Adaptive immune system
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
How is the helper T cell activated?
interacts with B cell when it sees its antigen
interacts with APC that displays an antigen
How does the helper T cell respond?
amplifies antibody production
activates CD8 T-cell to become cytotoxic and kill target cells
How is the cytotoxic T cell activated?
identifies MHC I with recognized antigen
How does the cytotoxic T cell respond?
inserts perforins
secretes granzymes into cell membrane to trigger apoptosis
How is the regulatory t cell activated?
dampens immune response to some antigens
How does the regulatory t cell respond?
prevents autoimmune activation
releases inhibitory cytokines to dampen immune response
How is a memory cell activated?
either a T or B cell previously saw an antigen or learned about it
How does memory cells respond?
Memory T - induces proliferation and activates T cells
Memory B - induces proliferation and activates B cells
How is the B cell activated?
recognizes antigen
How do B cells respond?
differentiates plasma cell to make antibodies
How are plasma cells activated?
after antigen recognition and B cell differentiation
How do plasma cells respond?
generates antibodies against specific antigens
How are the APCs (antigen-presenting cell) activated?
presents antigens to T cells so they can learn
How does the APCs respond?
educates T cell
What is an antigen?
protein fragment that is used to develop memory or recognized for an immune response
What is an antibody?
immunoglobin protein that recognizes a specific antigen
What is immunogenicity?
ability to induce immune cell proliferation
What is reactivity?
ability of lymphocytes and antibodies to recognize or attack an antigen
What is a MHC protein?
major histocompatibility protein
What is the MHC class I protein?
self cell that presents foreign antigen
What is the MHC class II protein?
APC showing a T-cell the antigen to learn about
How are antigens and antibodies are related to each other?
antibodies bind to antigens and that leads to them becoming a target for destruction via the complement pathway via phagocytosis
What is humoral immunity?
antibodies and B cells in the humors (fluid) in the body
does not attack cells but marks target
What is cellular immunity?
attacks foreign pathogens and cancer cells
complete antigens are
immunogenic and reactive
hapten antigens are
only reactive
What are the structures of antibodies?
2 heavy chains and 2 light chains
constant regions
variable regions
What are IgM antibodies responsible for?
primary response
What are IgM antibodies secreted by?
plasma cells
What are IgG antibodies responsible for?
secondary response and late primary
What is IgA responsible for?
stopping pathogens from attaching to epithelial surfaces
What is the IgD responsible for?
doesn’t circulates
educates B cells
increases antibody production
Where are IgD antibodies located?
on the B cell
What are IgE antibodies responsible for?
triggers histamine and leads to inflammation
What do IgE antibodies bind to?
mast cells or basophils
How do lymphocytes develop, mature, and activate?
red blood marrow
immunocompetence and self-tolerance is developed
seeding lymphocytes - t cell circulate
antigen encounter and activation
proliferation and differentiation - effector cells and memory cells
What is immunocompetence?
learning to recognize one specific antigen
What is self-tolerance?
must not recognize any self antigens
What are the adaptive defense characteristics?
specific immunity, systemic immunity, and immunity memory
What is specific immunity?
targeting specific antigens and variants
What is systemic immunity?
antibodies move through lymph
What is immunity memory?
storing knowledge of past viruses so response next time to same virus is more efficient
What shape are IgG, IgD, and IgE?
y shaped (monomer)
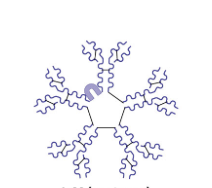
What is this?
IgM antibody and it’s a pentamer
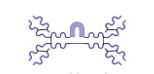
What is this?
IgA antibody and it’s a diamer
How many antigens can bind to a monomer shaped antibody?
2
How many antigens can bind to a diamer antibody?
4
How many antigens can bind to a pentamer?
5
How does immunological memory work?
First, a person’s body has to be exposed to a new pathogen. In the primary response, new plasma cells are being made, but memory cells are also being made. If the pathogen enters the immune system again, the immune system will be able to respond faster and produce antibodies at a faster rate.
What is an example of naturally acquired active immunity?
coming into contact with a pathogen
What is an example of an artificially acquired active immunity?
vaccine
What is an example of a naturally acquired passive immunity?
antibodies passed from the mother when the child is in the womb
What is an example of an artificially acquired passive immunity?
injection of someone else’s antibodies
How are b cell activated?
antigen binds to B cell
activates b cells to proliferate into plasma cells and memory cells
IgM antibodies are secreted by plasma if it is a primary response
How is the b cell differentiated?
memory cells are activated
more plasma cells and some memory cells are immediately made
secretes IgG antibodies
Where are IgA antibodies found?
body secretions such as saliva, sweat, intestinal juice, and milk
Where do the T cells mature?
thymus
Where do the B cell mature?
red blood marrow
What are MHC proteins?
glycoproteins that are unique to each individual
What are the functions of MHC proteins?
present antigens to T lymphocytes so they can bind to that antigen
prevents your cells from attacking each other
What can MHC protein hold in their deep groove?
peptide, self antigen, and foreign antigen
What do APCs do?
engulf and present those fragments to T cells to MHC II proteins
What are APCs?
dendritic cells, macrophages, and b lymphocytes
What receptors are on a CD4 cell?
CD4 receptor, T cell receptor, and MHC II receptor
What do CD4 cells differentiate into?
helper T cells and regulatory cells
What receptors do CD8 cells have?
CD8 receptor, T cell receptor, and MHC I receptor
What does CD8 cells differentiate into?
cytotoxic T cells
What are the steps for T cell differentiation?
Antigen is presented by APC
Double recognition
TCR and CD cell binds to MHC proteins and costimulatory molecule binds
CD cell is activated and proliferates to become memory and effector T cells
How are T cells activated?
the CD cell must interact with a MHC protein, a costimulatory molecule, and antigen bound to T cell receptor
What MHC protein is on all cells except erythrocytes?
MHC I
What are antigens called in healthy cells?
endogenous antigens
When MHC I proteins survey and find foreign antigens being secreted from cells it
activates CD8 cells and informs cytotoxic cells
Where are MHC II proteins found?
only on cells that present antigens to CD4 cells
dendritic cells
macrophages
b cells
What stimulates helper t cells?
interleukins
What does the helper t cell do?
enhances lymphocyte functions
How do cytotoxic cells function?
releases perforin to break the target cell membrane and then releases granzymes to induce apoptosis
What occurs when the antigen-antibody complex is formed?
neutralization
agglutination
precipitation
complement activation
What is neutralization?
antigens and antibodies bind and prevents viruses/bacteria from attaching and infecting host cells
What is precipitation?
antibodies bind to proteins and this results in antigens dissolving
What does the complement activation result in?
enhancement of phagocytosis and inflammation
cell lysis
What does neutralization, agglutination, and precipitation enhance?
phagocytosis
Where do CD4 cells and CD8 cells go before they become effector cells?
lymphoid tissues and organs