Biochemistry Quiz 2 and Exam 2 supplements
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:03 AM on 3/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
![Platelet-activating factor \[PAF\] plays a role in allergic and inflammatory responses, as well as toxic shock syndrome. The structure of PAF is shown below__.__ __**How does it match/differ f**__**rom the structure of the commonly referred phospholipids**?](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/32ace90239e540f9a30404844fb00d65.jpeg)
Platelet-activating factor \[PAF\] plays a role in allergic and inflammatory responses, as well as toxic shock syndrome. The structure of PAF is shown below__.__ __**How does it match/differ f**__**rom the structure of the commonly referred phospholipids**?
**The C16 alkyl chain is attached by and ether linkage. The C-2 carbon atom of**
**glycerol has only an acetyl group attached by and ether linkage of fatty acids, as**
**in the case with most lipids.**
**(2/4) points**
**PAF has a long chain alkyl group which merges with glycerol back bonne in ether**
**linkage at position one and at acetyl group at a position 2**
**PAF represents a family of phospholipids and that is because the alkyl group is in**
**glycerol has only an acetyl group attached by and ether linkage of fatty acids, as**
**in the case with most lipids.**
**(2/4) points**
**PAF has a long chain alkyl group which merges with glycerol back bonne in ether**
**linkage at position one and at acetyl group at a position 2**
**PAF represents a family of phospholipids and that is because the alkyl group is in**
2
New cards
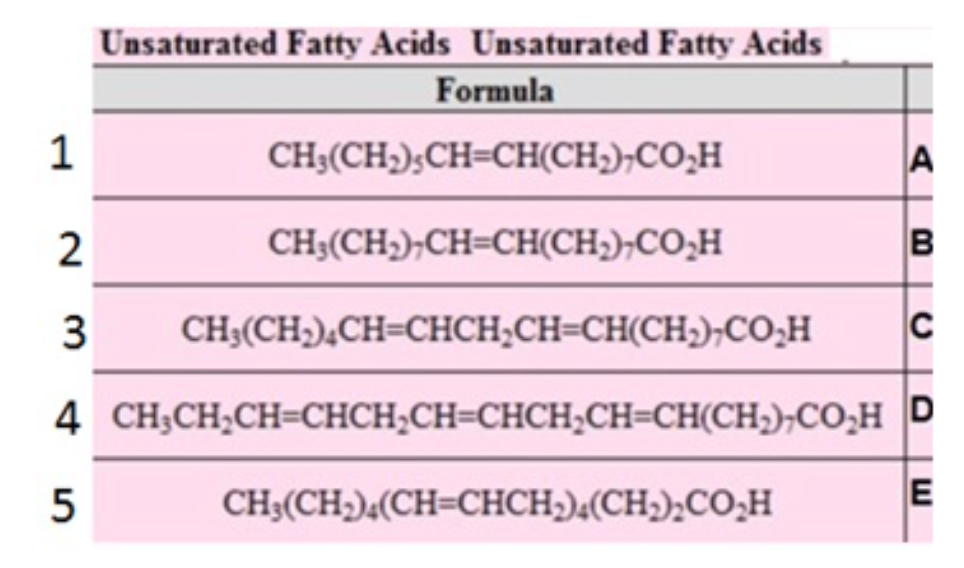
Name these Fatty acids and arrange their melting temp in increasing order ( lowest to highest)
1. palmitoleic acid
2. oleic acid
3. linoleic acid
4. linolenic acid
5. arachidonic acid
3
New cards
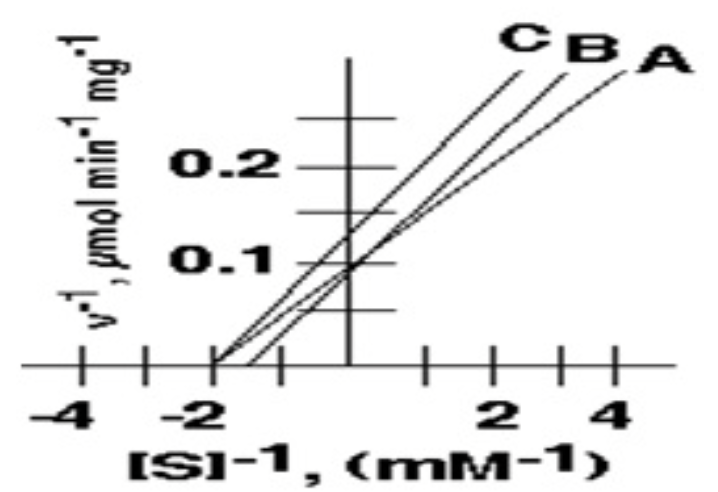
1. The value of KM for the enzyme depicted by curve **A i**s:
* 5 mM
* 1 mM
* 0.5 mM
* 0.5 μmol min-1 mg-1
* 10 μmol min-1 mg-1
.5mM
4
New cards
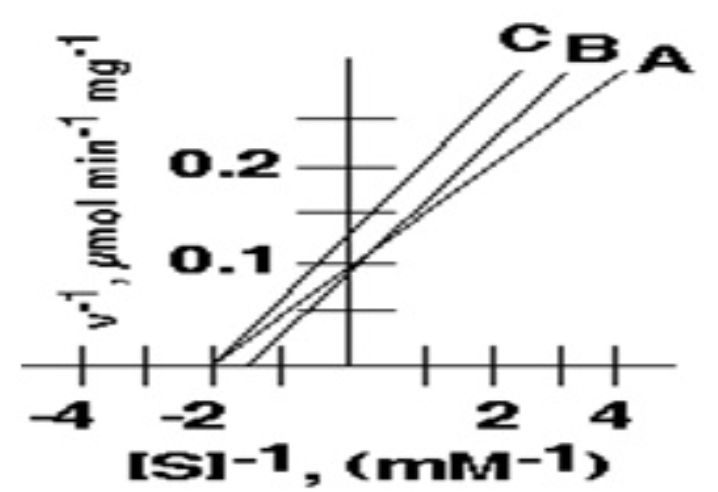
2. The value of Vmax for enzyme depicted by curve **A** is:
* 1 μmol min-1 mg-1
* 1 μmol min-1 mg-1
* 10 μmol min-1 mg-1
* 5 μM
* 2mM
* 10 μmol min-1 mg-1
5
New cards
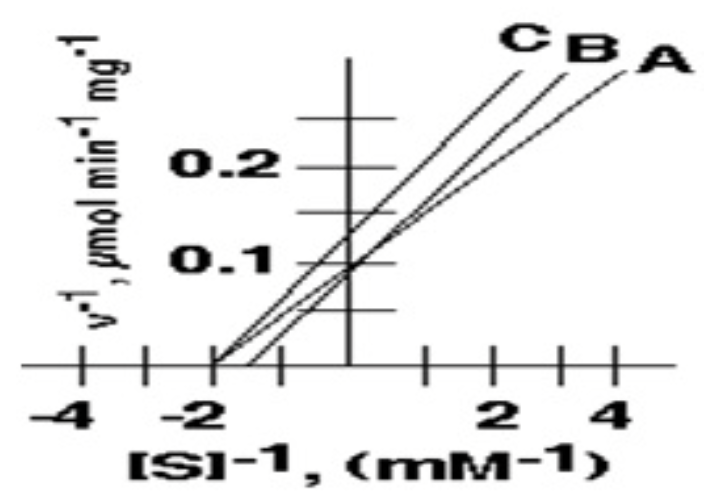
3. Curve **B** depicts the effect of an inhibitor on the system described by curve **A**. This inhibitor:
* Is a competitive inhibitor
* Is a non competitive inhibitor
* Increases the Vmax
* Decreases the KM
* None
Is a competitive inhibitor
6
New cards
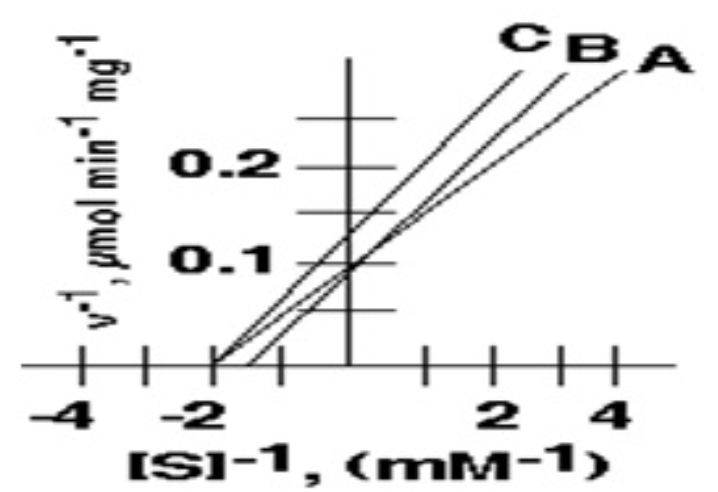
4. Curve **C** depicts the effect of a different inhibitor of the system described by curve **A**. This second inhibitor :
* Is a competitive inhibitor
* Is a non-competitive inhibitor
* Increases the Vmax
* Decreases the KM
* None
non competitive inhibitor
7
New cards
A recently diagnosed “hypersensitive patient” has been prescribed an ACE inhibitor \[Angiotensin Concerting Enzyme inhibitor\] which is known to act by __lowering Vmax without altering Km__, what is the possible mechanism of inhibition of this drug?
non-competitive inhibition
8
New cards
Consider a reaction catalyzed by enzyme A with a Km value of **5 x10-6 M** and Vmax of **20 mmol. min**. At a concentration of **5 x10-6M** substrate, the rate of the reaction will be:
10mM/sec
9
New cards
The structure of an unsaturated fatty acid:
A. is one in which all the carbons are saturated with hydrogen atoms
B. contains three fatty acids and one glycerol
C. contains double bonds between carbons
D. is made with interconnected rings of carbon atoms
A. is one in which all the carbons are saturated with hydrogen atoms
B. contains three fatty acids and one glycerol
C. contains double bonds between carbons
D. is made with interconnected rings of carbon atoms
C. contains double bonds between carbons
10
New cards
Linoleic acid and linolenic acid are known as __________ because the body cannot synthesize them.
\
A. eicosanoids
B. trans-unsaturated fatty acids
C. cis-unsaturated fatty acids
D. essential fatty acids
\
A. eicosanoids
B. trans-unsaturated fatty acids
C. cis-unsaturated fatty acids
D. essential fatty acids
D. essential fatty acids
11
New cards
Which blood lipoproteins (increased levels) appear to increase the risk of plaque formation the most?
A. LDL
B. HDL
C. VLDL
D. chylomicrons
A. LDL
B. HDL
C. VLDL
D. chylomicrons
A. LDL
12
New cards
True or false: One method of determining if a fat is saturated or unsaturated is to observe if the fat is solid or liquid at room temperature.
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
13
New cards
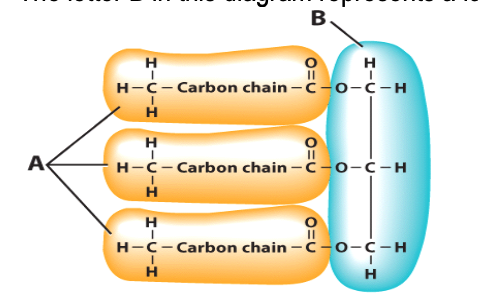
True or false: The letter B in this diagram represents a fatty acid molecule.
\
True
False
\
What does A represent?
\
True
False
\
What does A represent?
False
fatty acid molecules
fatty acid molecules
14
New cards
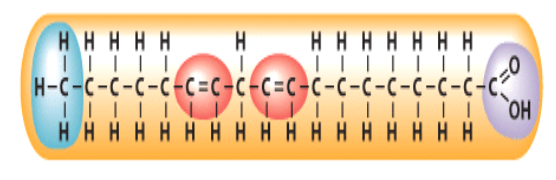
Which of the following describes the fatty acid depicted in this \n diagram?
\
saturated
trans fat
monosaturated
polyunsaturated
\
saturated
trans fat
monosaturated
polyunsaturated
polyunsaturated
15
New cards
The process whereby hydrogen atoms are added to the carbon-carbon double bonds making them more saturated is called?
hydrogenation
16
New cards
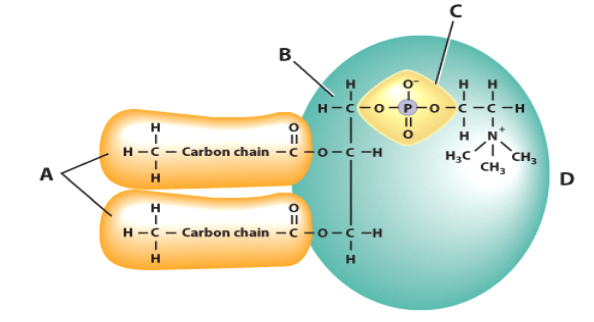
Identify the molecule in this diagram of a lipid labeled C
phosphate group
17
New cards
Good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include all of the following except
\
salmon
walnuts
flaxseeds
tilapia
\
salmon
walnuts
flaxseeds
tilapia
tilapia
18
New cards
Which of the following is a phospholipid?
\
Sphingosine
glycogen
oleic acid
cardiolipin
\
Sphingosine
glycogen
oleic acid
cardiolipin
cardiolipin
19
New cards
The maximum number of doubles in an unsaturated fatty acid is?
4
20
New cards
Example of monounsaturated fatty acid:
\
oleic acid
palmitic acid
linoleic acid
arachidic acid
\
the number of carbons and double bonds? draw structure
\
oleic acid
palmitic acid
linoleic acid
arachidic acid
\
the number of carbons and double bonds? draw structure
oleic acid 18C, double bond on carbon 9
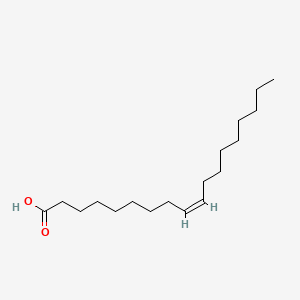
21
New cards
Which of the following is a glycerol-based phospholipid? Draw its structure and list carbons/double bonds.
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
cardiolipin
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
cardiolipin
cardiolipin
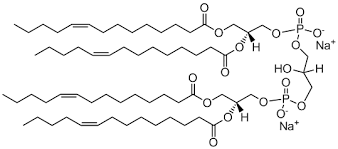
22
New cards
Which of the following is a glycolipid? Draw its structure and list carbons/double bonds.
\
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
Arachidonate
\
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
Arachidonate
arachidonate??
23
New cards
Which is the backbone of a glycolipid? Draw its structure and list carbons/double bonds.
\
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
Arachidonate
\
Sphingomyelin
Cerebroside
Sphingosine
Arachidonate
Sphingosine, 18C, DB on 5
\
\
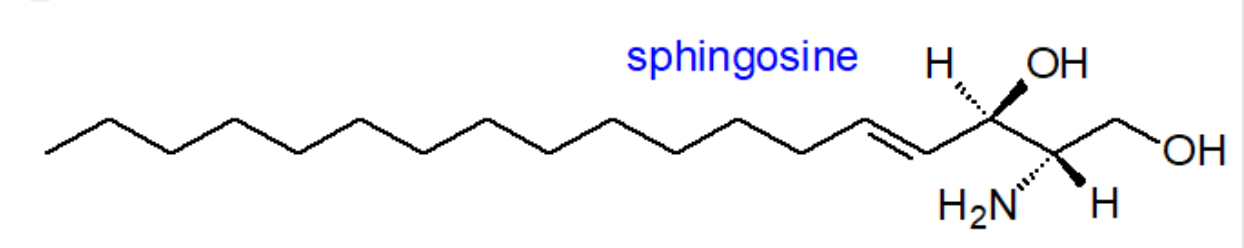
24
New cards
QUIZ 2 BELOW
25
New cards
what is the slope (m) of a double rciprocal plot?
km/Vmax
26
New cards
Enzymes, serving as catalysts require small modules for a catalytic activity known as cofactors. An enzyme with a cofactor is referred to as:
Apoenzyme
Holoenzyme
Abzyme
Coenzyme
Ribozyme
Apoenzyme
Holoenzyme
Abzyme
Coenzyme
Ribozyme
**Holoenzyme**
27
New cards
Enzymes are quite specific. Trypsin is partially specific in its catalysis, What terminus of what amino acids does it cleave at?
C terminus of Arginine R or Lysine K
28
New cards
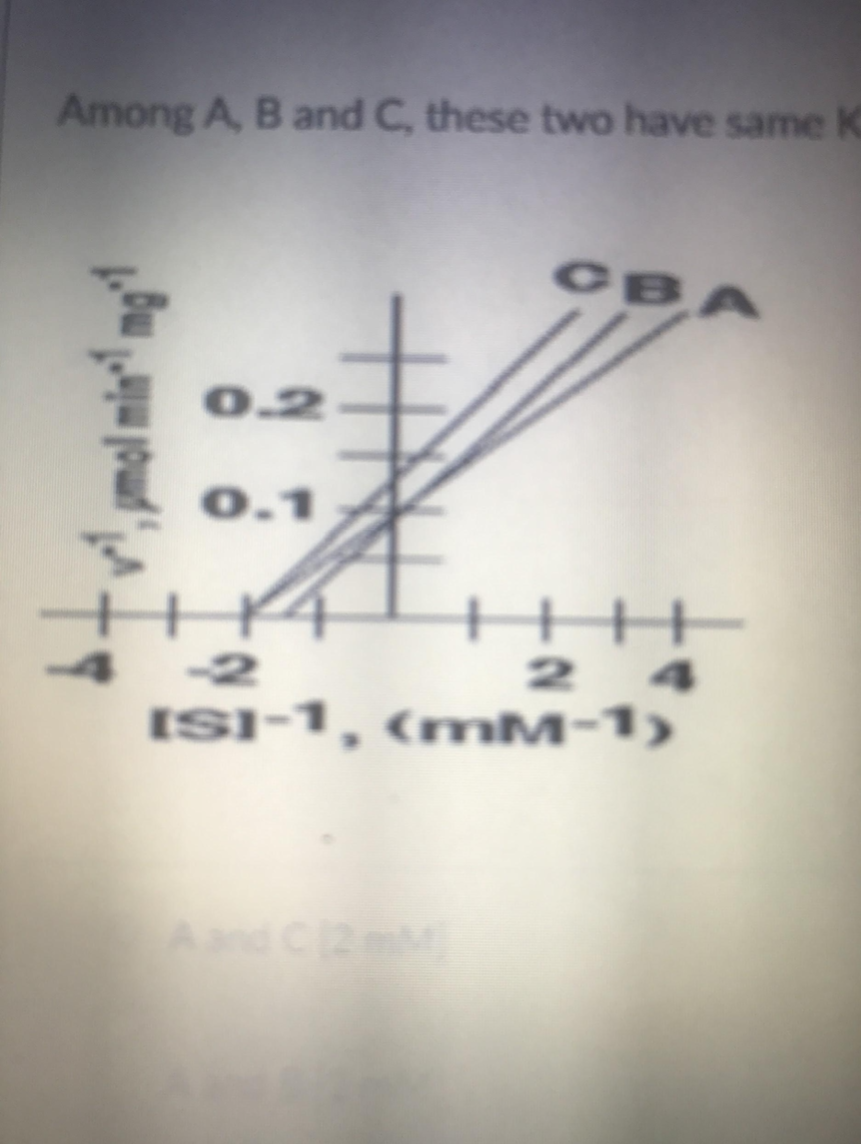
Among A,B, and C, these two have the same Km value
\
\
A and C (0.5mM)
29
New cards
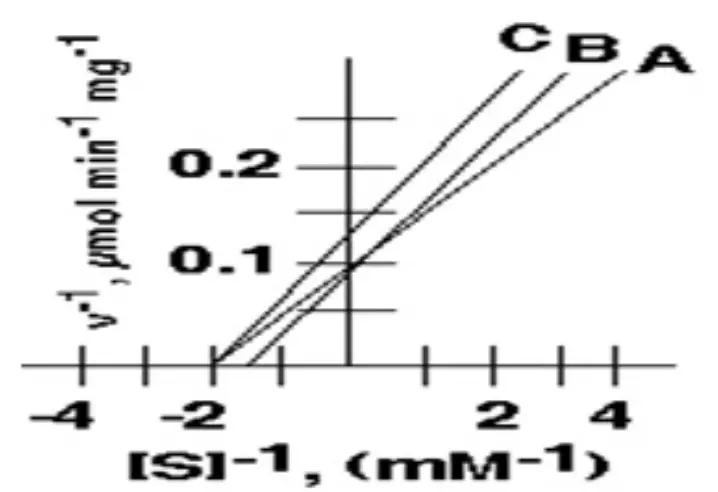
In the following inhibition plot, these two could represent the "Uncompetitive inhibition "
\
all of them
B and C
A and B
none of them represent it
A and C
\
all of them
B and C
A and B
none of them represent it
A and C
B and C
30
New cards
As per Michalis Menten's relationship, what will be the rate of catalysis, if the \[S\] and K M are the same and V max is 20 nmol/sec?
10
Km=S means that Vmax/2 = Vo
Km=S means that Vmax/2 = Vo
31
New cards
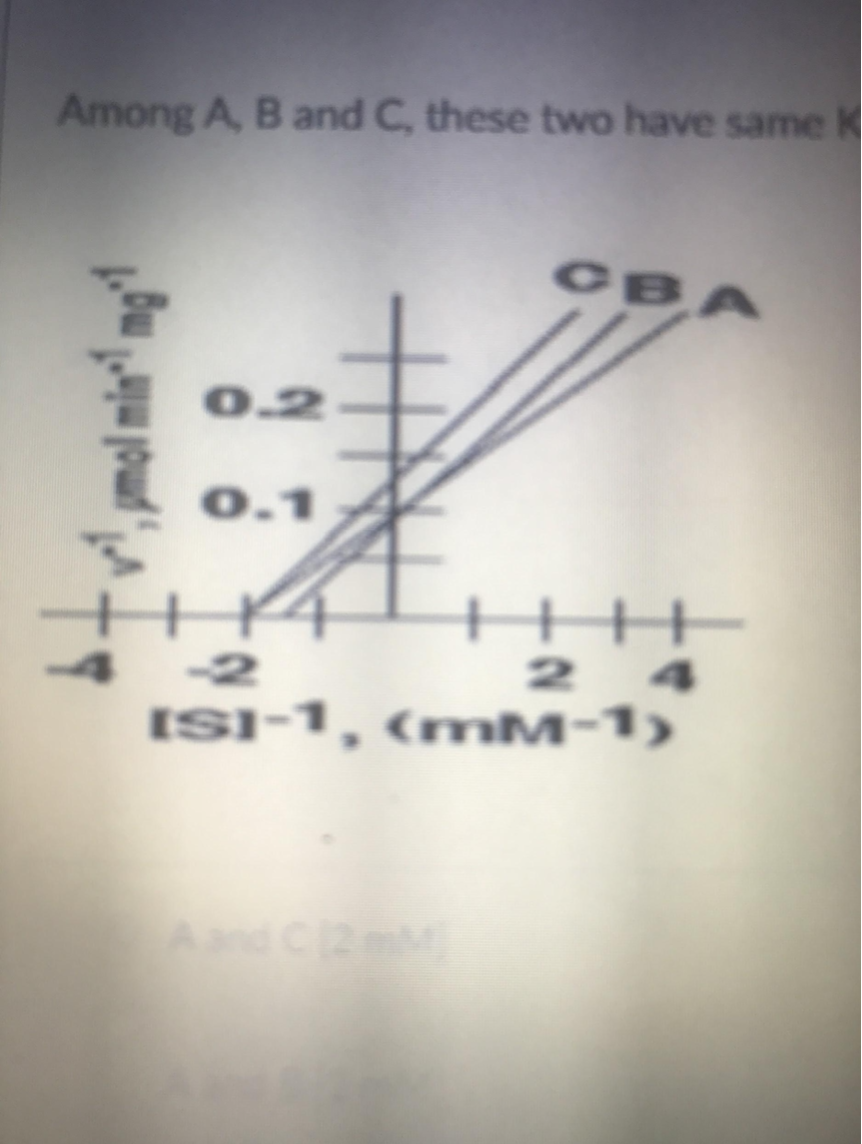
what is the Vmax of inhibitor A in micromol/min/mg?
10
32
New cards
As per Michalis Menten relationship, what will be the rate of catalysis, if the \[S\] = 1mM and K M 0.5 mM with value V max is 1.5 mM/sec
\
* 3.0 mM/sec
* 1.0mM/sec
* Can not compute from given data sets
* 1.0 mM/sec
* 2.5 mM/sec
\
* 3.0 mM/sec
* 1.0mM/sec
* Can not compute from given data sets
* 1.0 mM/sec
* 2.5 mM/sec
1mM/sec
33
New cards
in Lineweaverplot (1/S X-axis) and 1/V o \[as Y-a axis), the linear equation is: Y = 0.25X + 0.02 The numerical value of K M will be \[ Hint the Vmax=50\]
\
* 0.02
* can not compute from a given data set
* 0.25
* 12.5
* 0.25
\
* 0.02
* can not compute from a given data set
* 0.25
* 12.5
* 0.25
12\.5
34
New cards
Enzymes are quite specific. Thrombin is highly specific for its catalysis, how many location will it cleave the given peptide with a sequence of: Gly-Ala- Lys-Glu- Arg -Lys-Val -Ser-Arg-Val-Gly
NONE
35
New cards
What does thrombin cut?
Arginine-Glycine bonds
36
New cards
this enzyme cuts any peptide bond
papain
37
New cards
True or False: The free energy changes provides information about the spontaneity but not the rate of reaction. A reaction can take place spontaneously only if delta G is negative reaction is exergonic ).
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
38
New cards

Among the following unsaturated fatty acids, this will have **higher** melting point compared to others
oleic acid , 2
39
New cards
Thiamine pyrophosphate TPP) serves as a coenzyme for the following enzyme.
\
Succinate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Glycogen phosphorylase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase
\
Succinate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Glycogen phosphorylase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
40
New cards
The physiological consequence of K M is linked to the sensitivity of certain group of people to the alcohol. Most people has two form of aldehyde dehydrogenase , the KM ----form less active in susceptible persons .
\
* high, mitochondrial
* low, mitochondrial
* low, cytoplasmic
\
* high, mitochondrial
* low, mitochondrial
* low, cytoplasmic
low, mitochondrial
41
New cards
True or false: According to chemical kinetics, **reactions that are directly proportional to the reactant concentration** are called **zero-order reactions**, with a typical rate constant unit of sec^ -1
False, this is a first order reaction
42
New cards
The active site of enzymes has some standard and specific features, which is NOT a common feature of the active site.
\
* usually water is present at active site
* usually involves multiple weaker interactions
* usually relatively smaller compared to total volume
* usually three-dimensional cleft
* usually water is excluded from active site
\
* usually water is present at active site
* usually involves multiple weaker interactions
* usually relatively smaller compared to total volume
* usually three-dimensional cleft
* usually water is excluded from active site
usually water is present at active site
43
New cards
what kind of enzyme inhibition does this depict?
\
\
Non competitive inhibition
44
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a common feature of membranes?
\
* are noncovalent assemblies
* are covalent assemblies
* are asymmetric
* electrically polarized
* are sheetlike structures
\
* are noncovalent assemblies
* are covalent assemblies
* are asymmetric
* electrically polarized
* are sheetlike structures
are covalent assemblies
45
New cards
Enzymes, serving as catalysts requires small modules for catalytic activity known as cofactors . Divalent cation Mg^ 2+ is NOT an essential cofactor for…
carbonic anhydrase
46
New cards
Among the following unsaturated fatty acids, this will have the lowest melting point compared to others
arachidonic acid \n 5 or E
47
New cards
Notes
\
48
New cards
what side of the fatty acid do you count carbons from?
\
\
carboxyl side
49
New cards
what is the carbon:double bond name for arachidonate?
20:4
50
New cards
what is the carbon: double bond name for arachidate (arachidic acid)?
20:0
51
New cards
Where is the omega carbon found?
the opposite end of the carboxyl side of the fatty acid
52
New cards
this ratio of body lipids are phospholipids
2/3
53
New cards
What fatty acid tail is always unsaturated?
first
54
New cards
What glycerol based phospholipid is PS?
Phosphatudlyserine
55
New cards
this phospholipid contains serine (NH3 and COO-)
Phosphatudlyserine
56
New cards
What glycerol based phospholipid is PC?
phosphatidylcholine
57
New cards
this phospholipid contains multiple methyl groups
phosphatidylcholine
58
New cards
What glycerol based phospholipid is PE?
phosphatidylethanolamine
59
New cards
this phospholipid contains NH3 and 2(CH2)
phosphatidylethanolamine
60
New cards
What glycerol based phospholipid is PI?
phosphatidylinositol
61
New cards
this phospholipid has a chair confirmation and a bunch of OH
phosphatidylinositol
62
New cards
What phospholipid is DPG?
diphosphatidylglycerol
63
New cards
what is another name for the phospholipid diphosphatidylglycerol
cardiolipin
64
New cards
this phospholipid is very large and has two symmetrical sides
diphosphatidylglycerol (cardiolipin)
65
New cards
True or false: Sphingosine is a backbone for both non-glycerol phospholipids and glycerol based phospholipids
True
66
New cards
What are three features of sphingosine
long chain
has amino group
has a double bond
has amino group
has a double bond
67
New cards
this phospholipid is phosphatidylcholine with a sphingosine replacing glycerol
sphingomyelin
68
New cards
this type of bond connects amino acids
amide bond
69
New cards
what is an example of a simple glycolipid?
cerebroside
70
New cards
what is an example of a complex glycolipid?
ganglioside
71
New cards
What is the chemical formula for cholesterol?
C27H45OH or C27H46O
72
New cards
True or false: Bacteria have cholesterol
False
73
New cards
How does degrees of unsaturation influence melting point and membrane fluidity?
higher degrees of unsaturation means increased membrane fluidity due to double bonds creating more space between lipids, and this lowers the melting point as well
74
New cards
which of the following structures is a 20:2 ^ (◬4,9) fatty acid ?
\
CH3(CH2)1OCH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH CH2 COOH
CHS(CH2)2CH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)9COOH
CH3(CH2)9CH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)2C COOH
CH3CH2CH CH=CH(CH2)3C=CH(CH2)10COOH
\
CH3(CH2)1OCH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH CH2 COOH
CHS(CH2)2CH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)9COOH
CH3(CH2)9CH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)2C COOH
CH3CH2CH CH=CH(CH2)3C=CH(CH2)10COOH
CH3(CH2)9CH=CH(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)2C COOH
75
New cards
**Which of the following is/ are represented by a phospholipid?**
**sphingosine**
**cardiolipin**
**Gasolio Side** \n **Cerebroside** \n **Cardiolipin and and sphingosine both**
**sphingosine**
**cardiolipin**
**Gasolio Side** \n **Cerebroside** \n **Cardiolipin and and sphingosine both**
cardiolipin
76
New cards
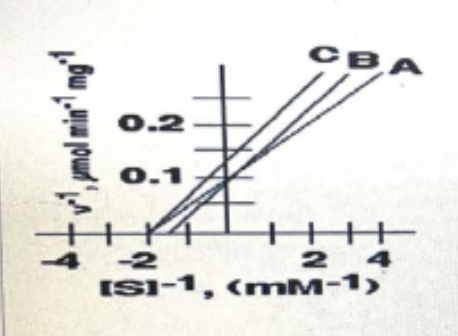
**In the following inhibition plot, these two could represent the competitive inhibition**
\
\
A and B
77
New cards
**Following glucose transporters GLUT-) family in mammalian tissues is present in ----- and pancreas in with very high Km of value of 2----**
\
**GLUT -2 in liver 1- 5mM**
**GLUT -4 in liver 15=20 mM**
**GLUT -2 in muscle 15-20mM**
**GLUT -2 in liver 15-20mM**
**GLUT -1 in muscle 15-20mM**
\
**GLUT -2 in liver 1- 5mM**
**GLUT -4 in liver 15=20 mM**
**GLUT -2 in muscle 15-20mM**
**GLUT -2 in liver 15-20mM**
**GLUT -1 in muscle 15-20mM**
**GLUT -2 in liver 15-20mM**
78
New cards
**which of the following is not true of glycolysis?**
\
The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled
The 10 reactions of glycolysis take place in the cytoplasm
Glycolysis is the set of reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate
The pathway does not require oxygen
The pathway oxidizes two moles of NADH and NAD+ for each mole of glucose
\
The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled
The 10 reactions of glycolysis take place in the cytoplasm
Glycolysis is the set of reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate
The pathway does not require oxygen
The pathway oxidizes two moles of NADH and NAD+ for each mole of glucose
The pathway oxidizes two moles of NADH and NAD+ for each mole of glucose
79
New cards
At psychological PH, the carboxyl group is readily ionized, rendering a negative charge onto fatty acids in bodily fluids
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
80
New cards
which of the epimer pair given below for monosaccharide is INCORRECT?
\
D- fructose and D-psicose
D-glucose and D-galactose
D-Ribose and D- Arabinose
D- Erythrose and D-threose
D-glucose and D-mannose
\
D- fructose and D-psicose
D-glucose and D-galactose
D-Ribose and D- Arabinose
D- Erythrose and D-threose
D-glucose and D-mannose
D-glucose and D-galactose
81
New cards
in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate into phosphoenol pyruvate \[PEP\] begins with the enzyme -----
\
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Enolase
Triose phosphate isomerase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
\
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase
Enolase
Triose phosphate isomerase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
\
Pyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase
82
New cards
Cardiolipin is a glycolipid that contains sphingosine"amino alcohol that contains a long unsaturated hydrocarbon chain as the backbone
\
**True**
**False**
\
**True**
**False**
False. cardiolipin is phospholpid not glycolipid
83
New cards
In Micheli- enzyme kinetics, when \[s\] is much higher compared to the reaction is represented as the FIRST order
\
**True**
**False**
\
**True**
**False**
False, this would be a zero order reaction
84
New cards
Certain enzyme requires metal ion small organic molecule etc such as cofactor. An Enzyme with a cofactor is known as APOENZYME
\
True
False
\
True
False
False
85
New cards
the stereoisomer of D- Erythrulose is represented by the following:
\
D-arabinose
D-Ribose
D- Threose
L- threose
L- Erythrulose
\
D-arabinose
D-Ribose
D- Threose
L- threose
L- Erythrulose
L- Erythrulose
86
New cards

CH3( C=0)COOH
2 molecules of CH3(C=0)CO0H
2 molecules of CH3(CH2)COOH CH3(CH0H) COOH CH30H(CH2)COOH
2 molecules of CH3(C=0)CO0H
2 molecules of CH3(CH2)COOH CH3(CH0H) COOH CH30H(CH2)COOH
2 molecules of CH3(C=0)CO0H
87
New cards
Error in glycosylation leads to pathological conditions . The N linked protein glycosylation begins in Endoplasmic reticulum and completes in golgi complex
\
**True**
**False**
\
**True**
**False**
True
88
New cards
Which of the following given statements is incorrect to glycolysis?
\
Unlike TCA, glycolysis does not produce any electron carrier
\
Glycolysis connected to TCA cycle using pyruvate
\
The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled
\
Glycolysis uses 2 ATP and produces 4 ATP per glucose
\
Glycolysis is the set of reactions that converts to glucose in pyruvate
\
Unlike TCA, glycolysis does not produce any electron carrier
\
Glycolysis connected to TCA cycle using pyruvate
\
The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled
\
Glycolysis uses 2 ATP and produces 4 ATP per glucose
\
Glycolysis is the set of reactions that converts to glucose in pyruvate
Unlike TCA, glycolysis does not produce any electron carrier
89
New cards
why does the glycolytic pathway continue in the direction of glucose catabolism?
There are three irreversible reactions that stop the process from recreating glucose
90
New cards
Amylose is a branched polysaccharide while amylopectin is an unbranched polysaccharide (plant starch)
\
True
False
\
True
False
False, amylopectin is highly branched
91
New cards
Glycolysis \[ a ten step metabolic pathway that oxidizes glucose to produce two pyruvate molecules \] produces very little ATP but produces several molecules of NADH and FADH 2
\
True
False
\
True
False
false
92
New cards
The unique enzymatic process/step in glycolysis involves removal of water
\
Aldolase
Pyruvate carboxylase
None of the listed options
Triose phosphate isomerase
Pyruvate kinase
\
Aldolase
Pyruvate carboxylase
None of the listed options
Triose phosphate isomerase
Pyruvate kinase
None of the listed options
93
New cards
In model bacteria, membrane fluidity is controlled by the fatty acid composition and cholesterol content
\
True
False
\
True
False
false
94
New cards
In gluconeogenesis , conversion of pyruvate into phosphoenol pyruvate |PEP| begins with formation of---------------
\
2-phosphoglycerate
3-phosphoglycerate
Acetyl CoA \n Lactase
Oxaloacetate
\
2-phosphoglycerate
3-phosphoglycerate
Acetyl CoA \n Lactase
Oxaloacetate
**Oxaloacetate**
95
New cards
Enzyme Aldolase catalyzes the readily reversible splitting of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-BP), into the products glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
96
New cards
The free energy changes provides information about the spontaneity but not the of reaction A reaction can take place spontaneously only if delta G is negative ( reaction is exergonic )
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
97
New cards
In------------- the amino group of the sphingosine backbone is linked to a fatty acid by an amide bond. The primary hydroxyl group estered to phosphorylcholine.
\
\
Sphingomyelin
98
New cards
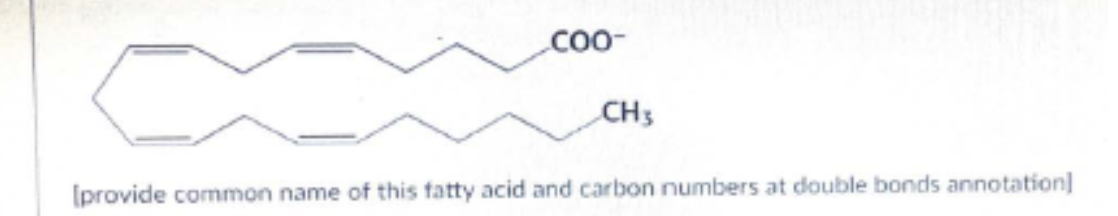
following fatty acid is characterized and identified commonly as a polyunsaturated fatty acid. Provide its common and positions of double bonds by numbering system
Arachidonic acid, 20:4 (5,8,11,14)
99
New cards
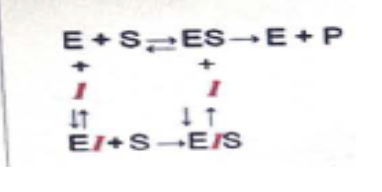
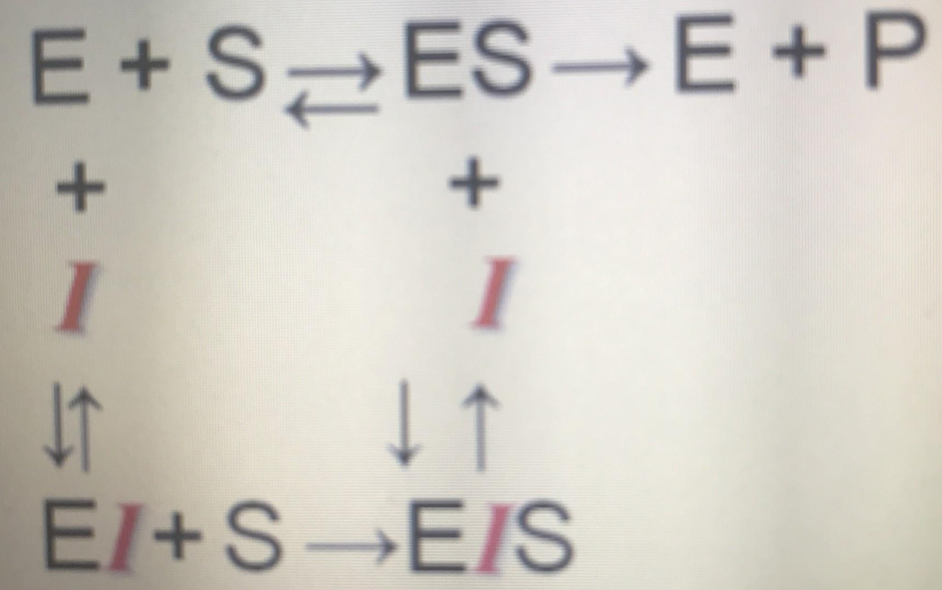
observe the given scheme and predict the mode of inhibition
\
\
noncompetitive inhibition
100
New cards
**Enzyme........... Traps glucose in the cell and begins glycolysis: Glucose enters cells through specific transport proteins GLUT) and has one principal fate: it is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate**
Hint: name the enzyme
Hint: name the enzyme
Hexokinase