VT 111 Lec 13 Urinary System
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Waste Excretion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Metabolic Waste Products
potentially harmful substances to the body
must be eliminated
of no further use
can be harmful if allowed to accumulate
examples
carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
nitrogenous wastes, primarily urea
bile salts and pigments
various salts
Routes for Waste Product Elimination
respiratory system
carbon dioxide, water vapor
sweat glands
water, salts, urea
digestive system
bile salts, pigments
urinary system
urea, salts, water, other soluble waste products
The Urinary System
single most important route for removal of waste products
removes nearly all soluble waste from blood
transports soluble waste out of the body
major route for elimination of excess water
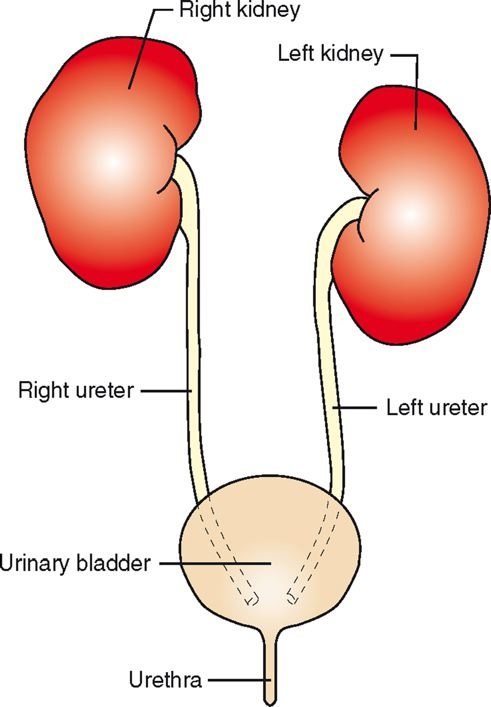
Parts of the Urinary System
kidneys (2)
ureters (2)
urinary bladder (1)
urethra (1)
Kidney Function
production of urine to facilitate elimination of metabolic waste materials
maintenance of homeostasis through:
blood filtration, reabsorption, secretion
fluid balance regulation
antidiuretic hormone (ADH), aldosterone
acid-base balance regulation
production of hormones
Erythropoietin (EPO), prostaglandins
blood pressure regulation
The Kidneys
located in dorsal abdominal area
ventral to first few lumbar vertebrae
on either side of first few lumbar vertebrae
retroperitoneal to the abdominal cavity
surrounded by layer of perirenal fat
right kidney more cranial than left (except pigs)
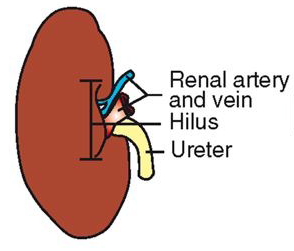
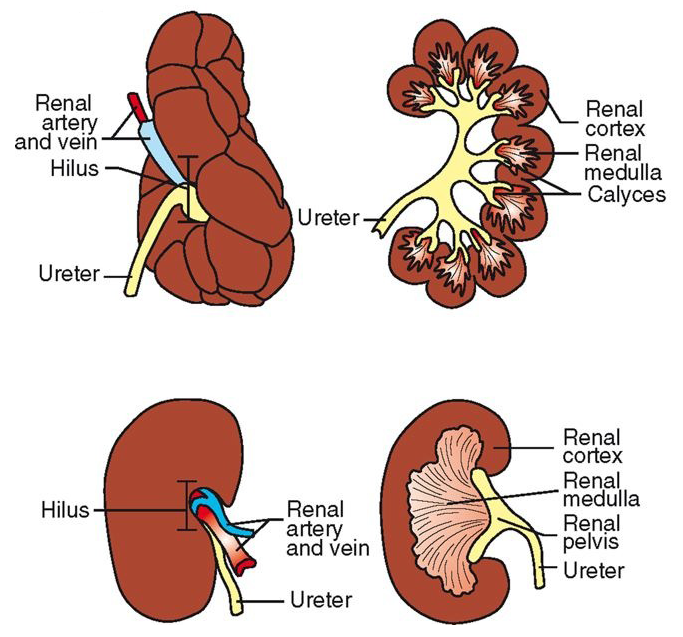
Gross Anatomy of the Kidneys
fibrous connective tissue capsule
hilus: indented area on medial side
ureters, nerves, blood and lymph vessels enter and leave
renal pelvis: funnel-shaped area inside hilus/hilum
renal cortex – surrounds medulla
renal medulla – shape can vary (multilobar vs. unilobar)
calyx – cup-like extension of pelvis; directs urine to pelvis
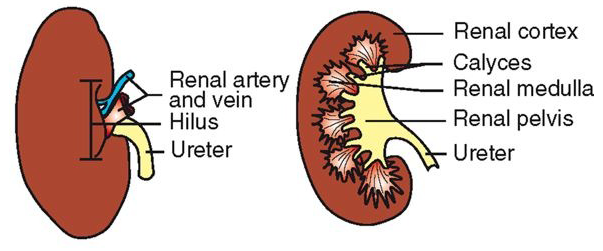
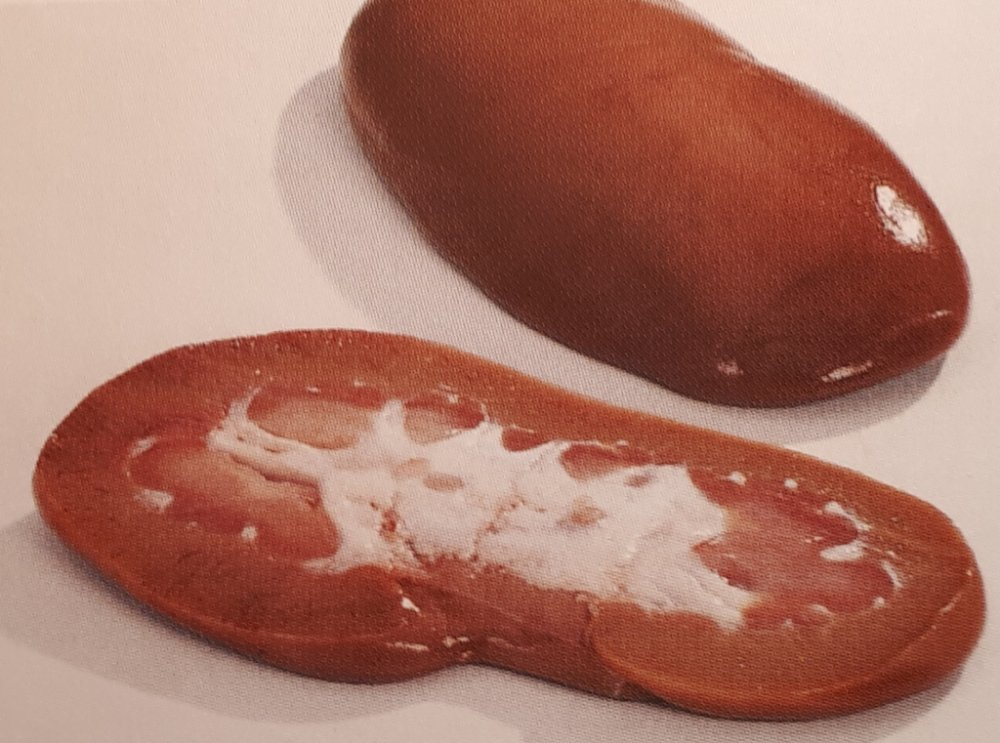
Gross Anatomy of Kidneys Continued…
Multilobar
Unilobar
Porcine Kidneys

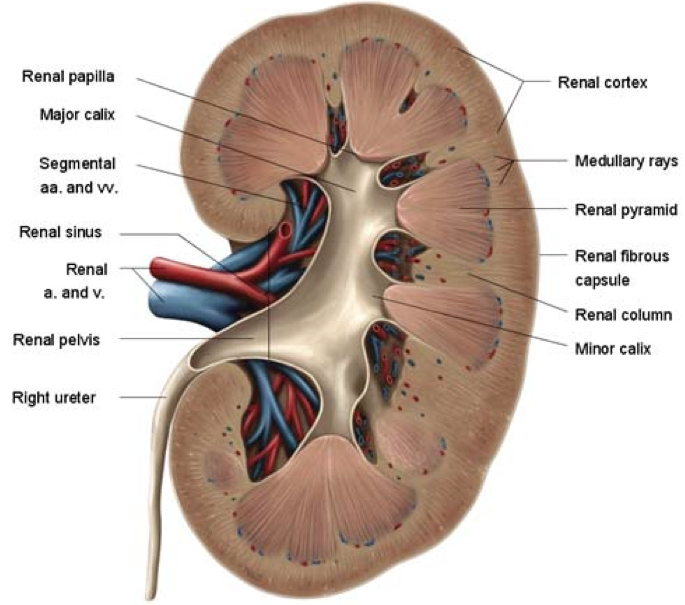
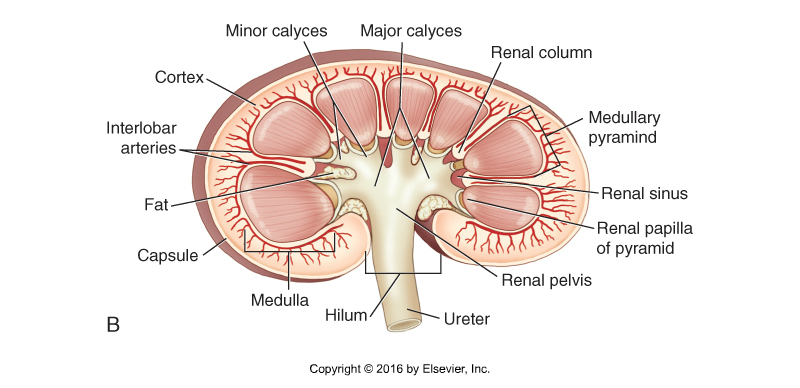
Interior Structure of the Kidney
Cortex
Medulla
Medullary pyramid
Minor calyces
Major calyces
Pelvis
Ureter
Fat
Microscopic Anatomy of Kidneys
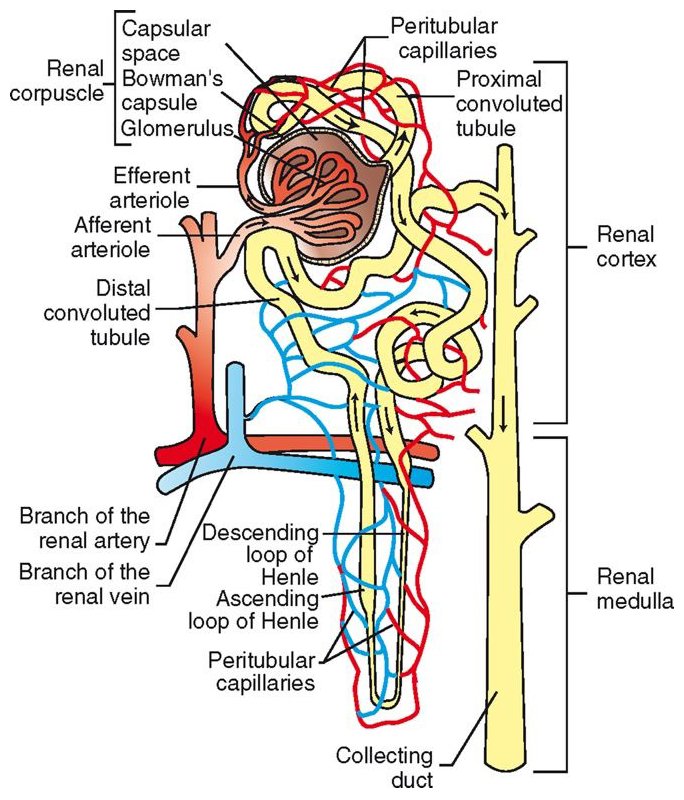
nephron = basic functional unit
number varies with size of the animal
cat ~200,000/kidney
human ~ 1 million/kidney
composed of:
renal corpuscle
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
loop of Henle
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
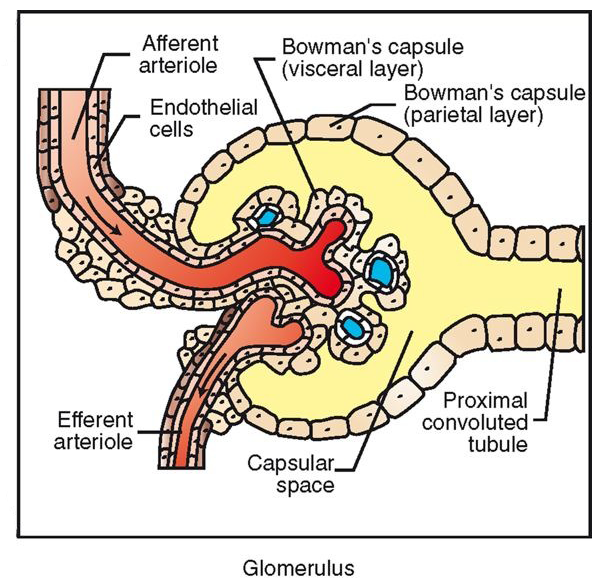
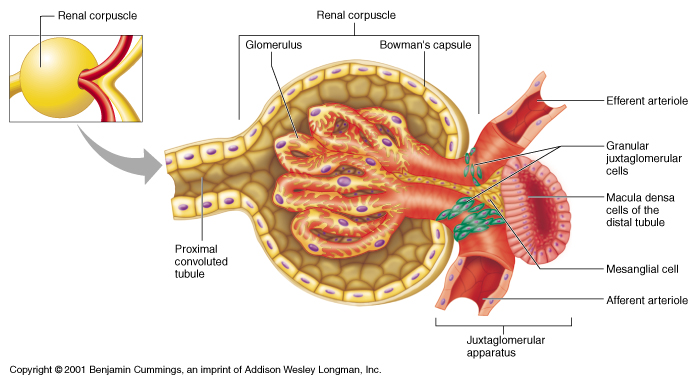
Renal Corpuscle
located in renal cortex
glomerulus (capillaries) surrounded by Bowman’s capsule (2 layers)
filters blood in first stage of urine production: Bowmaglomerular filtrate
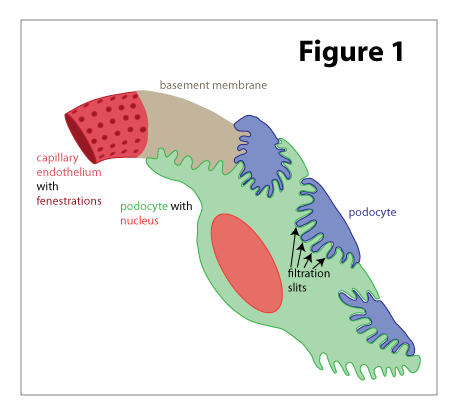
Bowman’s Capsule
Double-walled capsule
Inner (visceral) layer
Visceral layer
Adheres closely to capillaries
Composed of podocytes that create a permeable layer
Outer (parietal) layer
Simple squamous epi
Space between layers
Capsular space
Where filtration from glomerulus enters
Collects into convoluted tubule
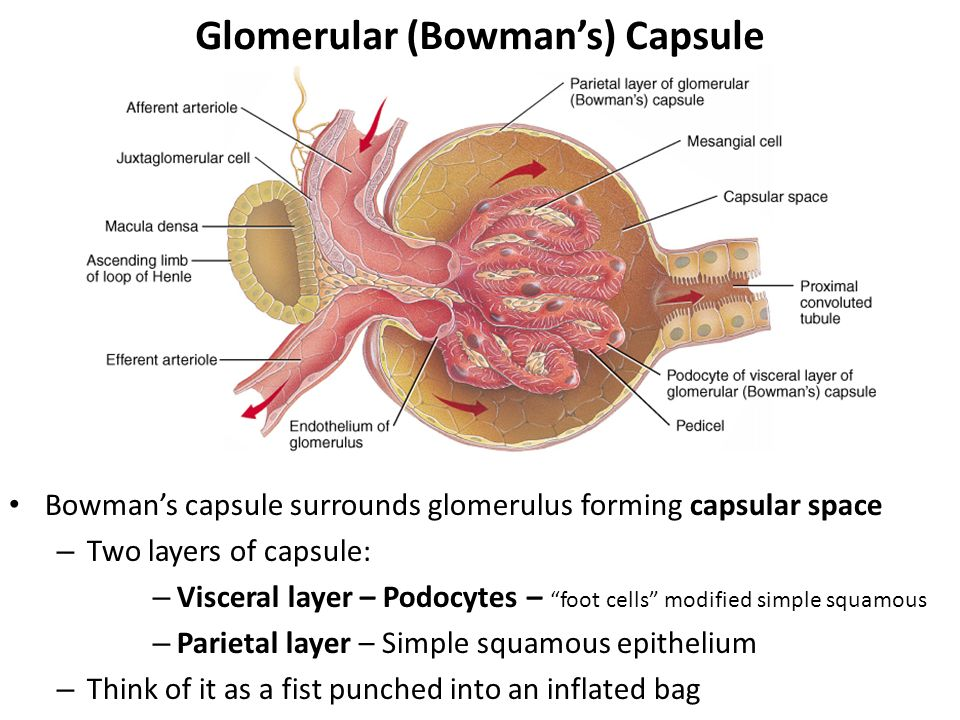
Glomerulus
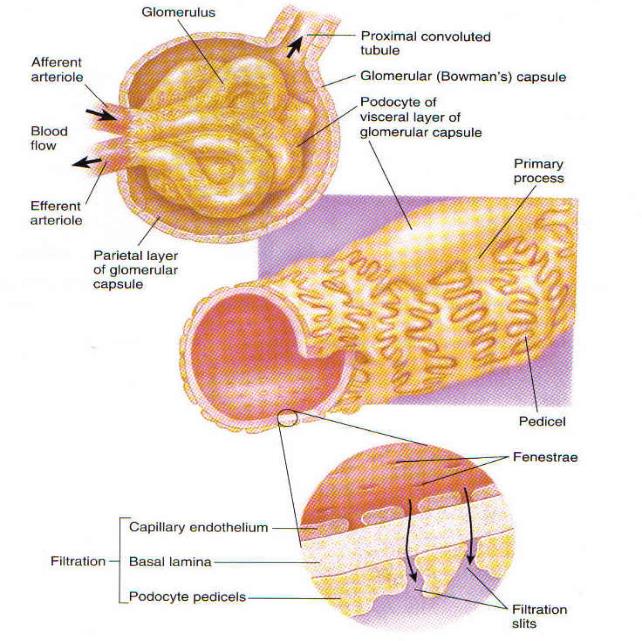
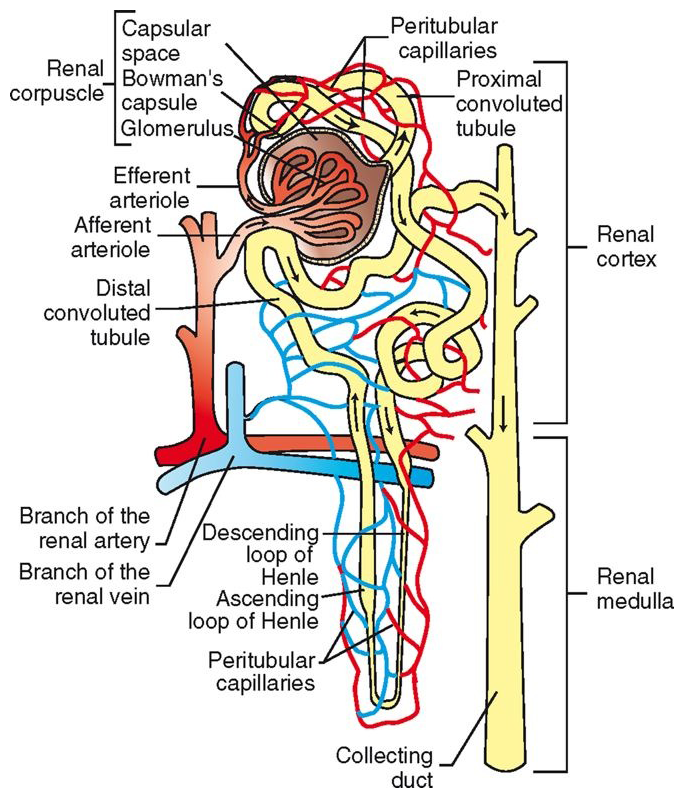
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
continuation of capsular space of Bowman’s capsule
Lined with cuboidal epithelial cells with brush border
twists through cortex
reabsorption and secretion functions
glomerular filtrate now called tubular filtrate
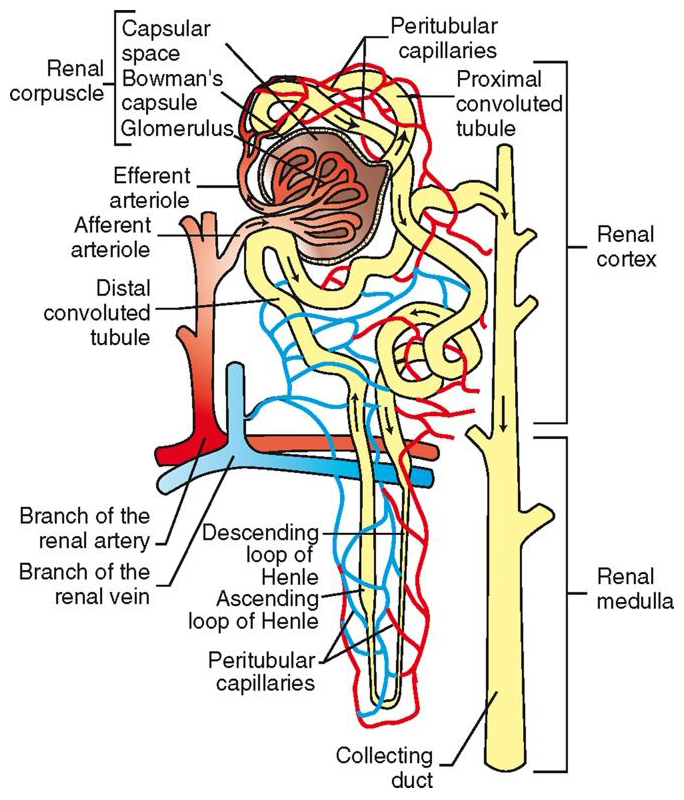
Loop of Henle
continues from PCT, descends into medulla, makes a U-turn, and heads back into cortex
At U-turn, narrows and wall thins
Simple squamous epithelial cells
No brush border
ascending wall becomes thicker again
Ascending Limb of Loop of Henle
Ascending limb has active transport pumps
No water channels, no water reabsorption here
Na+ is actively transported from loop
Amount of Na+ reabsorbed is dependent on concentration of filtrate
Volume does not change here
Concentration decreases due to loss of Na+
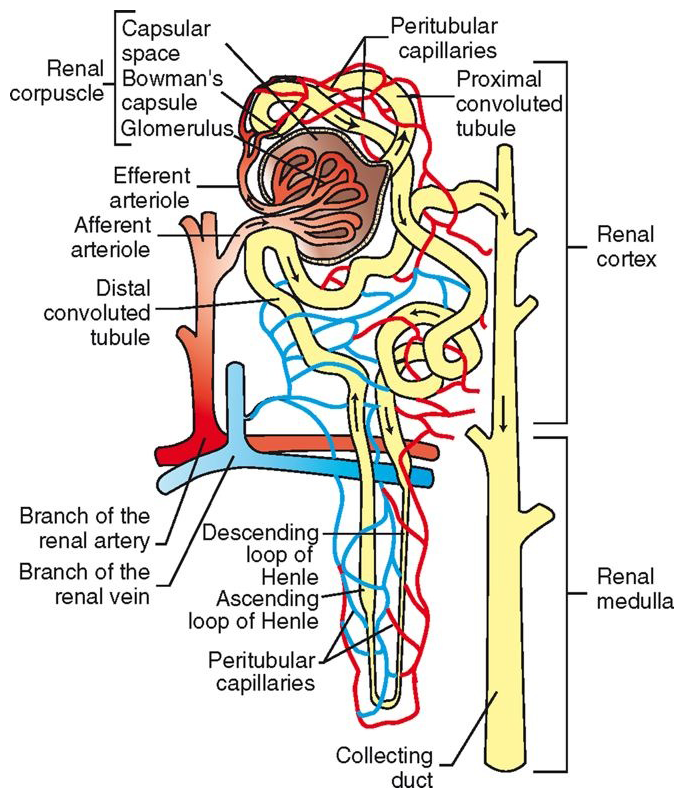
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
continuation of ascending loop of Henle
twists through cortex
DCTs from all nephrons in the kidney empty into collecting ducts
empty into calyces à renal pelvis
primary site of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) action
regulation of potassium and acid-base balance
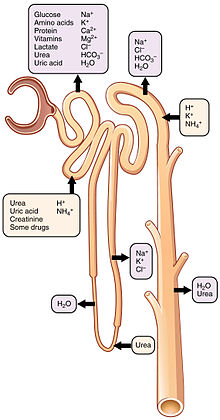
Movement of Nutrients & Wastes
Nerve Supply to the Kidney
primarily from sympathetic portion of the autonomic nervous system
not essential for kidney function
transplants
sympathetic stimulation causes vasoconstriction of renal vessels
temporarily decreases urine function
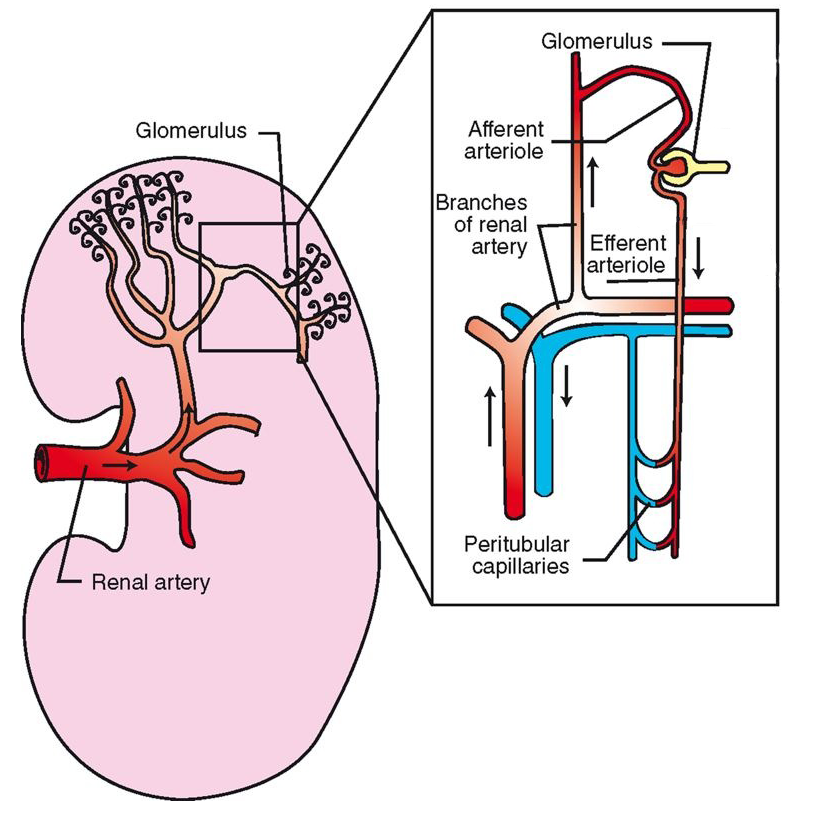
Blood Supply to the Kidney
LARGE supply
~25% of CO
All circulating blood passes through every 4-5 min
renal artery (branch off aorta) enters at hilus
subdivides to become series of afferent glomerular arterioles
afferent glomerular arterioles carry blood to renal corpuscle
glomerular capillaries filter some plasma out of the blood: glomerular filtrate
Blood leaves glomerulus and enters efferent glomerular arteries
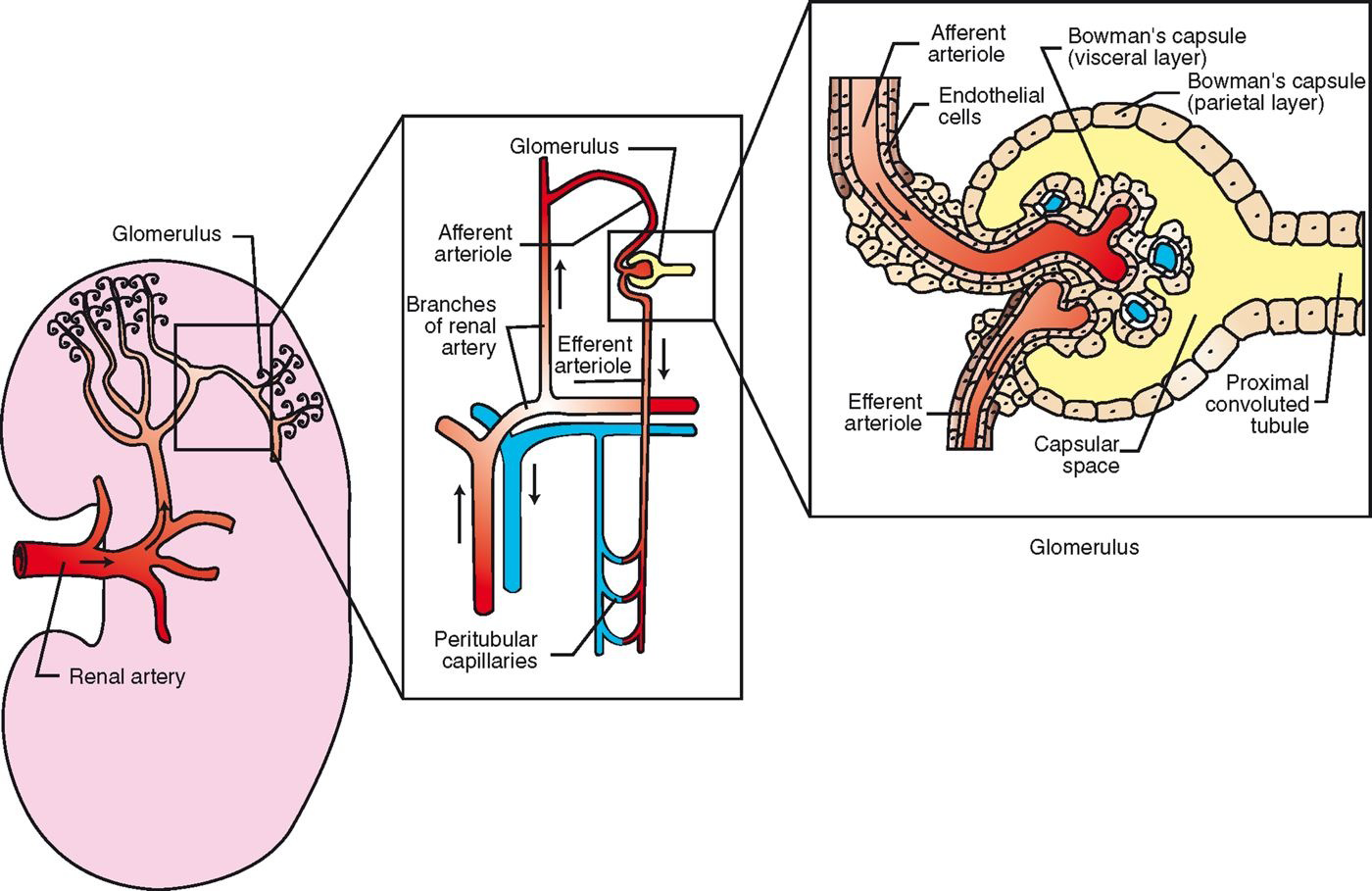
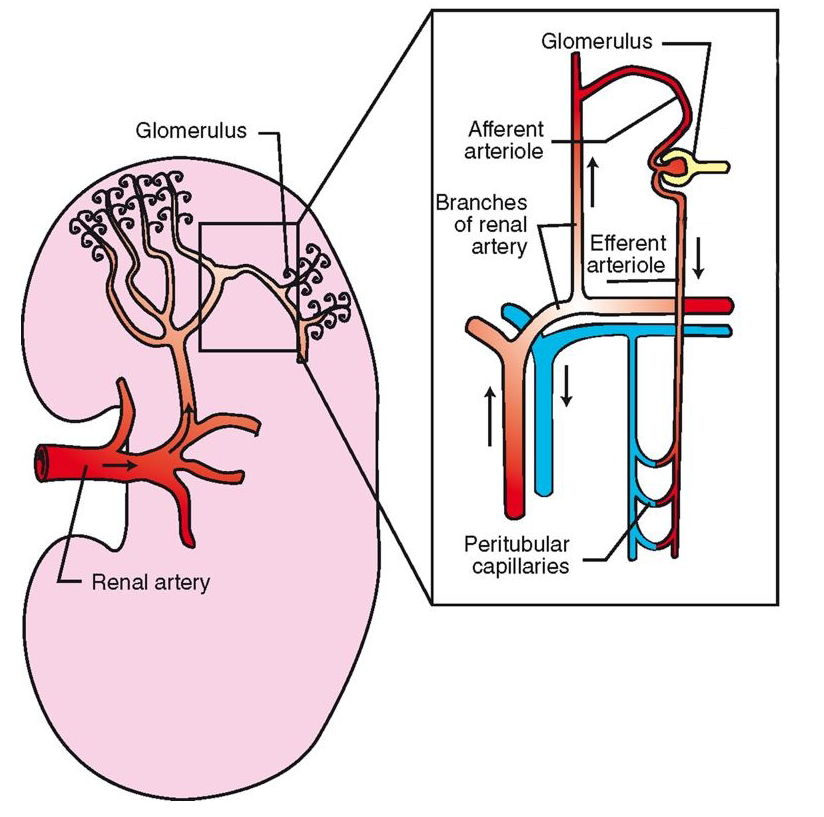
Blood Supply to the Kidney Continued…
Efferent glomerular arterioles divide into capillaries that surround rest of nephron
peritubular capillaries
Site of oxygen transfer to cells of nephron
Tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion also occur at this levelPeritubular capillaries converge to form venules à larger veins à renal vein
Renal vein leaves kidney at hilus
Joins caudal vena cava to return to heart
“clean blood”
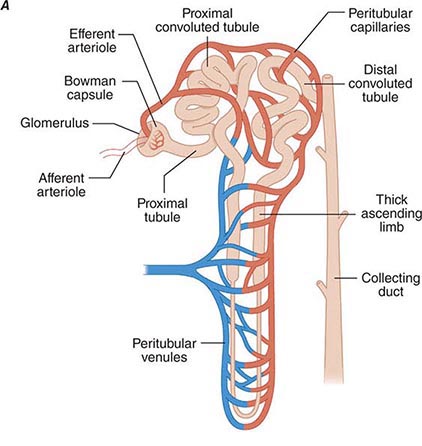
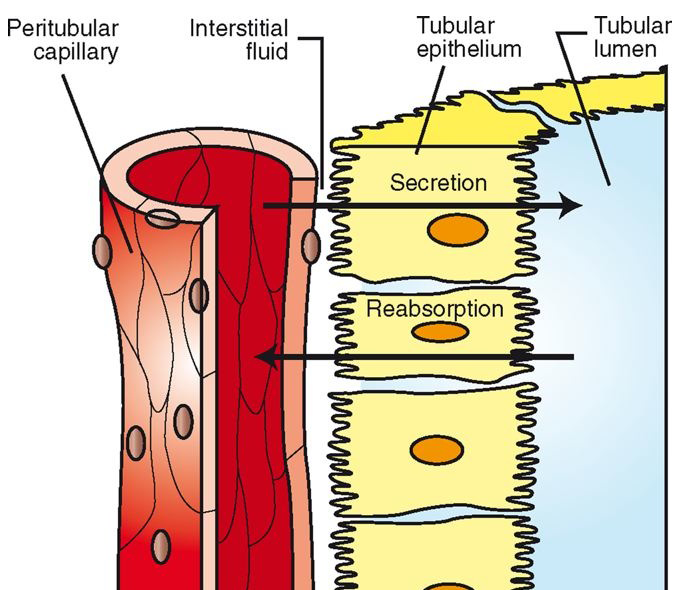
Mechanisms of Renal Action
filtration of the blood
reabsorption of useful substances
back into the bloodstream
secretion of waste products
from the blood
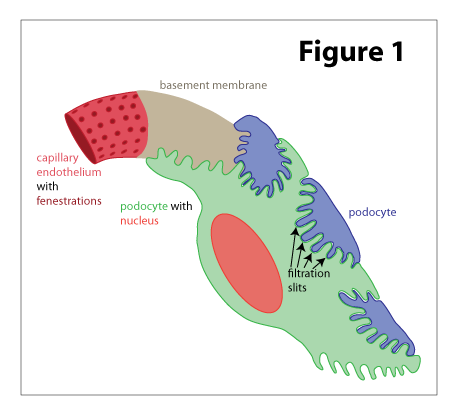
Filtration of Blood
occurs in renal corpuscle
afferent → efferent arterioles
blood pressure much higher than in other capillaries
Only ~30% lower than aorta
due to pressure from difference in size between afferent and efferent glomerular arterioles
high blood pressure in glomerular capillaries forces some plasma into capsular space of Bowman’s capsule
large fenestrations in capillary endothelium
glomerular filtrate formed
no proteins or blood cells → too large to fit through fenestrations
may see in urine if damage to glomerulus
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
depends on rate of blood flow to kidney
ml/min
On average, ~25% of plasma is removed from circulation each minute!
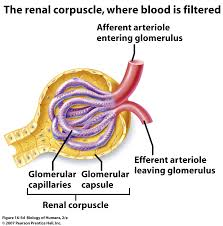
Glomerular FIltrate
Flows through fenestrations in capillaries à into capsular space à into tubules (now tubular filtrate)
Fluid with small molecules
Some is waste
Some the body still needs!
K, Na, Ca, Mg, a.a., Cl, H2O
The body needs to reabsorb the needed elements out of the glomerular filtrate before it leaves the body.
→ reabsorption
Takes these elements out of tubules and BACK into the blood stream
Passive: osmosis, diffusion
Active: transport across cell membranes
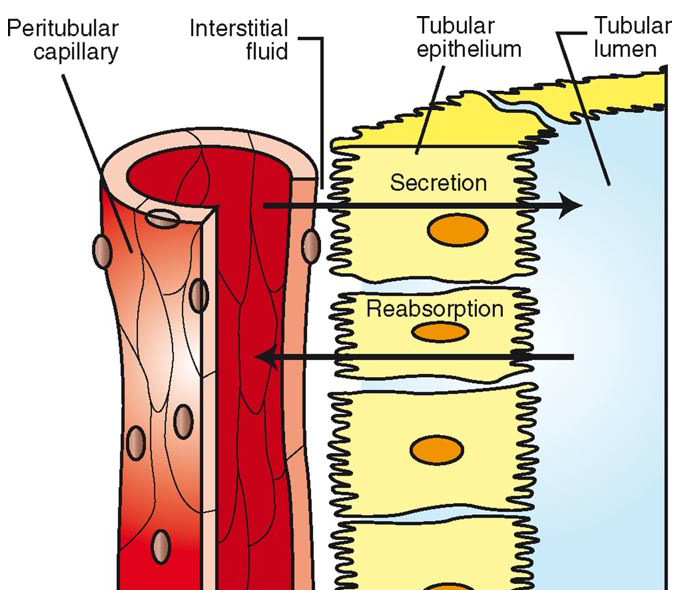
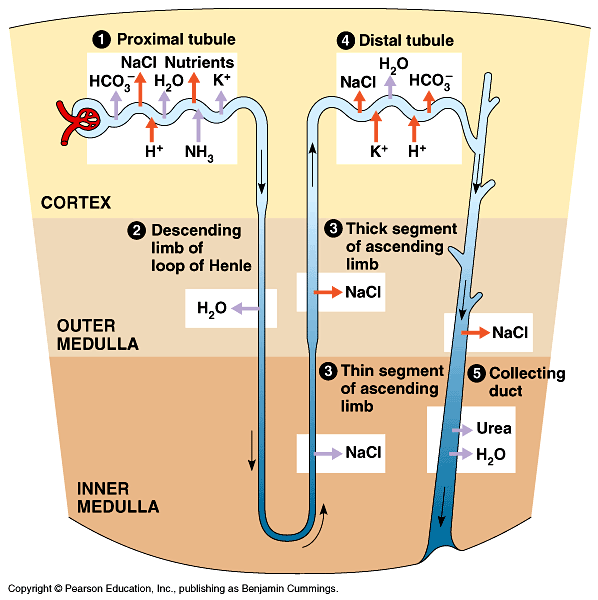
Reabsorption Part 1
useful substances exit into tubules of nephron (as well as wastes): secretion
sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, glucose, amino acids, chloride, bicarbonate, and water
these are needed by the body!
Reabsorption à process to move from nephron tubules back to peritubular capillaries
Passive or active
Sodium Reabsorption
sodium in tubular filtrate attaches to carrier protein
carried into cytoplasm of PCT epithelial cell
Requires energy!
Glucose and amino acids hitch a ride on the same carrier protein
Passive transport
Sodium cotransport
sodium actively pumped out of PCT cell into interstitial fluid, where it moves into peritubular capillaries
sodium ions also reabsorbed in ascending loop of Henle and DCT
usually exchanged for hydrogen, ammonium, or potassium ions
under influence of aldosterone (hormone from adrenal gland)
Sodium Reabsorption Continued
Sodium movement (Na+) creates an electrical imbalance
Actively pumped from tubule into tubular epithelial cell and then into interstitial space
Chloride (Cl-) diffuses into same space to restore neutrality
Water also follows due to osmosis
Remember, Na has brought along glucose and amino acids
Allows for passive reabsorption
Some wastes get reabsorbed, too (BUN)
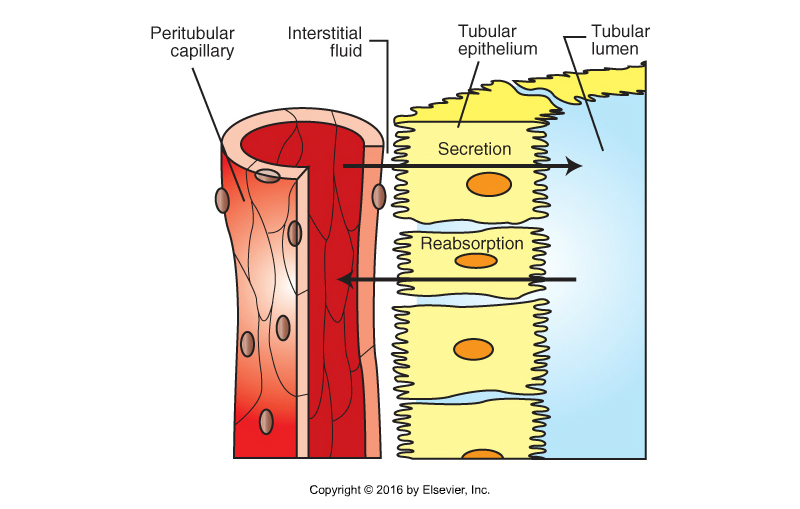
Reabsorption Part 2
chloride ions diffuse from tubular filtrate into epithelial cells and interstitial space
in response to electrical imbalance created by sodium removal
some of the water in the filtrate moves by osmosis into interstitial space and peritubular capillaries
after sodium, glucose, amino acids, and chloride have left tubular filtrate (change in concentration gradient)
urea also passively absorbed
Waste product, but some hangs around
BUN
Reabsorption Part 3
potassium
diffuses into interstitial fluid in the PCT, ascending loop of Henle and DCT
calcium
reabsorbed and moves through epithelial cells in the PCT, ascending loop of Henle, and DCT
under influence of Vitamin D, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and calcitonin (thyroid)
magnesium
reabsorbed from PCT, ascending loop of Henle, and the collecting duct
PTH increases its reabsorption
Reabsorption Part 4
~65% of tubular reabsorption happens in PCT
~80% of water, sodium, chloride and bicarbonate and 100% of glucose are reabsorbed in PCT
Remainder of absorption
DCT
Loop of Henle
Collecting ducts
Secretion
not all wastes are filtered by glomerulus
excess wastes are secreted primarily in DCT by secretion
hydrogen, potassium, ammonia
some medications also eliminated by secretion
E.g. penicillin, sulfonamides
where would these drugs concentrate?
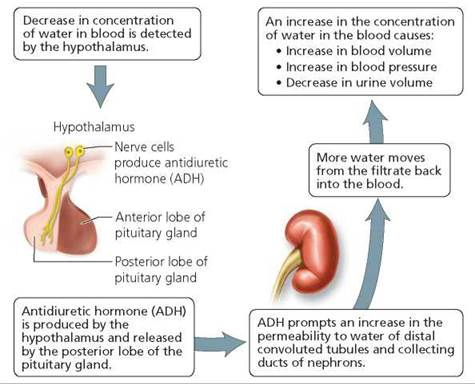
Urine Volume Concentration
urine volume is determined by amount of water contained in tubular filtrate when it reaches the renal pelvis
controlled by actions of 2 hormones
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
from posterior pituitary
acts on DCT and collecting ducts promote water reabsorption
if absent, polyuria results
aldosterone
from adrenal cortex
Increases reabsorption of sodium into bloodstream in DCT and collecting ducts → osmotic imbalance → water follows
ADH & Aldosterone
Regulation of Blood Pressure (BP)
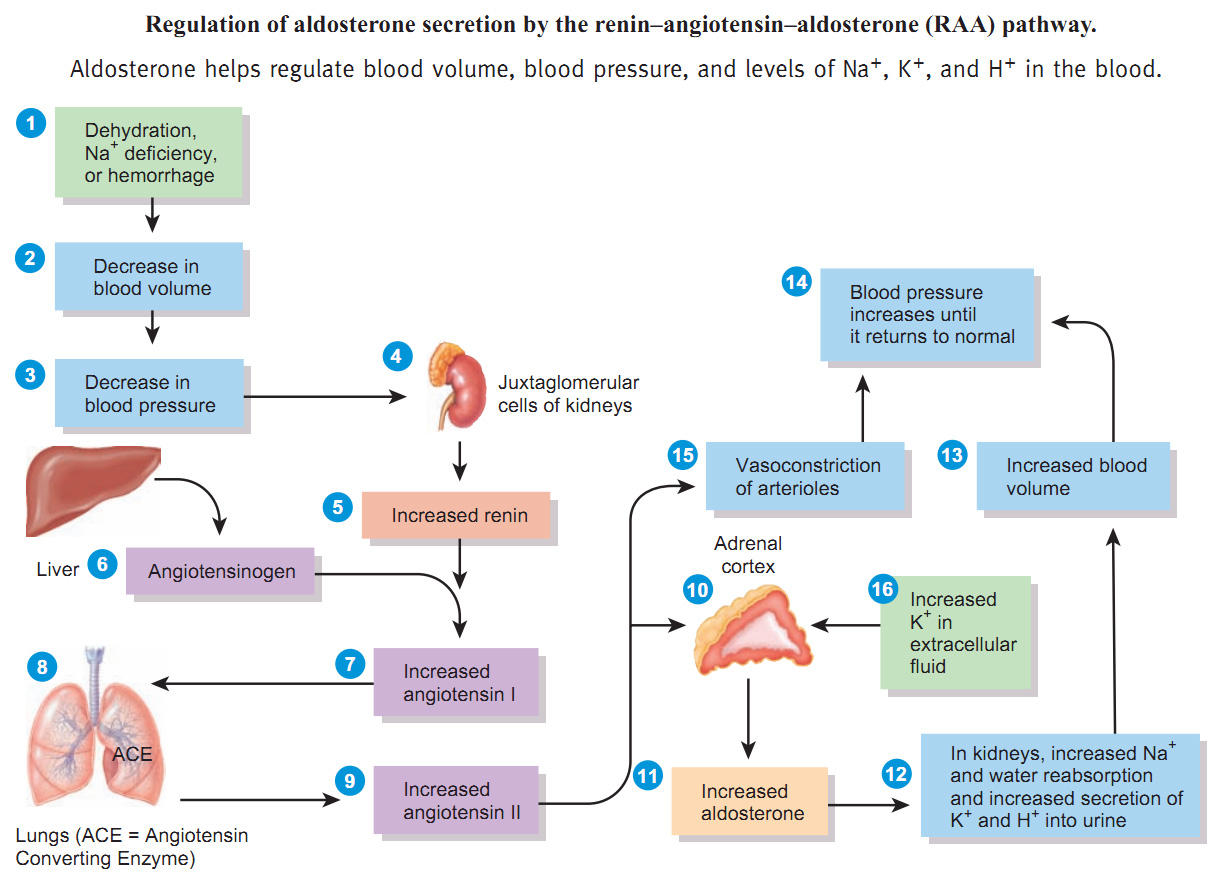
kidneys help maintain homeostasis by their role in regulating blood pressure
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system responds when BP falls
Monitoring cells
Afferent glomerular arterioles
Juxtaglomerular cells
Monitor blood pressure
Ascending limb of loop of Henle
Macula densa
Monitors NaCl concentration
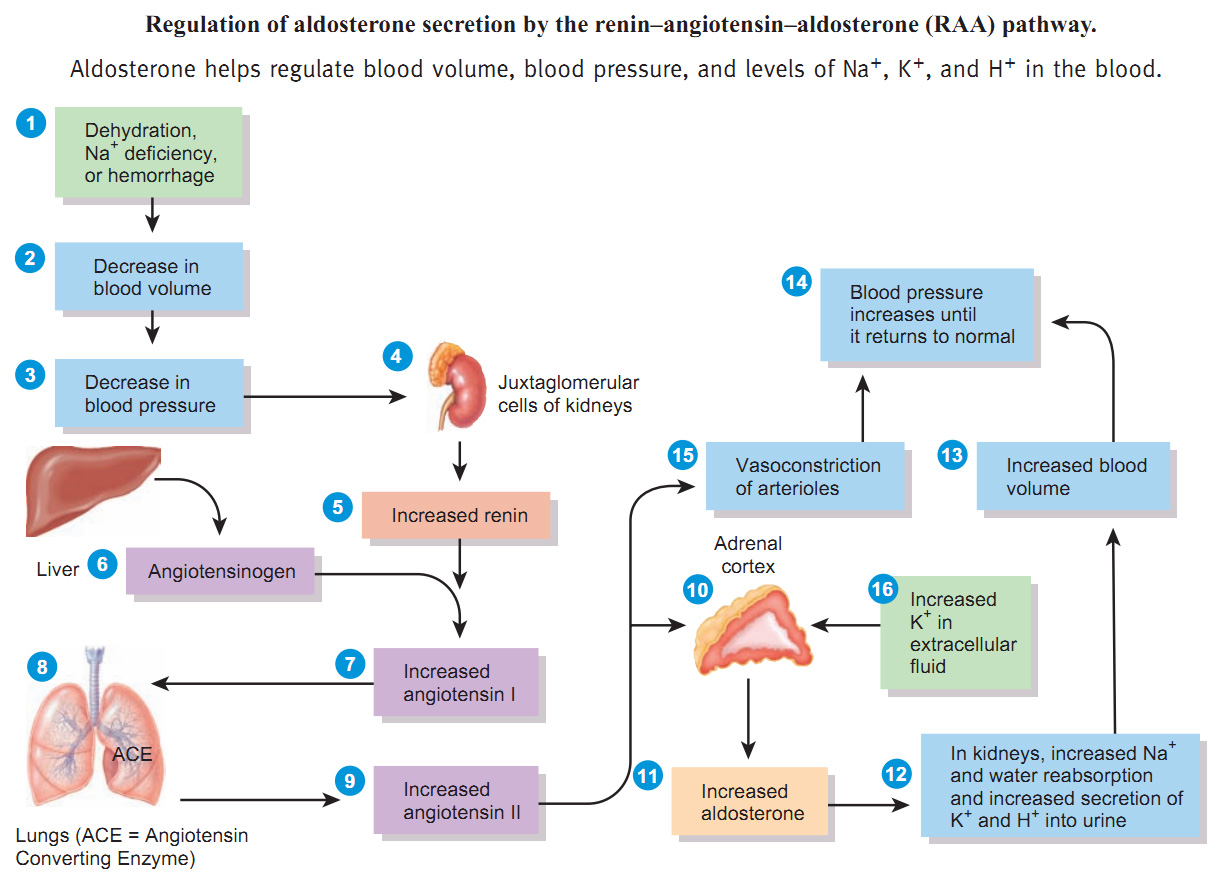
Regulation of Blood Pressure (BP) Continued
If BP falls or NaCl decreases
renin is released
Enzyme that splits angiotensin
angiotensin I converted to angiotensin II by ACE
angiotensin II causes arterial constriction and stimulates release of aldosterone
increased amounts of sodium and water reabsorbed back into bloodstream, causing an increase in blood volume
as blood volume increases, so does blood pressure
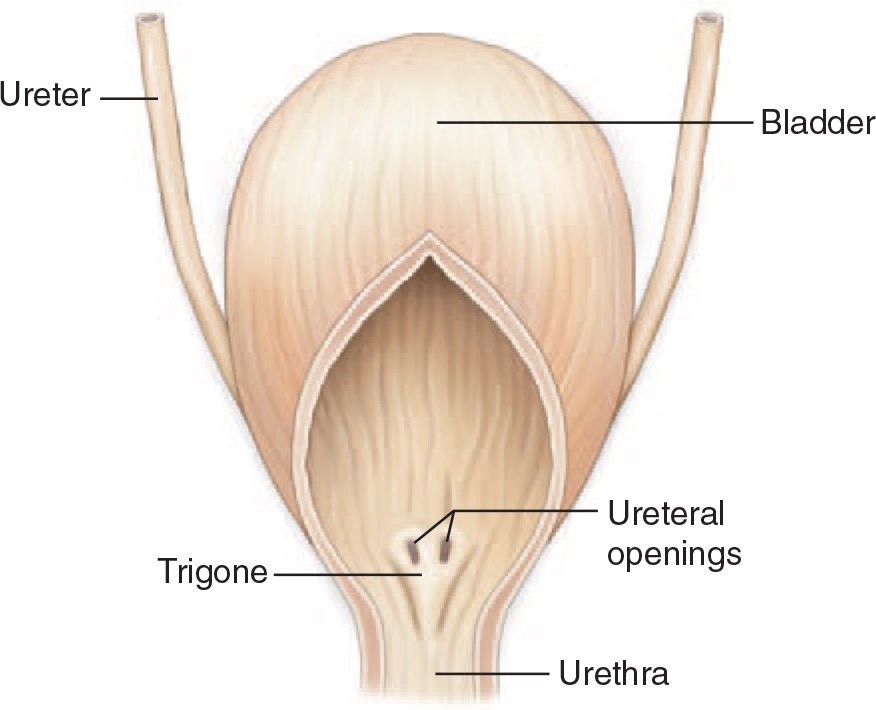
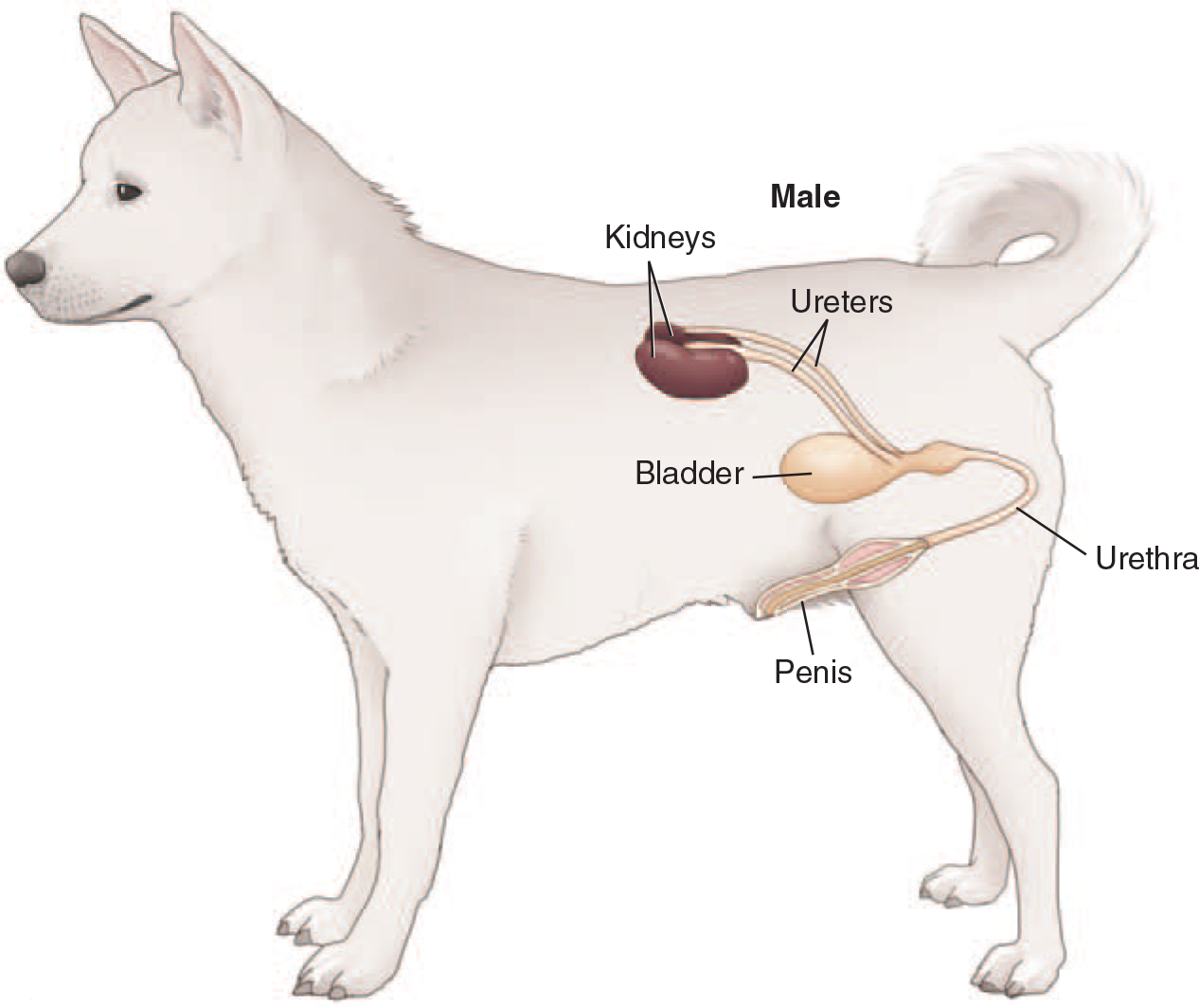
Ureters
tubes that exit the kidney at the hilus and then connect to the urinary bladder at the neck
trigone: arrangement of openings of ureters into bladder and opening from bladder into urethra
a continuation of the renal pelvis
each ureter leaves its kidney at the hilus
composed of 3 layers:
outer fibrous layer
middle muscular layer
smooth muscle propels urine by peristalsis
Doesn’t require gravity
inner epithelial layer
Lines with transitional epithelium
allows ureters to stretch when urine passes through
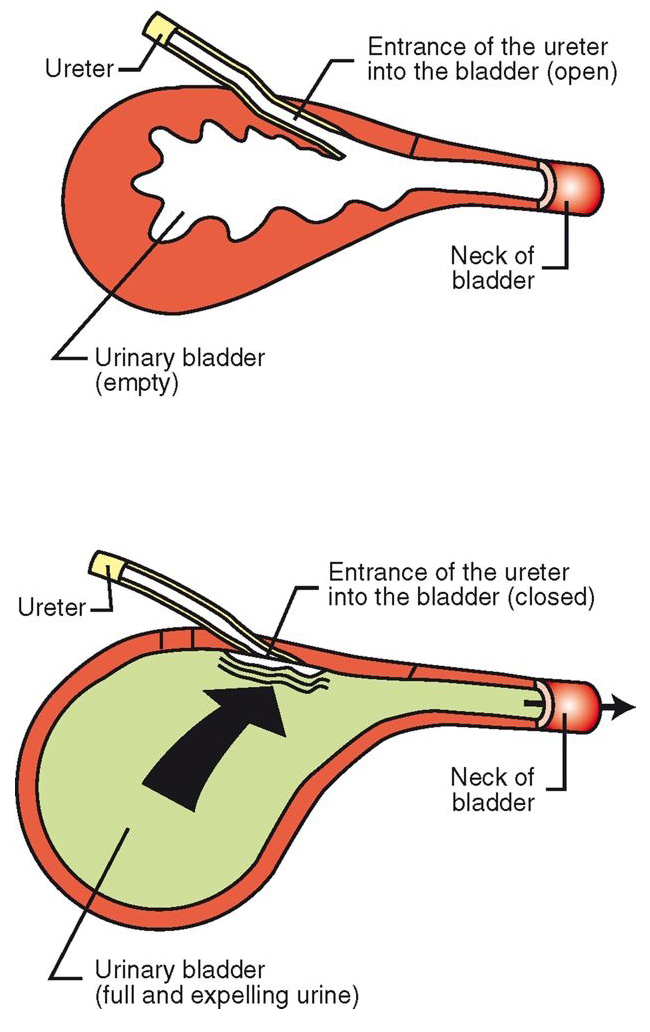
Ureters Continued…
enter bladder at an oblique angle
openings collapse when bladder is full
prevent backup of urine into ureters
peristalsis still allows urine to enter bladder
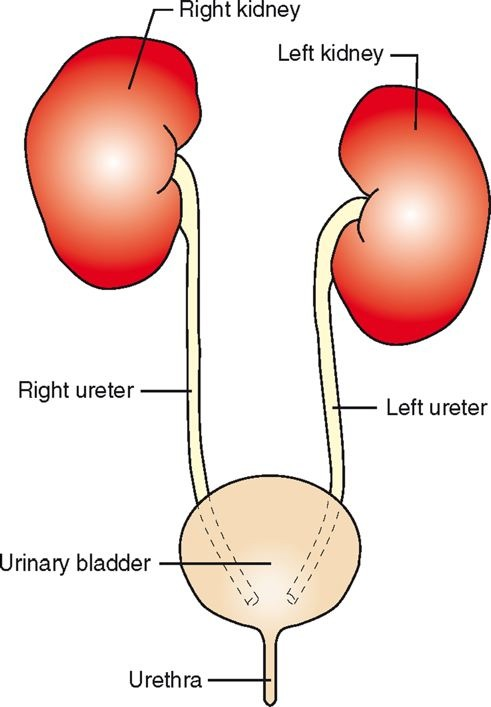
Urinary Bladder
stores urine as it is produced
lined with transitional epithelium
releases urine periodically from the body
2 parts: muscular sac neck
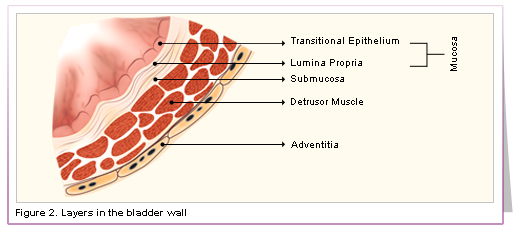
Anatomy of the Urinary Bladder
size and position vary depending on amount of urine it contains
transitional epithelium stretches as bladder fills with urine
detrusor muscle (smooth) contracts to expel urine
circular sphincter muscles (skeletal) around neck of bladder
provides voluntary control over urination process
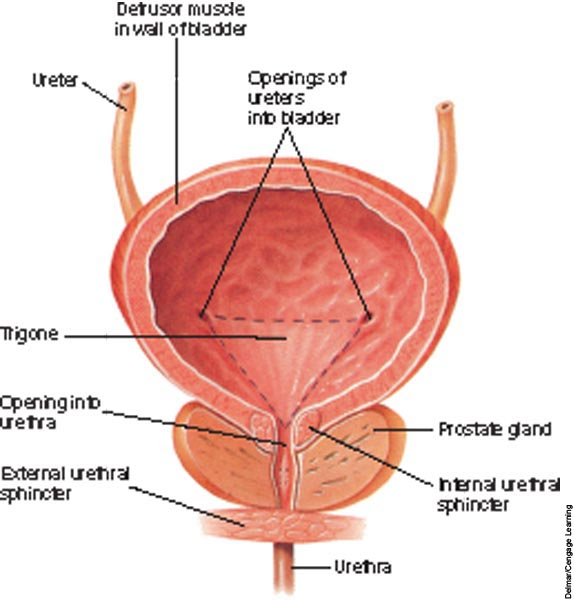
Function of the Urinary Bladder
collect urine
kidneys constantly produce urine
store urine
release urine
Urination = Micturition = Uresis
expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder into the urethra for elimination from the body
2-3 steps in process:
urine accumulation
muscle contraction
sphincter muscle control
Control of Urination
urine accumulation
bladder constantly accumulates urine
pressure of filling bladder reaches certain trigger point
stretch receptors in bladder wall are activated
muscle contraction
spinal reflex is activated
motor impulse sent to detrusor muscle
smooth muscle in bladder wall contracts
This is the sensation of the need to urinate
bladder emptied if animal is not housebroken
Control of Urination Continued…
sphincter muscle control
voluntary control of sphincter around neck of bladder offers temporary control of urination
the fuller the bladder, the more pressure on the sphincter muscle
eventually the sphincter muscle relaxes
urine is released
“accident”
full bladders also have thinner walls
More susceptible to damage (trauma)
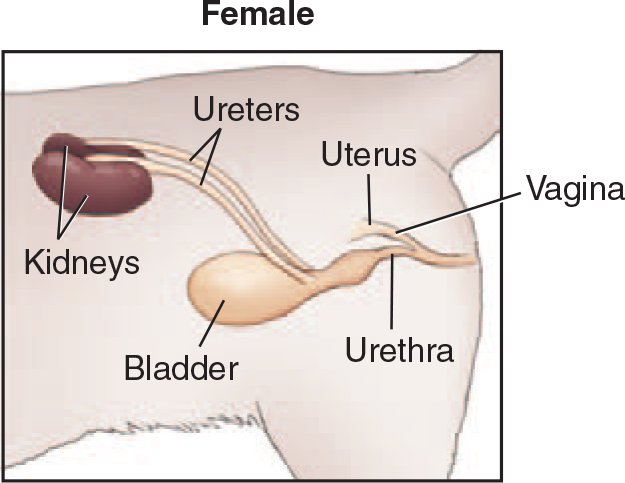
Urethra
continuation of the neck of the bladder; lined with transitional epithelium
carries urine from bladder to the external environment
runs through pelvic canal
much longer in male; runs along ventral aspect of penis
Anatomy of the Urethre
Female Urethra:
shorter and straighter
opens on floor (ventral portion) of vestibule of the vulva
lined with transitional epithelium which allows it to expand
Male Urethra:
longer and curved
runs along the ventral aspect of the penis
lined with transitional epithelium which allows it to expand
Function of the Urethra
Female Urethra:
strictly a urinary function
carries only urine
Male Urethra:
has both urinary and reproductive functions
carries urine or semen
semen (sperm + seminal fluid) enters the urethra as it passes through pelvic canal
At ejaculation, sphincter of bladder neck closes
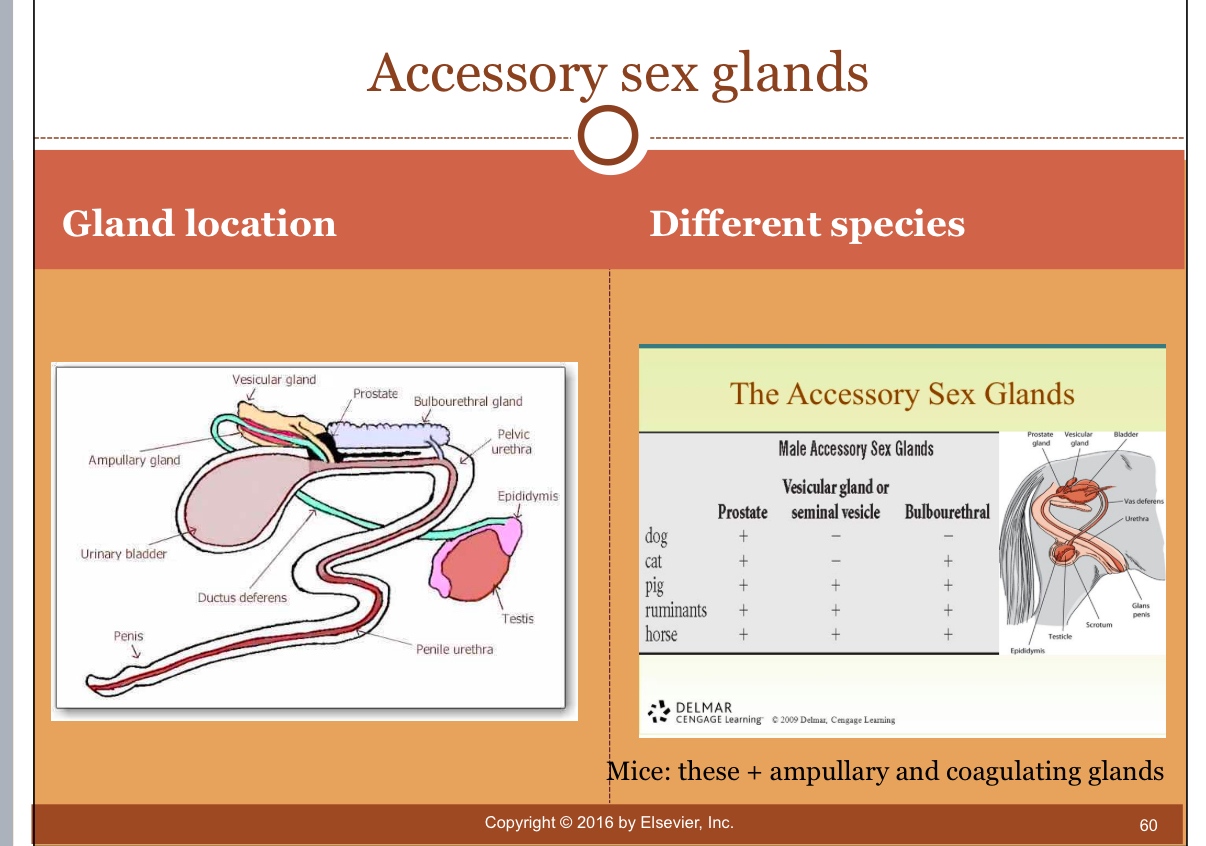
Accessory Sex Glands