Ch 7:Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic gene mappingt4
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Recall
principle of segregation. Alleles separate during meiosis
Independent assortments leads to
4 types of gametes
Completely Linked genes
linked genes that do not exhibit crossing over. Only 2 kinds of gametes
What are recombinant gametes with linked genes?
Crossing over has occured, so we get a new recombination of two alleles. Half with have unchanged chromosome an dhalf will have a recombinant chromosome. There are now 4 types of gametes
When recombinant
2/4 gametes are recombinant.
Genetic mapping based on recombination frequencies between genes.
Specifically means using recombination frequencies between genes. Genes that are further apart (less closely linked) will have a higher recombination frequency than genes closer together
Recombination frequency is measured in
Map units (M.U.) or centiMorgans (cM)
Complete linkage leads to
nonrecombinant gametes and nonrecombinant progeny
Nonrecombinant
An offspring whose combination of traits has not changed from the parental generation.
Crossing over between linked genes
Does lead to recombinant gametes and recombinant progeny
Any time we have 1 crossover
Creates 2 recombinant gametes
Complete linkage compared with independent assortment
heteroz x homozygous recessive= test cross.
Heterozygous x Homozygous recessive
Test cross
coupling (cis) configuration
one homolog contains both wild-type alleles, the other homolog contains both mutant alleles
repulsion (trans) configuration
One wild-type and one mutant allele on each chromosome.
recombinant frequency
Number of recombinant types / total number of offspring x100
Three point test cross
A test cross where one parent is heterozygous for 3 genes. Used in linkage analysis and gene mapping. Allows us to know the order of genes on a chromosome. The order of three geens can be established in the F1
Steps in determining gene order in a three-point cross
1- Identify the nonrecombinant progeny (two most numerousphenotypes)
2- Identify the double-crossover progeny (two least numerousphenotypes).
3. Compare the phenotypes of double-crossover progeny with thephenotypes of nonrecombinant progeny. They should be alike in twocharacteristics and differ in one
.4. The characteristic that differs between the double crossover

independent assortment
alleles at one locus sort independently from alleles at another locus. shuffles different chromosomes
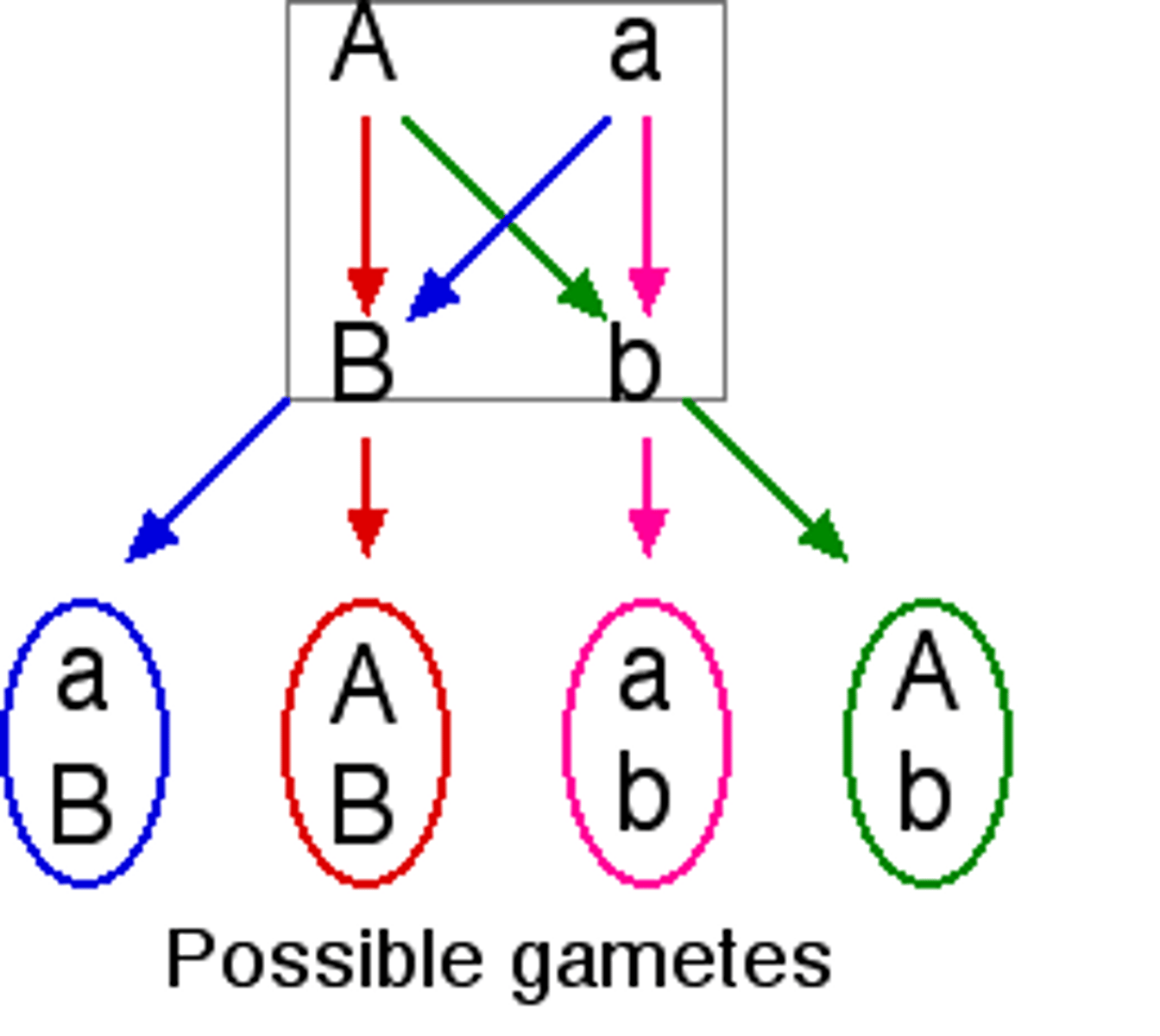
Recombination
alleles sort into new combinations
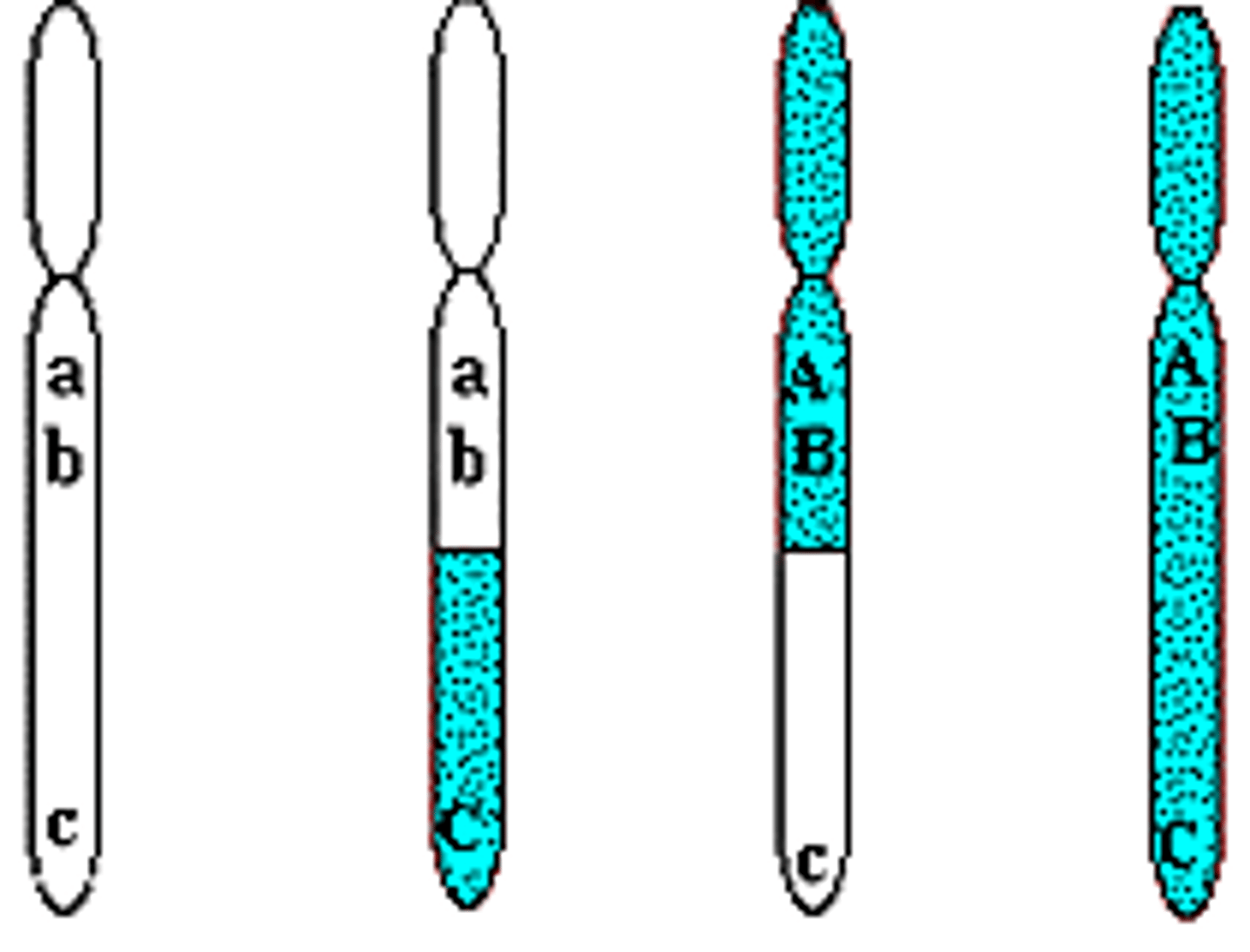
Crossing over
Linked genes ability to become recombinant
The further genes are on a chromosome
higher level of crossing oveer
For single crossovers, the frequency of recombinant gametes is half the frequency of crossing over because
each crossover takes place between only two of the four chromatids of a homologous
Calculating Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency = (No. recombinant progeny/Total no. of progeny) x 100%
Genetic mapping based on recombination frequencies between Genes
Genetic maps determined by recombinant frequency; genes further apart have higher recombination frequencies than genes closer together• RF is measured in map units (M.U.)or centiMorgans (cM) -> they're the same thing• Genetic maps are different thanPhysical maps (which are measuredin basepairs)
the following test cross produces the progeny shown ( AaBbx aaBb= 10AaBb, 40 aaBb, and 10 aabb). Were the A and B alleles in the Aa Bb parent in coupling or repulsion?
Repulsion
4 Chromosomes coem together in a Tetrad during crossing over but
only two chromatids exchange genetic info
How does a genetic map differ from a physical map?
Genetic maps are based on rates of recombination. Physical maps are based on physical distances.
Constructing a genetic map:
Determine the gene order. Determine the location of crossovers.
Somatic-cell hybridization
Fusion of somatic cells of different types.
in situ hybridization
A technique using nucleic acid hybridization with a labeled probe to detect the location of a specific mRNA in an intact organism.
Somatic-cell hybridization is used to
determine which chromosome contains a gene of interest