15- Anterior & Medial Thigh
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
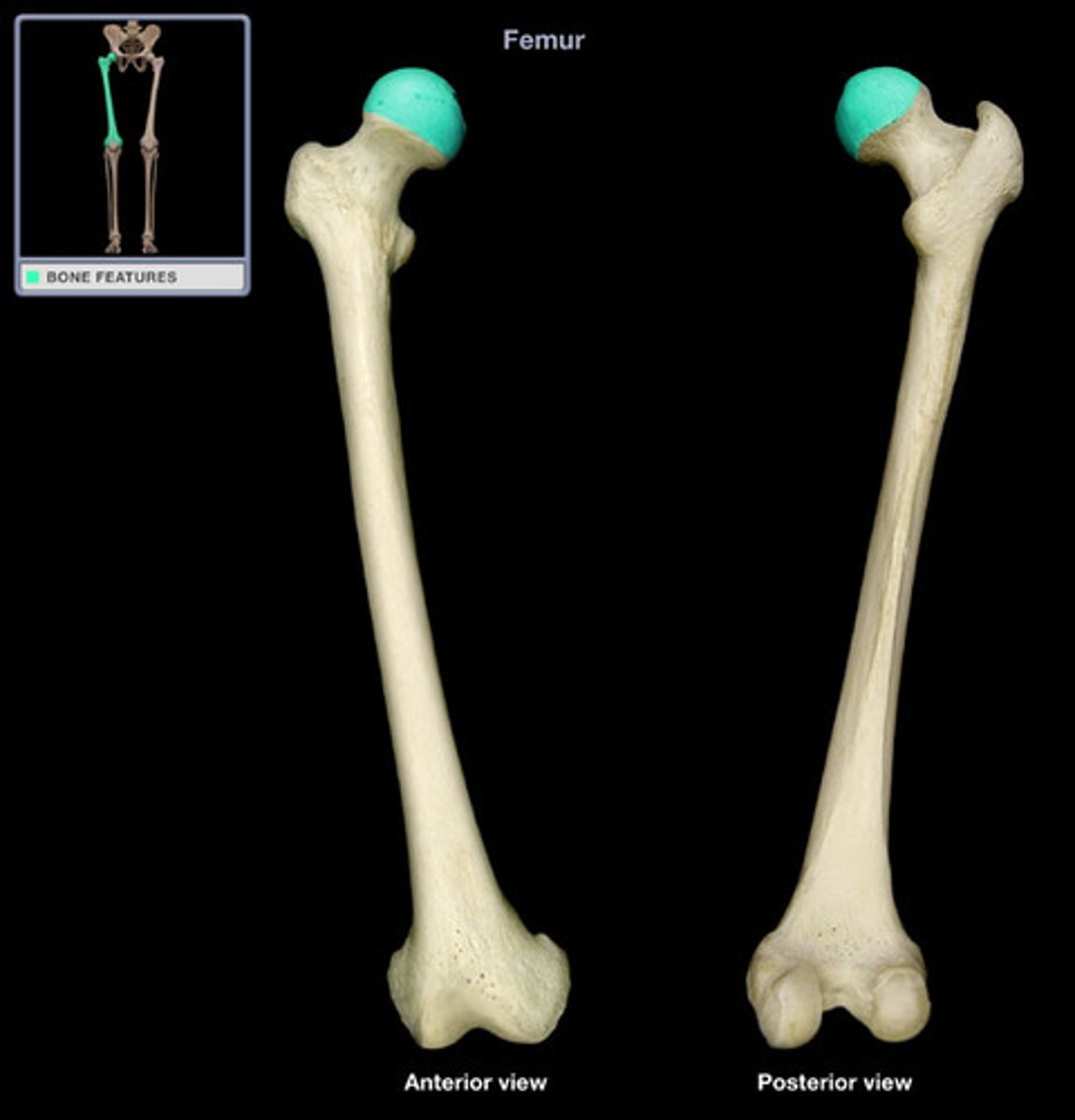
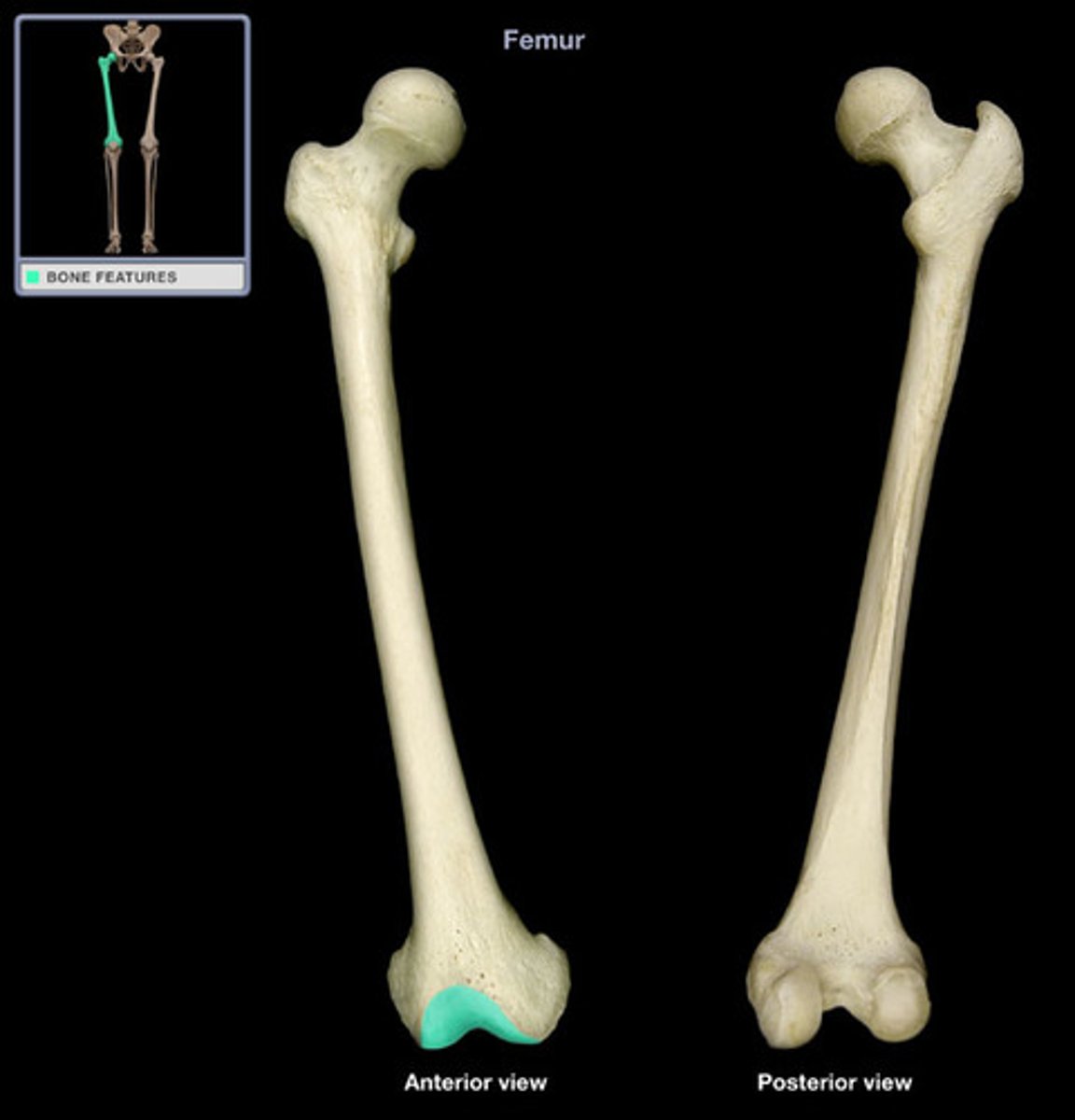
head of femur
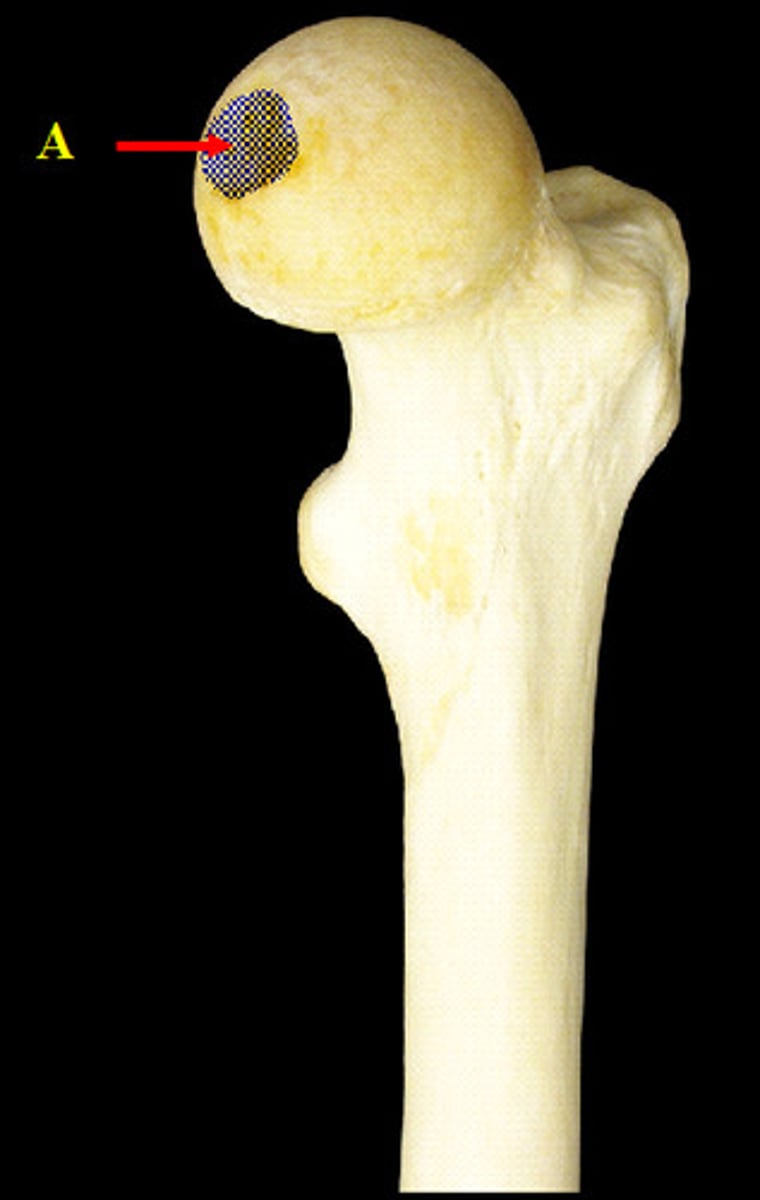
fovea of femur
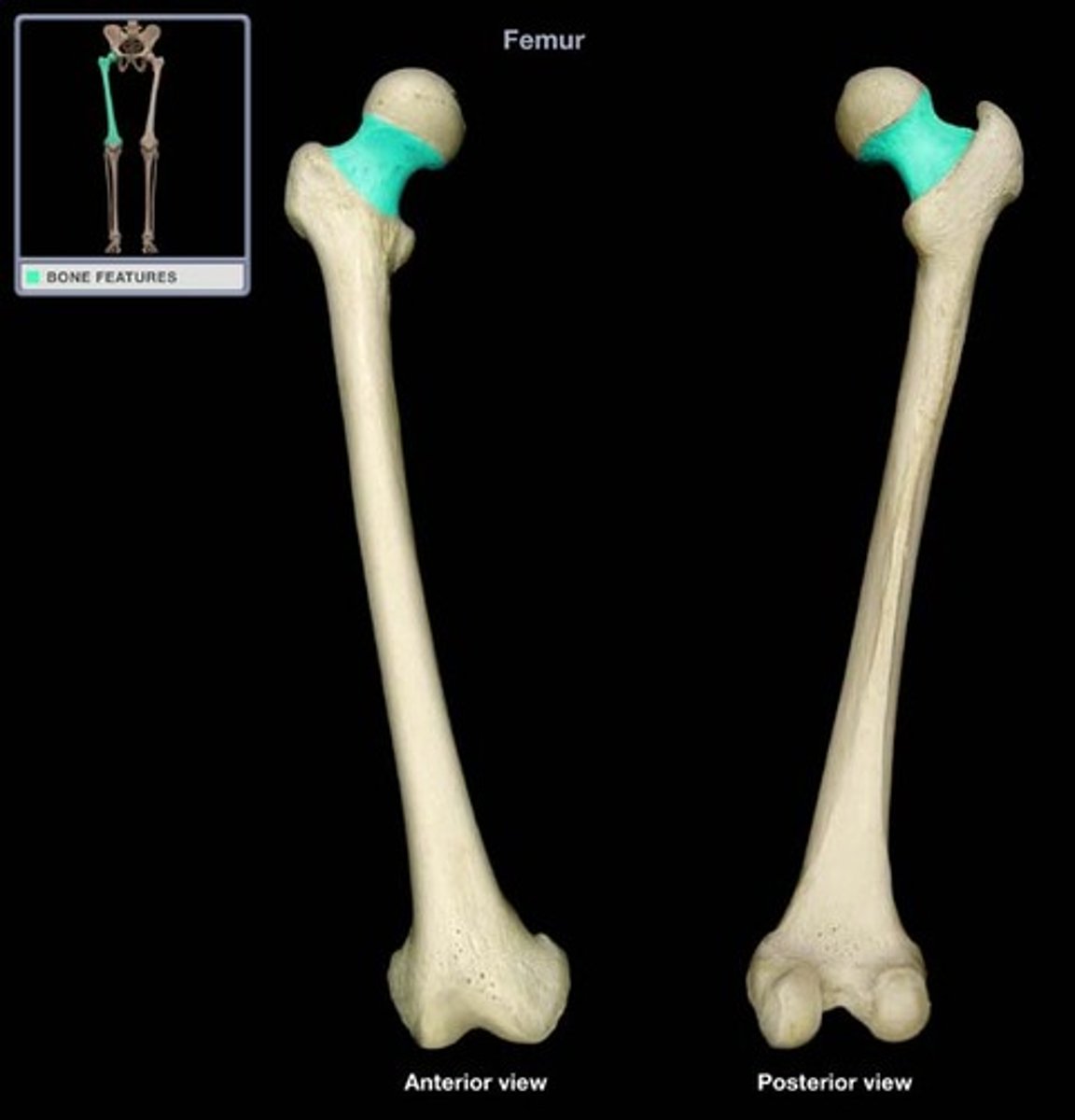
neck of femur
greater trochanter of femur
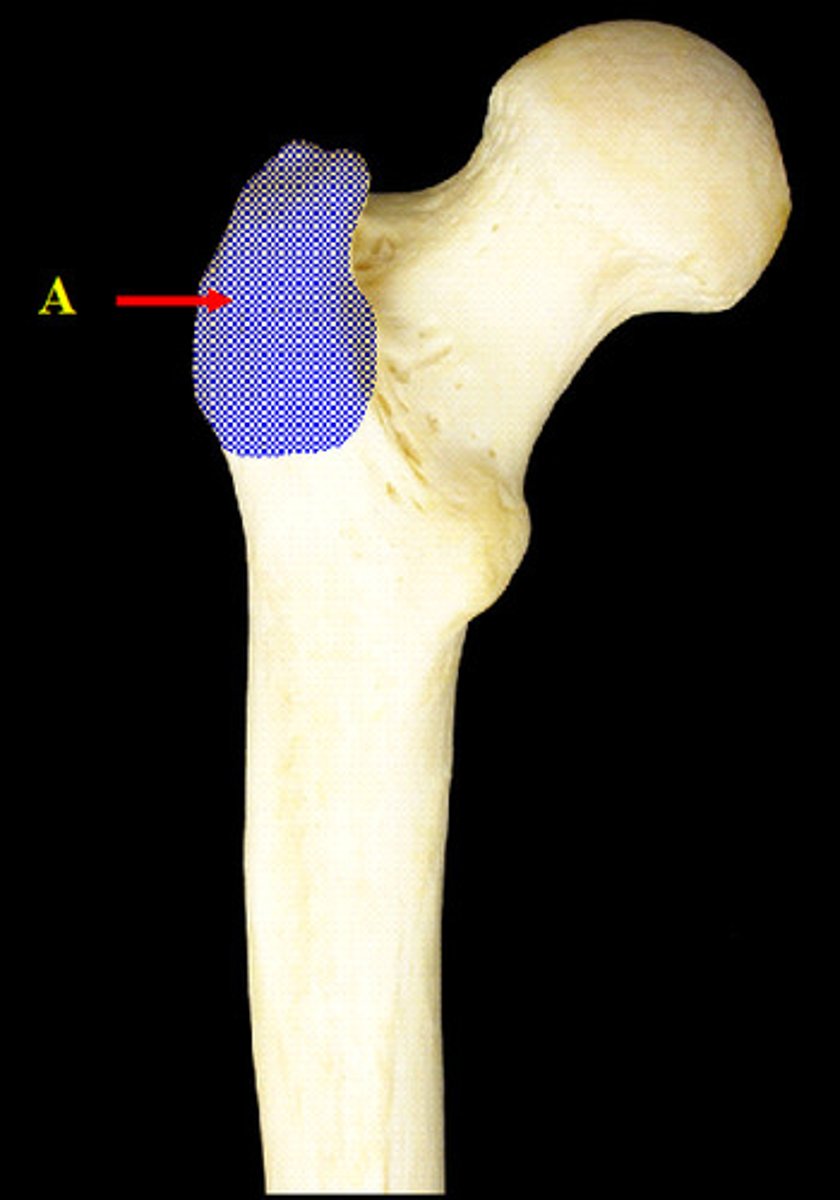
lesser trochanter of femur
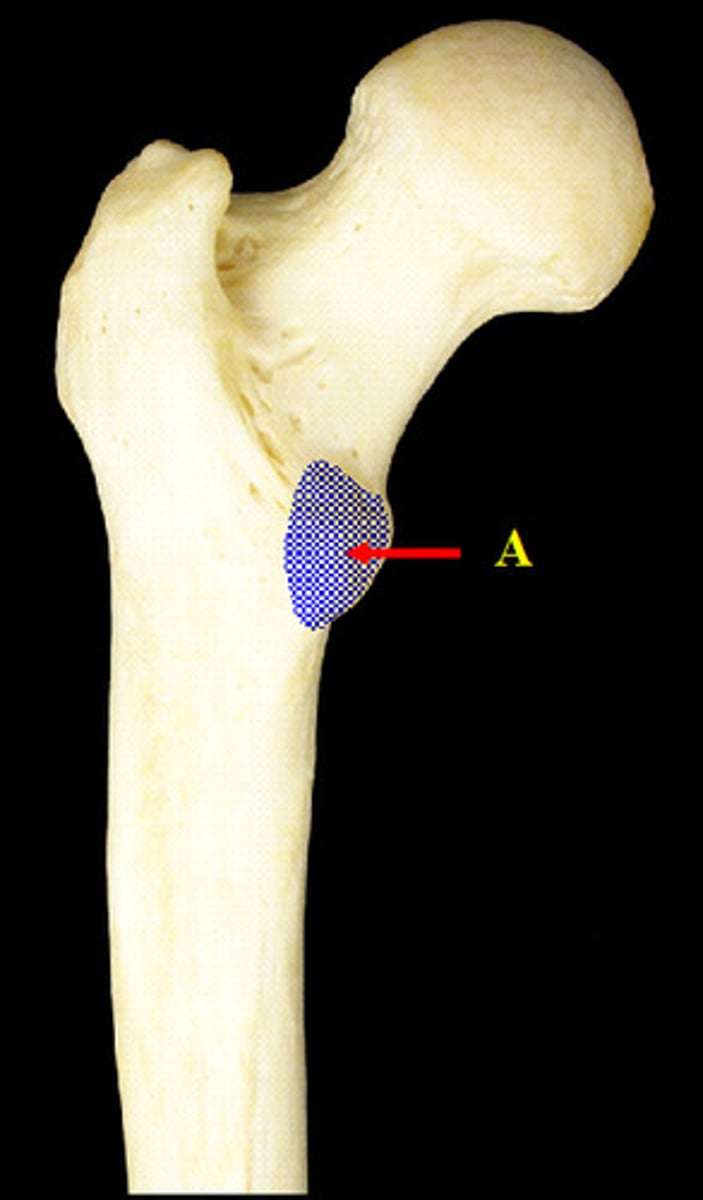
intertrochanteric line
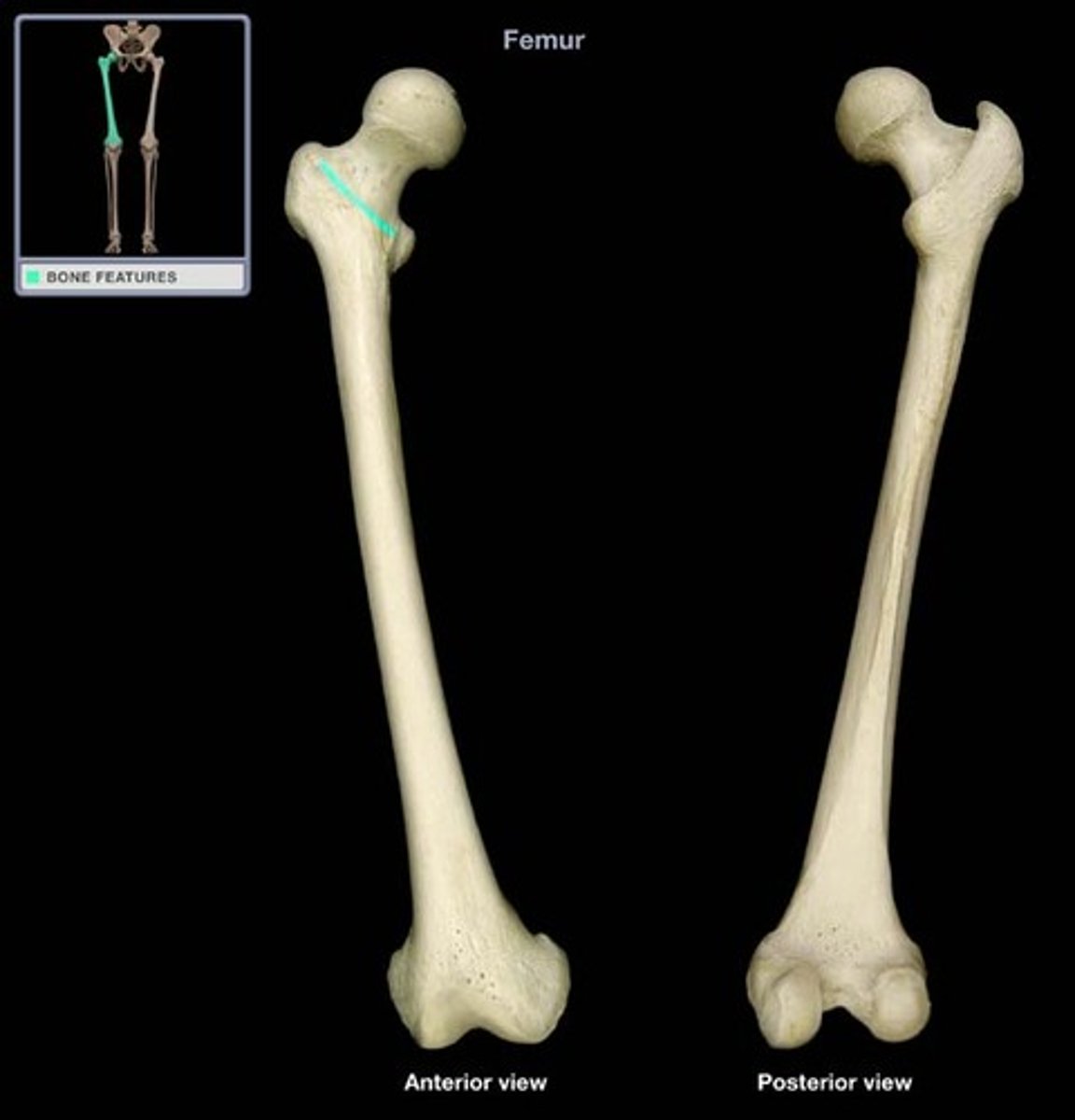
intertrochanteric crest
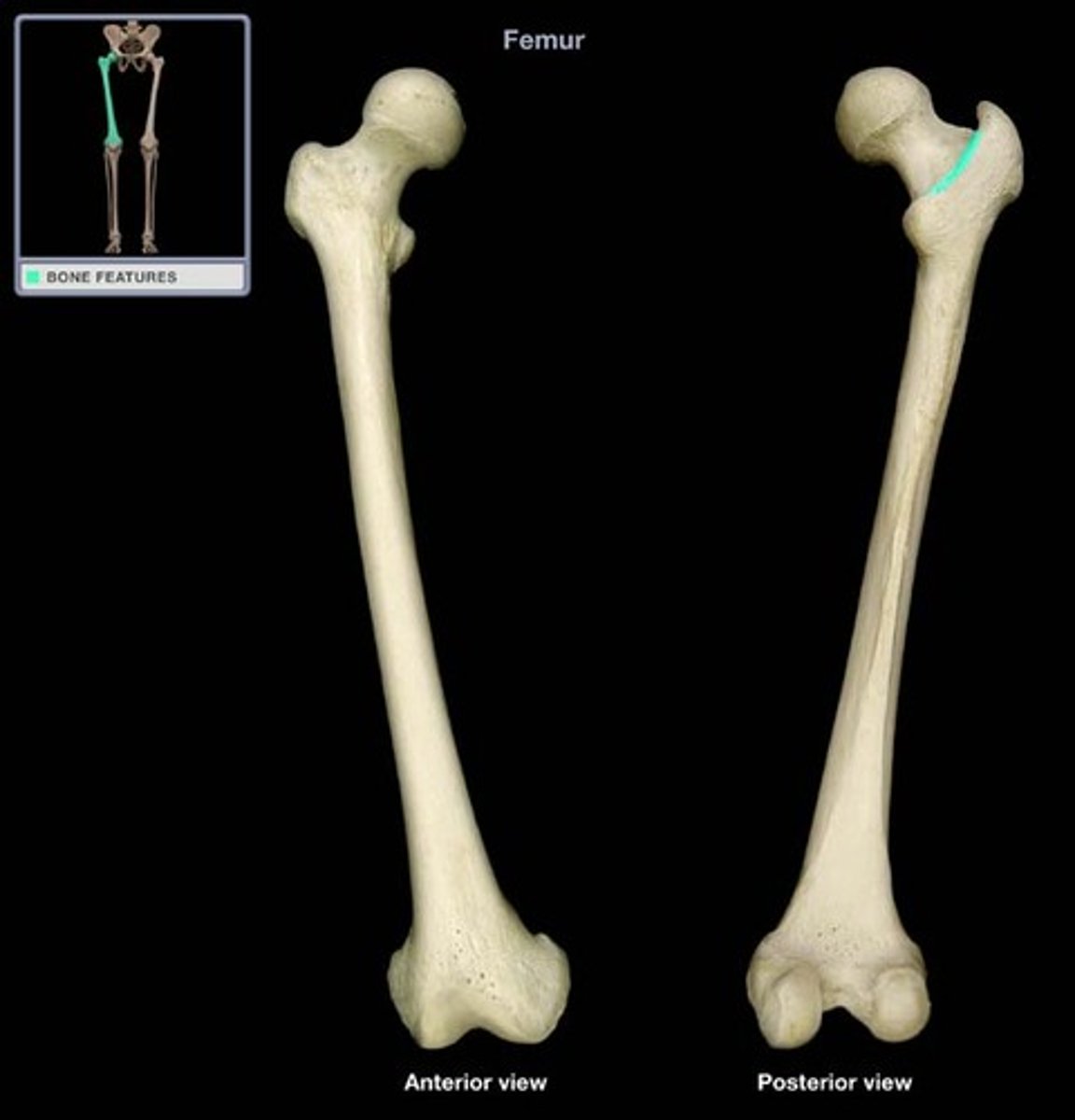
quadrate tubercle of femur
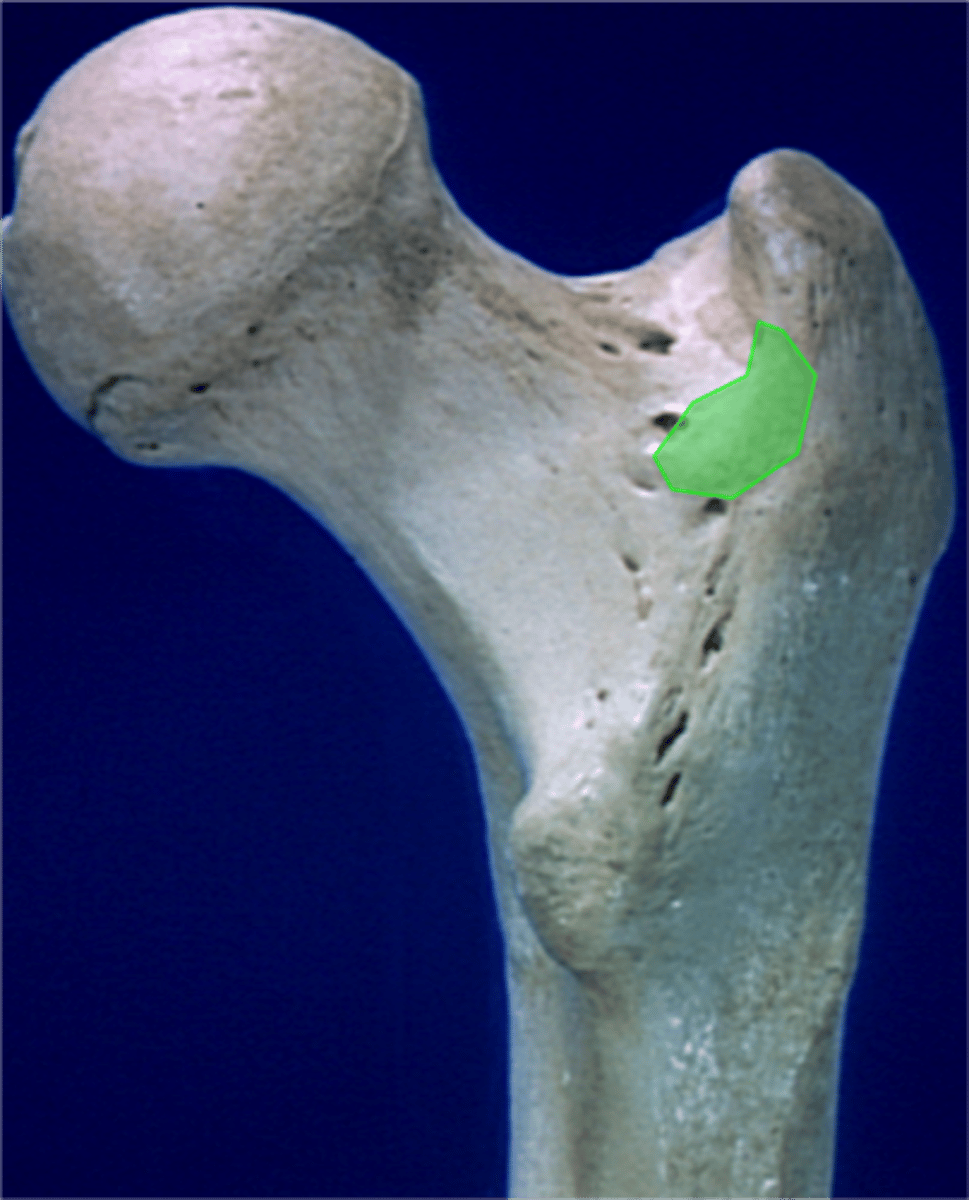
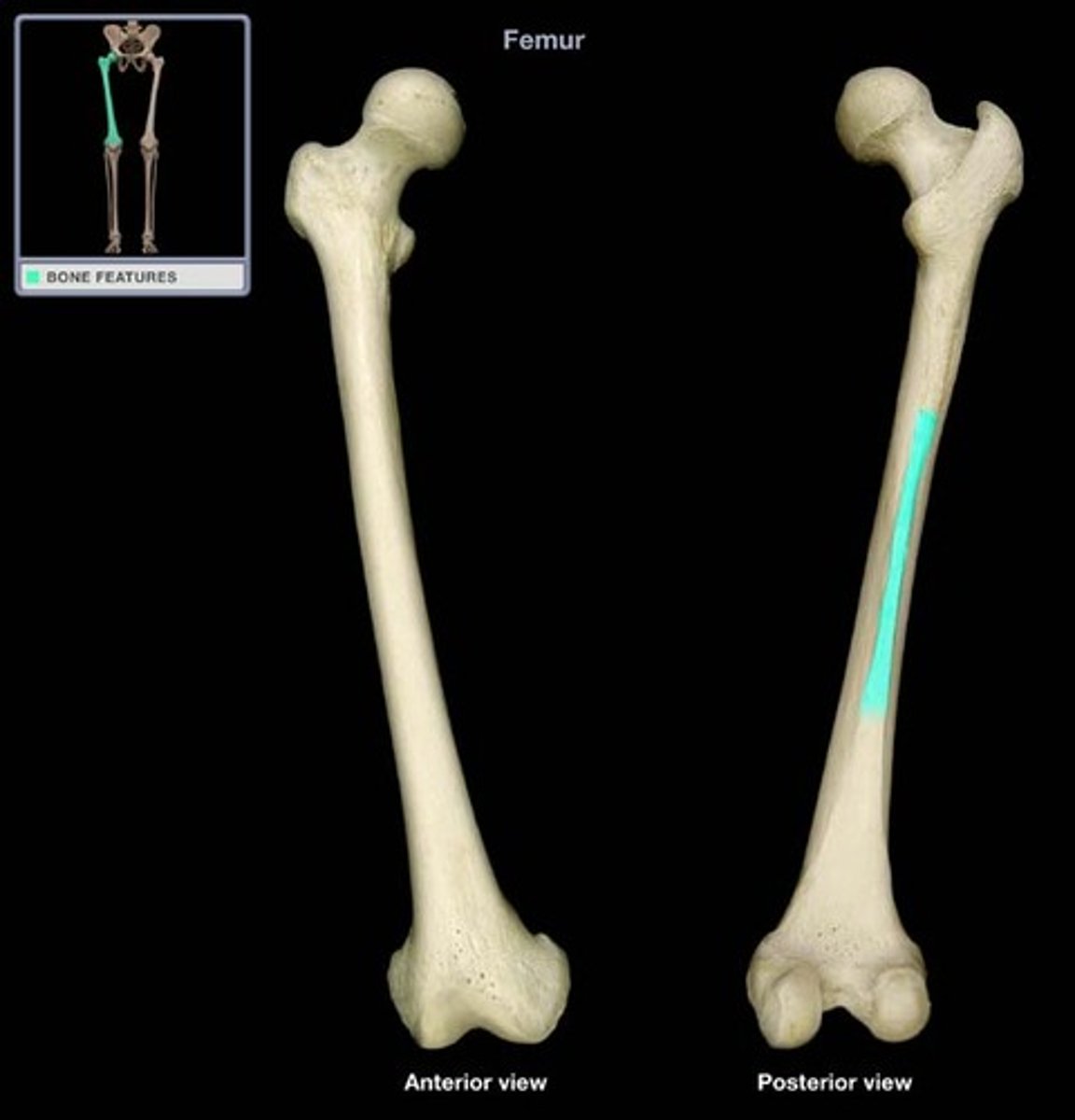
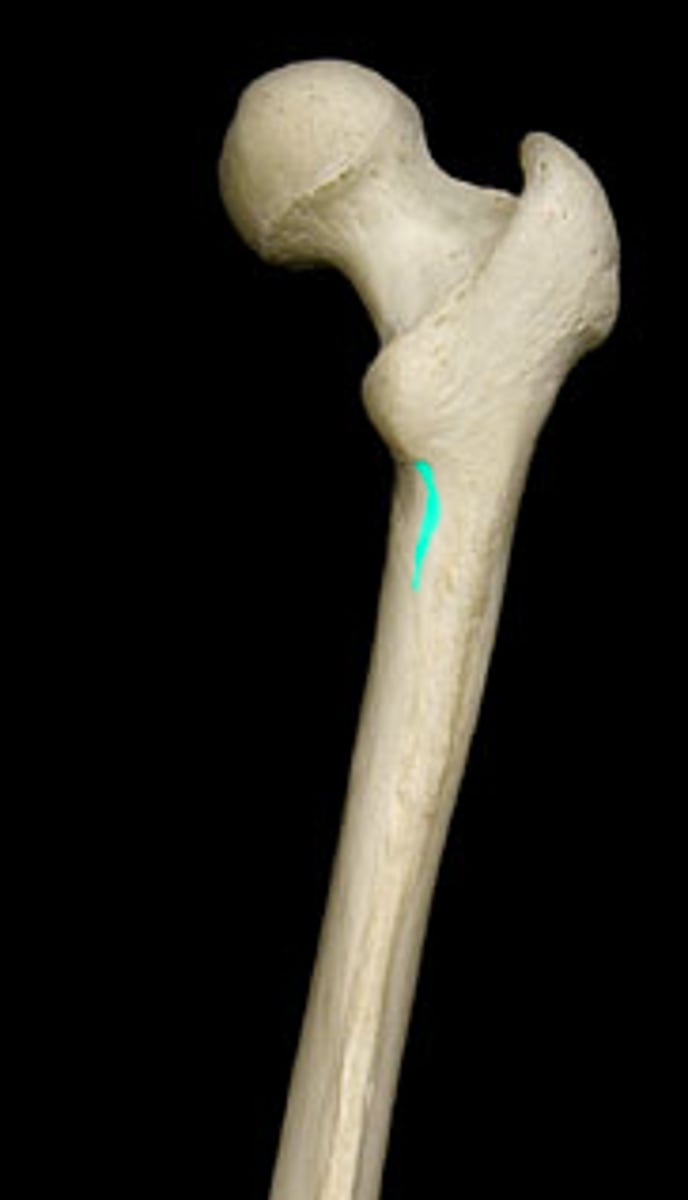
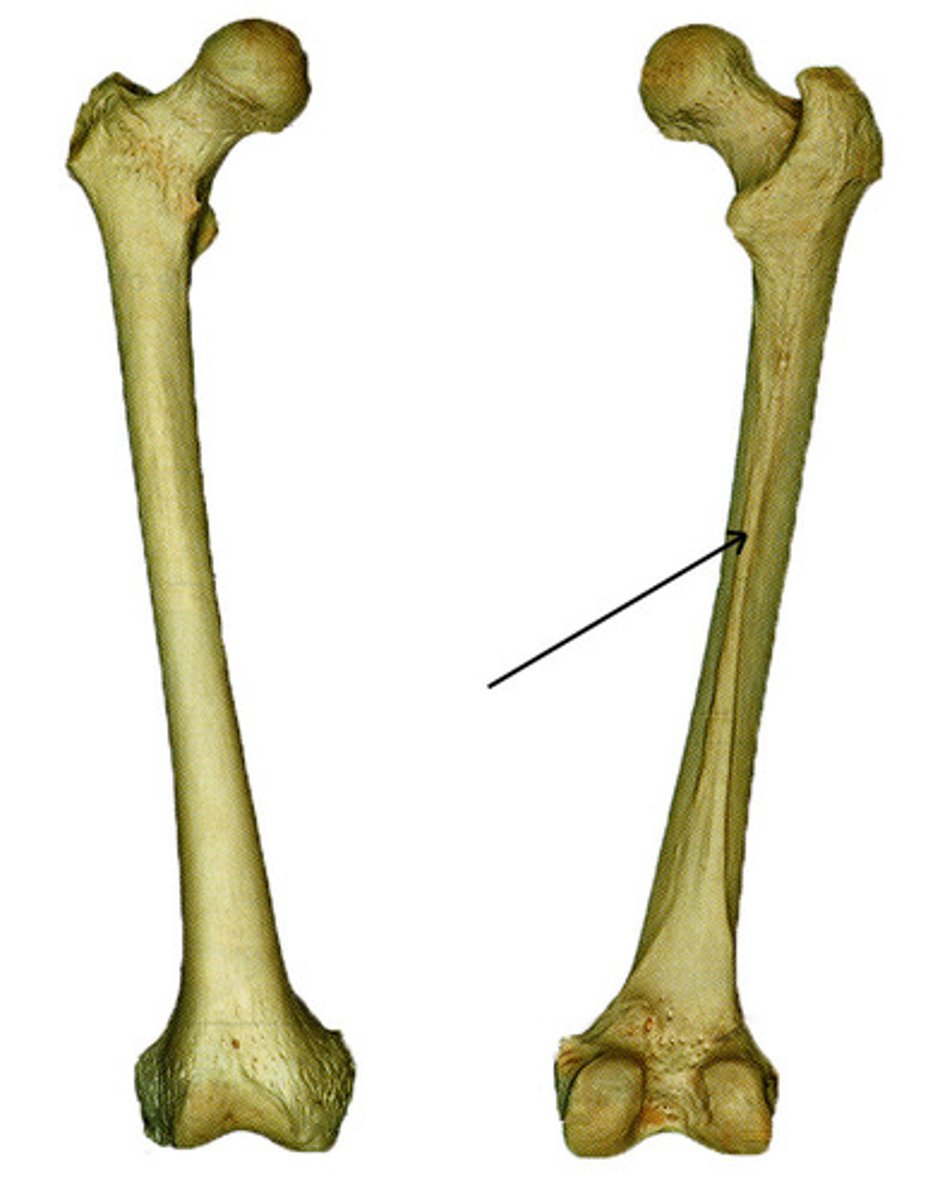
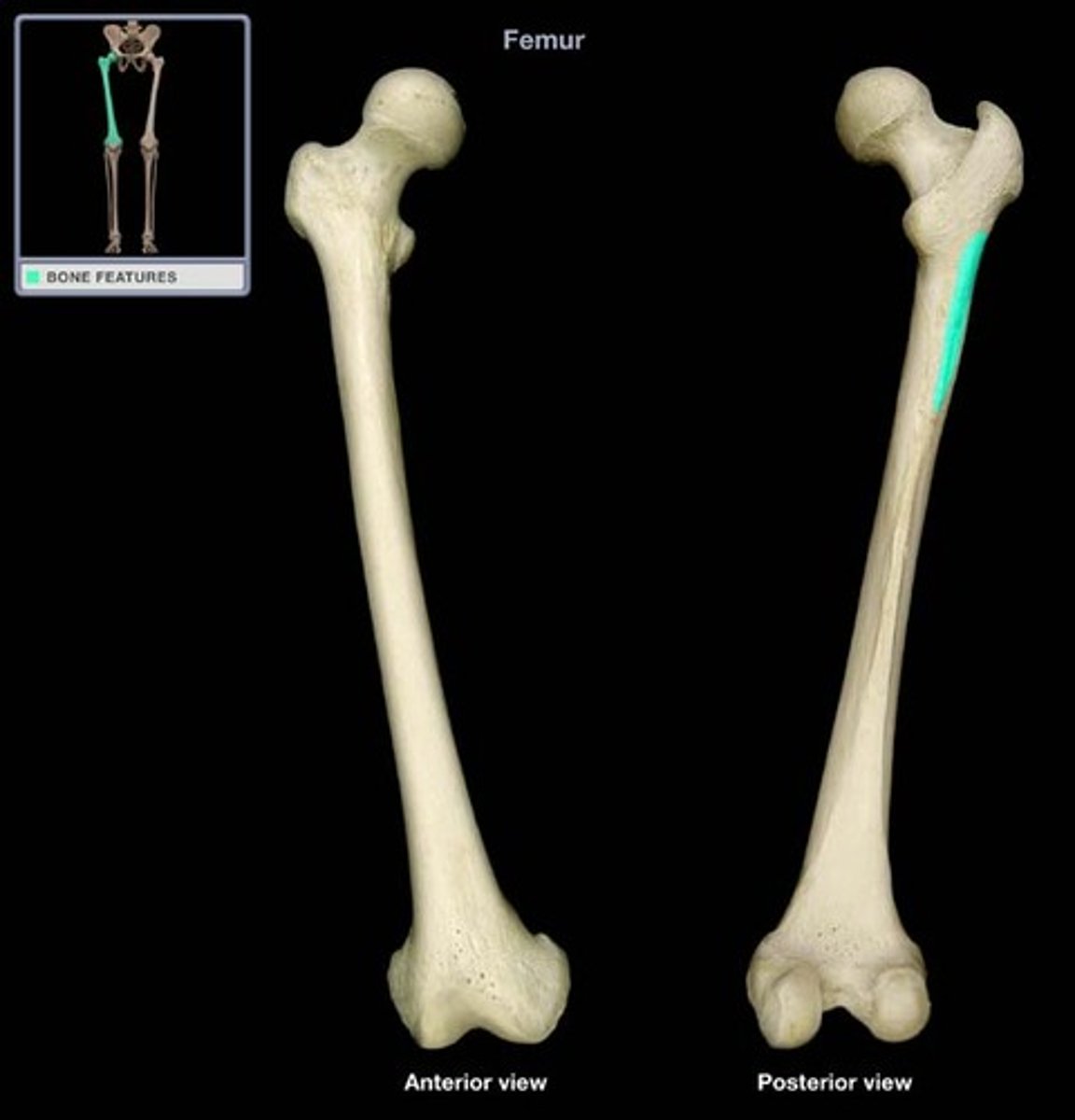
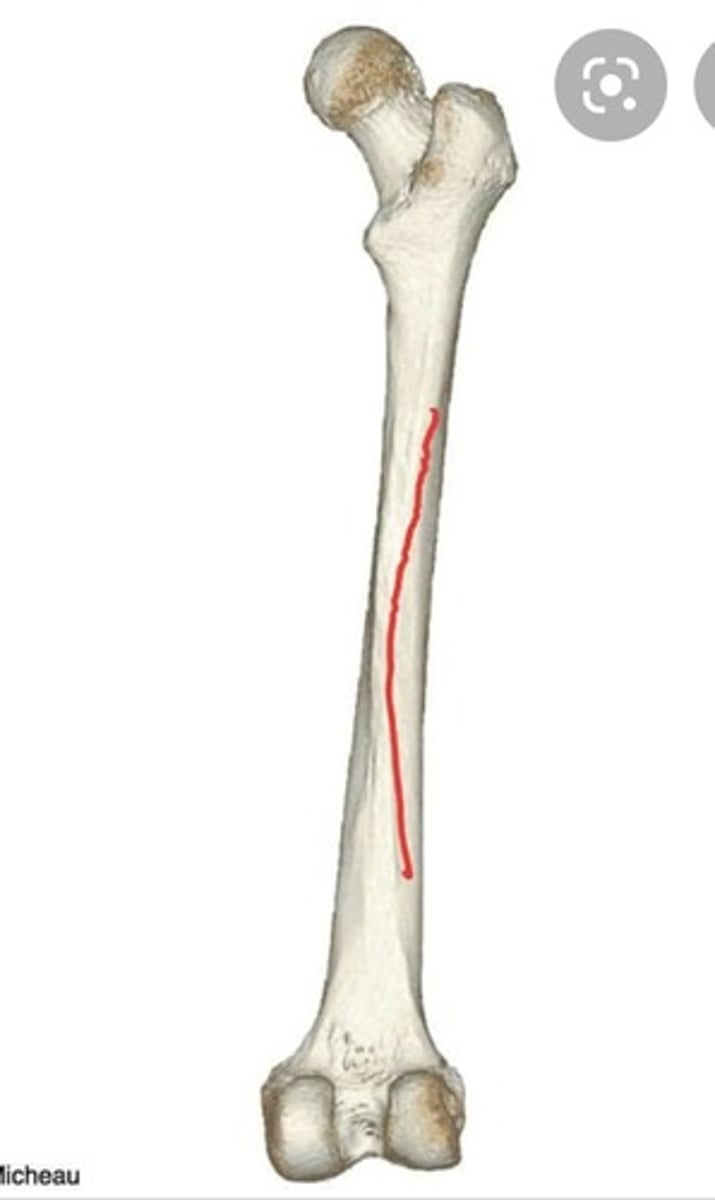
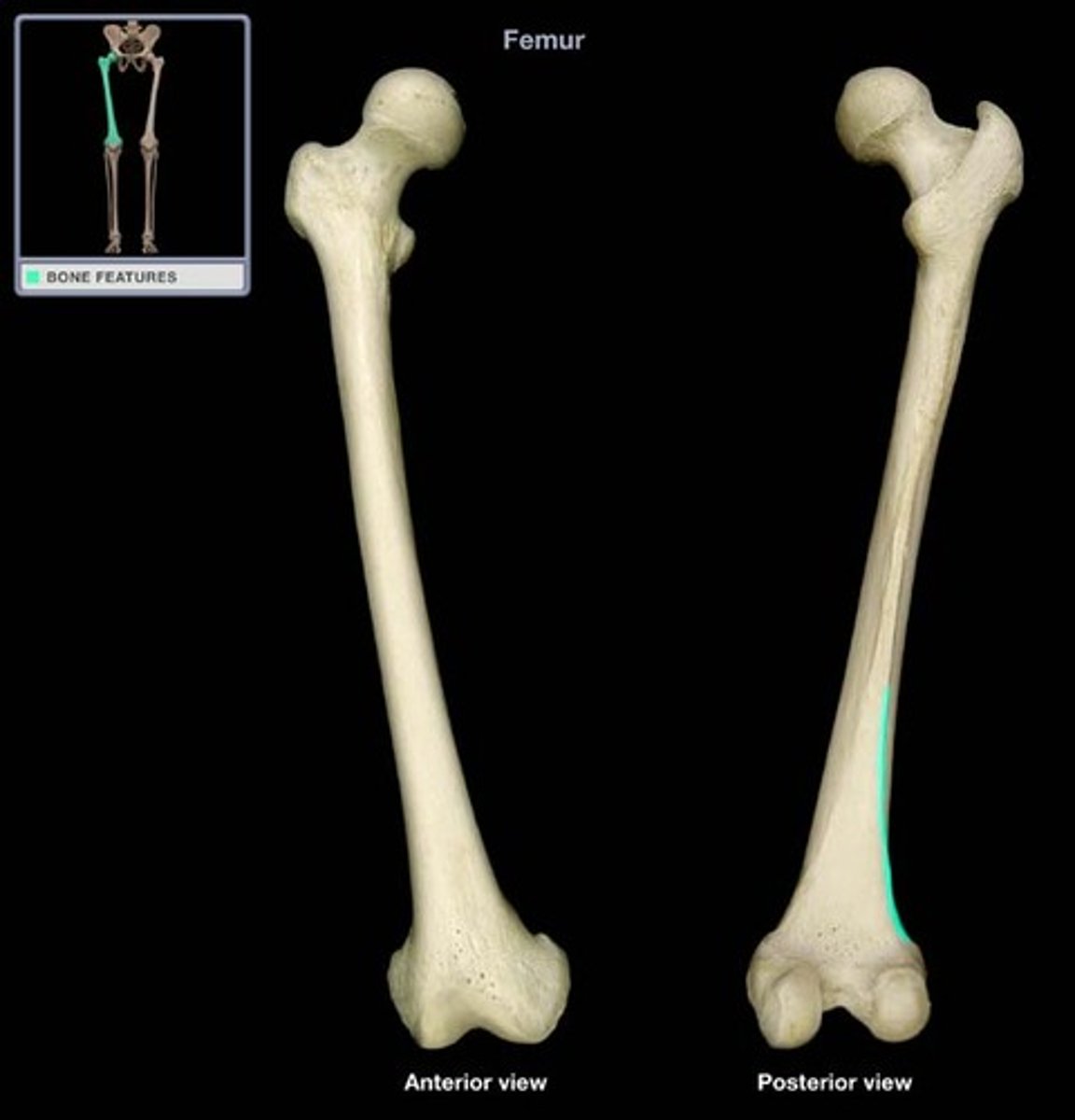
linea aspera of femur
pectineal line of femur
medial lip of linea aspera
medial supracondylar line of femur
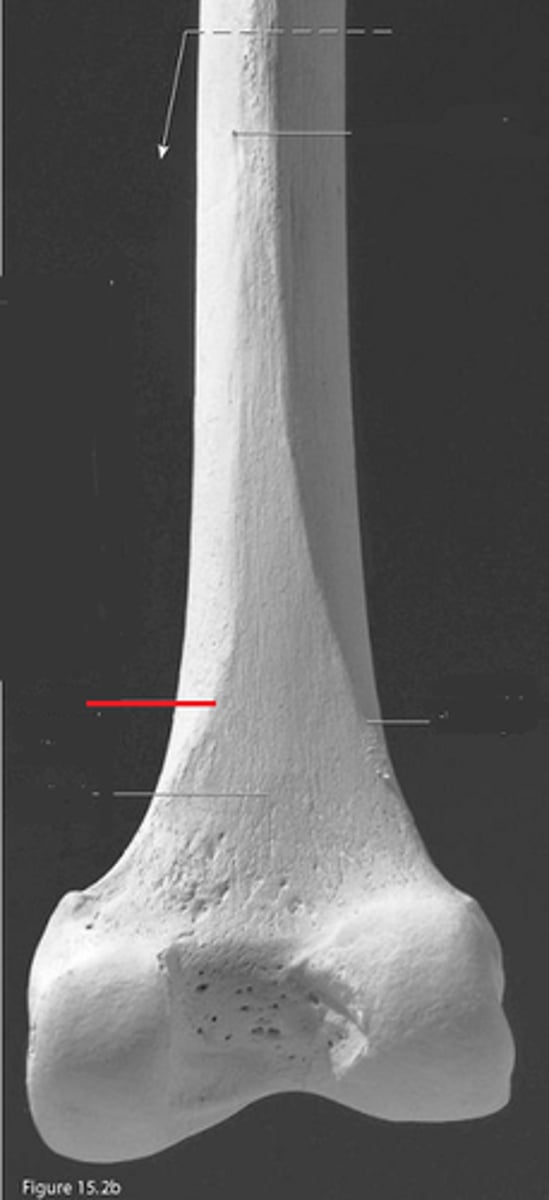
gluteal tuberosity of femur
lateral lip of linea aspera
lateral supracondylar line of femur
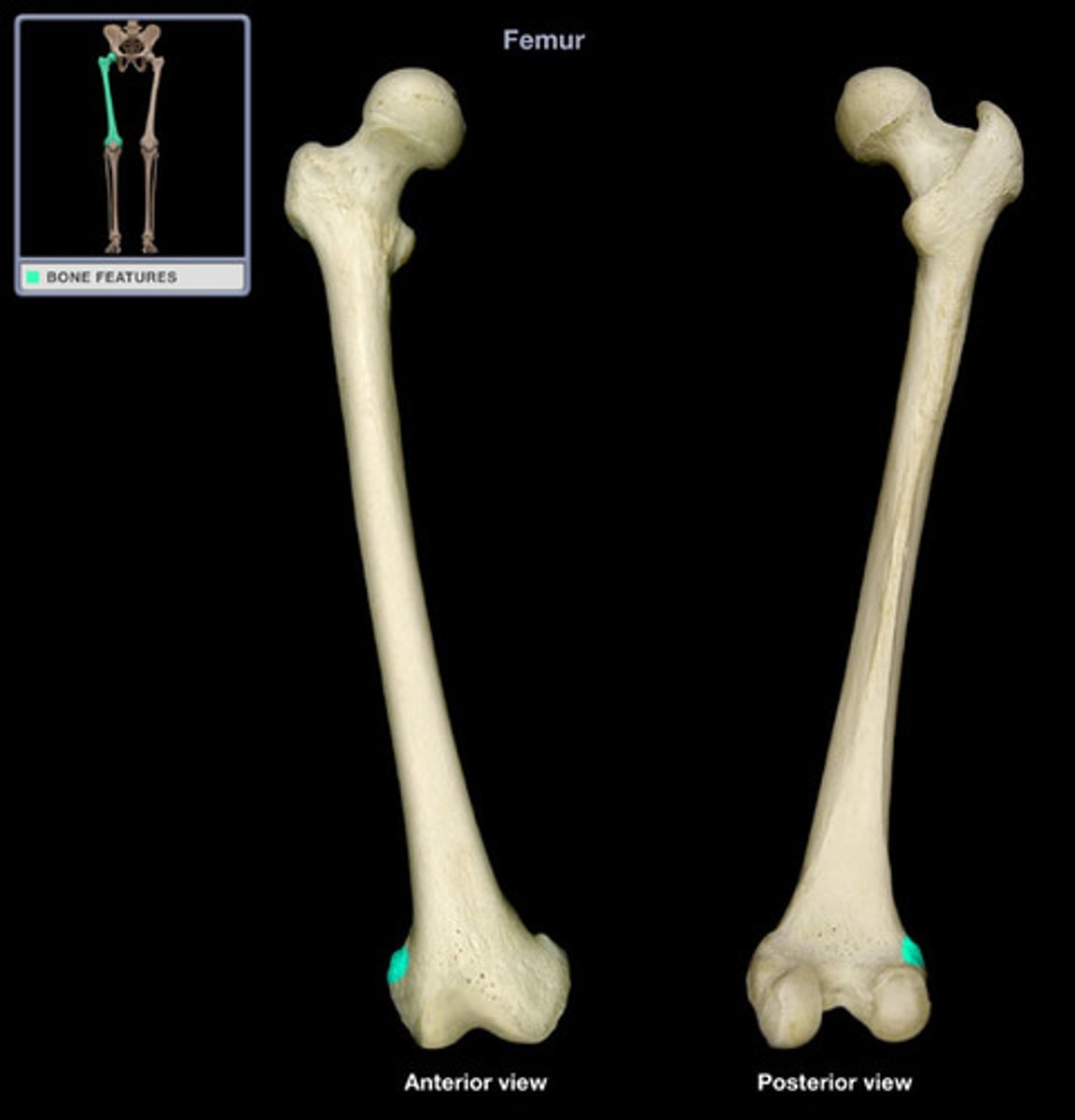
medial condyle of femur
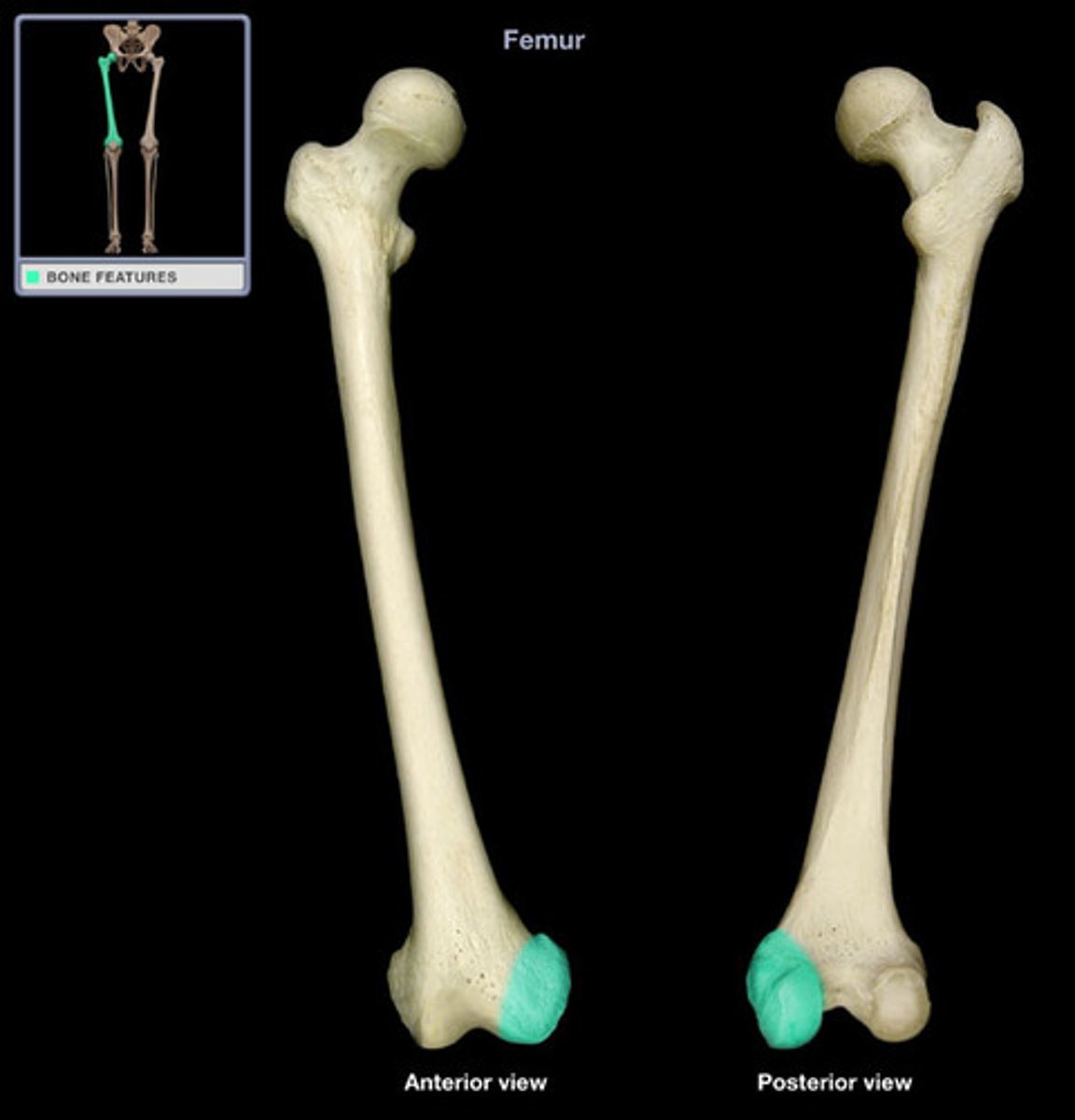
medial epicondyle of femur
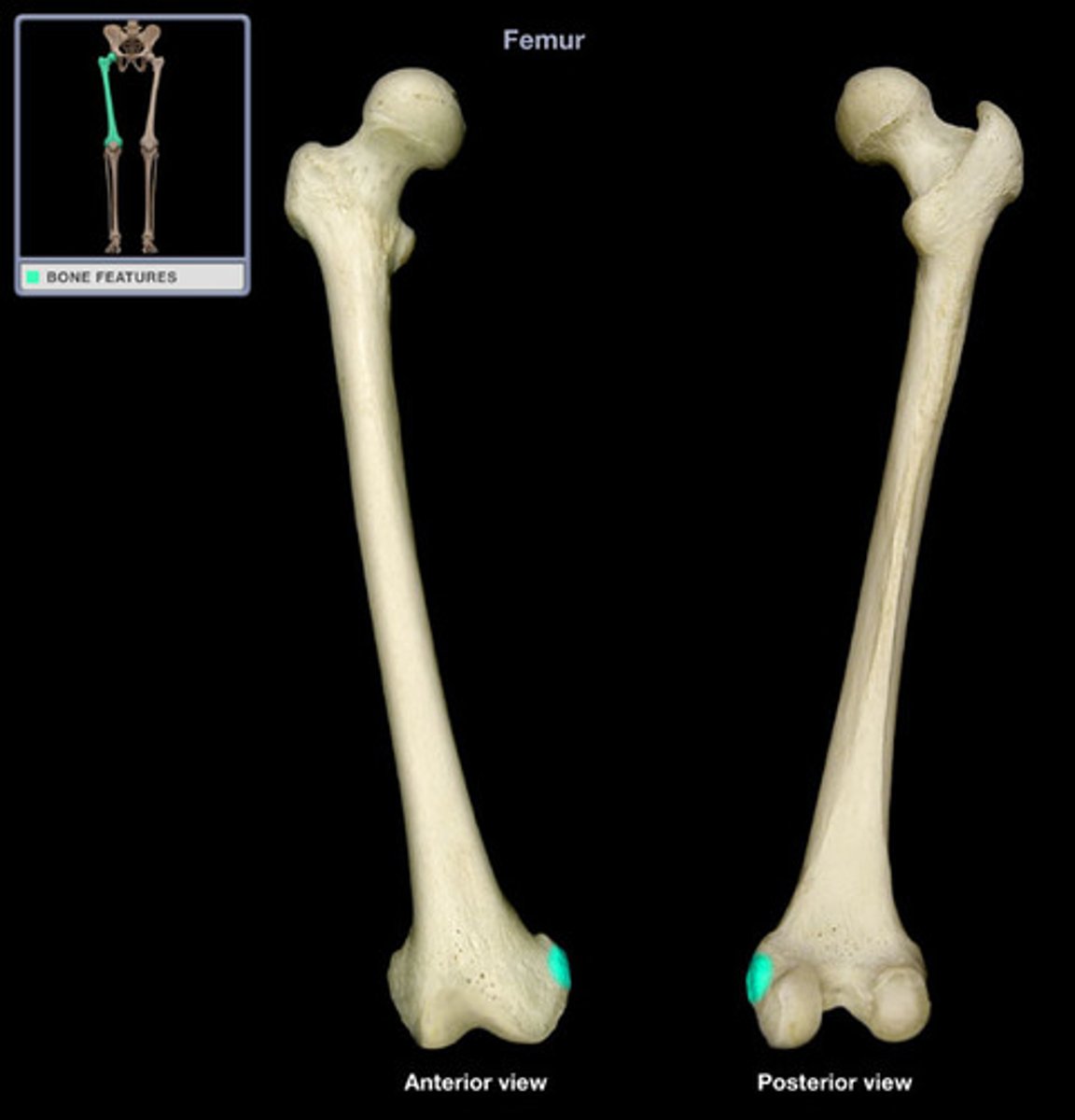
adductor tubercle of femur
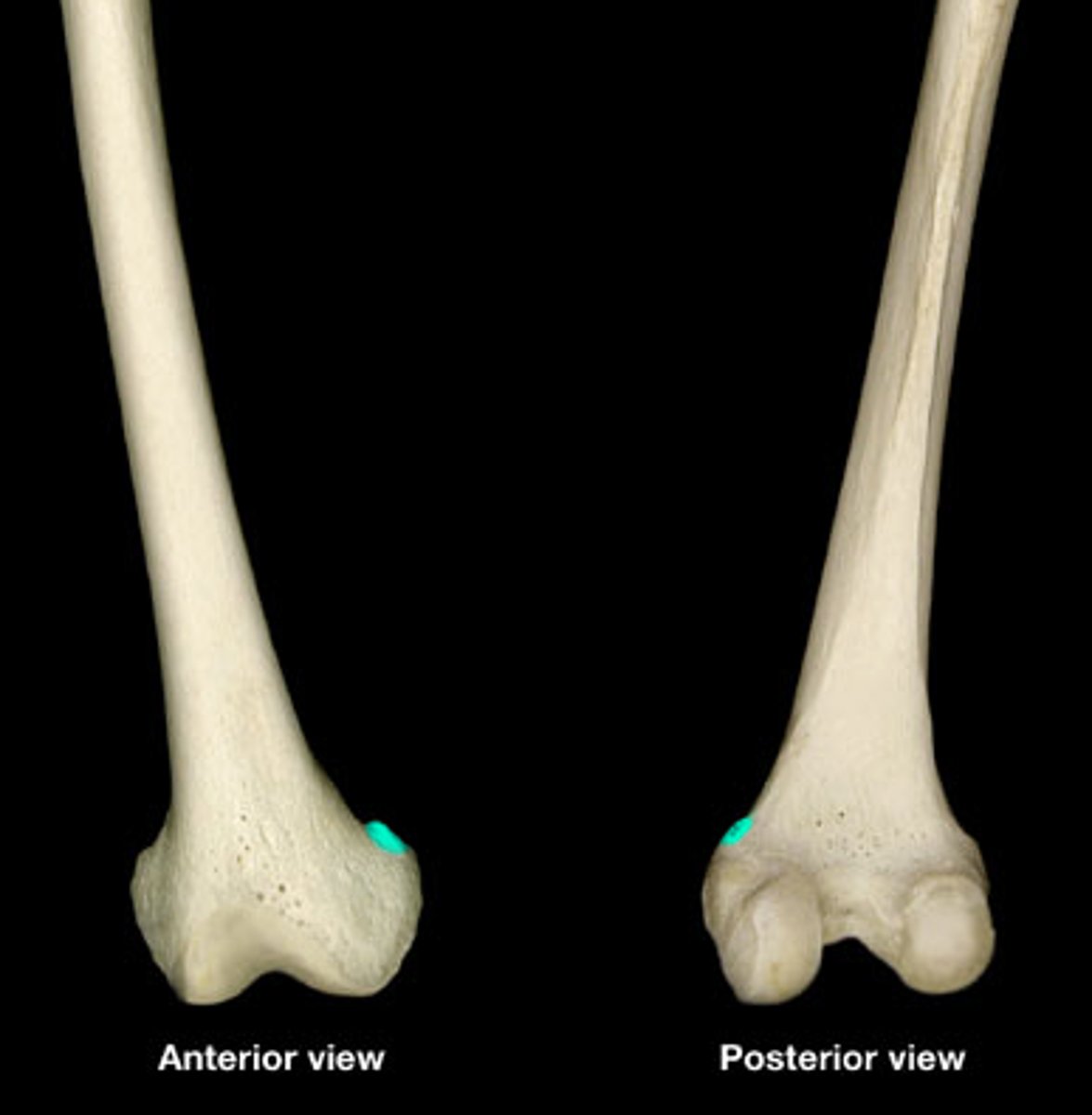
tibial articular surface of femur
lateral condyle of femur
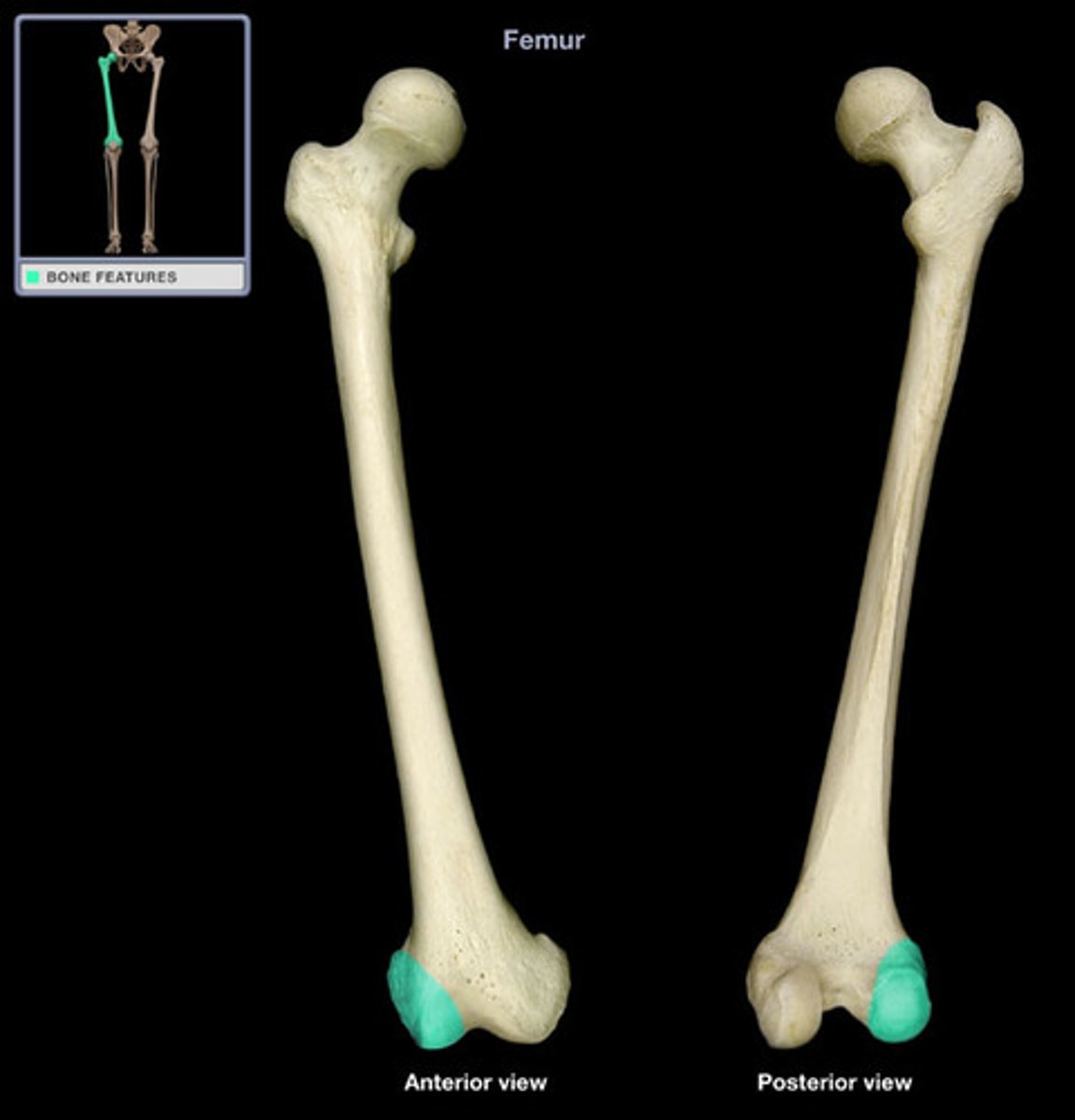
lateral epicondyle of femur
tibial articular surface
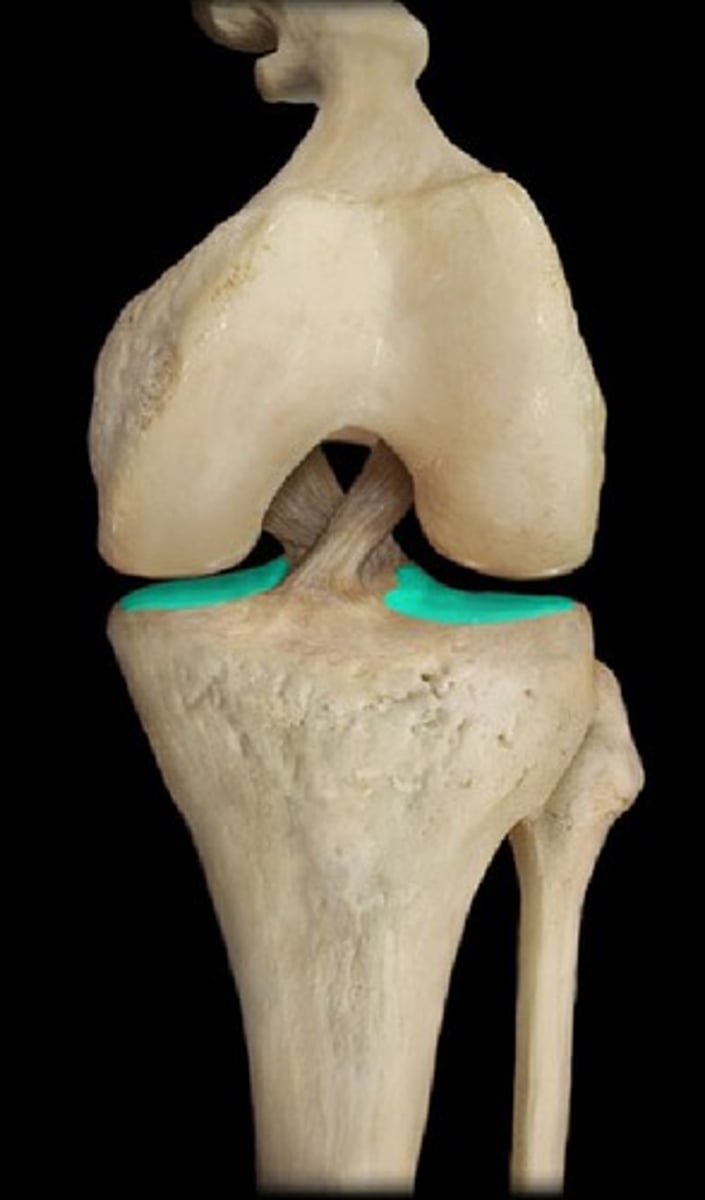
intercondylar fossa of femur
patellar articular surface of femur
superficial fascia of hip and thigh
-continuous with fascia from the inferior part of the anterolateral abdominal wall and buttocks
-loses its fat anteriorly and laterally and blends with the deep fascia
fascia lata
-limits outward extension of contracting muscles-->compresses veins to push blood towards the heart and make muscular contractions more efficient
anterior, medial, posterior
3 fascial compartments of the fascia lata
intermuscular septa
-attach to linea aspera on posterior femur
-lateral is strongest and continuous with fascia lata
saphenous opening
-gap in the fascia lata inferior to the medial part of the inguinal ligament
-great saphenous vein and lymphatic vessels pass through to enter femoral vein
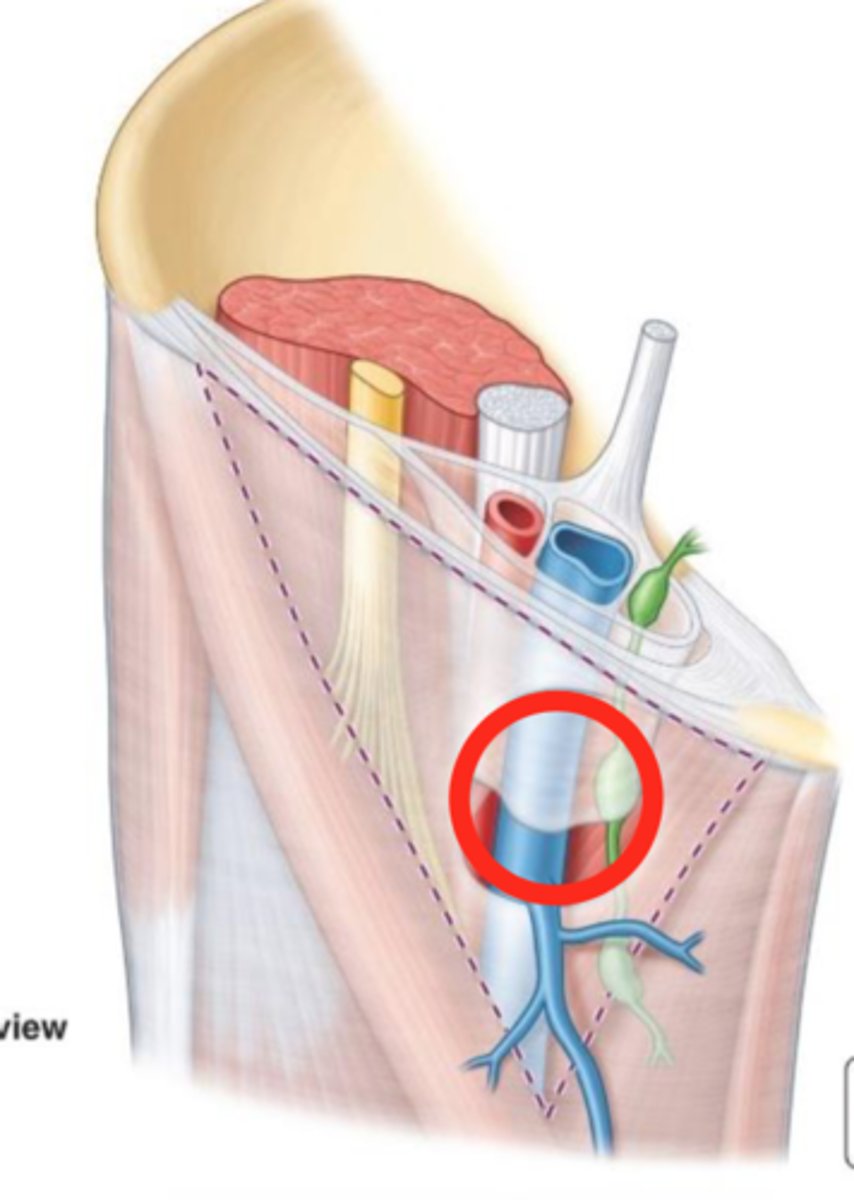
great saphenous vein and lymphatic vessels
What is in the saphenous opening?
cribiform fascia
localized membrane layer of subcutaneous tissue that encloses the saphenous opening
crural fascia
-deep fascia
-continuous with fascia lata and attaches to anterior and medial borders of tibia and periosteum
-thick in proximal part of anterior aspect of leg--> forms part of proximal attachments of underlying muscle
extensor retinaculum
contains tendons as they descend along the anterior tibia into the ankle/foot
anterior and posterior intermuscular septa
-pass from deep surface of crural fascia
anterior, posterior, lateral
3 fascial compartments of the lower leg
transverse intermuscular septum
divides plantarflexor muscles in the posterior compartment into superficial and deep
great saphenous vein
-in subcutaneous tissue
-numerous valves
-formed by union of dorsal digital vein of the great toe and dorsal venous arch of the foot
-ascends anterior to medial malleolus
-passes posterior to medial femoral condyle
-traverses saphenous opening in fascia lata
-drains into femoral vein
union of dorsal digital vein of great toe and dorsal venous arch of the foot
What is the great saphenous vein formed by?
femoral vein
What does the great saphenous vein drain into?
small saphenous vein
-in subcutaneous tissue
-ascends posterior to lateral malleolus
-passes along lateral border of Achilles tendon
-Inclines to midline of fibula and penetrates deep fascia
-Ascends b/w Gastroc heads
arises on lateral side of foot from the union of dorsal digital vein of 5th digit with dorsal venous arch
What forms the small saphenous vein?
popliteal vein
What does the small saphenous vein drain into?
perforating veins
-pass between superficial and deep veins
-contain valves that allow blood to flow only from superficial and deep veins
-penetrate deep fascia at oblique angles
-prevents blood from flowing from deep to superficial veins
deep veins
-accompany major arteries and their branches
-contained within a vascular sheath with the artery whose pulsations help compress and move blood in the veins
popliteal vein
Where do deep veins from the leg drain?
joins terminal portion of femoral vein to become external iliac vein
What does the Profunda Femoris vein become?
external iliac vein
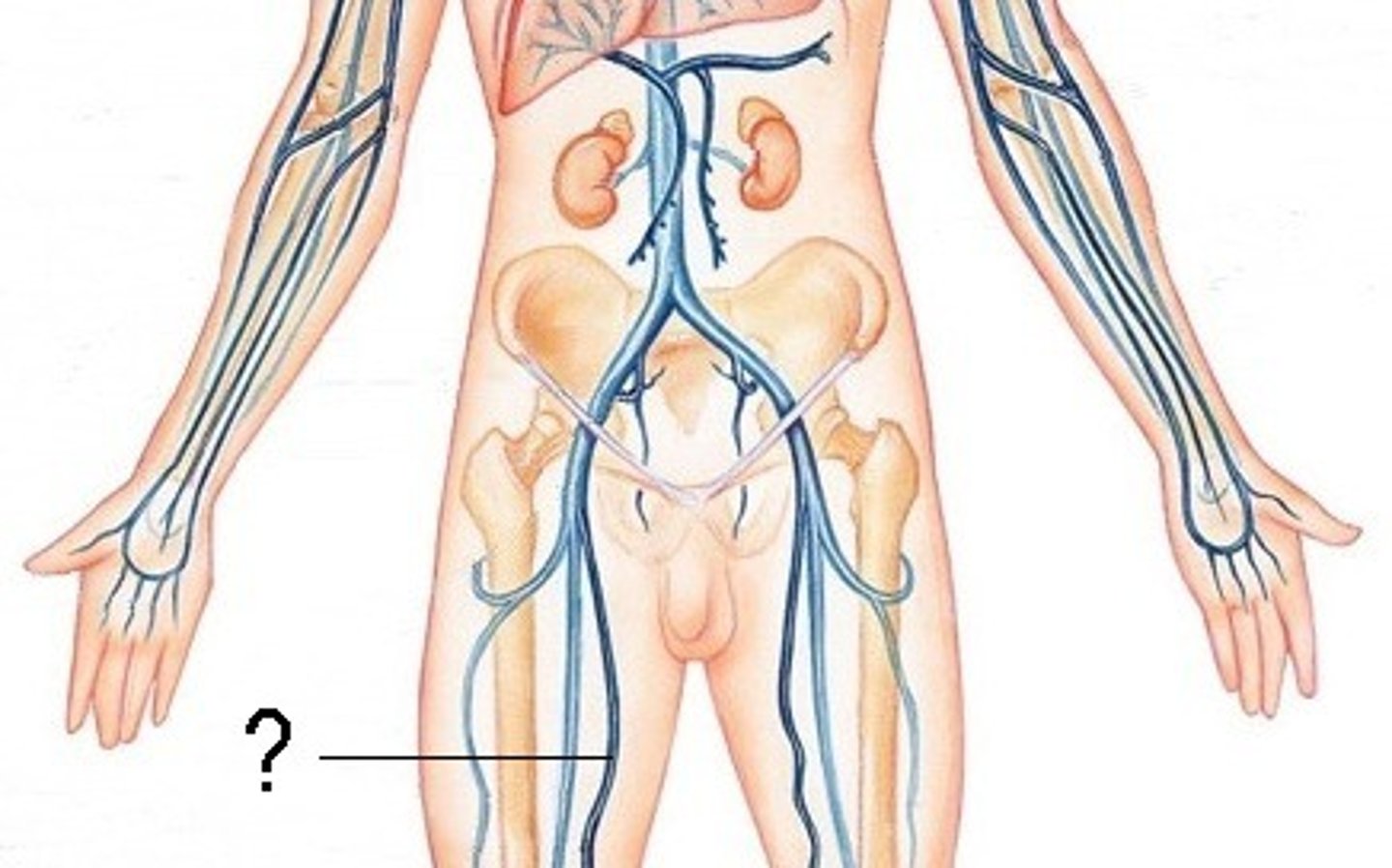
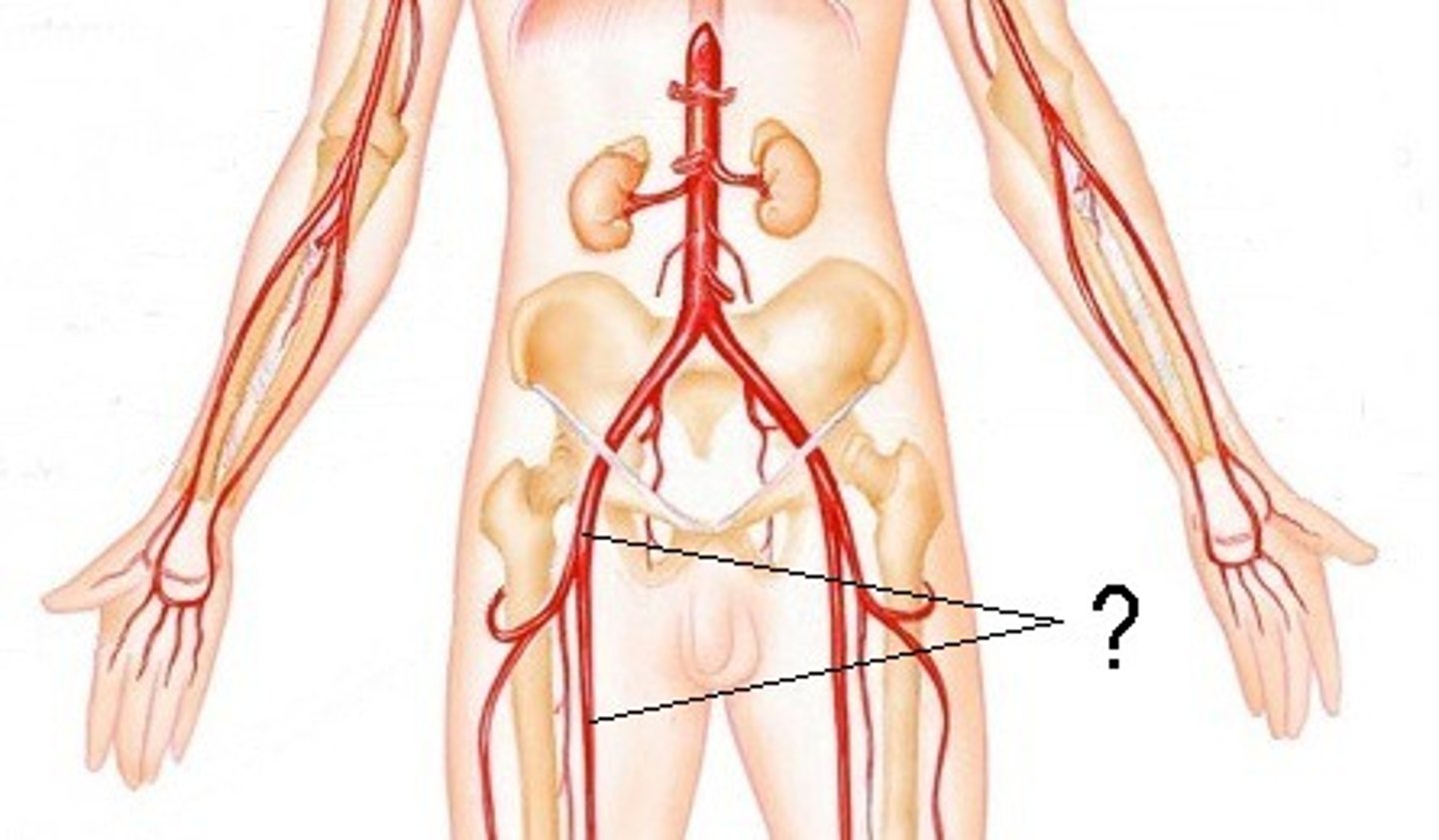
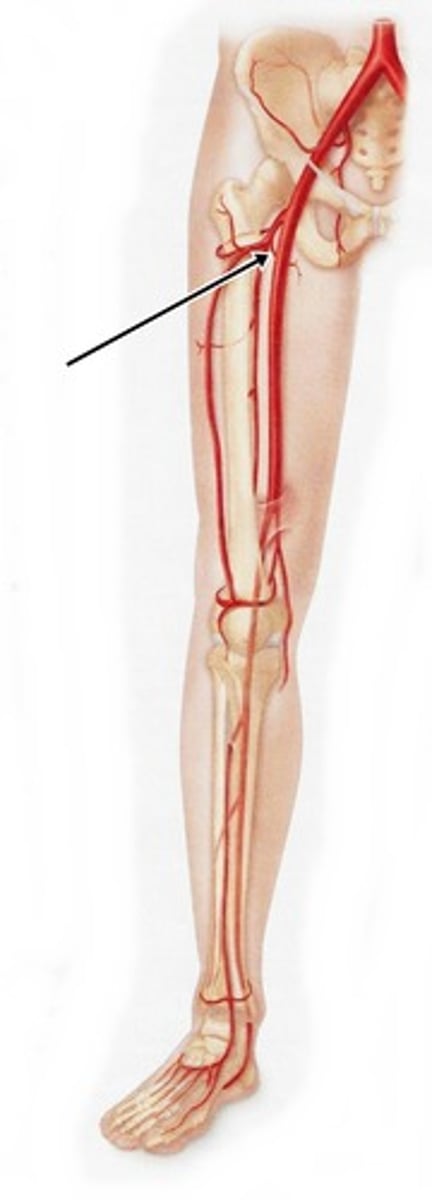
femoral artery
-main blood supply to the lower limb
-enters femoral triangle, continues through anterior compartment of thigh and passes through adductor hiatus to popliteal region
femoral artery
What does the external iliac artery become?
profunda femoris artery
supplies posterior and lateral thigh
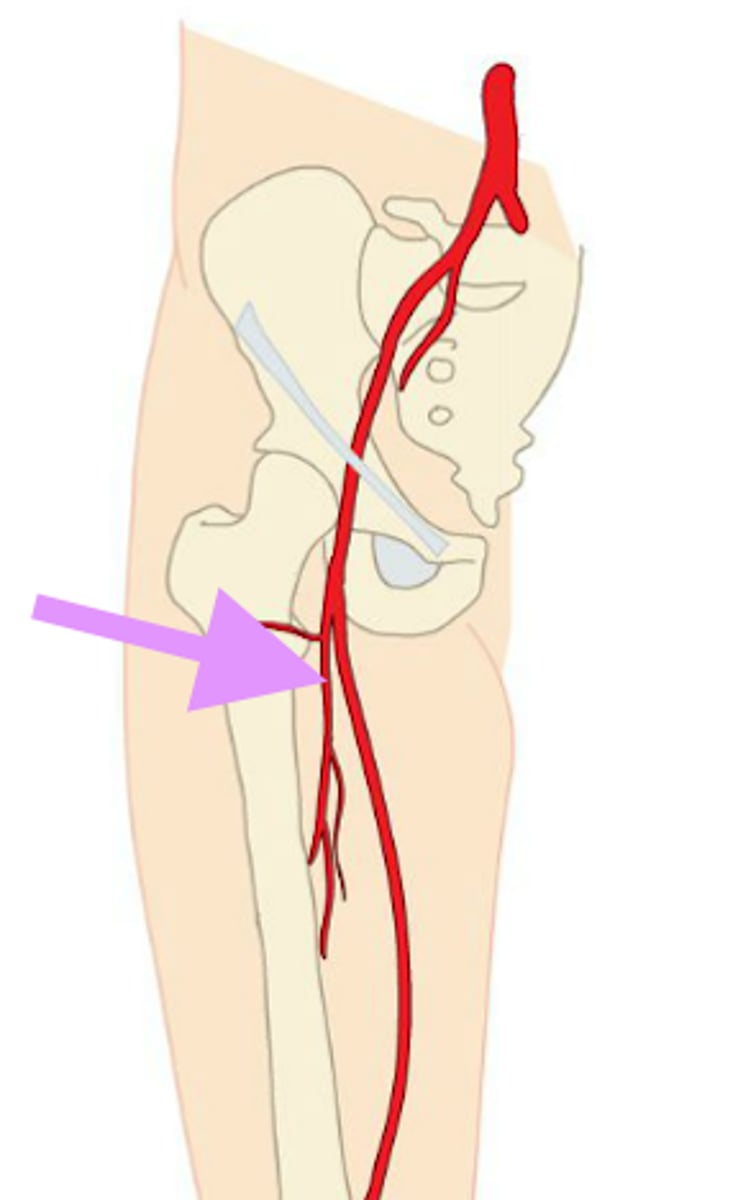
adductor hiatus
When does the femoral artery become the popliteal artery?
anterior and posterior tibial arteries
What does the popliteal artery branch into?
posterior tibial artery
-courses through deep posterior compartment posterior to medial malleolus
medial and lateral plantar arteries
What are the branches of the posterior tibial artery?
dorsalis pedis artery
What does the anterior tibial artery branch into?
obturator artery
-supplies medial compartment of thigh
-arises from internal iliac artery
-passes through obturator foramen to medial compartment of thigh-->divides into anterior and posterior branches
-supplies obturator externus, pectineus, adductors, gracilis
-posterior branch gives off acetabular branch that supplies femoral head
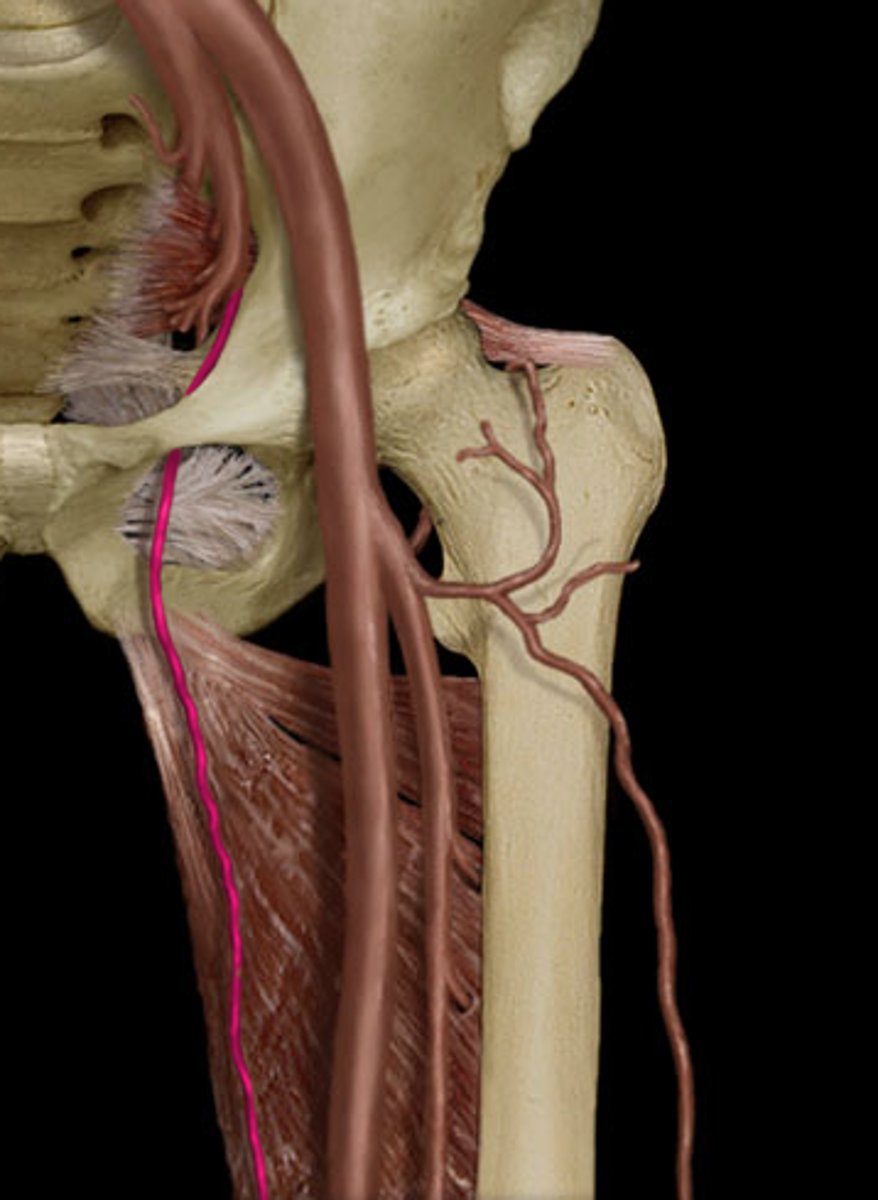
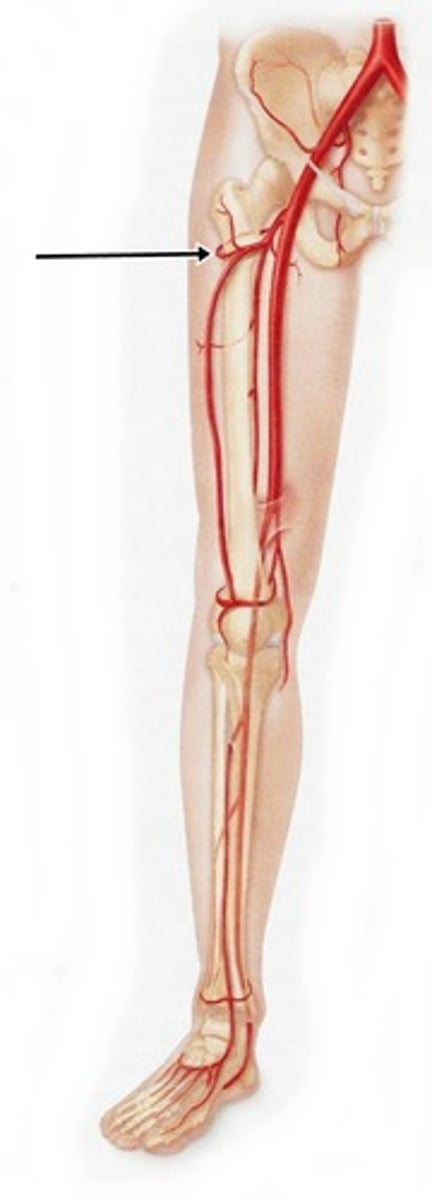
medial circumflex femoral artery
-branch of the femoral artery
-passes between iliopsoas and pectineus to posterior femoral head and neck (anterior to quadratus femoris muscle)
lateral circumflex femoral artery
-branch of the femoral artery
-passes laterally across joint capsule to supply muscles on the lateral thigh
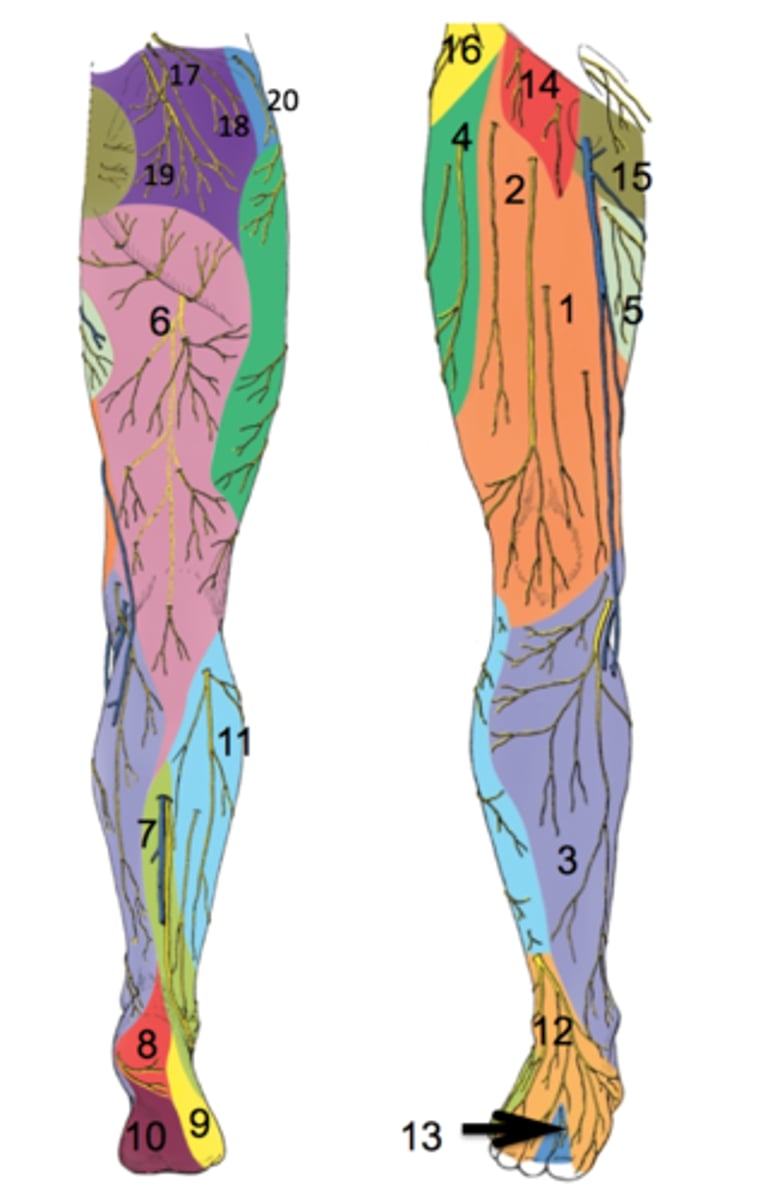
lateral cutaneous branch of subcostal nerve
-T12
-anterolateral hip
-#16
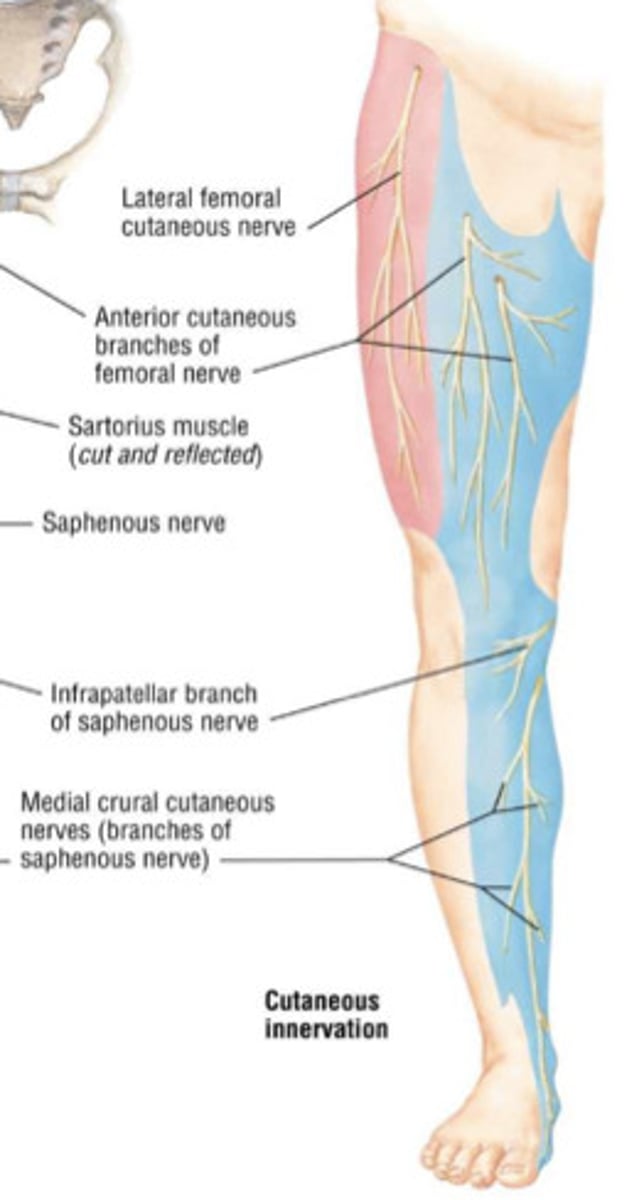
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
-L2, L3
-anterolateral thigh
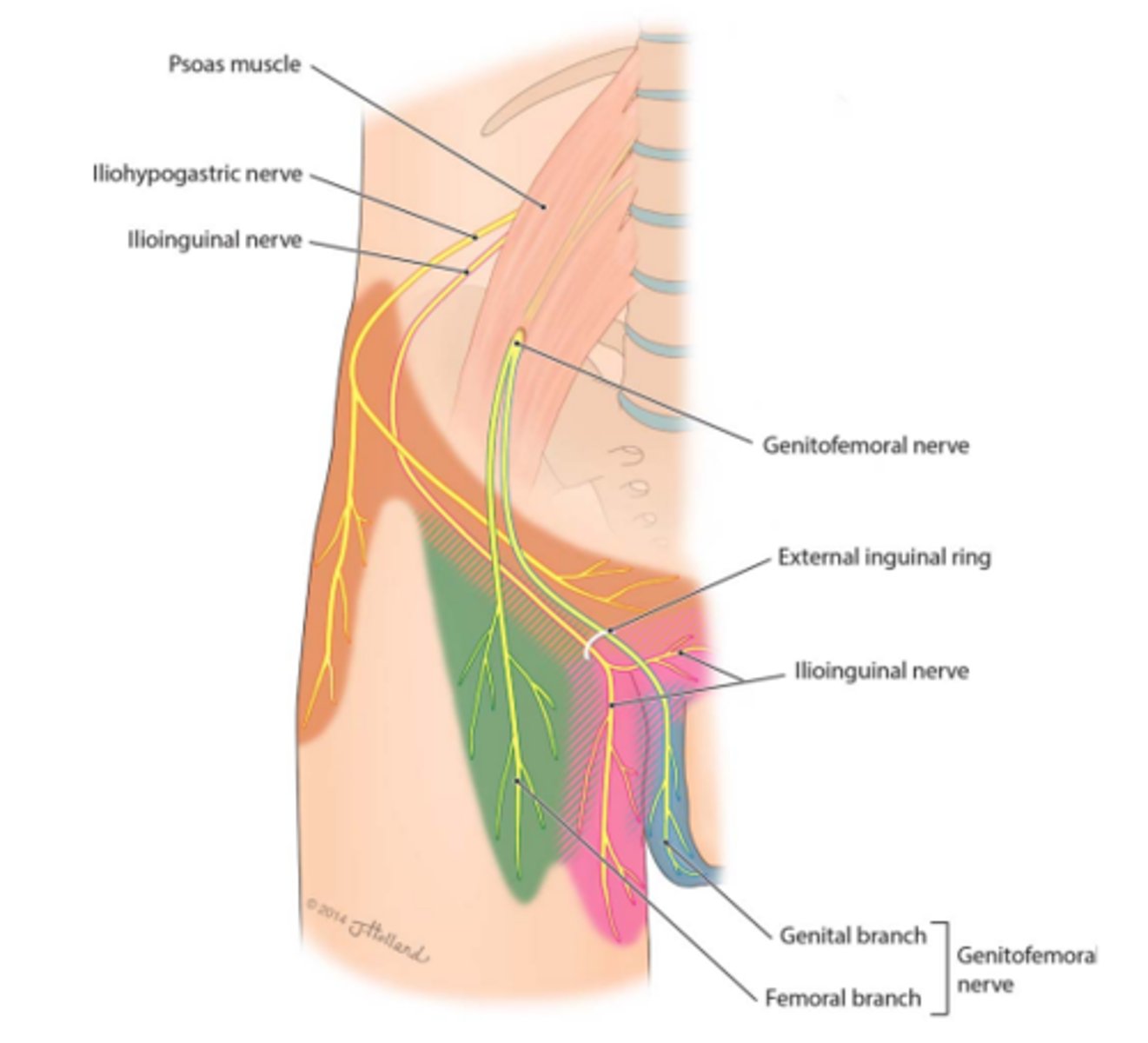
genitofemoral nerve
-L1, L2
-proximal anterior thigh inferior to inguinal ligament
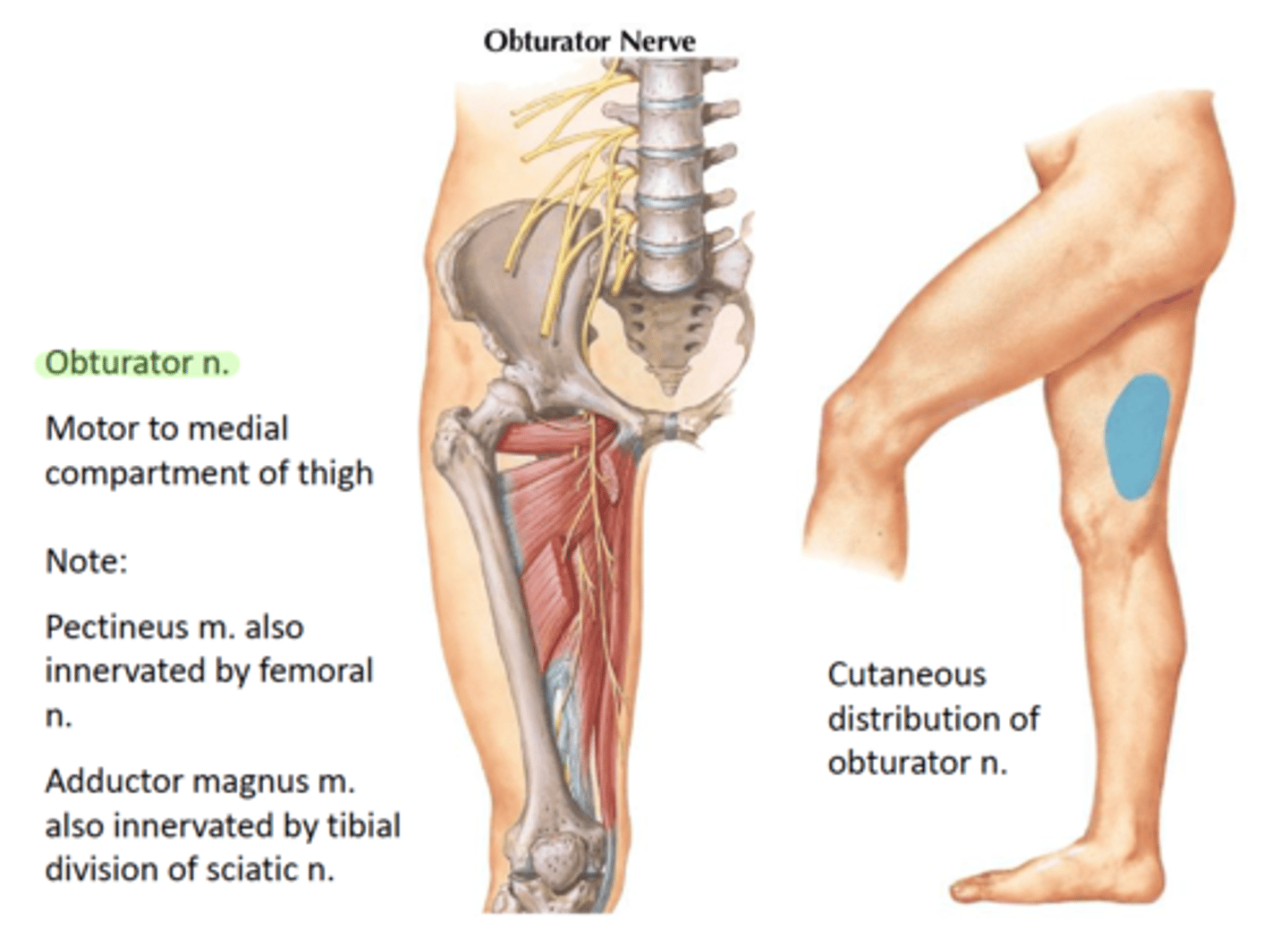
cutaneous branch of obturator nerve
-L2, L3, L4
-proximal medial thigh
-L
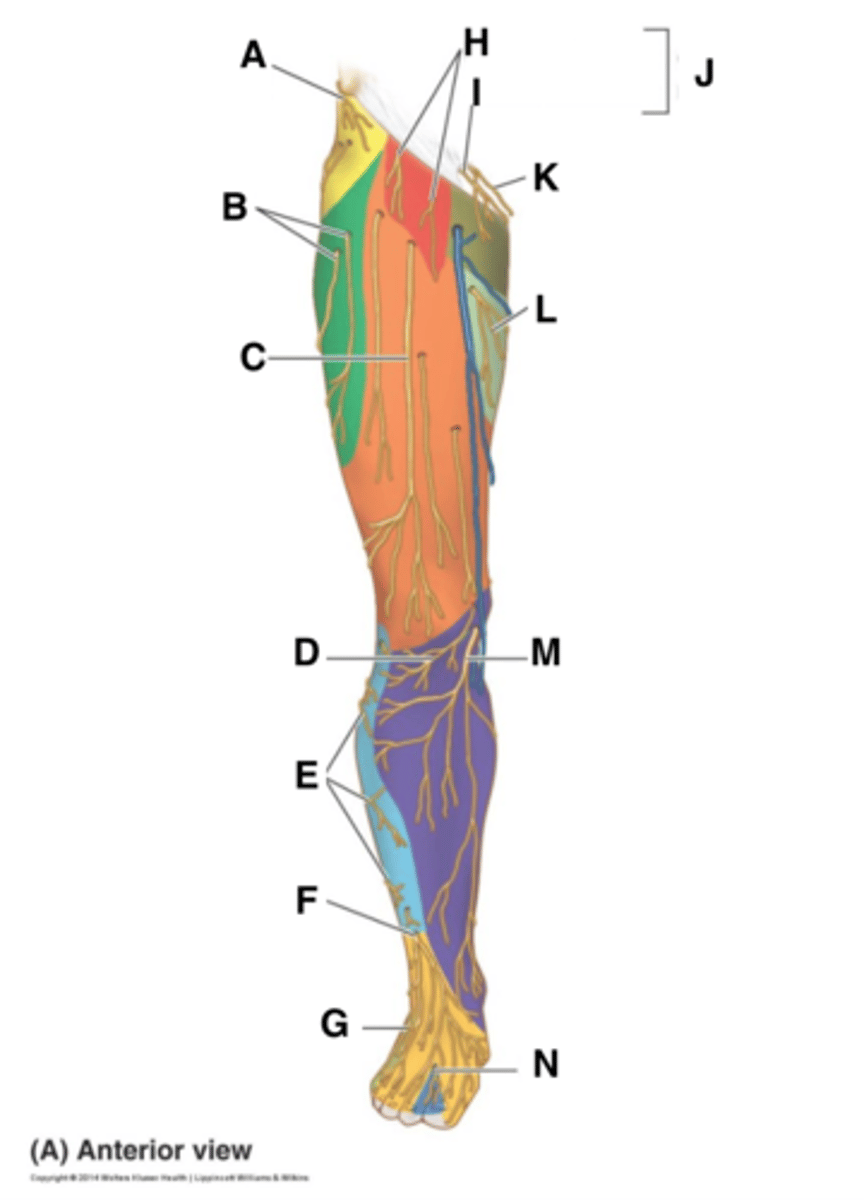
anterior cutaneous branch of femoral nerve
-L2, L3, L4
-anterior thigh and distal medial thigh
-#1
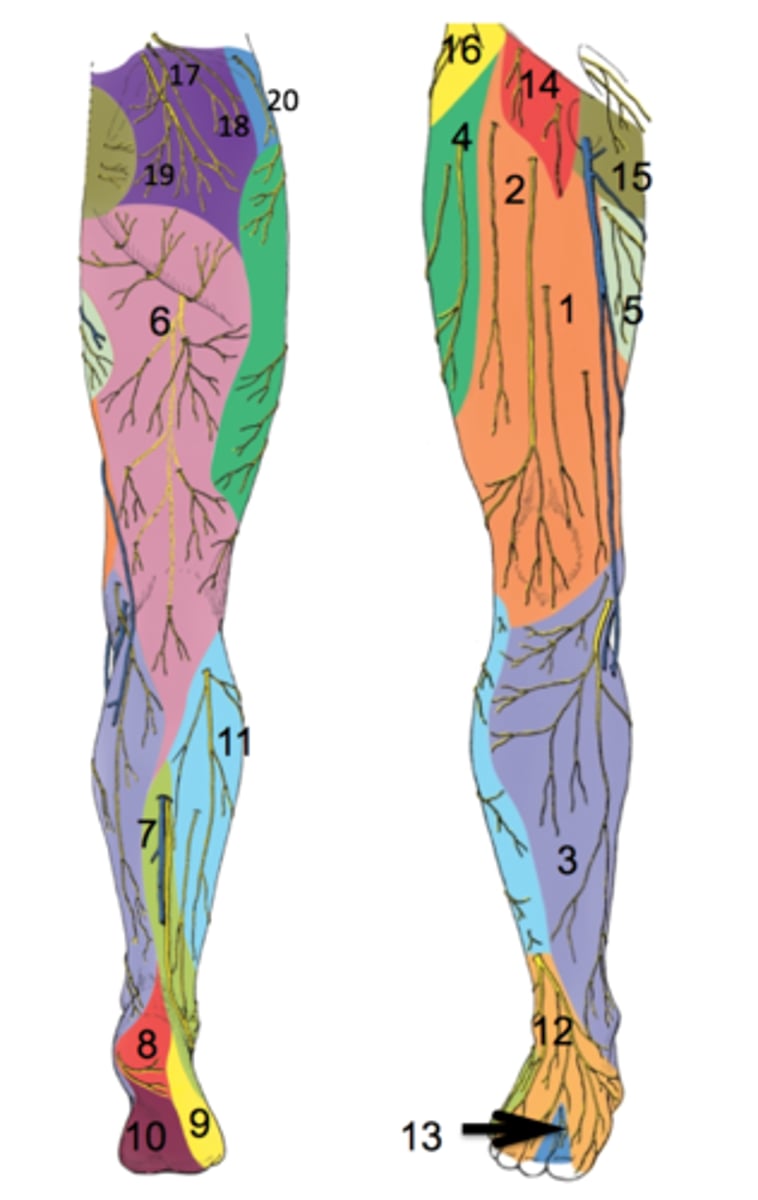
ventral rami
-L1, L2, L3
-Psoas Major
-Motor
femoral nerve
-L2, L3, L4
-Iliacus, sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, pectineus (with obturator)
-motor
obturator nerve (motor)
-L2, L3, L4
-obturator externus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, adductor magnus (with sciatic), pectineus (with femoral)
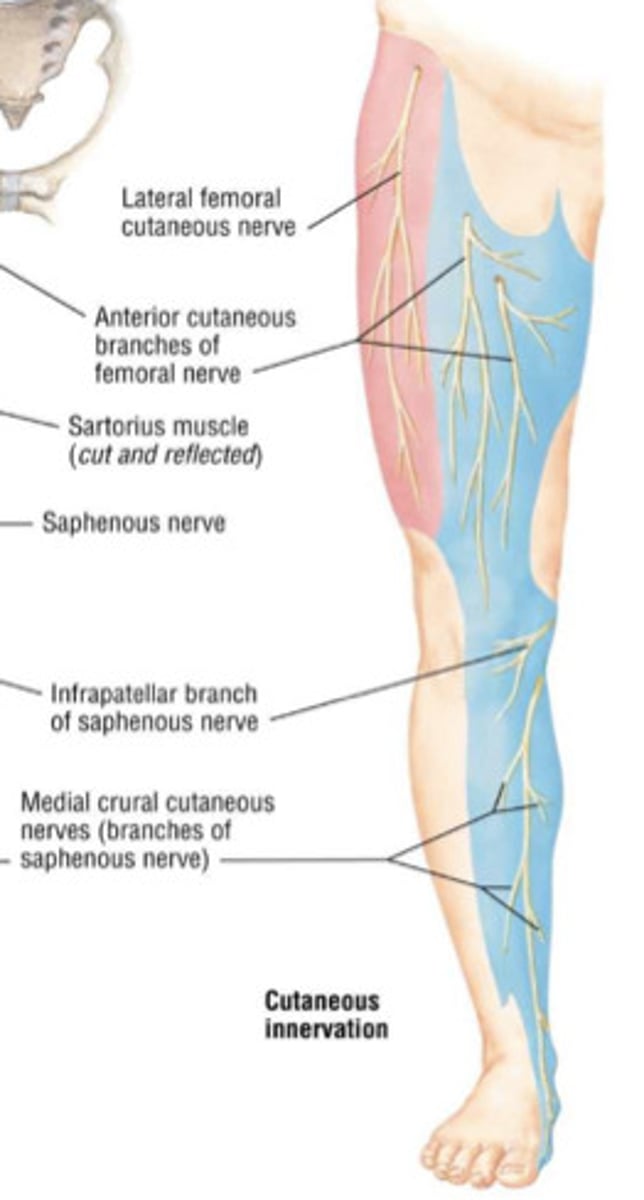
saphenous nerve
-Supplies impulses to the skin of the inner side of the leg and foot
-branch of the femoral nerve
psoas major
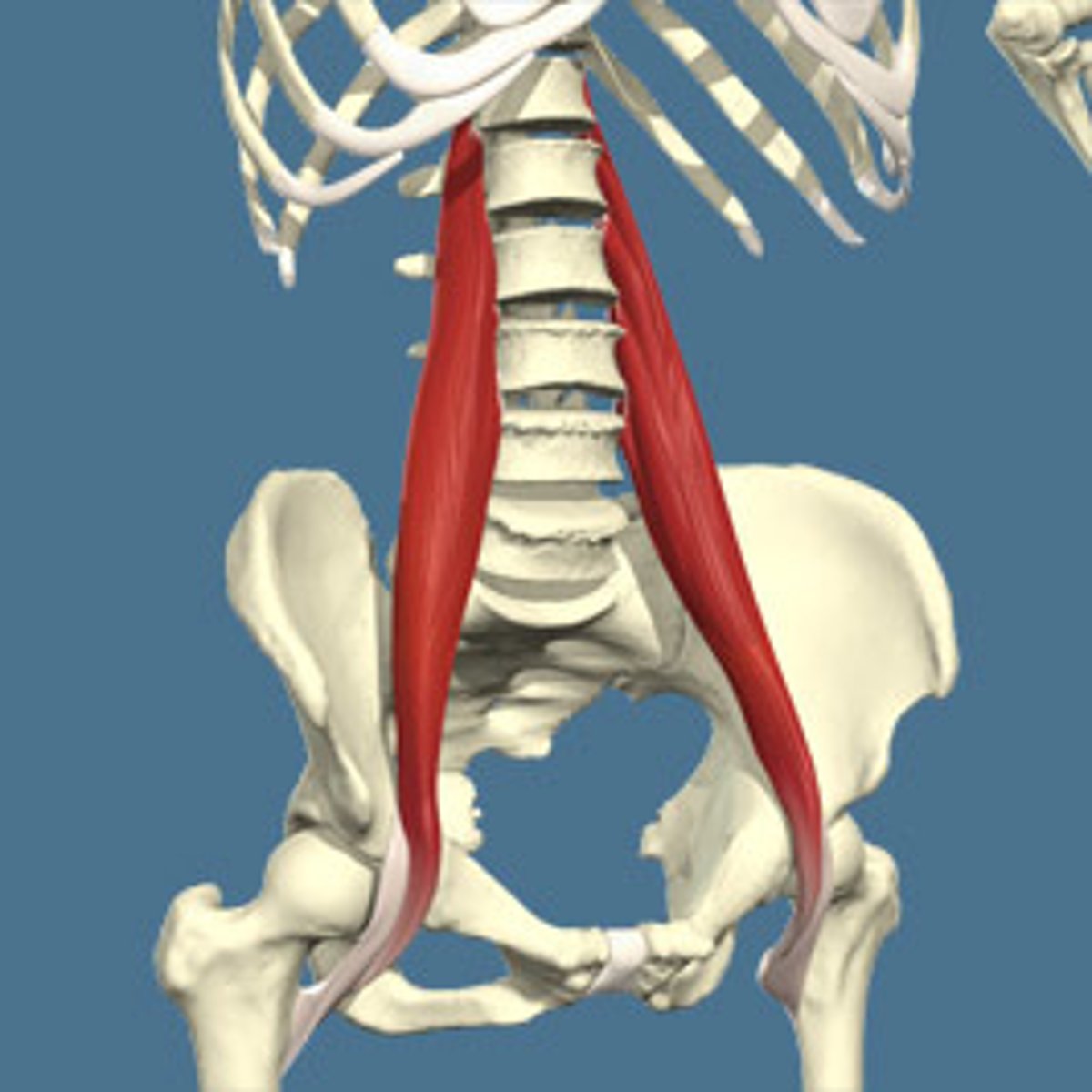
transverse processes L1-L5, vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs T12-L5
Origin of psoas major
lesser trochanter of femur
Insertion of psoas major
hip flexion, trunk flexion
Action of psoas major
anterior rami L1, L2, L3
Innervation of psoas major
psoas minor
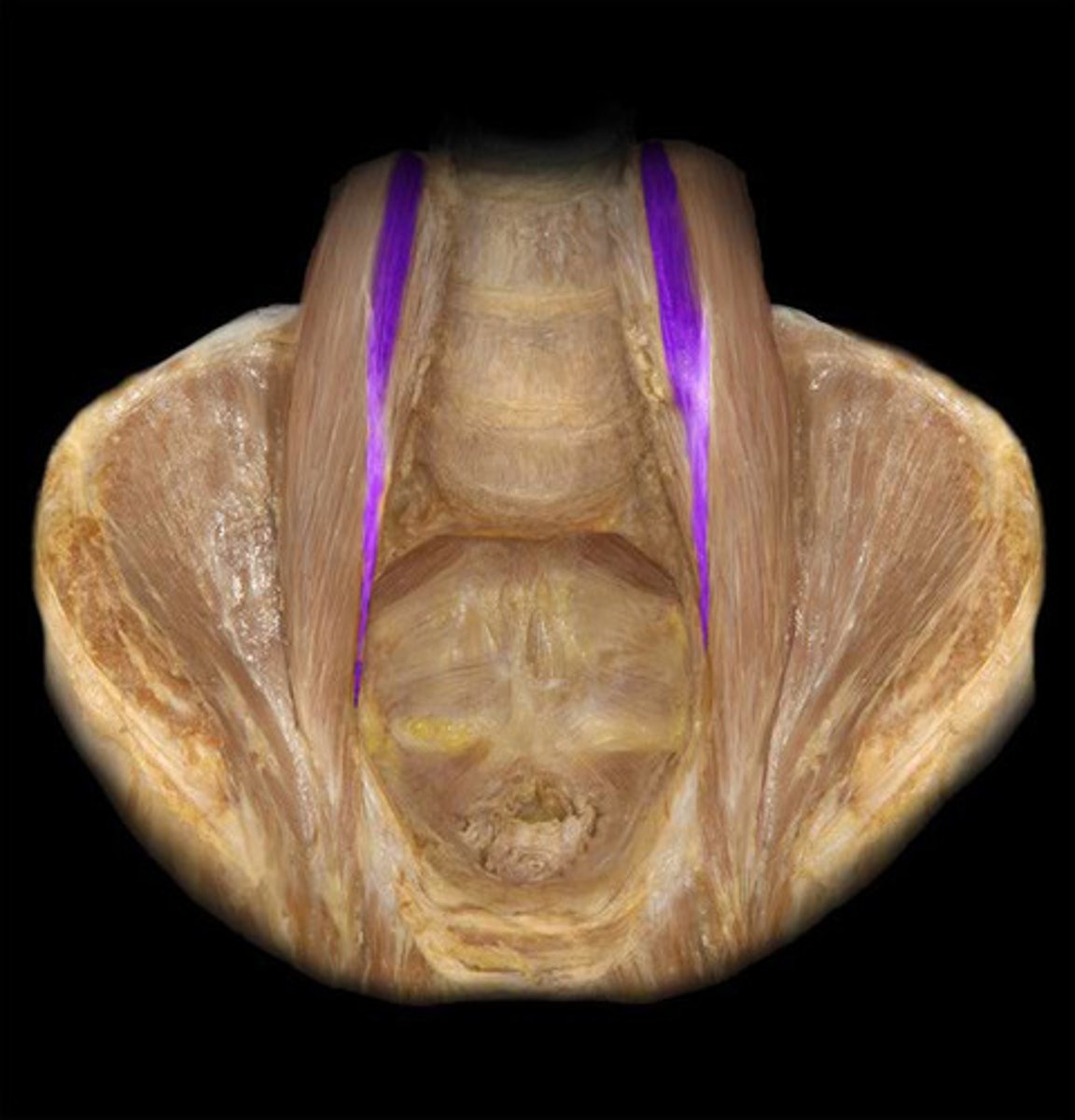
assists with trunk flexion
Action of psoas minor
vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs T12-L1
Origin of psoas minor
iliopectineal eminence and pecten pubis
Insertion of psoas minor
anterior rami L1
Innervation of psoas minor
true
t/f psoas minor may be absent in some individuals
iliacus
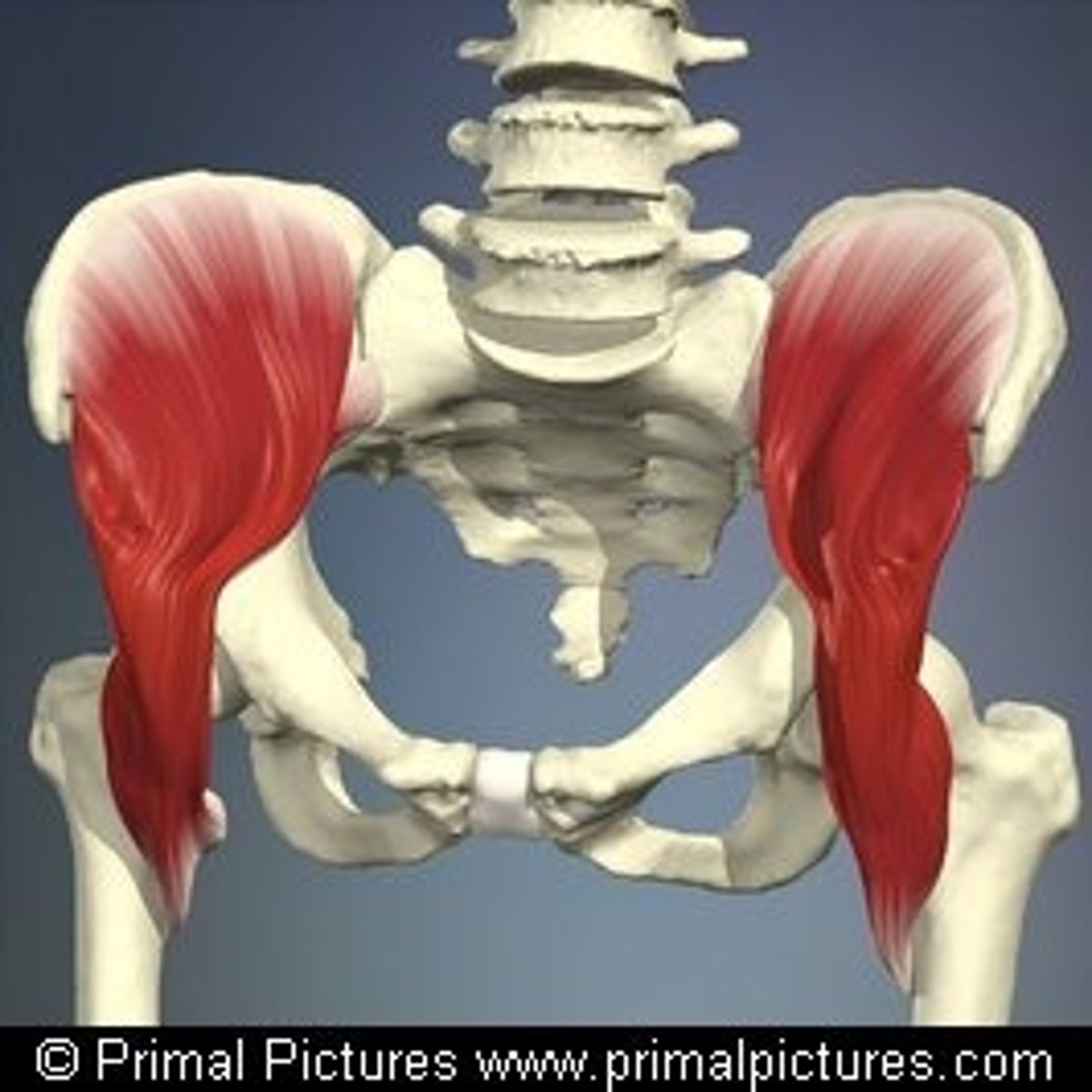
hip flexion, trunk flexion
Action of iliacus
iliac crest, superior 2/3 of iliac fossa, ala of sacrum, anterior sacroiliac ligaments
Origin of iliacus
lesser trochanter of femur via tendon of psoas major
Insertion of iliacus
femoral nerve (L2, L3)
Innervation of iliacus
pectineus
bridges gap between anterior and medial compartments
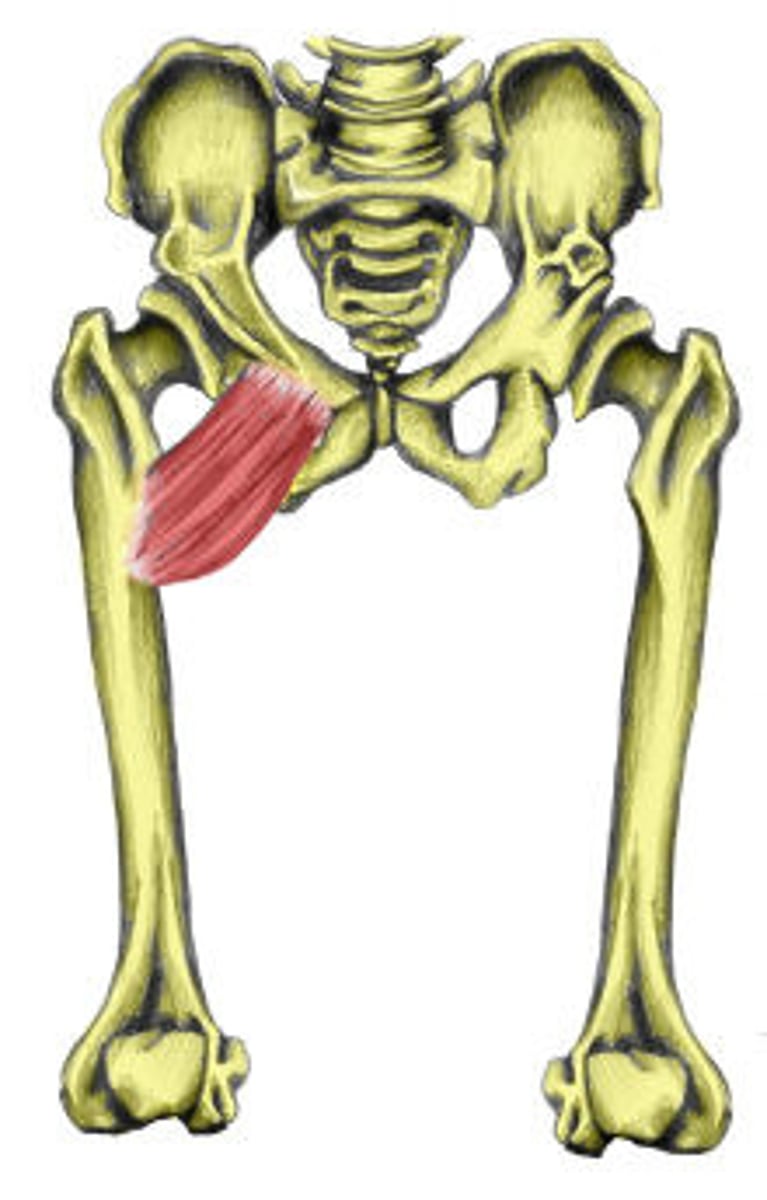
hip adduction and flexion
Action of pectineus
superior pubic ramus
Origin of pectineus
pectineal line of femur
Insertion of pectineus
femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4); may also receive branches from obturator nerve
Innervation of pectineus
sartorius
longest muscle in the body
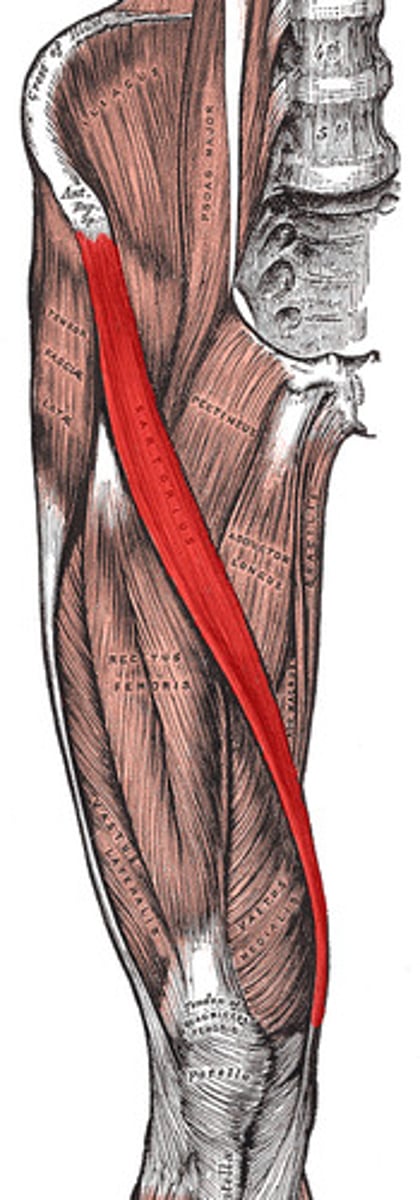
hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation; knee flexion and internal rotation
Action of sartorius
ASIS
Origin of sartorius
medial aspect of proximal tibia
Insertion of sartorius
femoral nerve (L2, L3)
Innervation of sartorius
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius
What are the four quadriceps muscles?
rectus femoris
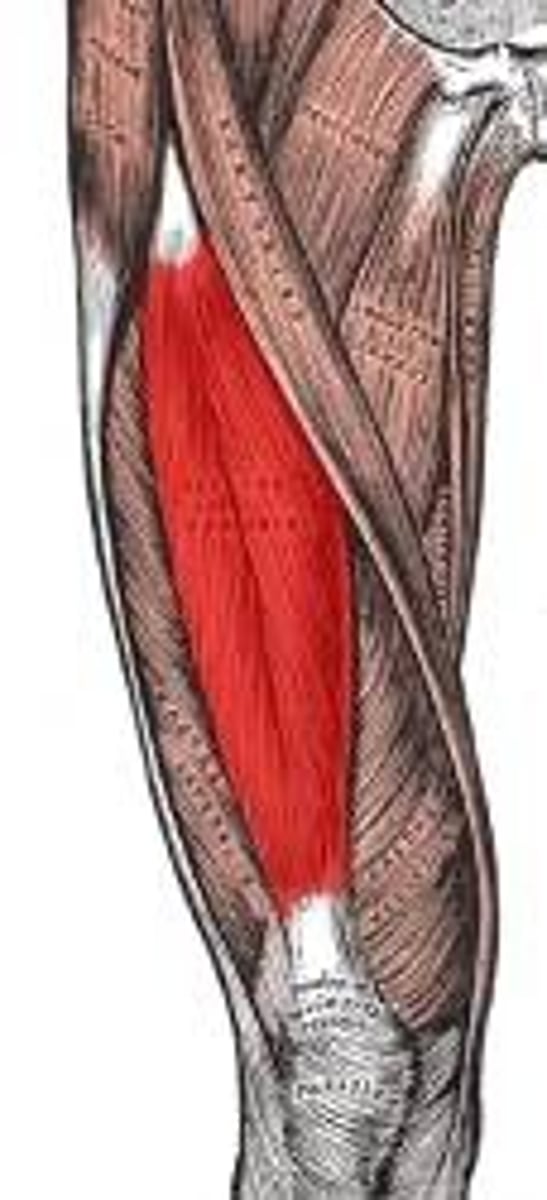
hip flexion, knee extension
Action of rectus femoris
ASIS and supra-acetabular groove of ilium
Origin of rectus femoris
tibial tuberosity via quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament
Insertion of rectus femoris
femoral nerve (L2, L3)
Innervation of rectus femoris
vastus lateralis