Muscle Tissues
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
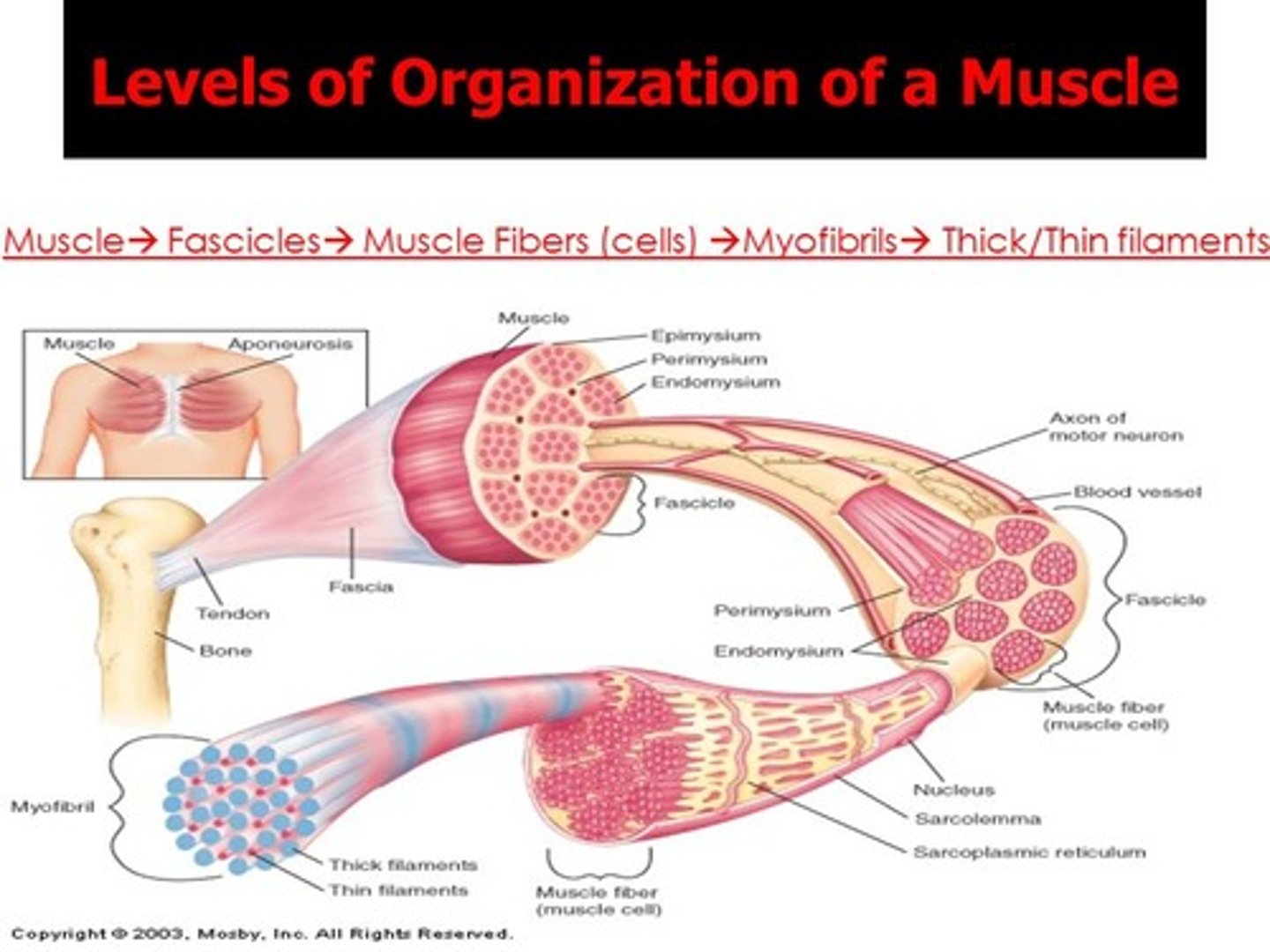
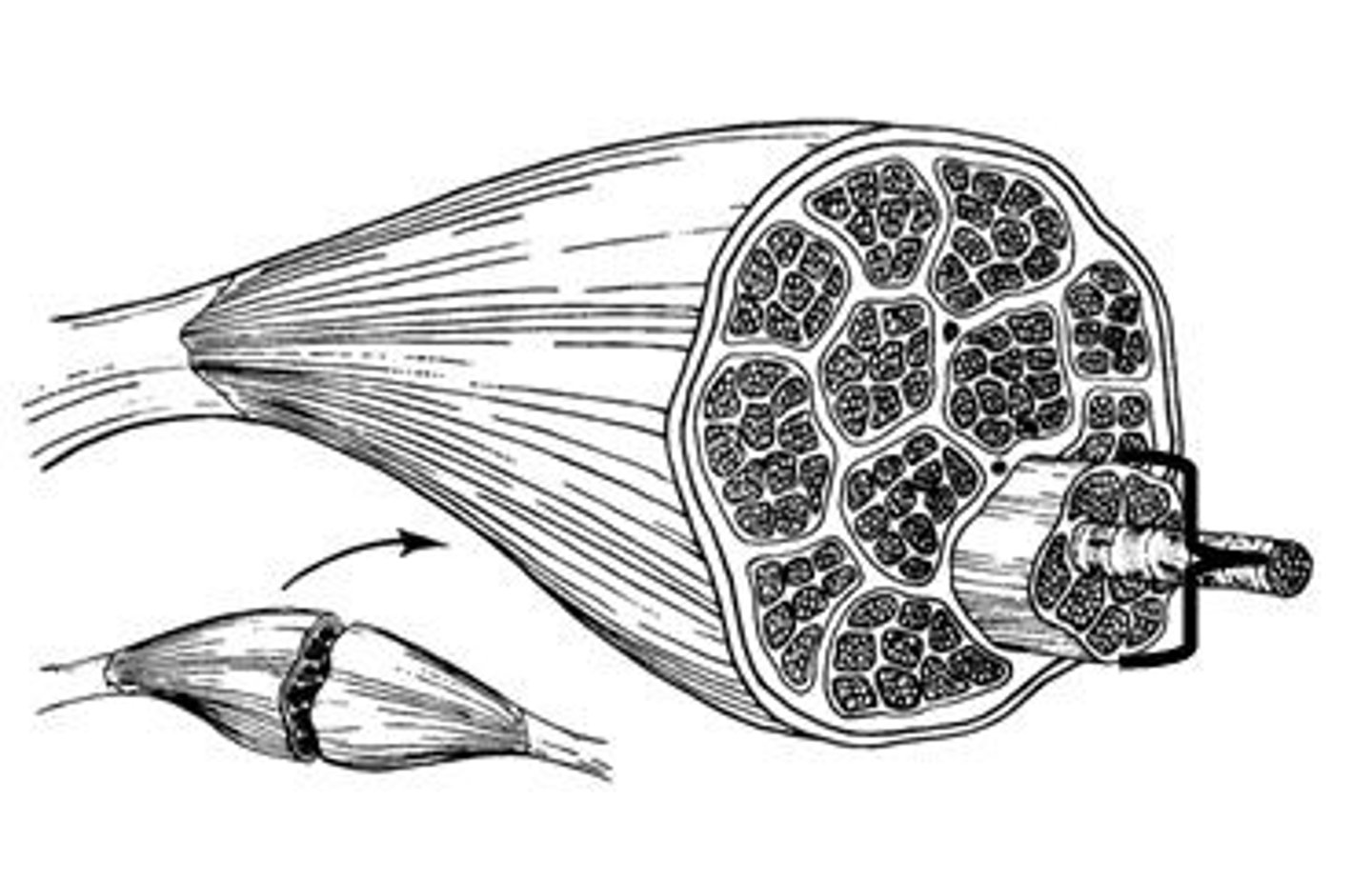
What's inside a whole muscle?
smallest to largest:
myosin
sarcomere
myofibril
muscle fiber
fascicle
myosin
The contractile protein that makes up the thick filaments of muscle fibers
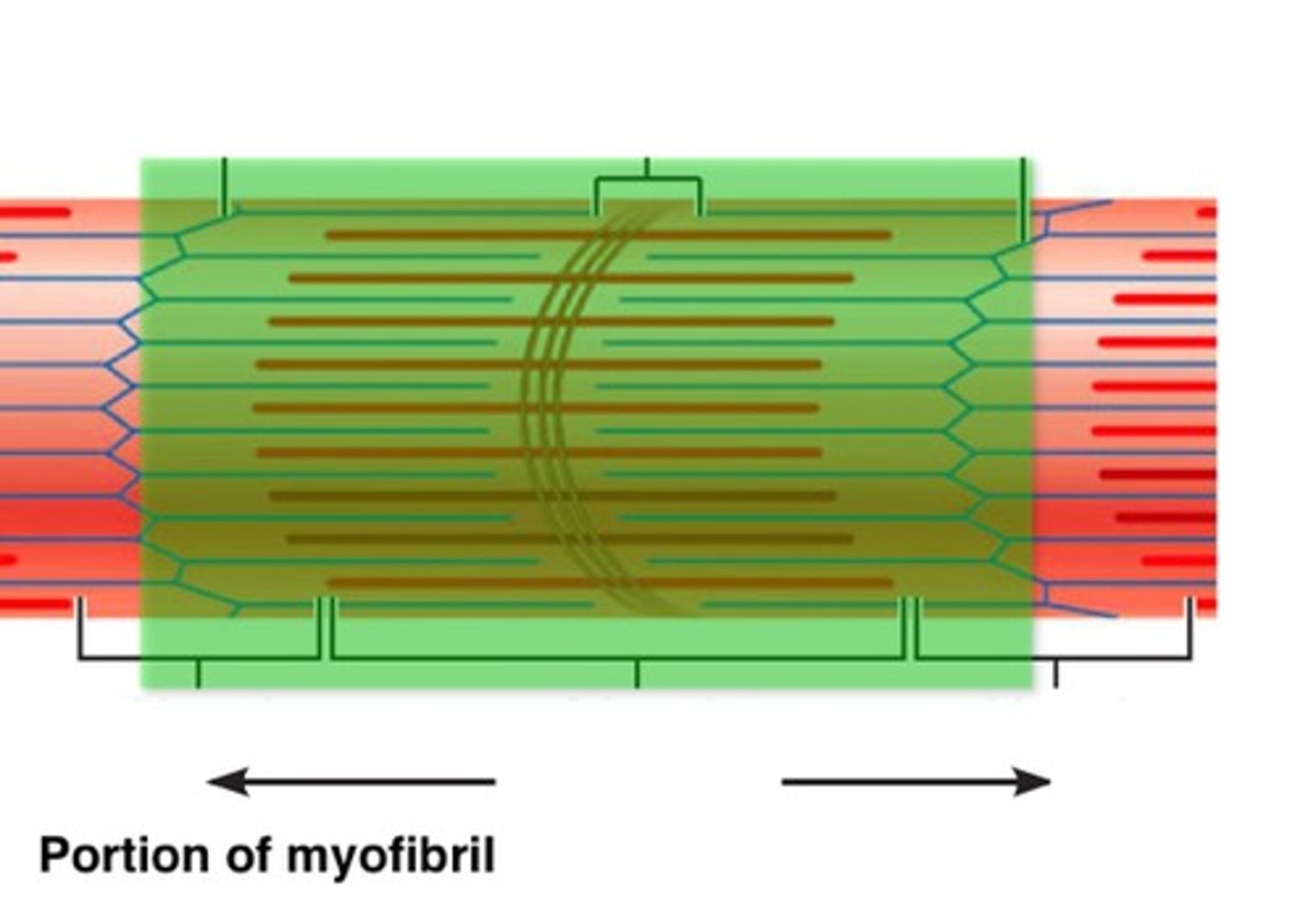
sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber; contains actin & myosin
myofibril
any of the elongated contractile threads found in striated muscle cells.
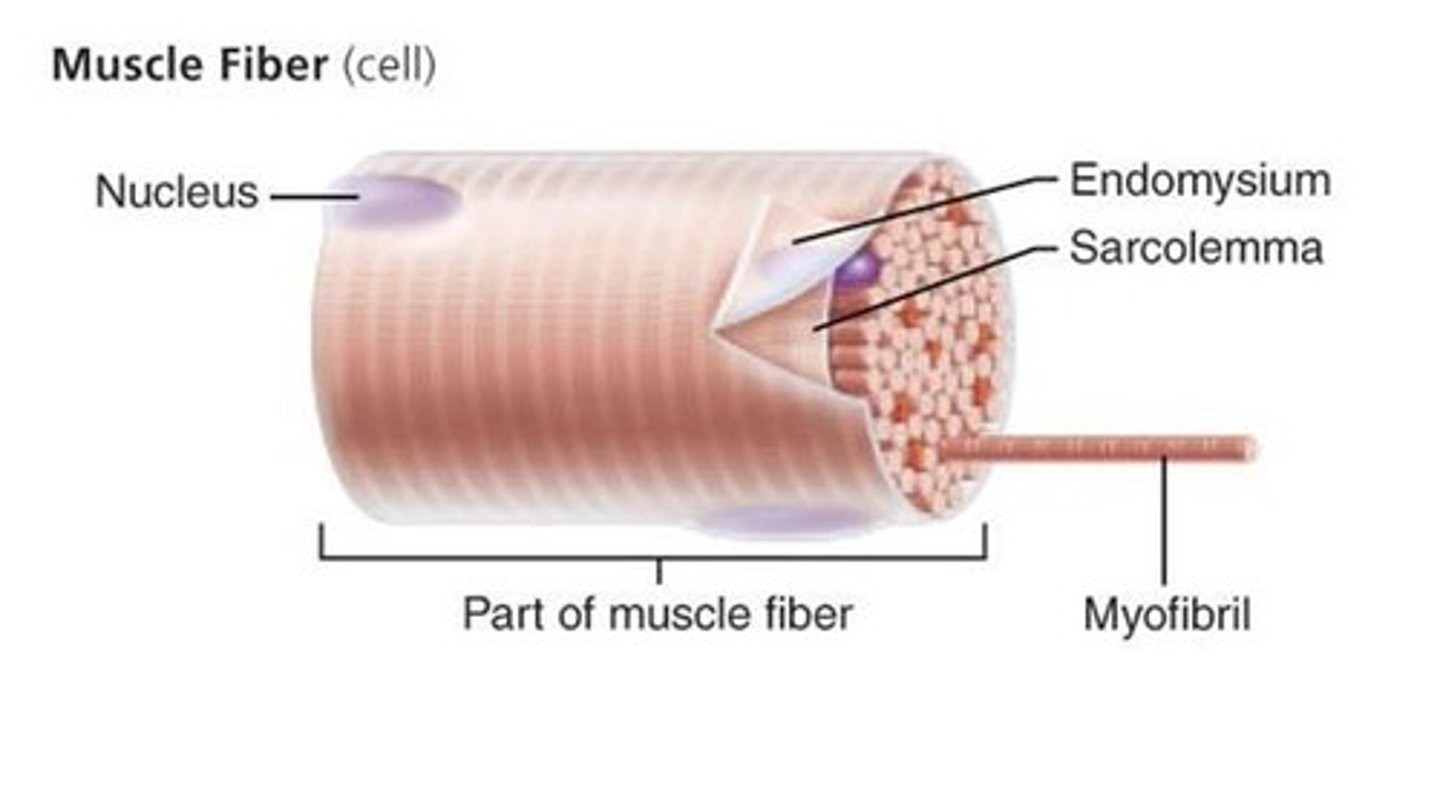
muscle fiber
a single muscle cell
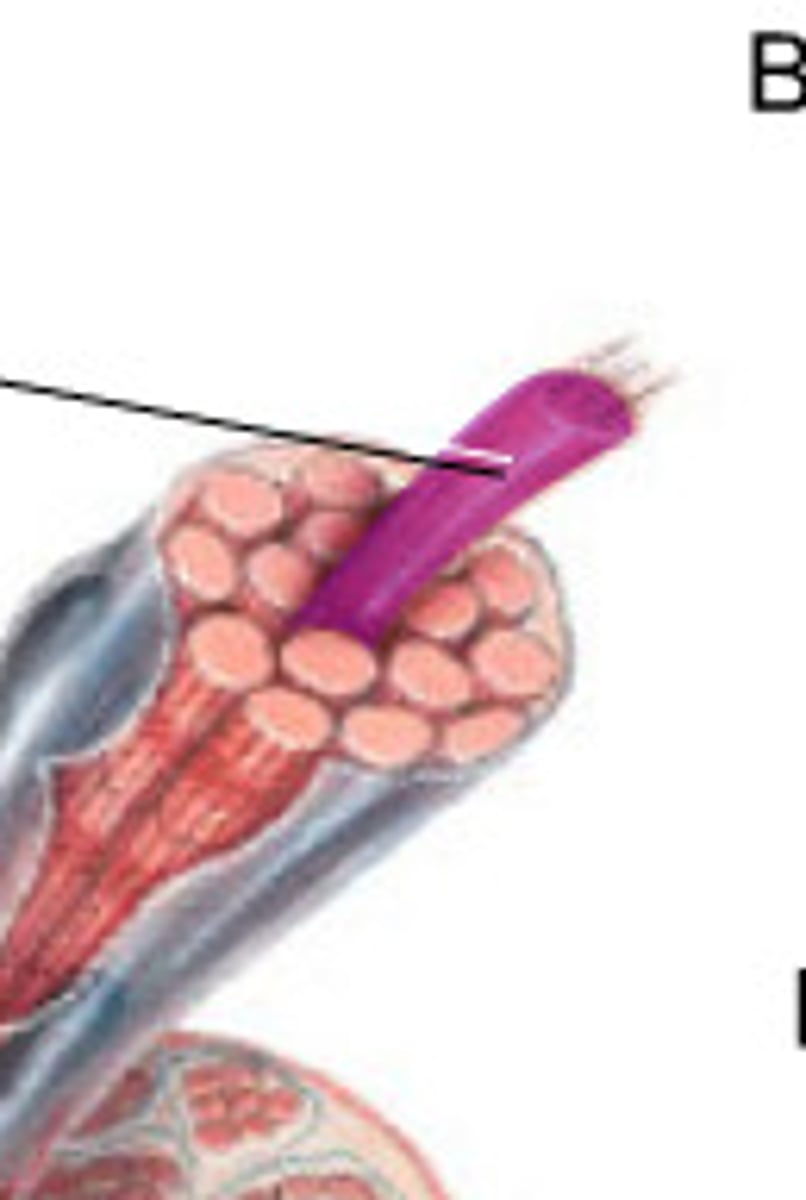
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
How does actin and myosin cause muscle contraction?
myosin heads grab onto actin at binding sites and pulls to shorten muscle
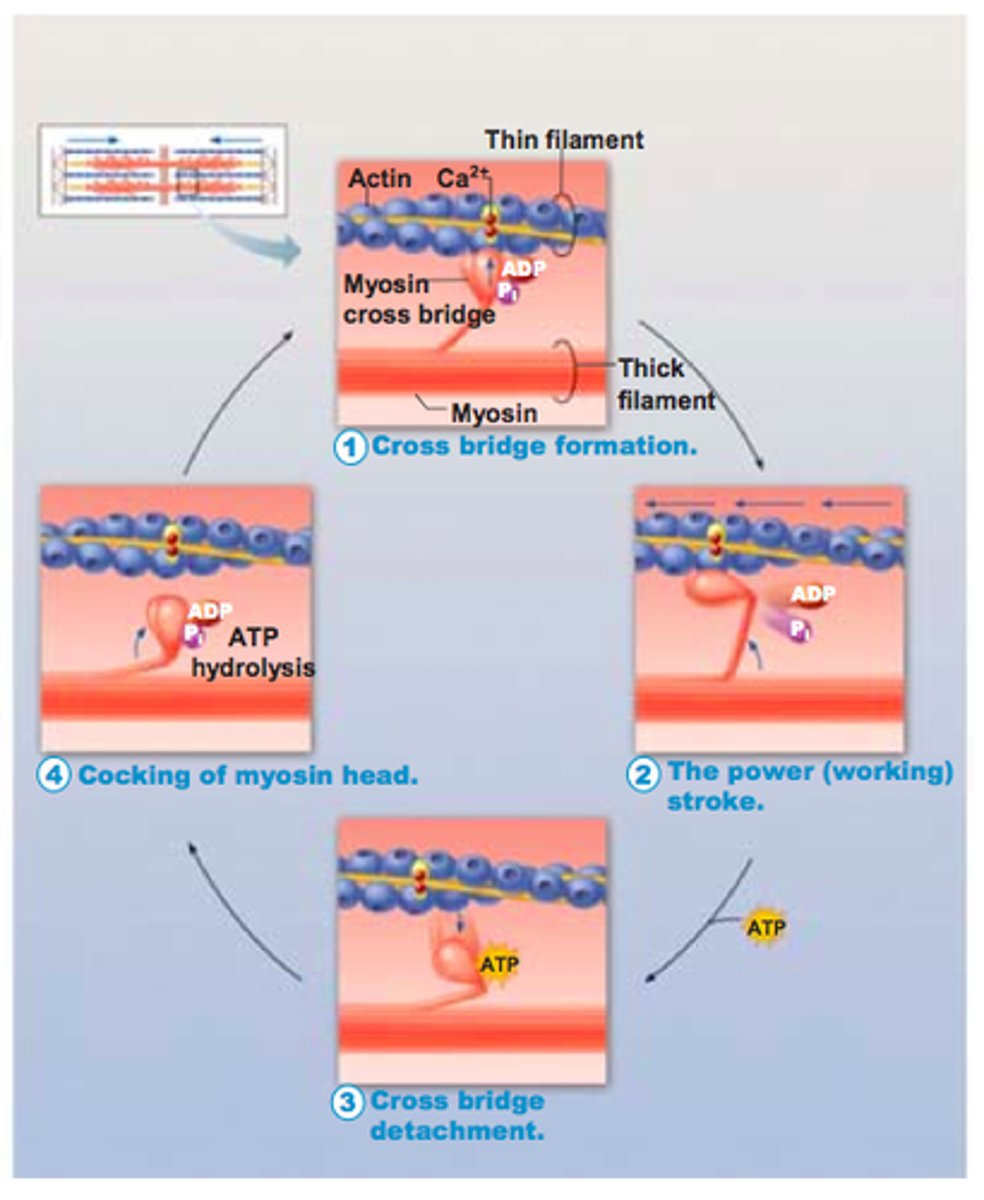
What are the steps of cross-bridge cycling?
1. myosin head binds to actin
2. inorganic phosphate (Pi) is released, leading to the power stroke (sliding of thin filaments along thick filaments)
3. ADP is released from myosin and a new ATP binds
4. Binding of ATP releases myosin head from actin
5. Myosin ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to ADP+Pi, which resets the myosin head to its starting position
6. If calcium remains bound to troponin, then cross-bridge cycling will continue
How does the release of calcium cause muscles to contract?
Ca is released onto sarcomere when the muscle needs to contract. calcium binds to Traponin causing it to change shape. this moves Tripomysoin out of the way exposing binding sites
When a nerve signal reaches a muscle fiber, what happens?
t-tubules transmit nervous signal deep into the muscle fiber to release calcium inside so cross-bridge cycling can occur
How does a muscle's length affect its strength?
muscles generate the greatest force when at their resting (ideal) length, and the least amount of force when shortened or stretched relative to the resting length.
How does the frequency of stimulation affect the force of a muscle?
higher frequency= higher force
What is tetanus?
a smooth, sustained contraction of maximal strength
What is the latent period and why does it exist?
Short duration of time where nothing happens before a muscle contracts. Necessary for signal to travel to muscle and steps occur to contract muscle.
What are motor units, and how do we control how strongly one of our muscles contracts?
The combination of an individual motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers that it innervates
more motor units= stronger force
red muscle fibers
lots of capillaries
lots of blood
increased myoglobin
aerobic respiration
thin
weak
slow fatigue
white muscle fibers
few capillaries
little blood
anaerobic respiration (glycolysis)
thicker
stronger
fast fatigue
What are the 5 steps occur at the neuromuscular junction for muscle contraction to occur?
1. a nerve signal reaches neuromuscular junction
2. neurotransmitters bind to the sarcolemma
3. a signal travels down the t tubules
4. calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
5. cross-bridge cycling occurs
This blocks the binding sites on actin
tropomyosin
This is the neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction
acetylcholine
Calcium binds to this protein when released onto the sarcomeres
troponin
The thick protein of the sarcomere that "pulls"
myosin
The thin protein of the sarcomere, called the thin filament
actin
These tiny tubes carry a signal deep into a muscle fiber
t tubules