Animal Behavior Midterm - Behavioral Plasticity
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are fixed action patterns, sign stimulus, and innate releasing mechanisms?
1) fixed action pattern - sequence of instinctive behaviors that an organism performs in response to a specific stimulus
2) sign stimulus - a physical stimuli that causes a direct response, not logical reactions caused by thought
3) innate releasing mechanism - FAPS are produced by a neural network (the IRM)
What is the Interactive Theory of Development?
The development of traits, including behaviors, requires both genetic information and environmental inputs. The interaction between genes and the environment produces a behavior and leads to its evolution
What is imprinting?
An extremely close and dependent bond with the first animal they see after being born
What is operant conditioning?
An animal learns to associate a voluntary action with the consequences that follow that action
What is the evo-devo approach to behavior?
The evolutionary history of a trait - a series of modifications of an ancestral trait and its reconfiguration into a new attribute
ex: a shared gene in drosophila and honey bees due to common ancestor codes for the protein royalactin, this codes for body size
What is developmental homeostasis?
The ability of animals to develop more or less normally despite defective genes or deficient rearing conditions
ex: baby monkey with wire and cloth mom, developed normally physically, but would rock back and forth and withdrew from others
Explain phenotypic plasticity and its role in animal behavior.
Changes in an organism’s behavior, morphology, or physiology in response to a unique environment, it’s fundamental to the way organisms cope with environmental variation
How is plasticity different from evolutionary traits?
Plasticity is a temporary phenotypic change while evolutionary traits are a permanent genetic trait
What is a gene x environment interaction?
The ability of one genotype to produce more than one phenotype when exposed to different environments.
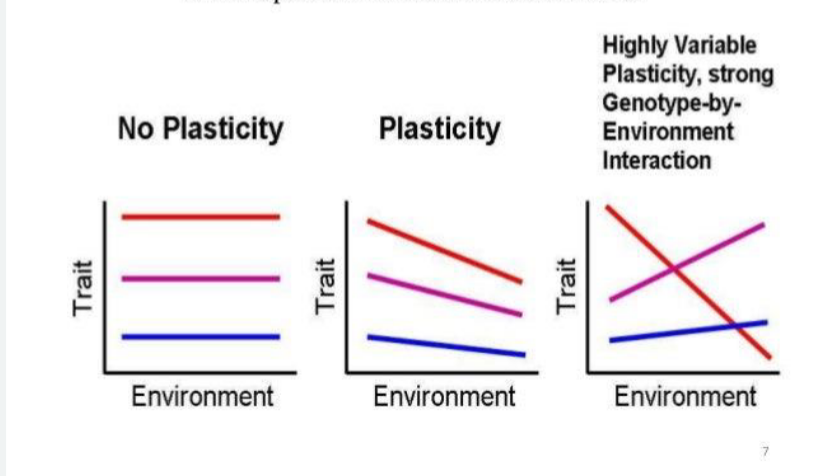
How can behavioral plasticity be beneficial for animals?
Behaviors can change faster than physiological or morphological traits, individuals can buffer themselves from stress