Aquatic Entomology Lecture 5 - Reproduction and Mating behavior
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
# of eggs carried
Potential fecundity
Ability to produce egg or sperm
Sexual Maturation
Timeline (Organisms (3))
Time it takes to mature
odonates: days-weeks
mayflies/stoneflies: hours
Two variables that affect sexual maturation and fecundity
Temperature: Abiotic
Resources: Food, space
Need to eat prior to laying eggs
Anautogenous
Do not need to eat prior to laying eggs (+ why)
Autogenous, bc of resource limitation
What do insects do when food resources scarce
Catabolize their own body
breakdown flight muscles
Cannibalize their own eggs
Corixidae, Dysticidae
Where do insects mate?
In the air, on the ground, on water surfaces
Swarms
Group of same species that come together
Swarms
How can swarms form
Really short-lived insects
Mostly males
Low density
Communication in mating systems (4)
Vision
Vibrational signals
Sound communication
Chemical

Vision (organism)
allows organism to find own species and correct sex (dimorphism)
organism: dragonflies

Vibrational signals (Organisms (2))
strikes substrates which causes vibration
organism
stonefly —> vibration on surface
toe-biters —> creates waves in water

Sound communication (organism)
organism: water boatman
Males creates several sounds
Females create one

Chemical (organism)
Releases pheromone
chemoreceptors in antennae pick up pheromones to attract mates
organism: stonefly
After finding a mate what happens? (2, 1)
Where: in the air, on the ground, on the water surface
1.) Copulation
2.) Sperm transfer
Then either fertilization or reproduction again
Copulation
when genitals connect
Sperm transfer
packaged as spermatophore
sperm can be in it
sperm can be divided from non-sperm protein part
term for when females reproduce again
Polyandry
term for when males reproduce again
Polygyny

male is transferring sperm from posterior to anterior abdomen

male is transferring sperm to female
Males remain with femauls after mating
Male gaurding
Males insert fluid in female genital hole, fluid hardens
Mating plug

Intersexual arm race concept (organism)
Organism: Dytiscidae
Males: suction pads
Females: striations on elytra
Insect growth stage
Exoskeleton prevents too much growth without molting
Each time insects molt
New instar (stadia)
Types of immature
Nymphs
Larvae
Types of Larvae (8)
Oligopodous
Campodeiform
Scarabaeiform
Polypodous
Apodous
Eucephalous
Hemicephalus
Acephalous
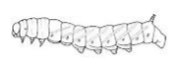
Type of larva: 3 pair jointed, well developed legs
Oligopodous
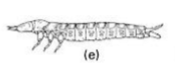
Type of larva: 3 pair jointed, well developed legs + dorsal-ventrally flattened
Campodeiform
Type of larva: 3 pair jointed, well developed legs + NOT dorsal-ventrally flattened
Scarabaeiform
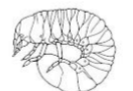
Type of larva: well-developed head capsules, 3 pairs of small legs
Polypodus
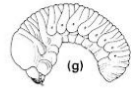
Type of larva: lacks leg
Apodous

Type of larva: lacks leg + well developed head capsule
Eucephalous

Type of larva: lacks legs + reduced head capsule
Hemicephalus

Type of larva: lacks legs + lack head capsule
Acephalous
Molting process (7 steps)
Under endocrine and nervous control
1.) Epidermal cells separate from cuticle
2.) Epidermal cells undergo mitosis
3.) Molting fluid released in gap between cuticle and epidermal cells
4.) Form new cuticle
5.) Molting fluid break downs old cuticle
6.) Molting fluid reabsorbed
7.) Ecdysis occurs
What is pupal stage and what are the types (2)
Little movement and non-eating stage
Types: Exarate and Obtect
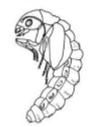
type of pupae: legs and wings are free
exarate
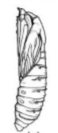
type of pupae: wings are glued down
obtect
Environmental influences on number of generations per year (5)
1.) Temperature
2.) Photoperiod
3.) Water chemistry
4.) Food resources
5.) Biotic Resources
# of generations per year
one generation per year
Univoltine
two generations per year
Bivoltine
3 or more generations per year
Multivoltine
More than 1 year per generation
Semivoltine
What do insects do when habitats become inhabitable (3)
Dormancy
Quiescence
Diapause
state of suppressed development
Dormancy
immediate response to limiting environmental factors
quiescence
programmed into lifecycle
Diapause
Diapause phases controlled by hormones (3)
Pre Diapause (larva)
Diapause (pupa)
Diapause Termination (adult)