Master Budgeting M5
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what is a budget?
a detailed plan for the future that is expressed in formal quantitative terms
what functions do budgets support?
planning and control
what is planning?
developing goals and preparing strategies to achieve them
what is controlling?
gathering feedback to ensure the plan is being properly executed and modified as circumstances change
why do orgs make budgets from a planning standpoint?
to encourage mgmt to think about and plan for the future
to communicate financial goals throughout the org
to allocate resources effectively
to coordiante the plans of departmental mngrs
to uncover potential bottlenecks before they occur
why do orgs make budgets from a controlling standpoint?
to improve efficiency and effectiveness of operations
to evaluate and reward employees
what is a self-imposed/participative budget?
a budget prepared with the full cooperation and participation of mngrs at all levels
what happens in a top-down budgeting approach?
top mngrs issue profit target then lower level managers are supposed to prepare budgets that will meet those guys
do lower-level managers like the top-down approach?
no because it can be demoralizing since top mngrs might have unrealistically low/high expectations
why is it beneficial to use the participative budgeting approach?
it shows respect to the opinions of lower level managers
it leverages their knowledge to provide more accurate estimates
it increases motivation to reach goals that are set by themselves
it empowers them to take control of the budget and be accountable for deviation from it
what are the limitations of participative budgets?
lower level mangers might not posess the strategic vision that top mngrs have
if the budget is used to reqard employees lower level mngrs might create too much budgetary slack to ensure that results exceed the plan
what is the first step in the budgeting process?
creating the sales budget
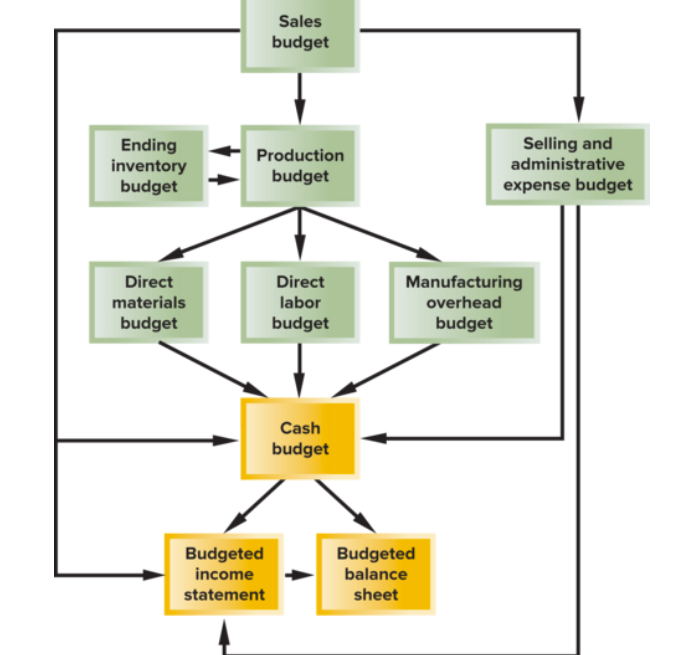
what is a master budget?
a number of separate but interdependent budgets that formally lay out the company’s sales, prodcution, and financial goals
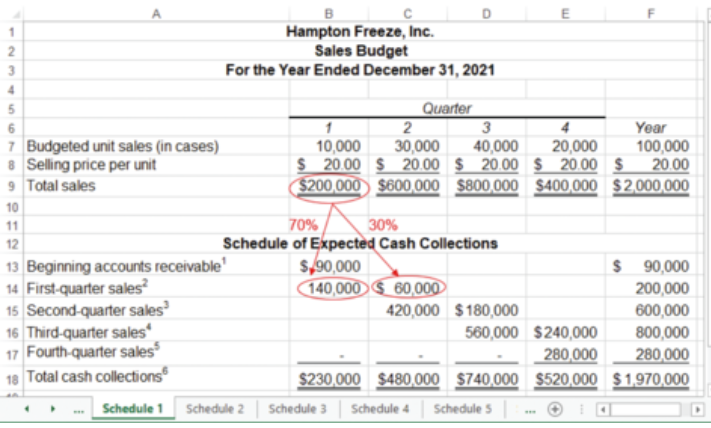
what is the sales budget?
a detailed schedule showing the expected sales for the budget period
Y or N? If the sales budget is inacurrate, the rest of the master budget will be inacurrate.
Y
information from which budgets influence the cash budget?
sales, selling and admin expense, and manufacturing cost budgets
what is the cash budget?
a detailed plan showing how cash resources will be acquired and used
what are the estimates and assumptions for the sales budget?
What are the budgeted unit sales?
What is the budgeted selling price per unit?
What percentage of accounts receivable will be collected in the current and subsequent periods?
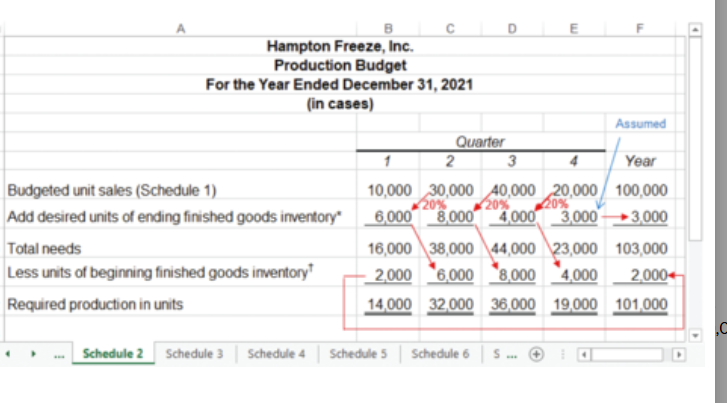
what are the estimates and assumptions for the production budget?
What percentage of next period’s unit sales needs to be maintained in ending finished goods inventory?
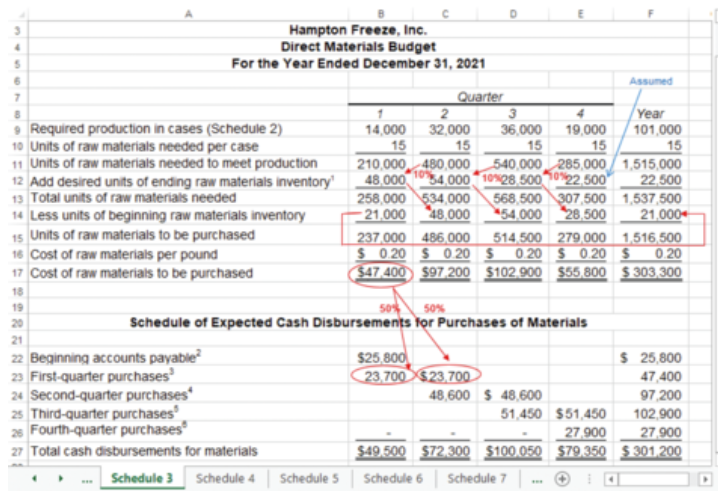
what are the estimates and assumptions for the direct materials budget?
How many units of raw material are needed to make one unit of finished goods? What is the budgeted cost for one unit of raw material?
What percentage of next period’s production needs should be maintained in ending raw materials inventory?
What percentage of raw material purchases will be paid in the current and subsequent periods?
what are the estimates and assumptions for the direct labor budget?
How many direct labor-hours are required per unit of finished goods? What is the budgeted direct labor wage rate per hour?
what are the estimates and assumptions for the manufacturing overhead budget?
What is the budgeted variable overhead cost per unit of the allocation base
What is the total budgeted fixed overhead cost per period?
What is the budgeted depreciation expense on factory assets per period?
what are the estimates and assumptions for the selling/admin expense budget?
What is the budgeted variable selling and administrative expense per unit sold?
What is the total budgeted fixed selling and administrative expense per period?
What is the budgeted depreciation expense on non-factory assets per period?
what are the estimates and assumptions for the cash budget?
What is the budgeted minimum cash balance?
What are our estimated expenditures for noncurrent asset purchases and dividends?
What is the estimated interest rate on borrowed funds?
what is the general order of preparing a master budget?
A sales budget, including a schedule of expected cash collections.
A production budget (a merchandise purchases budget would be used in a merchandising company).
A direct materials budget, including a schedule of expected cash disbursements for purchases of materials.
A direct labor budget.
A manufacturing overhead budget.
An ending finished goods inventory budget.
A selling and administrative expense budget.
A cash budget.
A budgeted income statement.
A budgeted balance sheet.
budgeting assumption example
n/a
budgeting assumption example: sales
n/a
Y or N? The sales budget is prepared after the production budget.
N
what is the production budget?
a budget that lists the number of units that must be produced to satisfy sales needs and result in the desired ending finished goods inventory

why are inventories carefully planned?
insufficient inventories can lead to lost sales and high-cost production efforts
excessive invetories tie up funds and create storage problems
budgeting example: production budget
n/a
What type of budgets do merchandising companies produce?
merchandise purchases budget
What type of budgets do manufacturing companies produce?
production budget
what goes on the merchandise purchases budget?
budgeted cogs (budgeted unit sales) + desired ending merch inventory, total needs, - bg. merch inventory, and required purchases
what is the direct materials budget?
details the raw materials that must be purchases to fulfill the production budget and help make adequate inventories
direct materials budget example
n/a
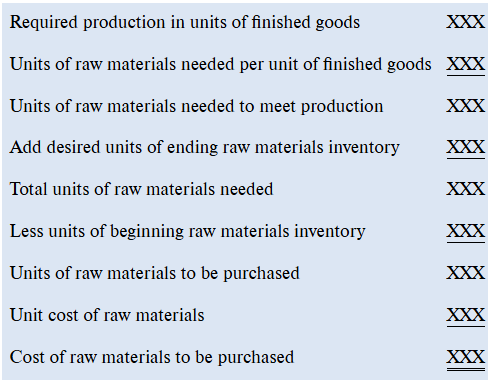
what is the direct labor budget?
a budget to show the direct labor hours needed to satisfy the production budget
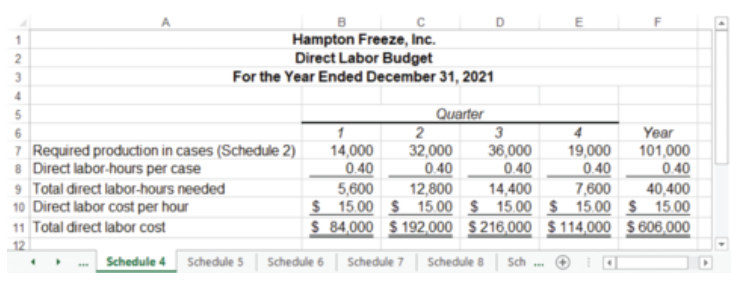
direct labor budget example
n/a
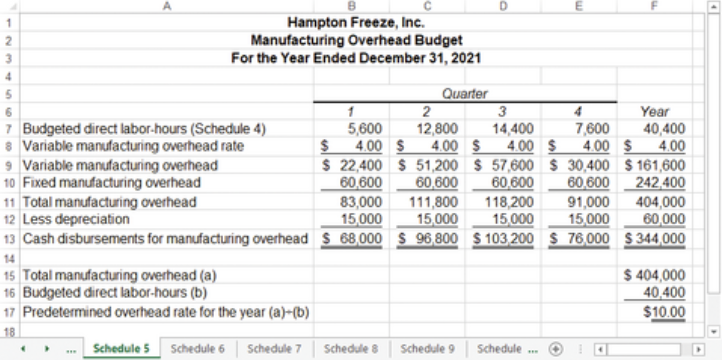
what is the manufacturing overhead budget?
a budget that lists all the costs of production aside from direct materials/labor
manufacturing overhead budget example
n/a
what is the ending finished goods inventory budget?
the budget that details the cost of unsold units
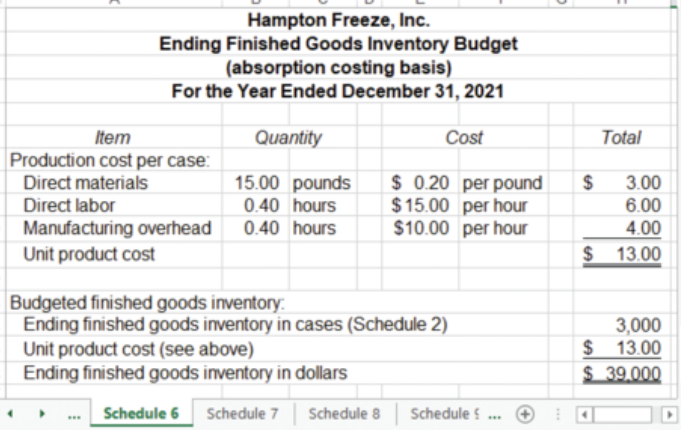
ending finished goods inventory budget
n/a
what is the selling and administrative expense budget?
a budget that lists the budgeted expenses for areas other than manufacturing
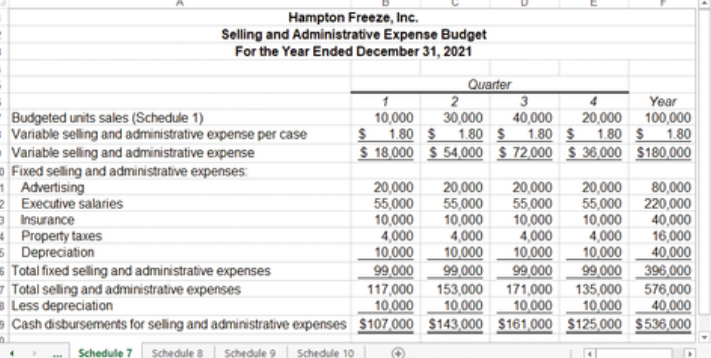
selling and administrative expense budget example
what is the cash budget?
a budget that details the cash transactions of the org
what are the sections of the cash budget?
cash receipts
cash disbursements
cash excess/deficiency
financing section
explain the receipts section of the cash budget
expected cash inflows (usually from sales) unless they’re from financing for a period
explain the disbursements section of the cash budget
all cash payments that are planned for a period
what are examples of items that go in the disbursements section of a cash budget?
includes raw materials purchases, direct labor payments, manu overhead costs, etc…
how to calculate cash excess/deficiency
beg cash balance + receipts = total cash available (tca) - cash disbursements = tca/disbursements
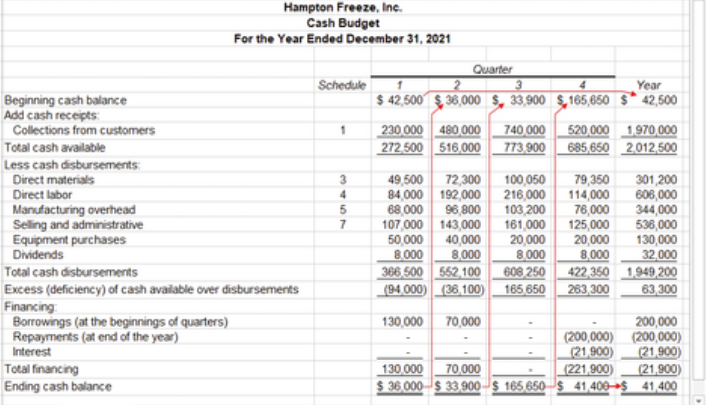
cash budget example
n/a

how to calculate the min required borrowings at the beg of the 1st quarter
n/a
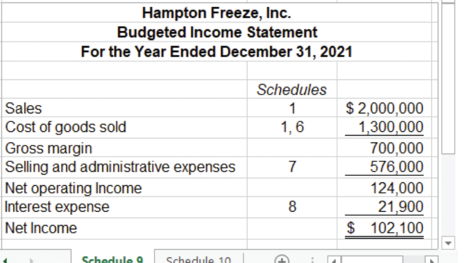
budgeted income statement example
n/a
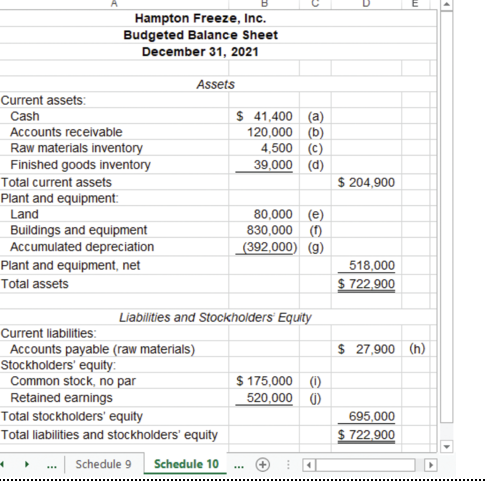
budgeted balance sheet example
n/a