chemistry - FIRE :)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what are the necessary ingredients for fire
heat, oxygen GAS (oxygen 2), and fuel
what is fire made of
not a stuff but a chemical reaction!
what causes different colors in fire
electrons jump energy levels and emit light depending on how far they fall, temperature of the fire
why does water put out fires
water absorbs heat which blocks the fuel from getting the oxygen it needs to sustain itself
can smoke burn
yes weirdly
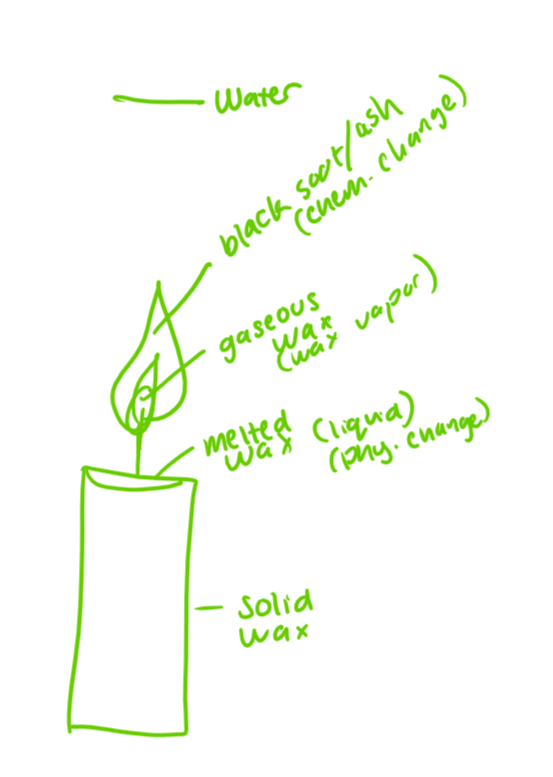
describe the changes wax undergoes as a candle burns
physically, wax melts then boils
chemically, wax burns and interacts with oxygen
how is burning something different from heating something?
burning something: object uses its own energy to produce heat
heating something: object gets energy from outside source
can all substances change into solid, liquid, and gas form
yes…ish. some have to break down into smaller particles before they change phase
hotter means particles are moving…
faster
as substances change solid to gas, density usually…
decreases. an exception is H20
intermolecular force
force that draws particles towards one another
conservation of motion
the idea that particles transfer motion to each other on collisions
what types of motion does each state have?
solid- vibrational
liquid- rotational, vibrational
gas- translational, rotational, vibrational
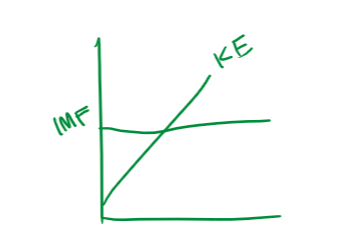
explain the relationship between kinetic energy and intermolecular forces
kinetic energy increases from solids to gasses. as this happens, intermolecular forces become less effective at holding the particles together
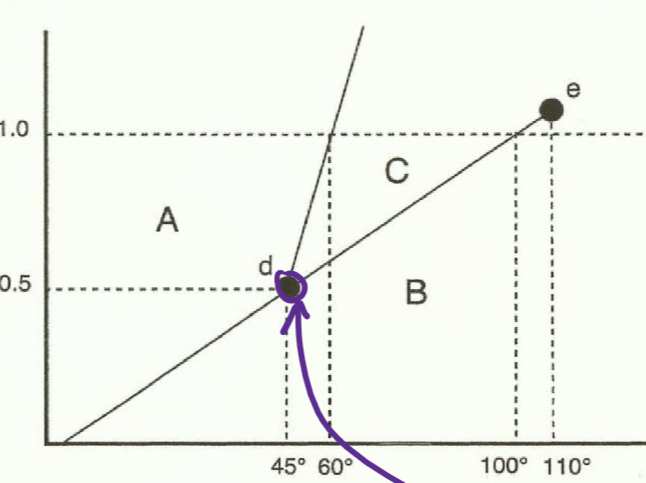
phase diagrams
A-solid
B-gas
C-liquid
D-triple point, where your particles start acting a lil funky and do everything at once (multitasking ally)
E-critical point, after which you get supercritical fluid
3 parts to kinetic molecular theory
all matter is made of particles, so everything can be described by particle motion
particles are always moving (0 Kelvin is called absolute zero but we don't know if it exists)
particle collisions are perfectly elastic, no energy is lost
temperature vs heat
temperature is the average KE of particles in a system
heat is the amt of energy transferred from system to surroundings due to temperature difference
all abt celsius (not the drink sadly)
celsius got water and said “hey, my water boiled. im calling this 100 degrees celcius.” then his water froze and he said “this point is 0 degrees celcius” and then he divided up everything between into hundredths
we use it for measuring
C=K-273.15
kelvin stuff
kelvin literally said “alr this is an absolute scale so we are making it celsius without negatives”
we use it for calculating
K=C+273.15
what happens to things as you heat them
they expand slightly!
why don’t you take temperature with your own hand
you only feel temperature when there is a heat exchange queen
specific heat capacity
amt of energy to heat 1 g of something by 1 degree C
c=J/g degrees C
calculate heat equation
Q=m*c*change in temp
temperature during a phase change
temp cannot change until a phase change is complete (see heating curves)
heat increases phase energy instead of kinetic energy, changes type of motion instead of increasing it
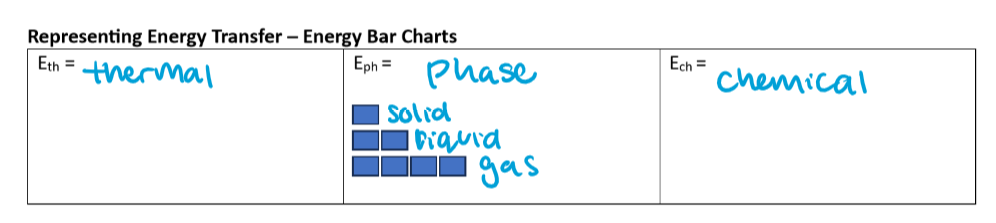
energy bar charts
j look at the photo
octet rule
elements/compounds tend to react in ways that lead to 8 valence electrons
closer to a full shell, more reactive
full shell, inert
describe what mendeleev did
he sorted the periodic table to predict missing elements!
he helped us see elements should be listed on atomic number
new period (or row)→ new energy level
periodic table
know how many valence electrons each column has
know what elements are metals, metalloids, and nonmetals
know the names for some of the columns
the rows are called periods, elements in the same period are not that similar
the columns are groups or families, they are similar
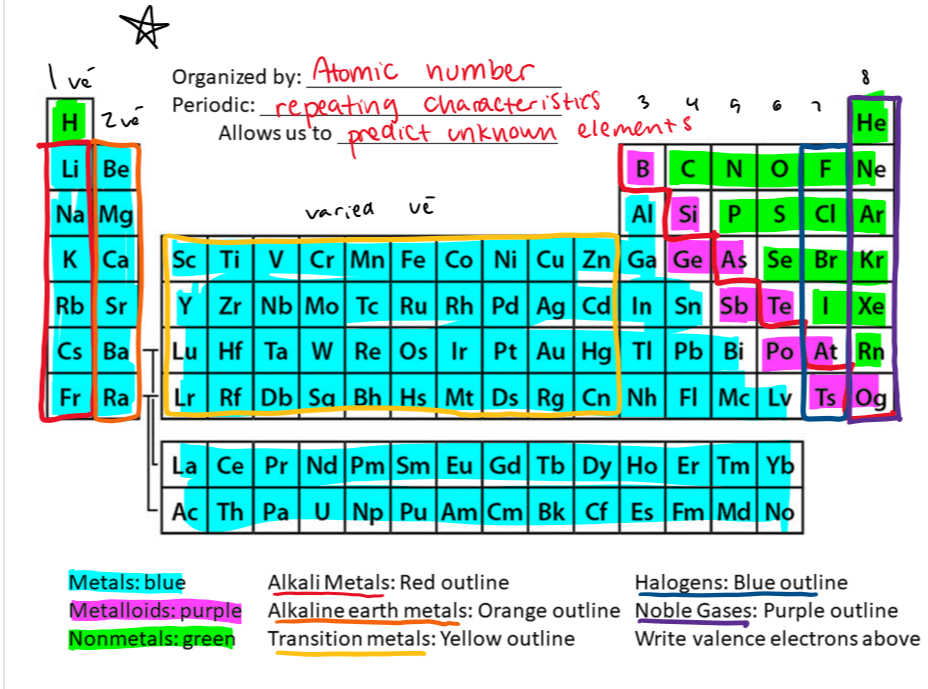
metals
good heat and electricity conductors
shiny
ductile (stretched thin)
malleable (pounded thinly)
nonmetals
the opposite of metals
bad conductors
brittle and break easily
dull just like making these flashcards tbh
metalloids
mix of both metals and nonmetals
can be shiny or dull
goodish conductors but not great
sorta ductile and malleable
basically manchild of metals and nonmetals
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At, Ts, Og
alkali metals (column 1)
very reactive because they only need to lose 1 valence electron to explode
alkaline earth metals (column 2)
reactive but not as reactive
transition metals
the metals that vary in valence electrons
halogens (column 17)
very reactive because they only need one electron for a full shell
noble gases (column 8)
inert because they have a full shell
when you burn a candle where does all the mass go lol
it escapes into the surroundings, wax undergoes chem reaction and turns into water+CO2. mass is not destroyed
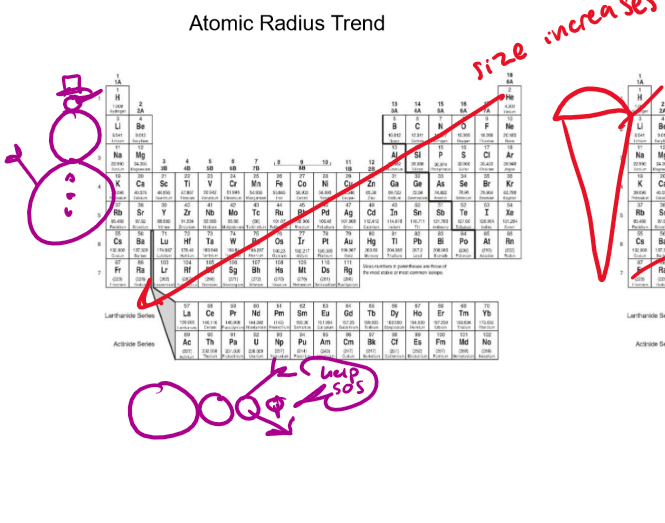
atomic radius trend
He has the smallest radius, Fr has the largest
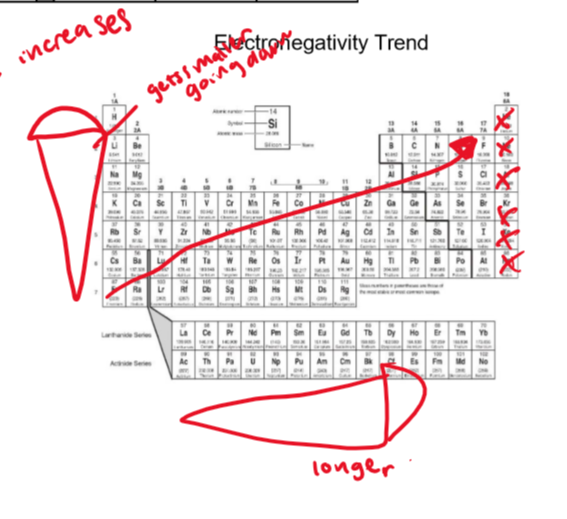
electronegativity trend
Fr has the weakest electronegativity, F has the strongest
noble gases are excluded
coulombs law! YOU NEED TO KNOW THIS PLS DON’T FAIL
like charges repel opposites attract
charge with higher magnitude has more magnetic force
weaker force when farther apart
as you go down the periodic table, atomic radius increases because new energy levels are necessarily bigger
greater distance of energy levels means that electronegativity will go down acc to #3
atomic radius decreases as you go across the periodic table because increased protons and electrons lead to greater force (because there is stronger attraction inside) acc to #2
smaller distance means electronegativity will go higher for the same reasons
energy
ability to cause change
energy can’t be destroted/created but it can be transferred or transformed
potential energy (name the four types)
gravitational - gravity
elastic - stored in an object under strain
nuclear- stored in an atom’s nucleus
chemical - stored in attractive force (bonds) bt atoms
kinetic energy (name 5 types)
radiant- light
sound - vibrations in matter
electrical-electrons motion
thermal-vibration of particles
mechanical-moving
t-e-r-m-s (lil acronym for u)
exothermic reaction
energy is lost
condensation, freezing, deposition
less energy going down a phase
FIRE IS EXOTHERMIC
endothermic energy
energy is gained
boiling, evaporation, melting, sublimation
how does fire grow?
fire is exothermic so it releases enough heat to set other things on fire
where does the energy come from to make fire hot?
As new bonds form, chemical (potential) energy is converted into thermal (kinetic) energy
coulombs law again
1. Opposite charges attract and like charges repel.
2. Larger chargers have a greater repulsive/attractive force while smaller charges are weaker.
3. When charges are close together, their repulsive attractive force is stronger and when they are far apart it grows weaker.
heat of fusion
the energy needed for one gram of a solid to melt or one gram of a liquid to freeze
heat of vaporization
the energy needed for one gram of a liquid to vaporize (boil) without a change in pressure
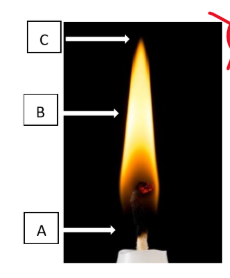
what happens at each point of this image
A-wax melts and vaporizes
B-wax collides with oxygen and forms new molecules through breaking apart
C-CO2 and vapor float away and sometimes smoke or ash is reaction does not finish
combustion
another term for burning, through combustion in fire you get water and carbon dioxide
where is the energy stored in an unlit candle
chemical potential energy is stored in the bonds (attractive forces) between atoms