AP Micro Unit 6
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:41 PM on 4/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
The “Invisible Hand” of Free Markets
the government doesn’t need to get involved since the needs of society are automatically met
2
New cards
Market Failure
a situation in which the free-market system fails to satisfy society’s wants
→ (when the invisible hand doesn’t work) private markets do not efficiently bring about the allocation of resources
→ (when the invisible hand doesn’t work) private markets do not efficiently bring about the allocation of resources
3
New cards
The Four Market Failures
( 1 ) Public Goods
( 2 ) Externalities (third-person side effects)
( 3 ) Imperfect Competition (monopolies)
( 4 ) Unequal distribution of income
( 2 ) Externalities (third-person side effects)
( 3 ) Imperfect Competition (monopolies)
( 4 ) Unequal distribution of income
4
New cards
Marginal Social Benefit
the demand is the MSB of the good and its usefulness to society
5
New cards
Marginal Social Cost
the supply is the MSC of providing each additional quantity
6
New cards
What is the socially optimal quantity?
where MSB = MSC
7
New cards
What are externalities?
→ a third-person side effect
→ there are EXTERNAL benefits or external costs to someone other than the original decision maker
→ there are EXTERNAL benefits or external costs to someone other than the original decision maker
8
New cards
Why are externalities market failures?
→ the free market fails to include external costs or external benefits
→ with no government involvement there would be too much of some goods and too little of others
→ with no government involvement there would be too much of some goods and too little of others
9
New cards
Negative Externalities
situation that results in a COST for a different person other than the original decision maker; the costs “spillover” to other people or society
10
New cards
What should the government do to fix a negative externality?
tax the amount of the externality (per unit tax)
11
New cards
Positive Externalities
situations that result in a BENEFIT for someone other than the original decision maker; the benefits “spillover” to other people or society
12
New cards
What should the government do to fix a positive externality?
subsidize the amount of the externality (per unit subsidy)
13
New cards
The Tragedy of the Commons
→ goods that are available to everyone (air, oceans, lakes, public bathrooms) are often polluted since no one has the incentive to keep them clean
→ there is no monetary incentive to use them efficiently
→ result is high spillover costs
→ there is no monetary incentive to use them efficiently
→ result is high spillover costs
14
New cards
Public Sector
the part of the economy that is primarily controlled by the government
15
New cards
Private Sector
the part of the economy that is run by private individuals and companies that seek profit
16
New cards
Free Riders
individuals that benefit without paying
17
New cards
Why must the government provide public goods and services?
→ it is impractical for the free-market to provide these goods because there is little opportunity to earn profit
→ this is due to the Free-Rider Problem
→ this is due to the Free-Rider Problem
18
New cards
What is wrong with Free Riders?
→ they keep firms from making profits
→ if left to the free market, essential services would be underproduced
→ to solve the problem, the government can: ( 1 ) find new ways to punish free-riders, (2) use tax dollars to provide the service to everyone
→ if left to the free market, essential services would be underproduced
→ to solve the problem, the government can: ( 1 ) find new ways to punish free-riders, (2) use tax dollars to provide the service to everyone
19
New cards
Definition of Public Goods
( 1 ) Non-exclusionary
→ cannot exclude people from enjoying the benefits (even if they don’t pay)
( 2 ) Shared Consumption (Non-rival)
→ one person’s consumption of a good does not reduce its usefulness to others
→ cannot exclude people from enjoying the benefits (even if they don’t pay)
( 2 ) Shared Consumption (Non-rival)
→ one person’s consumption of a good does not reduce its usefulness to others
20
New cards
Antitrust Laws
laws designed to prevent monopolies and promote competition
21
New cards
Why would the government regulate a monopoly?
( 1 ) to keep prices low
( 2 ) to make monopolies efficient
( 2 ) to make monopolies efficient
22
New cards
How does the government regulate a monopoly?
price ceilings (taxes don’t work because they limit supply which is the problem)
23
New cards
Where should the government place the price ceiling?
( 1 ) Socially Optimal Price
→ P=MC (allocative efficiency)
( 2 ) Fair-Return Price (Break-Even)
→ P=ATC (normal profit)
→ P=MC (allocative efficiency)
( 2 ) Fair-Return Price (Break-Even)
→ P=ATC (normal profit)
24
New cards
Natural Monopoly
one firm can produce the socially optimal quantity at the lowest cost due to economies of scale
25
New cards
Per Unit Tax/Subsidy
affects the variable costs so MC, AVC, and ATC will shift
→ this WILL affect the quantity produced
→ this WILL affect the quantity produced
26
New cards
Lump Sum Tax/Subsidy
only affects fixed costs and so only AFC and ATC will shift
→ WILL NOT affect the quantity produced
→ WILL NOT affect the quantity produced
27
New cards
Why does the government tax?
( 1 ) Finance government operations
→ public goods-highways, defense, employee wages
→ fund programs → welfare, social security
( 2 ) Influence the economic behavior of firms and individuals
→ EX. excise taxes on tobacco raises tax revenue and discourages the use of cigarettes
→ public goods-highways, defense, employee wages
→ fund programs → welfare, social security
( 2 ) Influence the economic behavior of firms and individuals
→ EX. excise taxes on tobacco raises tax revenue and discourages the use of cigarettes
28
New cards
Three Types of Taxes
( 1 ) Progressive Taxes
( 2 ) Proportional Taxes (flat rate)
( 3 ) Regressive Taxes
( 2 ) Proportional Taxes (flat rate)
( 3 ) Regressive Taxes
29
New cards
Progressive Taxes
takes a larger percent of income from high income groups (takes more from rich people)
30
New cards
Proportional Taxes (flat rate)
takes the same percent of income from all income groups
31
New cards
Regressive Taxes
takes a larger percentage from low income groups (takes more from poor people)
32
New cards
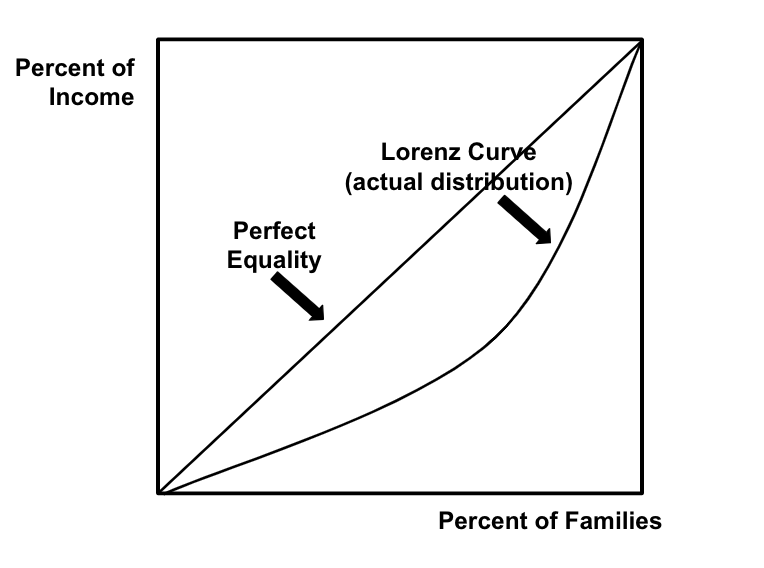
The Lorenz Curve