Foundations of Psychology
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Types of research data
qualitative
quantitative
Research data- qualitative
non-numerical (ex. structured interviews)
research data- quantitative
numerical data (ex. Likert scale)
types of bias
hindsight bias
overconfidence
confirmation bias
social desirability bias
false consensus effect
hindsight bias
“i knew it all along” phenomenon
overconfidence
we think we know more than we do
confirmation bias
seek out information that supports one idea
social desirability bias
answer in a way that will be viewed favorably by others
false consensus effect
overestimate how much others share our beliefs
Aspects of research
theory
hypothesis
falsifiable
operational definition
replication
operational definition
procedures used to define and simplify research variables
replication
repeating a study finding generalizing to other participants (see how specific it is using study)
Institutional review board (IRB) ethics
no coercion
safety
confidentiality
informed consent
debrief
stanley milgram’s shock experiment (how is it unethical/what is it)
conflict between obedience to authority and conscience, no debrief, psychological harm
philip zimbardo- stanford prison experiment (how is it unethical/what is it)
psychological effects of perceived power, safety
what are the three types of research methods?
non-experimental
correlational
experimental
case study
in depth study of an individual- no cuase/effect
Likert scale
scale used to measure opinions, attitudes
structured interviews
fixed set of closed questions are used
naturalistic observation
observing in natural environment
meta-analysis
result of multiple studies combined and analyzed
longitudinal
measures individual over extended period of time
cross-sectional
measures individuals of various ages at one point in time
non-experimental purpose
observe/describe behaviors without manipulating variables, cannot determine cause/effect
correlation
measure/observe relation between variables
correlational coefficient
indicates strength and direction between two variables
numbers range from -1 to 1, closer to one = stronger
positive= variables move in the same direction, negative= variables move in opposite directions
correlation and causation
indicates possibility of cause and effect, correlation does not prove causation
third/confounding variable
affects both variables; makes them seem casually related when they are not
scatterplot
slope suggests direction
scatter= strength
correlational research pros and cons
pro- describe relationship between two variables
con- can’t establish cause and effect
experimental research
manipulates factors - ind. variables - to observe effect on dep. variables
ind. variable
the “if”
manipulates
cause
what you’re studying
dep. variable
the “then”
measure effect- behavior or mental process
red bull experiment (IV, DV, confounding variable)
iv- red bull
dv- hyperactivity
confounding- breakfast before school
experimental vs control group
experimental- exposed to treatment, IV
control- serves as comparison
population
group you want to study
random sample
every subject in the population has equal chance of being chosen
random assignment
assigning participants to groups by chance
convenience sampling
data from easily accessible/available group
sampling bias
does not accurately represent the population being studied
generalized results
how representative your sample is of the target population
double-blind procedure
both researcher and participant are ignorant
single-blind procedure
subjects dont know
placebo
inert substance that triggers effect of the active agent
experimental research pros and cons
pros
cause and effect
replicate
manipulate
cons
artificial environment
confounding variables
bias
mean
average
mode
most frequently occurring score
median
middle score when in order
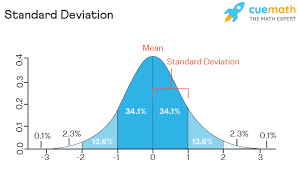
standard deviation
measurement of how much scores vary around the mean
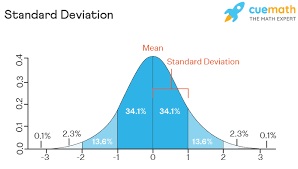
normal distribution
percentile rank
compare a specific raw score to the other scores
bimodal distribution
score with two peaks or modes
variance
how far a data set is spread out
variation (in relation to standard deviation)
larger variation= larger standard variation
range
variation between highest and lowest scores
skew
direction of the tail
positive skew
skewed right, tail on the right side
negative skew
skewed left, tail on left side
statistical significance
probability of result occurring by chance
effect size
size of relationship between two variables