3 DBSCAN
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Clustering
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
DBSCAN
used for clustering of data

DBSCAN Handle Clustering
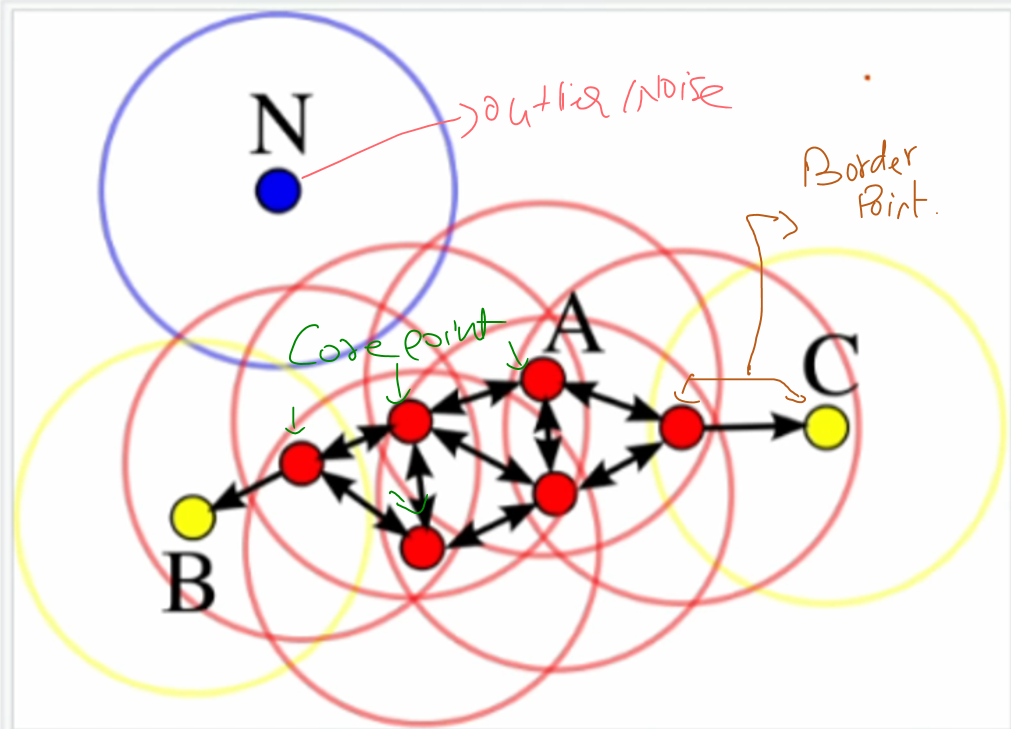
DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) is a density-based clustering algorithm that groups data points based on their density in the feature space. Unlike K-Means, DBSCAN does not require specifying the number of clusters in advance. It works by:
Core Points: Data points that have a minimum number of neighboring points (defined by a parameter called minPts) within a specified radius (denoted as epsilon) .
Border Points: Points that are within the epsilon radius of a core point but do not have enough neighbors to be core points themselves.
Noise Points: Points that are not core or border points and are considered outliers. DBSCAN creates clusters of arbitrary shape, as it relies on the density of points rather than their proximity to fixed centroids. It is particularly useful for detecting clusters in datasets with noise and varying cluster shapes.
we will find the min point using
seloutte Scoring
Core Point
number of points within epsilon >equal to min point
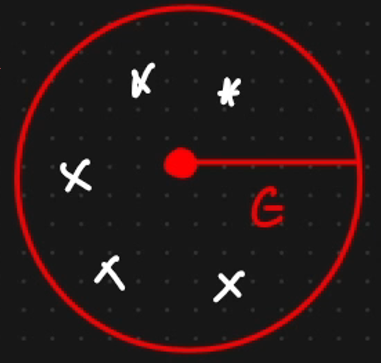
Border Point
Number of point within this radius

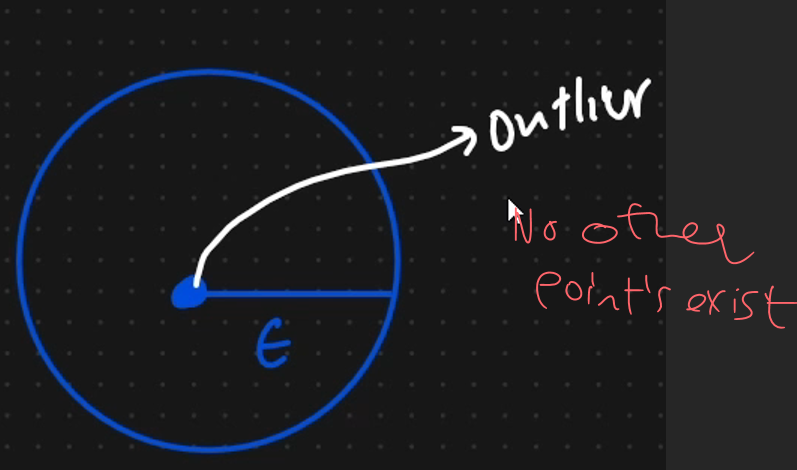
Outlier
The point that dont exit in border & core will be here
Representation of DBSCAN
Kmean vs DBSCAN interms of noise


can we solve this kind of cluster using DBscan
yes
Is dbscan is robust to outliers
Yes