4 MCQs - Head, Abdomen & Pelvis
1/345
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
346 Terms
Internal carotid artery has two cervical branches.
A. Yes
B. No
Internal carotid artery has two cervical branches.
B. No
The upper end of internal jugular vein dilates into internal jugular fossa.
A. Yes
B. No
The upper end of internal jugular vein dilates into internal jugular fossa.
A. Yes
Near the termination of the internal jugular vein is a smaller dilatation, the inferior bulb.
A. Yes
B. No
Near the termination of the internal jugular vein is a smaller dilatation, the inferior bulb.
A. Yes
The cutaneous branch of the posterior primary ramus of C2 is called the:
A. Accessory nerve
B. Great auricular nerve
C. Greater occipital nerve
D. Lesser occipital nerve
E. Superior ramus of the ansa cervicalis
The cutaneous branch of the posterior primary ramus of C2 is called the:
A. Accessory nerve
B. Great auricular nerve
C. Greater occipital nerve
D. Lesser occipital nerve
E. Superior ramus of the ansa cervicalis
Loss of sensation from the temporal region and loss of secretory function of the parotid gland would be caused by interruption of which nerve?
A. Auriculotemporal
B. Chorda tympani
C. Deep temporal, posterior
D. Facial
E. Great auricular
Loss of sensation from the temporal region and loss of secretory function of the parotid gland would be caused by interruption of which nerve?
A. Auriculotemporal
B. Chorda tympani
C. Deep temporal, posterior
D. Facial
E. Great auricular
An elderly man presented with severe pain beneath the left eye, radiating into the lower eyelid, lateral side of the nose and upper lip. What nerve was involved?
A. Buccal
B. Infraorbital
C. Mental
D. Supratrochlear
E. Zygomatic
An elderly man presented with severe pain beneath the left eye, radiating into the lower eyelid, lateral side of the nose and upper lip. What nerve was involved?
A. Buccal
B. Infraorbital
C. Mental
D. Supratrochlear
E. Zygomatic
Which nerve provides motor innervation to the buccinator muscle?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Buccal branches of VII
C. Buccal nerve
D. Mandibular division of V
E. Marginal mandibular nerve
Which nerve provides motor innervation to the buccinator muscle?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Buccal branches of VII
C. Buccal nerve
D. Mandibular division of V
E. Marginal mandibular nerve
Which nerve provides cutaneous innervation to the skin of the angle of the mandible?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Lesser petrosal nerve
C. Buccal branches of VII
D. Marginal mandibular nerve
E. Great auricular nerve
Which nerve provides cutaneous innervation to the skin of the angle of the mandible?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Lesser petrosal nerve
C. Buccal branches of VII
D. Marginal mandibular nerve
E. Great auricular nerve
Which nerve carries postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the parotid gland?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Lesser petrosal nerve
C. Glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Great auricular nerve
E. Marginal mandibular nerve
Which nerve carries postganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the parotid gland?
A. Auriculotemporal nerve
B. Lesser petrosal nerve
C. Glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Great auricular nerve
E. Marginal mandibular nerve
A patient is unable to wink; what muscle is affected?
A. frontalis
B. levator palpebrae superioris
C. orbicularis oculi
D. superior tarsal
E. zygomaticus major
A patient is unable to wink; what muscle is affected?
A. frontalis
B. levator palpebrae superioris
C. orbicularis oculi
D. superior tarsal
E. zygomaticus major
What structure lies deepest in the parotid gland?
A. External carotid artery
B. External jugular vein
C. Facial artery
D. Facial nerve
E. Retromandibular vein
What structure lies deepest in the parotid gland?
A. External carotid artery
B. External jugular vein
C. Facial artery
D. Facial nerve
E. Retromandibular vein
A deep laceration of the face in the middle of the parotid gland could affect the:
A. External jugular vein
B. Facial nerve
C. Glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Hypoglossal nerve
E. Lingual artery
A deep laceration of the face in the middle of the parotid gland could affect the:
A. External jugular vein
B. Facial nerve
C. Glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Hypoglossal nerve
E. Lingual artery
Pain elicited from an infected facial wound is primarily conveyed by what nerve?
A. Facial
B. Great auricular
C. Hypoglossal
D. Transverse cervical
E. Trigeminal
Pain elicited from an infected facial wound is primarily conveyed by what nerve?
A. Facial
B. Great auricular
C. Hypoglossal
D. Transverse cervical
E. Trigeminal
Inability to close the lips relates to the action of which muscle?
A. Anterior belly of the digastric
B. Mylohyoid
C. Orbicularis oris
D. Platysma
E. Zygomaticus major
Inability to close the lips relates to the action of which muscle?
A. Anterior belly of the digastric
B. Mylohyoid
C. Orbicularis oris
D. Platysma
E. Zygomaticus major
Which muscle will not be affected when the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3) is anesthetized?
A. Anterior belly of digastric
B. Buccinator
C. Medial pterygoid
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
Which muscle will not be affected when the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3) is anesthetized?
A. Anterior belly of digastric
B. Buccinator
C. Medial pterygoid
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
The parotid space contains all EXCEPT:
A. External carotid artery
B. Facial nerve
C. Intraparotid lymph nodes
D. Medial pterygoid muscle
E. Retromandibular vein
The parotid space contains all EXCEPT:
A. External carotid artery
B. Facial nerve
C. Intraparotid lymph nodes
D. Medial pterygoid muscle
E. Retromandibular vein
The facial muscle most responsible for moving the lips both upward and laterally to produce a smile is:
A. Buccinator
B. Levator anguli oris
C. Levator labii superioris
D. Platysma
E. Zygomaticus major
The facial muscle most responsible for moving the lips both upward and laterally to produce a smile is:
A. Buccinator
B. Levator anguli oris
C. Levator labii superioris
D. Platysma
E. Zygomaticus major
The predominant muscle most associated with retraction of the mandible is the:
A. lateral pterygoid
B. masseter
C. medial pterygoid
D. temporalis
E. mylohyoid
The predominant muscle most associated with retraction of the mandible is the:
A. lateral pterygoid
B. masseter
C. medial pterygoid
D. temporalis
E. mylohyoid
At the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), hinge movements occur between the:
A. condyle and articular eminence
B. articular disc and articular eminence
C. condyle and articular disc
D. articular disc and articular cavity
E. condyle and articular cavity
At the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), hinge movements occur between the:
A. condyle and articular eminence
B. articular disc and articular eminence
C. condyle and articular disc
D. articular disc and articular cavity
E. condyle and articular cavity
Incapacity to protrude the mandible indicates a dysfunction of which muscle?
A. Anterior belly of digastric
B. Buccinator
C. Lateral pterygoid
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
Incapacity to protrude the mandible indicates a dysfunction of which muscle?
A. Anterior belly of digastric
B. Buccinator
C. Lateral pterygoid
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
Damage to the facial nerve near the stylomastoid foramen would likely cause each of the following motor deficits EXCEPT:
A. Paralysis of the buccinator muscle
B. Inability to whistle
C. Paralysis of the muscles that elevate the mandible
D. Inability to close the lips
Damage to the facial nerve near the stylomastoid foramen would likely cause each of the following motor deficits EXCEPT:
A. Paralysis of the buccinator muscle
B. Inability to whistle
C. Paralysis of the muscles that elevate the mandible
D. Inability to close the lips
What bony feature of the mandible can be used to find and palpate the facial artery?
A. Oblique line
B. Mental trigone
C. Angle
D. Premasseteric notch
What bony feature of the mandible can be used to find and palpate the facial artery?
A. Oblique line
B. Mental trigone
C. Angle
D. Premasseteric notch
After the mandibular condyle is moved forward onto the articular eminence (e.g., by opening the mouth widely), what muscle can then retract the mandible?
A. Superficial head of masseter m.
B. Deep head of masseter m.
C. Posterior part of temporalis m.
D. Anterior part of temporalis m.
After the mandibular condyle is moved forward onto the articular eminence (e.g., by opening the mouth widely), what muscle can then retract the mandible?
A. Superficial head of masseter m.
B. Deep head of masseter m.
C. Posterior part of temporalis m.
D. Anterior part of temporalis m.
Two nerves usually emerge from between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle: the anterior deep temporal nerve and the:
A. Masseteric n.
B. Buccal n.
C. Lingual n.
D. Inferior alveolar n.
Two nerves usually emerge from between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle: the anterior deep temporal nerve and the:
A. Masseteric n.
B. Buccal n.
C. Lingual n.
D. Inferior alveolar n.
Paralysis of which of the following muscles would impede retraction of the mandible?
A. Buccinator
B. Lateral pterygoid, lower portion
C. Lateral pterygoid, upper (sphenomeniscus) portion
D. Medial pterygoid
E. Temporalis
Paralysis of which of the following muscles would impede retraction of the mandible?
A. Buccinator
B. Lateral pterygoid, lower portion
C. Lateral pterygoid, upper (sphenomeniscus) portion
D. Medial pterygoid
E. Temporalis
A cranial fracture through the foramen ovale that compresses the enclosed nerve, will have an effect on all muscles EXCEPT :
A. Tensor tympani
B. Masseter
C. Buccinator
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
A cranial fracture through the foramen ovale that compresses the enclosed nerve, will have an effect on all muscles EXCEPT :
A. Tensor tympani
B. Masseter
C. Buccinator
D. Mylohyoid
E. Temporalis
Which muscle is also known as the sphenomeniscus?
A. Inferior head of the lateral pterygoid
B. Masseter
C. Medial pterygoid
D. Superior head of the lateral pterygoid
E. Temporalis
Which muscle is also known as the sphenomeniscus?
A. Inferior head of the lateral pterygoid
B. Masseter
C. Medial pterygoid
D. Superior head of the lateral pterygoid
E. Temporalis
Forward movement of the condyle of the mandible during wide opening of the jaws is accomplished mainly by the:
A. anterior part of temporalis muscle
B. lateral pterygoid muscle
C. masseter muscle
D. medial pterygoid muscle
E. posterior part of the temporalis muscle
Forward movement of the condyle of the mandible during wide opening of the jaws is accomplished mainly by the:
A. anterior part of temporalis muscle
B. lateral pterygoid muscle
C. masseter muscle
D. medial pterygoid muscle
E. posterior part of the temporalis muscle
The middle meningeal artery:
A. enters the skull through the foramen ovale
B. passes through a split in the trunk of the mandibular nerve (V3)
C. is typically a branch of the second part of the maxillary artery
D. supplies blood to the temporal lobe of the brain
E. usually arises deep to the neck of the mandible
The middle meningeal artery:
A. enters the skull through the foramen ovale
B. passes through a split in the trunk of the mandibular nerve (V3)
C. is typically a branch of the second part of the maxillary artery
D. supplies blood to the temporal lobe of the brain
E. usually arises deep to the neck of the mandible
The temporomandibular joint is characterized by all EXCEPT:
A. A capsule strengthened by ligaments on its lateral side only
B. A completely flat surface for its gliding action
C. An articular disc
D. Extracapsular ligaments
E. Two joint cavities of different shapes
The temporomandibular joint is characterized by all EXCEPT:
A. A capsule strengthened by ligaments on its lateral side only
B. A completely flat surface for its gliding action
C. An articular disc
D. Extracapsular ligaments
E. Two joint cavities of different shapes
There is arterial bleeding on superficial surface of the of the posterior third of the tongue; which of the following arteries was involved?
A. Deep lingual
B. Dorsal lingual
C. Facial
D. Sublingual
E. Tonsillar
There is arterial bleeding on superficial surface of the of the posterior third of the tongue; which of the following arteries was involved?
A. Deep lingual
B. Dorsal lingual
C. Facial
D. Sublingual
E. Tonsillar
There is difficulty in swallowing due to involvement of which muscle that elevates the tongue?
A. Genioglossus
B. Hyoglossus
C. Styloglossus
D. Stylohyoid
E. Stylopharyngeus
There is difficulty in swallowing due to involvement of which muscle that elevates the tongue?
A. Genioglossus
B. Hyoglossus
C. Styloglossus
D. Stylohyoid
E. Stylopharyngeus
Cutting of the hypoglossal nerve in the hypoglossal canal would not interrupt the nerve supply to the:
A. Hyoglossus muscle
B. Genioglossus muscle
C. Palatoglossus muscle
D. Styloglossus muscle
Cutting of the hypoglossal nerve in the hypoglossal canal would not interrupt the nerve supply to the:
A. Hyoglossus muscle
B. Genioglossus muscle
C. Palatoglossus muscle
D. Styloglossus muscle
The contents of the paralingual space do NOT include the:
A. Hypoglossal nerve
B. Lingual artery
C. Lingual nerve
D. Submandibular gland
E. Sublingual gland
The contents of the paralingual space do NOT include the:
A. Hypoglossal nerve
B. Lingual artery
C. Lingual nerve
D. Submandibular gland
E. Sublingual gland
A patient is unable to taste a piece of sugar placed on the anterior part of the tongue. Which cranial nerve is most likely to have a lesion?
A. Facial nerve
B. Glossopharyngeal nerve
C. Hypoglossal nerve
D. Trigeminal nerve
E. Vagus nerve
A patient is unable to taste a piece of sugar placed on the anterior part of the tongue. Which cranial nerve is most likely to have a lesion?
A. Facial nerve
B. Glossopharyngeal nerve
C. Hypoglossal nerve
D. Trigeminal nerve
E. Vagus nerve
The chorda tympani contains which component before it joins the lingual nerve?
A. Preganglionic sympathetics
B. Postganglionic sympathetics
C. Preganglionic parasympathetics
D. Postganglionic parasympathetics
E. Taste fibers to the posterior third of the tongue
The chorda tympani contains which component before it joins the lingual nerve?
A. Preganglionic sympathetics
B. Postganglionic sympathetics
C. Preganglionic parasympathetics
D. Postganglionic parasympathetics
E. Taste fibers to the posterior third of the tongue
Which of the following structures is located in the vestibule of the oral cavity?
A. Tongue
B. Opening of the parotid duct
C. Opening of the submandibular duct
D. Sublingual fold
E. Uvula
Which of the following structures is located in the vestibule of the oral cavity?
A. Tongue
B. Opening of the parotid duct
C. Opening of the submandibular duct
D. Sublingual fold
E. Uvula
The muscle responsible for raising the floor of the mouth in the early stages of swallowing is the:
A. genioglossus
B. geniohyoid
C. hyoglossus
D. mylohyoid
E. palatoglossus
The muscle responsible for raising the floor of the mouth in the early stages of swallowing is the:
A. genioglossus
B. geniohyoid
C. hyoglossus
D. mylohyoid
E. palatoglossus
All of the following may be found in the paralingual space EXCEPT:
A. Hypoglossal nerve
B. Lingual nerve
C. Sublingual gland
D. Submandibular gland duct
E. Superficial lobe of the submandibular gland
All of the following may be found in the paralingual space EXCEPT:
A. Hypoglossal nerve
B. Lingual nerve
C. Sublingual gland
D. Submandibular gland duct
E. Superficial lobe of the submandibular gland
T/F Lamina superficialis of the deep cervical fascia
A. Covers entire neck
B. Forms fascia masseterica
C. Extends from the skull base to the bodies of T3-T4
D. Forms fascia of submandibular gland
E. Extends posteriorly to proc. transversi
T/F Lamina superficialis of the deep cervical fascia
T - A. Covers entire neck
F - B. Forms fascia masseterica
F - C. Extends from the skull base to the bodies of T3-T4
T - D. Forms fascia of submandibular gland
T - E. extends posteriorly to proc. transversi
T/F A. carotis externa:
A. is in the carotid triangle
B. gives off a. thyroidea inferior
C. supplies head and neck structures
D. has baroreceptors at its origin - the bifurcation of the common carotid artery
E. occurs at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage.
T/F A. carotis externa:
T - A. is in the carotid triangle
F - B. gives off a. thyroidea inferior
T - C. supplies head and neck structures
F - D. has baroreceptors at its origin - the bifurcation of the common carotid artery
T - E. occurs at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage.
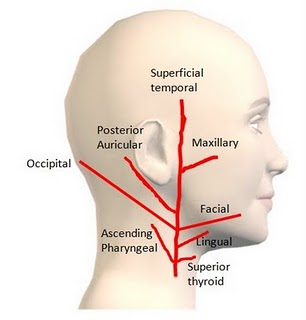
T/F Which of the following are NOT anterior branches of external carotid artery?
A. A. pharyngea ascendens
B. A. thyroidea superior
C. A. sternocleidomastoidea
D. A. lingualis
E. A. occipitalis
T/F Which of the following are NOT anterior branches of external carotid artery?
T - A. A. pharyngea ascendens
F - B. A. thyroidea superior
T - C. A. sternocleidomastoidea
F - D. A. lingualis
T - E. A. occipitalis
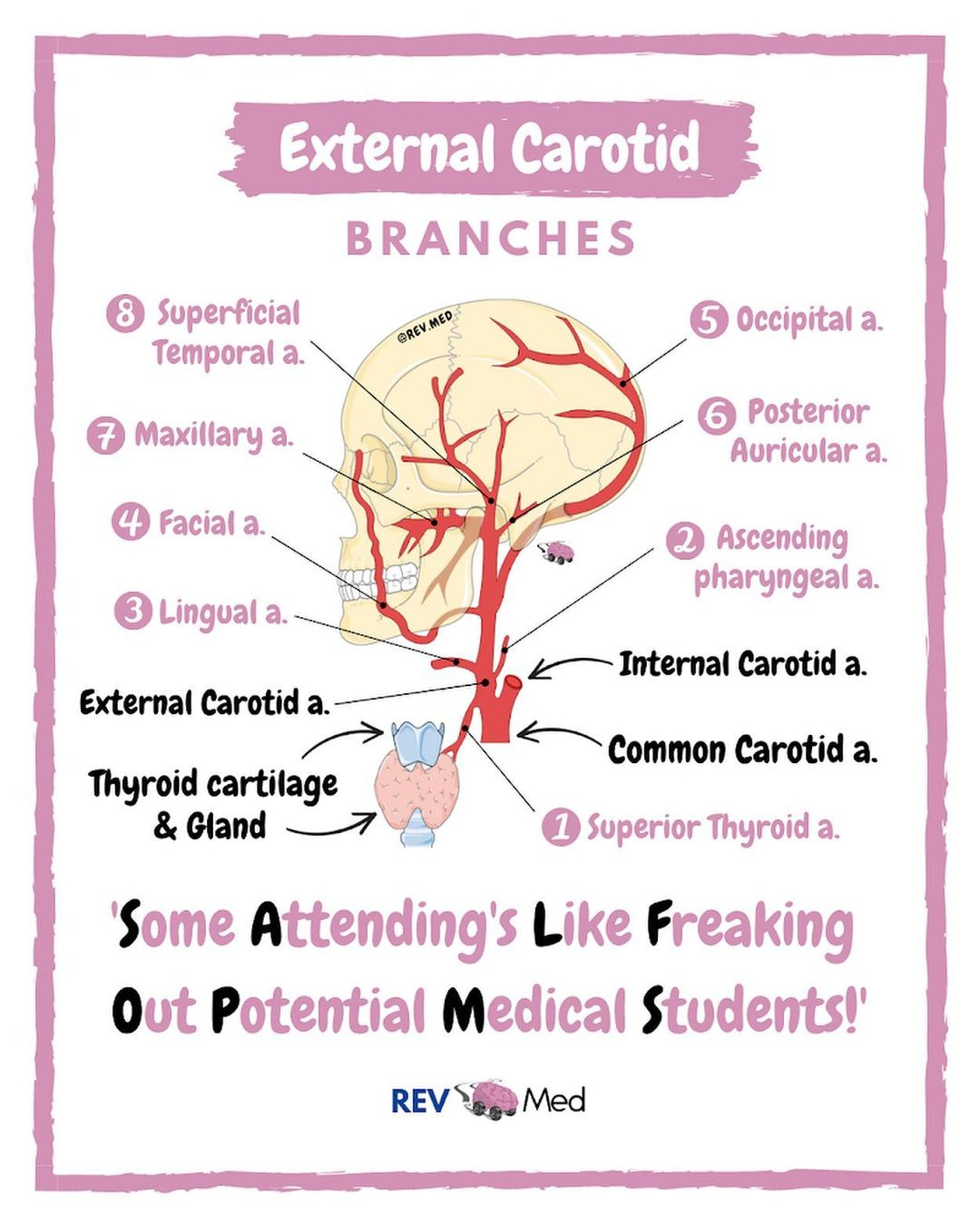
T/F Anterior branches of external carotid artery are:
A. A. thyroidea superior
B. A. occipitalis
C. A. lingualis
D. A. subscapularis
E. A. facialis
T/F Anterior branches of external carotid artery are:
T - A. A. thyroidea superior
F - B. A. occipitalis
T - C. A. lingualis
F - D. A. subscapularis
T - E. A. facialis
T/F The digastric muscle
A. has a motor innervation from nerves of the branchial arches
B. is inferior to the submandibular gland
C. is attached to the ramus of the mandible
D. is superficial,to the hypoglossal nerve
E. is deep to the carotid sheath.
T/F The digastric muscle
T - A. has a motor innervation from nerves of the branchial arches
T - B. is inferior to the submandibular gland
F - C. is attached to the ramus of the mandible
T - D. is superficial,to the hypoglossal nerve
F - E. is deep to the carotid sheath.
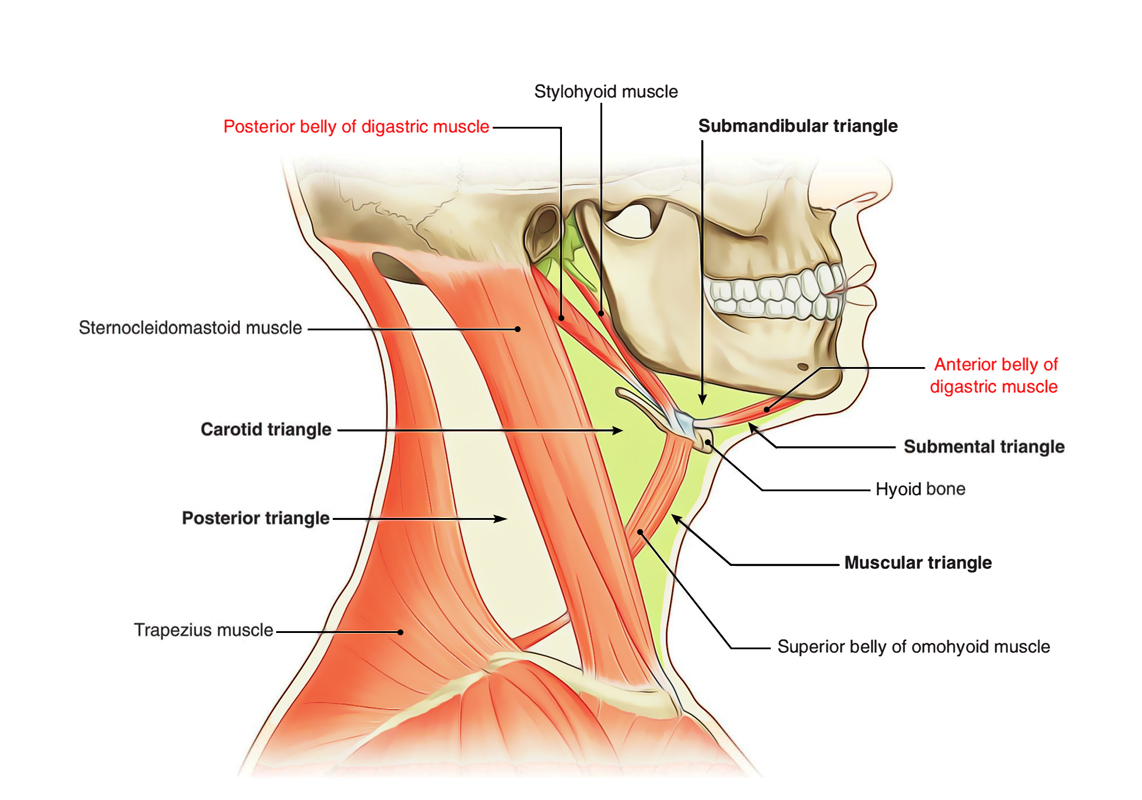
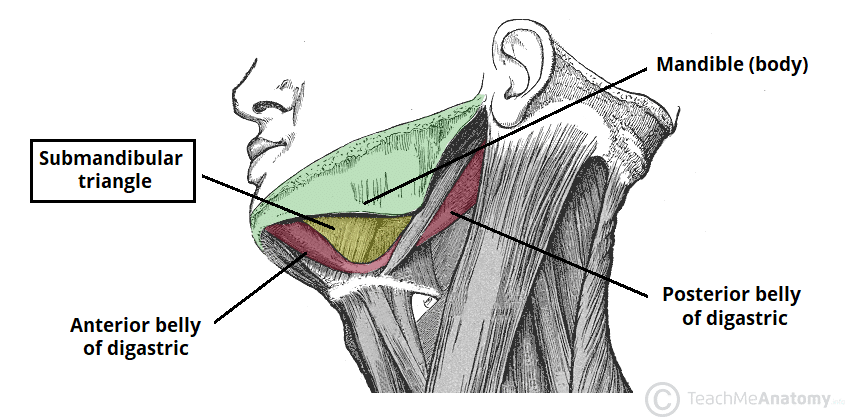
T/F Trigonum submandibulare contains:
A. glandula submandibularis
B. accessory nerve
C. phrenic nerve
D. facial artery
E. lingual nerve
T/F Trigonum submandibulare contains:
T - A. glandula submandibularis
F - B. accessory nerve
F - C. phrenic nerve
T - D. facial artery
T - E. lingual nerve
T/F The following elements are part of trigonum submandibulare:
A. n. mylohyoideus
B. n. hypoglossus
C. glandula thyroidea
D. trigonum Pirogovi
E. a. thyroidea inferior
T/F The following elements are part of trigonum submandibulare:
T - A. n. mylohyoideus
T - B. n. hypoglossus
F - C. glandula thyroidea
T - D. trigonum Pirogovi
F - E. a. thyroidea inferior
MATCH EACH NUMBERED TERM WITH THE MOST PROPER LETTERED ONE
Which of the following A to F supplies the muscles 1 to 6?
A. Cervical plexus
B. Spinal accessory nerve
C. Cranial accessory nerve
D. Facial nerve
E. None of these
1 Platysma
2 Infrahyoid
3 Sternocleidomastoid
4 Levator veli palatini
5 Orbicularis oculi
Which of the following A to F supplies the muscles 1 to 6?
A. Cervical plexus - 2 Infrahyoid
B. Spinal accessory nerve - 3 Sternocleidomastoid
C. Cranial accessory nerve
D. Facial nerve - 1 Platysma, 5 Orbicularis oculi
E. None of these - 4 Levator veli palatini
External carotid artery gives off the following branches from its anterior surface:
A.
B.
C.
External carotid artery gives off the following branches from its anterior surface:
A. superior thyroid a.
B. lingual aa.
C. facial aa.
Define the boundaries of trigonum submandibulare:
A.
B.
C.
Define the boundaries of trigonum submandibulare:
A. posterior bellies of digastric m.
B. anterior bellies of digastric m.
C. mandible
Vagina m. recti abdominis is formed by the aponeuroses of the anterolateral muscles of the abdominal wall.
A. Yes
B. No
Vagina m. recti abdominis is formed by the aponeuroses of the anterolateral muscles of the abdominal wall.
A. Yes
The spleen is located in the infracolic compartment.
A. Yes
B. No
The spleen is located in the infracolic compartment.
B. No
The fluid in the peritoneal cavity lubricates surfaces and facilitates the movement of viscera.
A. Yes
B. No
The fluid in the peritoneal cavity lubricates surfaces and facilitates the movement of viscera.
A. Yes
All of the extraperitoneal viscera are surrounded by visceral peritoneum.
A. Yes
B. No
All of the extraperitoneal viscera are surrounded by visceral peritoneum.
B. No
The peritoneum forms the largest of the serous sacs in the body.
A. Yes
B. No
The peritoneum forms the largest of the serous sacs in the body.
A. Yes
The peritoneal cavity is a slit-like internal between the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum.
A. Yes
B. No
The peritoneal cavity is a slit-like internal between the parietal and visceral layers of the peritoneum.
A. Yes
There are supracolic and infracolic compartments because of the presence of the transverse colon in the flap.
A. Yes
B. No
There are supracolic and infracolic compartments because of the presence of the transverse colon in the flap.
A. Yes
Epiploic foramen of the omental bursa (lesser sac) opens into its left part.
A. Yes
B. No
Epiploic foramen of the omental bursa (lesser sac) opens into its left part.
B. No
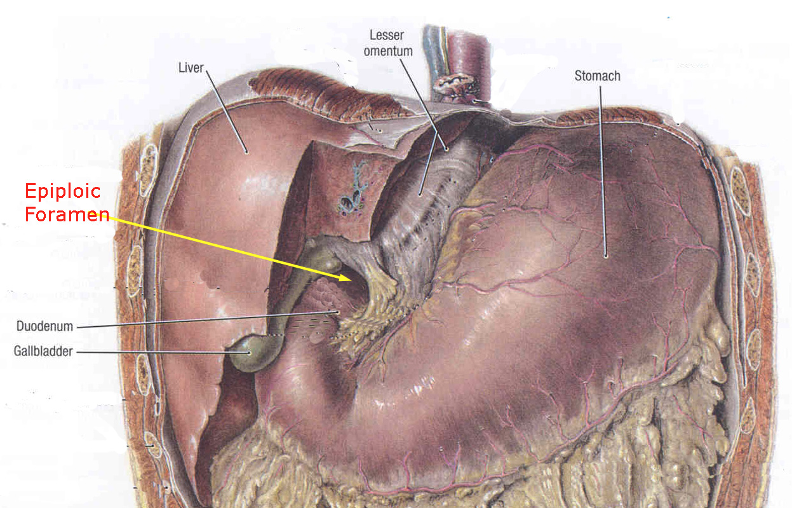
Bursa omentalis is a peritoneal space in the supracolic compartment.
A. Yes
B. No
Bursa omentalis is a peritoneal space in the supracolic compartment.
A. Yes
Nerve supply of the anterolateral abdominal wall is ensured only by the lower intercostal nerves.
A. Yes
B. No
Nerve supply of the anterolateral abdominal wall is ensured only by the lower intercostal nerves.
B. No
Portal vein lies in front of hepatic artery.
A. Yes
B. No
Portal vein lies in front of hepatic artery.
B. No
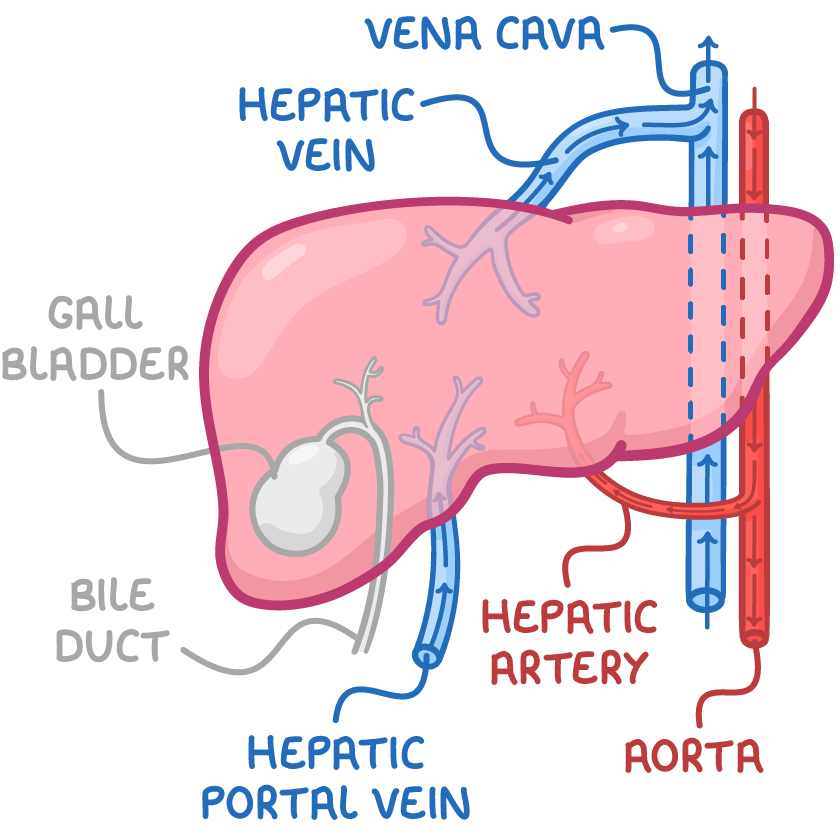
Common bile duct is posterior to the portal vein.
A. Yes
B. No
Common bile duct is posterior to the portal vein.
B. No
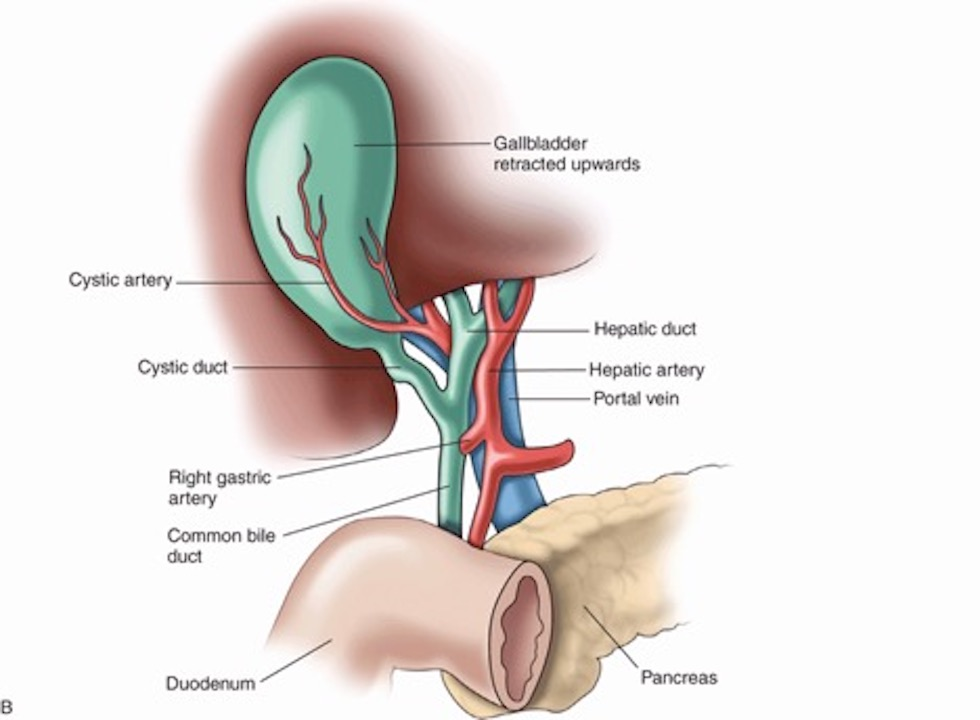
The portal vein is formed behind the neck of the pancreas.
A. Yes
B. No
The portal vein is formed behind the neck of the pancreas.
A. Yes
The portal vein is formed by the union of splenic and inferior mesenteric veins.
A. Yes
B. No
The portal vein is formed by the union of splenic and inferior mesenteric veins.
B. No
The portal vein ascends in the greater omentum.
A. Yes
B. No
The portal vein ascends in the greater omentum.
B. No
The liver lies mainly in the right hypochondrium.
A. Yes
B. No
The liver lies mainly in the right hypochondrium.
A. Yes
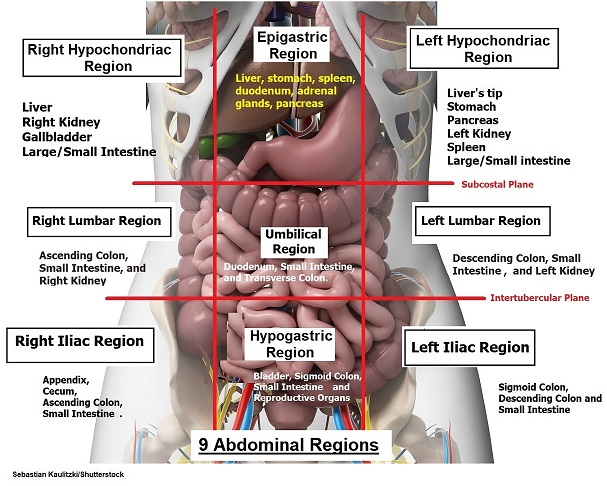
The lesser omentum is attached to the fissure for ligamentum venosum.
A. Yes
B. No
The lesser omentum is attached to the fissure for ligamentum venosum.
A. Yes
The liver is divided functionally into 8 segments.
A. Yes
B. No
The liver is divided functionally into 8 segments.
A. Yes
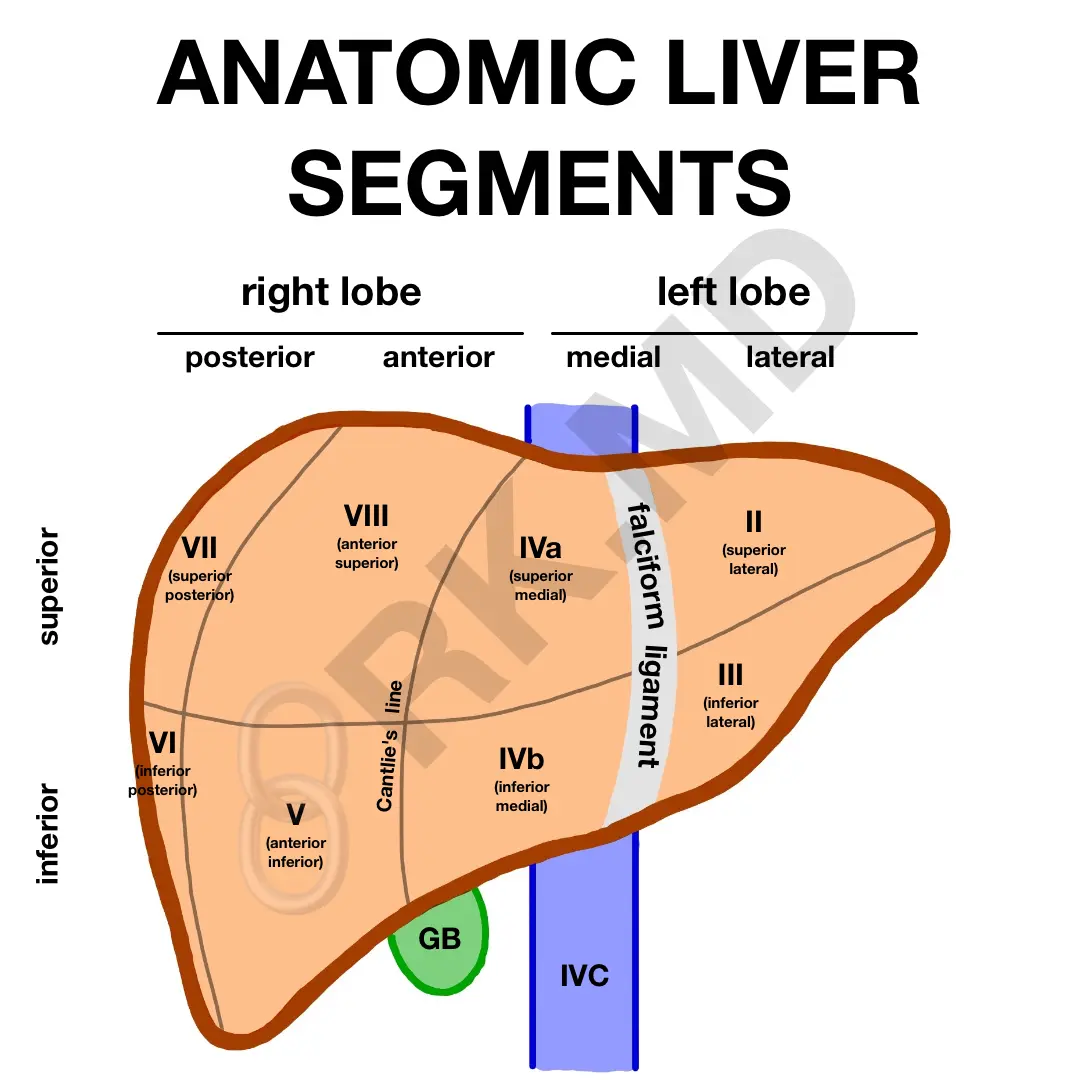
The left hepatic duct drains the left lobe.
A. Yes
B. No
The left hepatic duct drains the left lobe.
A. Yes
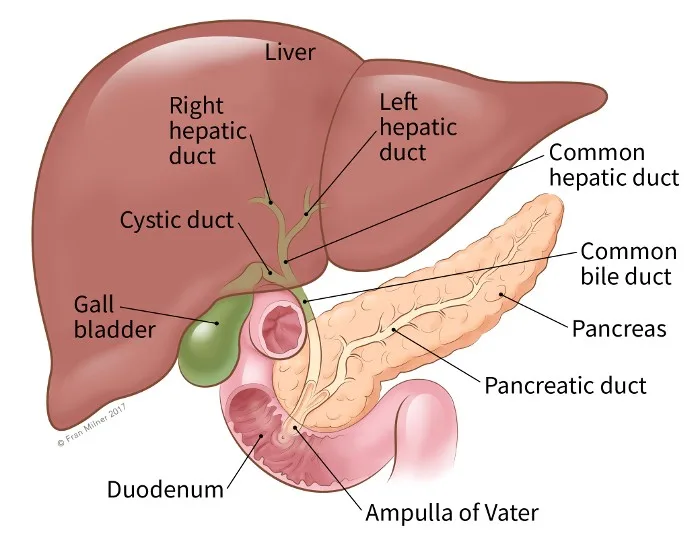
The right hepatic duct drains the quadrate lobe.
A. Yes
B. No
The right hepatic duct drains the quadrate lobe.
B. No
Omental bursa (lesser sac):
A. is part of the retroperitoneal compartment
B. is in the infracolic compartment
C. is in the supracolic compartment
D. has no communication with peritoneal cavity (greater sac)
Omental bursa (lesser sac):
A. is part of the retroperitoneal compartment
B. is in the infracolic compartment
C. is in the supracolic compartment
D. has no communication with peritoneal cavity (greater sac)
The peritoneum:
A. is a double-layered mucous membrane
B. is a double-layered serous membrane
C. covers entirely all the organs in the abdominal cavity
The peritoneum:
A. is a double-layered mucous membrane
B. is a double-layered serous membrane
C. covers entirely all the organs in the abdominal cavity
The inferior border of the rectus sheath posteriorly is called the:
A. Falx inguinalis
B. Inguinal ligament
C. Internal inguinal ring
D. Arcuate line
E. Linea alba
The inferior border of the rectus sheath posteriorly is called the:
A. Falx inguinalis
B. Inguinal ligament
C. Internal inguinal ring
D. Arcuate line
E. Linea alba
An obstetrician decides to do a Caesarean section on a 25-year-old pregnant woman. A transverse suprapubic incision is chosen for that purpose. All of the following abdominal wall layers will be encountered during the incision EXCEPT the:
A. Anterior rectus sheath
B. Posterior rectus sheath
C. Rectus abdominis muscle
D. Skin and subcutaneous tissue
E. Transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and peritoneum
An obstetrician decides to do a Caesarean section on a 25-year-old pregnant woman. A transverse suprapubic incision is chosen for that purpose. All of the following abdominal wall layers will be encountered during the incision EXCEPT the:
A. Anterior rectus sheath
B. Posterior rectus sheath
C. Rectus abdominis muscle
D. Skin and subcutaneous tissue
E. Transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and peritoneum
The internal thoracic artery is sometimes surgically cut near the caudal end of the sternum and used to supply blood to a region of the heart. In these cases, maintenance of adequate blood flow to the rectus abdominis may be dependent on increased flow through which artery?
A. Superficial epigastric
B. Inferior epigastric
C. Umbilical
D. Superficial circumflex iliac
E. Deep circumflex iliac
The internal thoracic artery is sometimes surgically cut near the caudal end of the sternum and used to supply blood to a region of the heart. In these cases, maintenance of adequate blood flow to the rectus abdominis may be dependent on increased flow through which artery?
A. Superficial epigastric
B. Inferior epigastric
C. Umbilical
D. Superficial circumflex iliac
E. Deep circumflex iliac
If one were to make an incision parallel to and 5 cm above the inguinal ligament, one would find the inferior epigastric vessels between which layers of the abdominal wall?
A. Camper's and Scarpa's fascias
B. External abdominal oblique and internal abdominal oblique muscles
C. Internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles
D. Skin and deep fascia of the abdominal wall
E. Tranversus abdominis muscle and peritoneum
If one were to make an incision parallel to and 5 cm above the inguinal ligament, one would find the inferior epigastric vessels between which layers of the abdominal wall?
A. Camper's and Scarpa's fascias
B. External abdominal oblique and internal abdominal oblique muscles
C. Internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles
D. Skin and deep fascia of the abdominal wall
E. Tranversus abdominis muscle and peritoneum
A loop of bowel protrudes through the abdominal wall to form a direct inguinal hernia; viewed from the abdominal side, the hernial sac would be found in which region?
A. Deep inguinal ring
B. Lateral inguinal fossa
C. Medial inguinal fossa
D. Superficial inguinal ring
E. Supravesical fossa
A loop of bowel protrudes through the abdominal wall to form a direct inguinal hernia; viewed from the abdominal side, the hernial sac would be found in which region?
A. Deep inguinal ring
B. Lateral inguinal fossa
C. Medial inguinal fossa
D. Superficial inguinal ring
E. Supravesical fossa
Which structure passes through the deep inguinal ring?
A. Iliohypogastric nerve
B. Ilioinguinal nerve
C. Inferior epigastric artery
D. Medial umbilical ligament
E. Round ligament of the uterus
Which structure passes through the deep inguinal ring?
A. Iliohypogastric nerve
B. Ilioinguinal nerve
C. Inferior epigastric artery
D. Medial umbilical ligament
E. Round ligament of the uterus
During your peer presentation of the inguinal region dissection, you would indicate the position of the deep inguinal ring to be:
A. Above the anterior superior iliac spine
B. Above the midpoint of the inguinal ligament
C. Above the pubic tubercle
D. In the supravesical fossa
E. Medial to the inferior epigastric artery
During your peer presentation of the inguinal region dissection, you would indicate the position of the deep inguinal ring to be:
A. Above the anterior superior iliac spine
B. Above the midpoint of the inguinal ligament
C. Above the pubic tubercle
D. In the supravesical fossa
E. Medial to the inferior epigastric artery
The normal pattern of venous and lymphatic drainage of the superficial tissues of the anterior abdominal wall is arranged around a horizontal plane. Above that plane, drainage is in a cranial direction; below the plane drainage is in a caudal direction. This reference plane corresponds to:
A. Transpyloric plane
B. Level of anterior superior iliac spines
C. Transtubercular line
D. Level of arcuate line
E. Level of umbilicus
The normal pattern of venous and lymphatic drainage of the superficial tissues of the anterior abdominal wall is arranged around a horizontal plane. Above that plane, drainage is in a cranial direction; below the plane drainage is in a caudal direction. This reference plane corresponds to:
A. Transpyloric plane
B. Level of anterior superior iliac spines
C. Transtubercular line
D. Level of arcuate line
E. Level of umbilicus
The boundaries of the inguinal triangle include all except:
A. Arcuate line
B. Inferior epigastric vessels
C. Inguinal ligament
D. Lateral border of rectus abdominus muscle
The boundaries of the inguinal triangle include all except:
A. Arcuate line
B. Inferior epigastric vessels
C. Inguinal ligament
D. Lateral border of rectus abdominus muscle
The superficial inguinal ring is an opening in which structure?
A. External abdominal oblique aponeurosis
B. Falx inguinalis
C. Internal abdominal oblique muscle
D. Scarpa's fascia
E. Transversalis fascia
The superficial inguinal ring is an opening in which structure?
A. External abdominal oblique aponeurosis
B. Falx inguinalis
C. Internal abdominal oblique muscle
D. Scarpa's fascia
E. Transversalis fascia
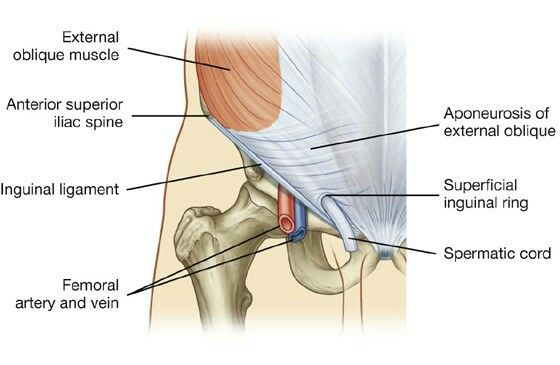
If a hernia enters into the scrotum, it is most likely a(n):
A. Direct inguinal hernia
B. Indirect inguinal hernia
C. Femoral hernia
D. Obturator hernia
If a hernia enters into the scrotum, it is most likely a(n):
A. Direct inguinal hernia
B. Indirect inguinal hernia
C. Femoral hernia
D. Obturator hernia
Which nerve passes through the superficial inguinal ring and may therefore be endangered during inguinal hernia repair?
A. Femoral branch of the genitofemoral
B. llioinguinal
C. Iliohypogastric
D. Obturator
E. Subcostal
Which nerve passes through the superficial inguinal ring and may therefore be endangered during inguinal hernia repair?
A. Femoral branch of the genitofemoral
B. llioinguinal
C. Iliohypogastric
D. Obturator
E. Subcostal
Occlusion of the inferior mesenteric artery is seldom symptomatic because its territory may be supplied by branches of the:
A. Gastroduodenal
B. Ileocolic
C. Middle colic
D. Right colic
E. Splenic
Occlusion of the inferior mesenteric artery is seldom symptomatic because its territory may be supplied by branches of the:
A. Gastroduodenal
B. Ileocolic
C. Middle colic
D. Right colic
E. Splenic
The presence of which feature (also obvious on a radiograph with barium contrast) distinguishes small from large bowel?
A. Circular folds of the mucosa
B. Circular smooth muscle layer in the wall
C. Mucosal glands
D. Longitudinal smooth muscle layer in the wall
E. Serosa
The presence of which feature (also obvious on a radiograph with barium contrast) distinguishes small from large bowel?
A. Circular folds of the mucosa
B. Circular smooth muscle layer in the wall
C. Mucosal glands
D. Longitudinal smooth muscle layer in the wall
E. Serosa
Which of the following veins does not run a course parallel to the artery of the same name?
A. superior epigastric
B. superficial circumflex iliac
C. inferior mesenteric
D. superior rectal
E. ileocolic
Which of the following veins does not run a course parallel to the artery of the same name?
A. superior epigastric
B. superficial circumflex iliac
C. inferior mesenteric
D. superior rectal
E. ileocolic
During development of the gut:
A. the sigmoid colon is retroperitoneal
B. the inferior mesenteric artery is the axis for rotation of the midgut loop
C. the stomach rotates around its longitudinal axis causing the ventral border to become the greater curvature
D. the liver is non-functional
E. none of the above
During development of the gut:
A. the sigmoid colon is retroperitoneal
B. the inferior mesenteric artery is the axis for rotation of the midgut loop
C. the stomach rotates around its longitudinal axis causing the ventral border to become the greater curvature
D. the liver is non-functional
E. none of the above
Visceral pain is often referred to a site on the body wall (where the patient "feels" it) that is innervated by the same spinal cord segment that innervates the visceral organ involved. Pain of appendicitis is often first felt around the umbilicus, indicating that the appendix receives its sympathetic (and thus visceral afferents) from which spinal cord segment?
A. T9
B. T 10
C. T 11
D. T 12
E. L 1
Visceral pain is often referred to a site on the body wall (where the patient "feels" it) that is innervated by the same spinal cord segment that innervates the visceral organ involved. Pain of appendicitis is often first felt around the umbilicus, indicating that the appendix receives its sympathetic (and thus visceral afferents) from which spinal cord segment?
A. T9
B. T 10
C. T 11
D. T 12
E. L 1
The spleen normally does not descend below the costal margin. However, it pushes downward and medially when pathologically enlarged. What structure limits the straight vertical downward movement?
A. Left colic flexure
B. Left suprarenal gland
C. Ligament of Treitz
D. Pancreas
E. Stomach
The spleen normally does not descend below the costal margin. However, it pushes downward and medially when pathologically enlarged. What structure limits the straight vertical downward movement?
A. Left colic flexure
B. Left suprarenal gland
C. Ligament of Treitz
D. Pancreas
E. Stomach
As the bowel is exposed, the surgeon says in amazement, "This is a loop of large bowel!" Which characteristic(s) would identify it specifically as large bowel?
A. A serosa
B. Circular folds
C. Epiploic appendages
D. Tenia
E. C and D
As the bowel is exposed, the surgeon says in amazement, "This is a loop of large bowel!" Which characteristic(s) would identify it specifically as large bowel?
A. A serosa
B. Circular folds
C. Epiploic appendages
D. Tenia
E. C and D
The anastomotic artery running along the border of the large intestine is called the:
A. Arcade
B. Arteriae rectae
C. Coronary
D. Ileocolic
E. Marginal
The anastomotic artery running along the border of the large intestine is called the:
A. Arcade
B. Arteriae rectae
C. Coronary
D. Ileocolic
E. Marginal
The inferior mesenteric artery is often occluded by atherosclerosis without symptoms; its normal area of distribution therefore must be supplied by collateral blood flow between which arteries?
A. Ileocolic and right colic
B. Left and middle colic
C. Left colic and sigmoidal
D. Right and middle colic
E. Sigmoidal and superior rectal
The inferior mesenteric artery is often occluded by atherosclerosis without symptoms; its normal area of distribution therefore must be supplied by collateral blood flow between which arteries?
A. Ileocolic and right colic
B. Left and middle colic
C. Left colic and sigmoidal
D. Right and middle colic
E. Sigmoidal and superior rectal
The artery of the midgut is the:
A. Celiac trunk
B. Inferior mesenteric
C. Proper hepatic
D. Splenic
E. Superior mesenteric
The artery of the midgut is the:
A. Celiac trunk
B. Inferior mesenteric
C. Proper hepatic
D. Splenic
E. Superior mesenteric
During a full workup on a 2-month-old infant with a history of intermittent gastrointestinal pain and vomiting, physicians discovered that the cause was lack of emptying of the stomach. They immediately suspected that the cause was a spasmodic contraction of which of the following parts of the stomach?
A. cardiac notch
B. fundus
C. lesser curvature
D. pylorus
E. rugae
During a full workup on a 2-month-old infant with a history of intermittent gastrointestinal pain and vomiting, physicians discovered that the cause was lack of emptying of the stomach. They immediately suspected that the cause was a spasmodic contraction of which of the following parts of the stomach?
A. cardiac notch
B. fundus
C. lesser curvature
D. pylorus
E. rugae
In order to do a vagotomy (section of vagal nerve trunks) to reduce the secretion of acid by cells of the stomach mucosa in patients with peptic ulcers, one needs to cut the gastric branches and retain vagal innervation to other abdominal organs. Where would a surgeon look for these branches in relation to the stomach?
A. along the gastroepiploic vessels
B. along the greater curvature
C. along the lesser curvature
D. in the base of the omental apron
E. in the gastrocolic ligament
In order to do a vagotomy (section of vagal nerve trunks) to reduce the secretion of acid by cells of the stomach mucosa in patients with peptic ulcers, one needs to cut the gastric branches and retain vagal innervation to other abdominal organs. Where would a surgeon look for these branches in relation to the stomach?
A. along the gastroepiploic vessels
B. along the greater curvature
C. along the lesser curvature
D. in the base of the omental apron
E. in the gastrocolic ligament
While performing a splenectomy (removal of the spleen) following an automobile accident, the surgeons were especially attentive to locate and preserve the tail of the pancreas which is closely associated with the spleen. This they found in the:
A. gastrocolic ligament
B. gastrosplenic ligament
C. phrenicocolic ligament
D. splenorenal ligament
E. transverse mesocolon
While performing a splenectomy (removal of the spleen) following an automobile accident, the surgeons were especially attentive to locate and preserve the tail of the pancreas which is closely associated with the spleen. This they found in the:
A. gastrocolic ligament
B. gastrosplenic ligament
C. phrenicocolic ligament
D. splenorenal ligament
E. transverse mesocolon
A twenty-year-old woman was broad-sided on the driver side by an SUV and was taken to the hospital emergency room. Examination showed low blood pressure and tenderness on the left mid-axillary line. Also, a large swelling was felt protruding downward and medially below the left costal margin. X-rays revealed that her 9th and 10th ribs were fractured near their angles on the left side. The abdominal organ most likely to be injured by the fracture is:
A. Descending colon
B. Left kidney
C. Pancreas
D. Spleen
E. Stomach
A twenty-year-old woman was broad-sided on the driver side by an SUV and was taken to the hospital emergency room. Examination showed low blood pressure and tenderness on the left mid-axillary line. Also, a large swelling was felt protruding downward and medially below the left costal margin. X-rays revealed that her 9th and 10th ribs were fractured near their angles on the left side. The abdominal organ most likely to be injured by the fracture is:
A. Descending colon
B. Left kidney
C. Pancreas
D. Spleen
E. Stomach
You are observing an operation to remove the left suprarenal gland. To expose the gland the surgeon mobilizes the descending colon by cutting along its lateral attachment to the body wall and dissecting medialward in the fusion fascia behind it. Suddenly the operative field is filled with blood. The surgeon realizes he has failed to cut a mesenteric attachment between the left colic flexure and another organ. As a result of the traction, the surface of the organ tore. Which organ was injured?
A. Duodenum
B. Kidney
C. Liver
D. Spleen
E. Suprarenal gland
You are observing an operation to remove the left suprarenal gland. To expose the gland the surgeon mobilizes the descending colon by cutting along its lateral attachment to the body wall and dissecting medialward in the fusion fascia behind it. Suddenly the operative field is filled with blood. The surgeon realizes he has failed to cut a mesenteric attachment between the left colic flexure and another organ. As a result of the traction, the surface of the organ tore. Which organ was injured?
A. Duodenum
B. Kidney
C. Liver
D. Spleen
E. Suprarenal gland
A patient presented with a swollen spleen, which protruded medially toward the umbilicus in the abdomen. A vertical and downward expansion of the spleen was resisted by the:
A. Tail of the pancreas
B. Left colic flexure
C. Left kidney
D. Left renal artery
E. Stomach
A patient presented with a swollen spleen, which protruded medially toward the umbilicus in the abdomen. A vertical and downward expansion of the spleen was resisted by the:
A. Tail of the pancreas
B. Left colic flexure
C. Left kidney
D. Left renal artery
E. Stomach
The spleen contacts all of the following organs EXCEPT:
A. Jejunum
B. Kidney
C. Left colic flexure
D. Tail of the pancreas
E. Stomach
The spleen contacts all of the following organs EXCEPT:
A. Jejunum
B. Kidney
C. Left colic flexure
D. Tail of the pancreas
E. Stomach