Art 100 test 4
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Last updated 3:43 PM on 1/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
Renaissance
Rebirth
2
New cards
Ghiberti
Rediscovered lost wax casting method, taught Donatello
3
New cards
Main artists of the high renaissance
Donatello, Leonardo Da Vinci, Michaelangelo, Raphael
4
New cards
"Renaissance Man"
Leonardo Da Vinci
5
New cards

Leonardo DaVinci, Last Supper, Italian Renaissance
6
New cards

Leonardo DaVinci, Mona Lisa, Italian Renaissance
7
New cards
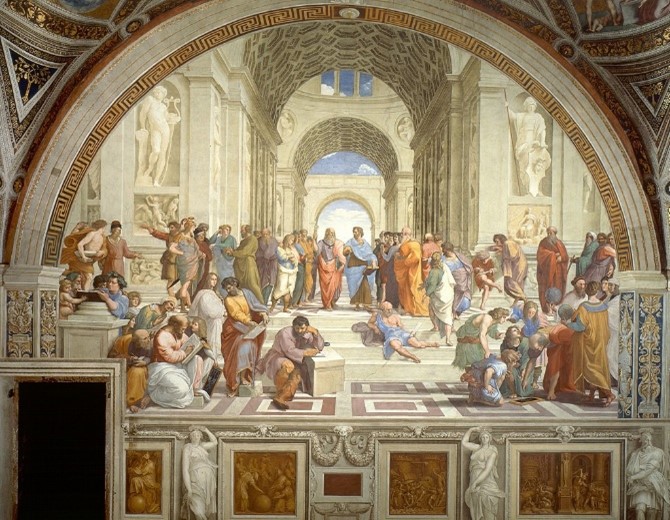

Raphael, The School of Athens, Italian Renaissance
8
New cards

A Burial at Ornans, Gustave Courbet 1849-50, Realism
9
New cards

Caravaggio, Entombment of Christ, 1604, Italian Baroque
10
New cards
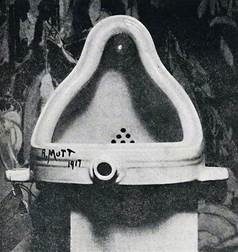
Marcel Duchamp, Fountain, 1917, Readymade, Dada
11
New cards

Gleaners, Jean-Francois Millet, 1857, Realism
12
New cards

Claude Monet, Impression, Sunrise, 1872
13
New cards
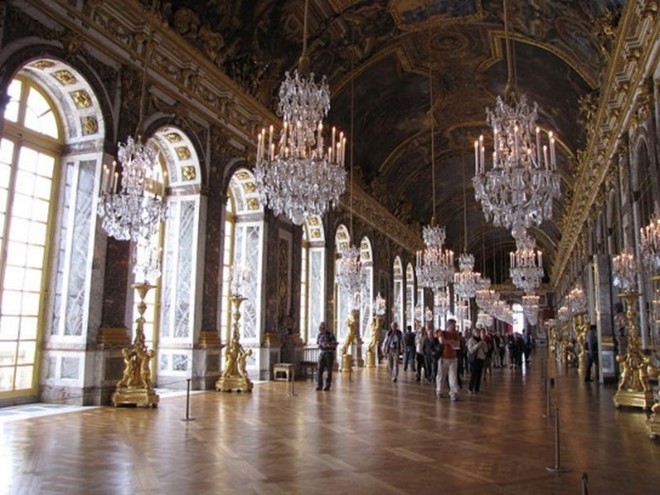

Palace of Versailles, The hall of Mirrors, French Baroque
14
New cards

Diego Velazquez, Las Minenas, 1656, Spanish Baroque
15
New cards

Pablo Picasso, Les Desmoiselles D’Avignon, 1907, oil on canvas, Cubism
16
New cards

Liberty Leading the People, Eugene Delacroix, 1830
17
New cards

Michaelangelo, David, Italian Renaissance
18
New cards

Paul Cezanne, Mont Saint-Victoire, 1902-04, oil on canvas, post imressionism
19
New cards

Salvador Dali, The Persistence of Memory, Oil on canvas, 1931, SURREALISM
20
New cards

Jaques-Louis David, The Oath of the Horatii, 1784, oil on canvas, Neoclassicism
21
New cards

Michaelangelo, Sistine Chapel Ceiling, Italian Renaissance
22
New cards

Gianlorenzo Bernini, St. Theresa in Ectasy, marble, Italian Baroque
23
New cards

Vincent Van Gogh, Starry NIght, 1889, oil on canvas, post-impressionism
24
New cards

Georges Seurat, A sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Latte, 1884-86, post impressionism
25
New cards

Eduard Manet, The Luncheon on the Grass, oil on canvas, 1863
26
New cards
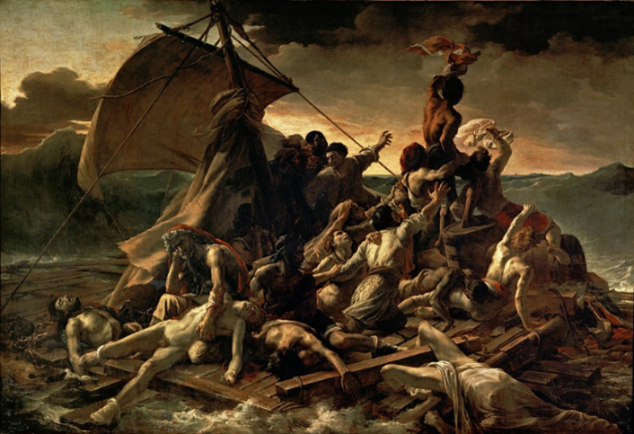

The Raft of the Medusa, Jean Louis Theodore Gericault, 1818-1821
27
New cards

Auguste Rodin, The Thinker, 1904. Bronze, Impressionist Sculpture
28
New cards

Henri Matisse, Woman with a Hat 1905, Fauvism
29
New cards

Jean-Honore Fragonard, The Pursuit from The Progress of Love, 1771-1773, Rococo
30
New cards
What are 2 factors that contributed to the development of Renaissance painting?
Oil paint and diversity of patrons
31
New cards
When did Northern European Renaissance artists began using the system of linear perspective?
75 years after it gained popularity in Italy
32
New cards
Mannerism
elaborate subject matter, elongated, twisting figures in illogical spaces. Rejected the harmony and ideal proportions of the Renaissance in favor of more irrational settings
33
New cards
Baroque
new explorations of naturalism, form, strong contrast in light and shadow, dramatic intensity. Works demonstrated movement and emotions and used bold color. Heavy ornamentation and used primarily public places (churches, palaces, etc.)
34
New cards
In Baroque architecture, wall surfaces often protrude into the viewer's space. In Baroque painting, this same effect is created through the use of ............
dramatic lighting, tenebrism
35
New cards
How did the Baroque differ in each Catholic region discussed? French, Italian, Spanish
Italy; showcased the Baroque through architecture sculpture and painting.
France; centered on interiors, specifically under the patronage of King Louis XIV, the "absolute" monarch. This can be seen in the Palace of Versailles' Hall of Mirrors.
Spain; had the court painter Velazquez who painted grand scenes of the Spanish monarchy.
France; centered on interiors, specifically under the patronage of King Louis XIV, the "absolute" monarch. This can be seen in the Palace of Versailles' Hall of Mirrors.
Spain; had the court painter Velazquez who painted grand scenes of the Spanish monarchy.
36
New cards
What kinds of figures is Artemisia Gentileschi known for painting?
strong, assertive women
37
New cards
How did Dutch Baroque art differ from the art of Catholic Italy, Spain and France?
it focused on the community, business life, family and the home. The Protestant Reformation created an attitude of hostility toward religious images, so Northern European artists burned to the everyday world around them for the subject matter.
38
New cards
What are the stylistic traits of the Rococo?
It is a playful, light-hearted, and sophisticated style that used softer, pastel colors (than the Baroque) and elaborate ornamentation.
39
New cards
Describe the Neoclassical style and identify which artist was most representative of the Neoclassical movement in 19th c. France?
Neoclassicism is defined stylistically by its use of straight lines, minimal use of color, simplicity of form and, of course, an adherence to classical values and techniques. Neoclassical paintings, produced by men ad women, drew its inspiration from the classical art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome.
40
New cards
What are the stylistic traits of Romanticism?
It stressed emotion, freedom and individual imagination. Its style is characterized by more painterly brushstrokes, softer edges, or contours, and areas of impasto paint (thicker paint).
41
New cards
What important event was happening in France that impacted the development of the Romantic style and its subject matter?
The French Revolution
42
New cards
What are the stylistic traits of Realism?
**Realists depicted everyday subjects and situations in contemporary settings and attempted to depict individuals of all social classes in a similar manner. The art works depicted people of all classes in ordinary life situations, which often reflected the changes brought on by the Industrial and Commercial Revolution.**
43
New cards
What was the Academy? How did it dictate style - for example, which subject matter was considered more or less significant? What did the art preferred by the Academy look like? What was the Salon?
The academy was the preserver of traditional French painting standards of content and style. Its style included a "licked clean", smooth finish and an idealistic depiction of figures to represent the ideals they stood for. Because history and mythology were considered fertile ground for important allegory, using themes from these subjects was considered the most serious form of painting. They maintained a stricture hierarchy of subject matter:
44
New cards
Èdouard Manet was a transitional figure from Realism to Impressionism. His controversial painting, Le déjeuner sur l'herbe, borrowed its composition from artwork created when?
Renaissance works by Raphael and Titian.
45
New cards
How did the Impressionists get their name?
A critic used the term to describe the movement after seeing the painting Impression: Sunrise, and it caught on.
46
New cards
**What kinds of scenes did Impressionist painters focus on?**
They depicted leisure activities involving the middle class.
47
New cards
List three stylistic characteristics of Impressionism (how did their paintings look and how did they paint them?)
1. Constructed their pictures with freely brushed colors using "broken" brush strokes of mixed and unmixed color
2. They capture the momentary and transient effect of sunlight by painting "en plein air" (outdoors)
3. They attempted to capture fleeting moments
48
New cards
Two important innovations of the later part of the 19th century impacted what the Impressionists were able to do with their work, the invention of photography and the manufacturing of oil paint in tubes. Explain how each of these innovations affected Impressionist art and artists.
1. Photography - the development of Impressionism can be considered partly as a reaction by artists to the challenge presented by photography, which seemed to devalue the artist's skill in reproducing reality. In spit of this, photography actually inspired artists to pursue other means of artistic expression, and rather than compete with photography to emulate reality, Impressionists sought to express their perceptions of nature and modern city life.
2. Tube Paints - Painting up until the availability of tube paint was largely a studio production because of the cumbersome materials involved. The manufacture of oil paint in the tubes made it possible for 19th-century European artists to make a painting a portable activity. The spontaneity and directness of painting outdoors ins evident in their works.
49
New cards
What does the term "Post-Impressionism" refer to?
It is essentially a neutral term describing the varied directions of the artists who both accepted and rejected some of the aims of Impressionism.
50
New cards
Who developed the idea of Pointillism and what was it?
Georges Seurat developed Pointillism based on new theories of optics being discovered at the time. The technique involved placing color in small brushstrokes - dots - next to each other and overlapping using optical effects to create color, light and shadows.
51
New cards
Describe Vincent van Gogh's style
He used vibrant colors and active brush strokes of thick paint (impasto).
52
New cards
Describe Cezanne's style
He structured his paintings by reducing objects to their basic shapes while retaining bright fresh colors of Impressionism.
53
New cards
What factors contributed to the rise of Modernism?
Modernism arose from the enormous transformations that occurred in the Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Among the factors that shaped modernism were the development of modern industrial societies and the rapid growth of cities, followed by the horror formulated by religion of science could be used to understand or explain reality.
54
New cards
Fauvism
subject matter/style and main artists: a short-lived movement (4 years) at the beginning of the 20th century. The work emphasized spontaneity and separates form from color. Subject matter had a high degree of simplification and abstraction, used vivid, non-natural color, and wild brushstrokes. Its main artists were Henri Matisse and Andre Derain.
55
New cards
German Expressionism
subject matter/style and main artists: Like the Fauves, Expressionist artists used arbitrary colors and jarring compositions and they emphasized the emotional experience rather than the physical reality. However, their subject matter tended towards the darker, sometimes sinister, aspect of the human psyche. Artists were Edvard Munch and Kirchner.
56
New cards
Cubism
subject matter/style and main artists: Picasso and Georges Braque co-founded the Cubist movement, one of the most influential movements in Modern Art. Cubism stressed basic abstract geometric forms that presented the subject from many angles simultaneously to create a greater scope of context. In Cubist artwork, objects were analyzed, broken up, and reassembled in an abstracted form instead of being depicted from one viewpoint.
57
New cards
Futurism
subject matter/style: Futurism was an Italian movement that emphasized and glorified themes associated with contemporary concepts of the future such as speed, technology, youth, and violence, as well as objects such as the car, the airplane, and the industrial city. Futurism as a movement didn't survive WWI. After witnessing the carnage machines enacted on the human body in that war the idealistic concept of progress by way of technology was diminished in Europe.
58
New cards
Surrealism
subject matter/style: Surrealist works drew inspiration from intuition, the power of the unconscious mind and various psychological schools of thought. The work often features unexpected juxtapositions, non sequiturs, and elements of surprise. Surrealism aimed to revolutionize human experience, in terms of the personal, cultural, social, and political aspects. Surrealists wanted to free people from false rationality, and also from restrictive customs and structures. Freud's work with free association, dream analysis, and the unconscious was of utmost importance to the Surrealists as they developed methods to liberate their imaginations.
59
New cards
Dada
subject matter/style: Dada was a multi-disciplinary art movement that rejected the prevailing artistic standards by producing "anti-art" cultural works. It expressed their rejection of the ideology of nationalism and cultural and intellectual conformity through their art, which often appeared to reject logic and embrace chaos and irrationality. Dada artists like Marcel Duchamp worked in collage, assemblage and photomontage as well as "ready-mades"
60
New cards
Russian Constructivism
subject matter/style: Sought to create art that was relevant to modern life in form, materials, and content. Rejected the traditional view of sculpture as a static volume - rather their preference was a dynamic form that, whenever possible, included moving elements. Rather than form, space was primary.
61
New cards
De Stijl
subject matter/style: 1917, Dutch, inspired by Cubism and it was nonrepresentational. Used newly independent vocabulary of "pure" visual form free of form the depiction of real objects and personal feelings. The goal was to create a world of universal harmony. De Stijl Architecture was asymmetrical designs to create dynamic balances of voids and solids - spaces flow into one another, The visual contrast between natural and manufactured forms.
62
New cards
Bauhaus
subject matter/style: Bauhaus = building house. School of design was founded by Walter Gropius. Wanted to eliminate divisions between artist, designers, architects, crafts people, etc. Paired down DESIGN, focus on clean lines without embellishment.
63
New cards
Sfumato
the definition in form in painting without abrupt outline by the blending of one tone into another. A thin later of glaze of oil paint or can be painted in Impasto. It softens the edges creating a more natural look Famous example is the Mona Lisa during the high Renaissance.
64
New cards
Tenebrism
A lighting style that is defined by expressive contrast between light and dark.
65
New cards
Pointillism
A technique of painting in which small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an imagine.
66
New cards