B5 - Chain integration and sustainability
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Customer vs. consumer
Basis for comparison | Customer | Consumer |
Definition | The purchaser of goods or services is known as the customer | The end user of goods or services is known as a consumer |
Resell | A customer can be a business entity, who can purchase it for the purpose of resale | Consumers not |
Purpose | Resale or consumption (consumption = raw material → new good) | Own consumption |
Person | Individual or organization | Individual, family or group of people |
B2B vs. B2C marketing
Business to Business vs. Business to customer
Narrower customer base in B2B: fewer customers, but larger order values
You cannot sell to as many businesses as you could to customers → however, business buys more than customer
B2B demand is inelastic (the demand doesn’t depend on price much)
Customers are more sensitive to price change.
More influencers and specialized members in B2B
Personal contact with customers is more important in B2B
Businesses have to be in good contact with other businesses that they are selling to compared to customers.
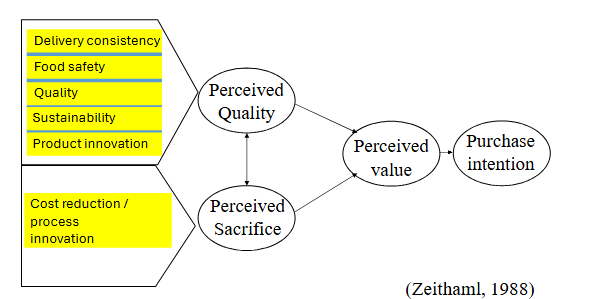
Goals of chain integration
Delivery consistency
Food safety
Quality
Sustainability
Process innovation
Product innovation
These goals eventually feed into the product attributes that constitute the benefits for the consumer
Some goals prevent dissatisfaction, others contribute to satisfaction, depending on how they contribute to the value of a product.
Hygiene factor
A basic expectation or requirement that customers or consumer have regarding a product.
Delivery consistency (goals)
Hygiene (dissatisfaction) factor
Right quantities in the right qualities at the right moment
Otherwise, they risk that a company switch suppliers
Ensure demands are met.
If delivery is not consistent, it may break relationships between businesses, as businesses may find suppliers elsewhere.
Food safety
Hygiene (dissatisfaction) factor
This is something that is expected by the consumer
Basic characteristic (bare minimum)
Prevent the spread of diseases
Tracking and tracing systems
Quality (goals)
Satisfier
Offer higher quality (taste, size, etc.) than competitors
Products designed to live up to or exceed customer expectations
Sustainability (goal)
Satisfier for involved customers/consumers, could be a hygiene factor for others
Production is less harmful to our planet
Ensure environmental sustainability, biodiversity and animal welfare.
Process innovation (goal)
Satisfier - because it is aimed at reducing costs
Cost reduction and increased efficiency
Enables price promotions and price reductions without losing profits
Why is the lowest price in process innovation not always good?
With the lowest price, you cannot guarantee quality and sustainability
Which is a hygiene factor for some.
Product innovation
“Satisfier”, because it increases value
Development of new and better quality products
Developing products with multiple parties in the chain helps to share risks
Enables food brands to stay ahead of supermarket brands.
Customer satisfaction (end goal)
Gets delivered on time with consistent quality
Is safe to eat and can be traced back to its roots
Is more delicious than other fries
Has less impact on the environment
Becomes cheaper and more accessible
Becomes super happy fry.
Perceived quality and perceived sacrifice
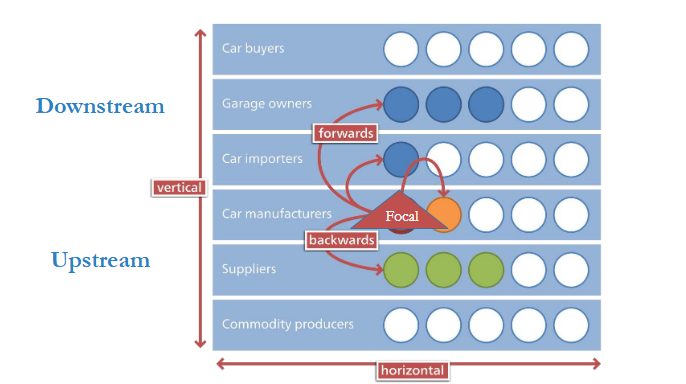
Horizontal vs vertical integration?
Horizontal = expanding market
Merging with competitors
e.g. Volkwagen acquiring Porsche
Because both are car manufacturers
Vertical = controlling supply chain
Integrating other members of the supply chain
E.g. integrating with customers as a business.
Horizontal integration (advantages vs. disadvantages)
Integration of competitors at the same level of the value chain
e.g. Facebook buying Instagram
advantages:
economies of scale (when production gets larger, the unit cost per product gets lower)
Larger market power over distributors and suppliers
product diversification
expand their market or enter new markets
disadvantage:
integration complexity (different norms, different strategy, different company culture)
the attention of the trade commissions (trade commissions watches out so that you as a company does not get too big)
Vertical integration
Integration of different stages of the supply chain - from raw materials to distribution
e.g. Netflix producing their own movies.
advantages:
Reduces dependency on suppliers
quality assurance
supply chain stability
creates barriers for competitors
disadvantages:
limits the ability to switch suppliers
operational complexity
risk concentration
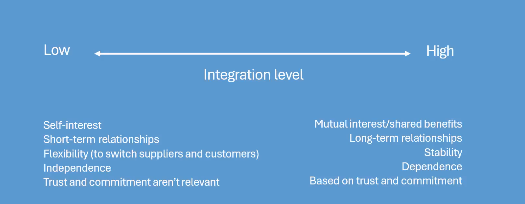
Relationship Continuum
Marketing threats to sustainability
Marketing is used by companies for the wrong purposes
Consumers are easy victims
The cheaper option wins
The power of the supermarket
Institutions are too weak
What if you don’t belong to a target market?