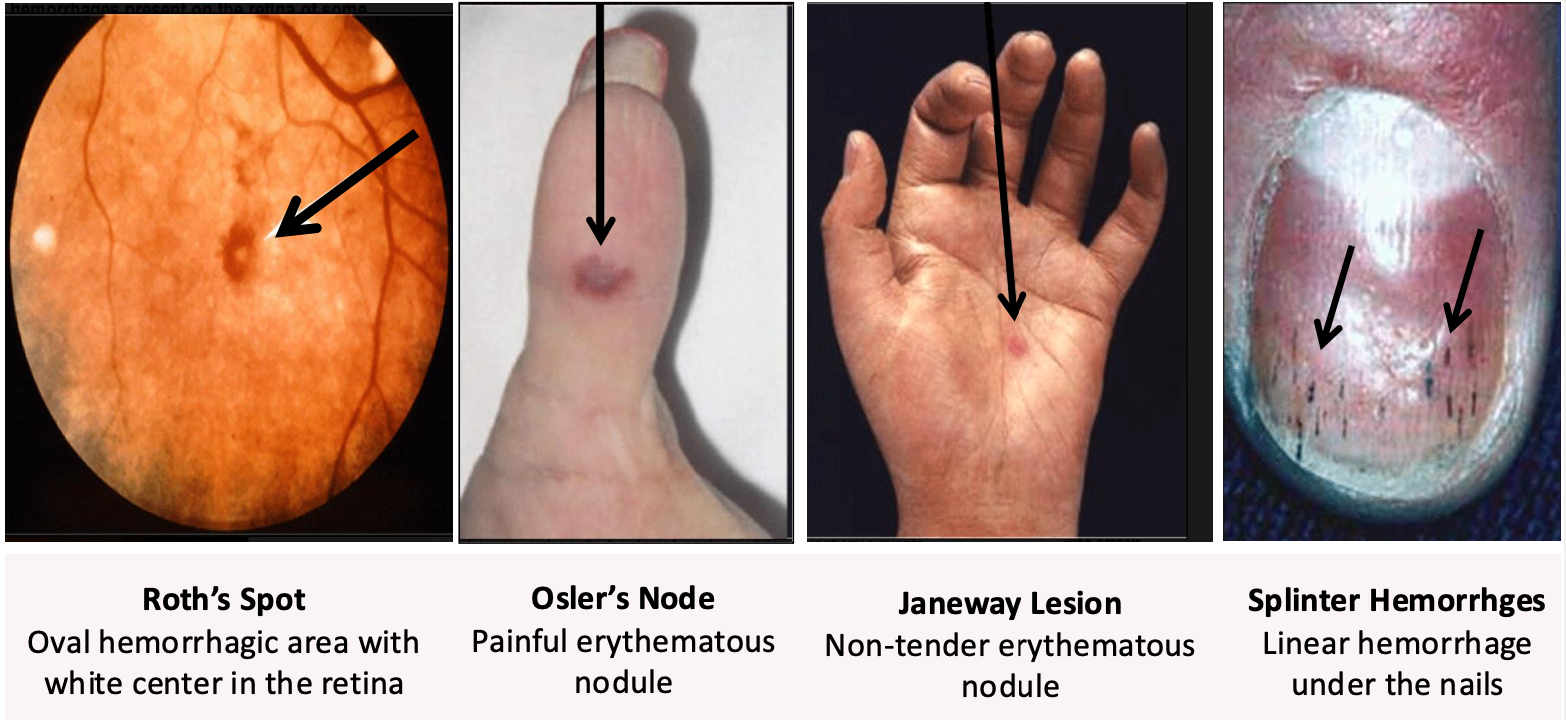
🔹 Vascular phenomena:Janeway lesions (painless, on palms/soles)
Arterial emboli (stroke, limb ischemia)
Intracranial hemorrhage
Conjunctival hemorrhage
🔹 Immunologic phenomena:Osler’s nodes (painful, on fingers/toes)
Roth spots (retinal hemorrhages with pale centers)
Glomerulonephritis
Rheumatoid factor
🔹 Microbiologic evidence (but doesn’t meet major criteria)
Definite IE
2 Major OR
- 1 Major + 3 Minor OR
- 5 Minor
possible IE
- 1 Major + 1 Minor OR
- 3 Minor
Rejected IE
- Clear alternative diagnosis
- Symptoms resolve in ≤4 days of antibiotics
- No pathological evidence
infective endocarditis signs
-if you press of osler’s node it is painful “ouch ouch osler”
-splinter hemorrhage can be seen in pts who are carpenters so ask about occupation
Mural Thrombi
thrombi that attach to the wall of a blood vessel and cardiac chamber (ventricle) due to blood stagnation
Forms in atrial or ventricular chamber in 40% of patients with rheumatic valvular disease.
mitral stenosis creates turbulent blood flow and stasis, increasing the risk of mural thrombus formation in the left atrium.
Adhesive Pericarditis
Fibrinous pericarditis occurs in conditions like rheumatic fever, myocardial infarction, uremia, or infections, where fibrin deposits form on the pericardial surface, leading to inflammation.
If the acute inflammation does not resolve completely, it organizes into fibrous tissue, leading to adhesions between the visceral and parietal pericardium.
This results in adhesive pericarditis, where the pericardial layers fuse together, causing restricted cardiac movement.
Congestive Heart Failure
Associated with rheumatic disease of both mitral and aortic valves.
-blood stagnation in ventricles and part of muscle not working due to MacCallom plaque leading to congestive HF