Middle Passage and Atlantic Slave Trade: Key Concepts and Impact
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Middle Passage
The voyage of slave ships (slavers) across the Atlantic Ocean from Africa to the Americas.
Learning Objective 2-1
How did the arrival of the Europeans affect Africa?
Learning Objective 2-2
How did the slave trade in Africa differ from the Atlantic slave trade?
Learning Objective 2-3
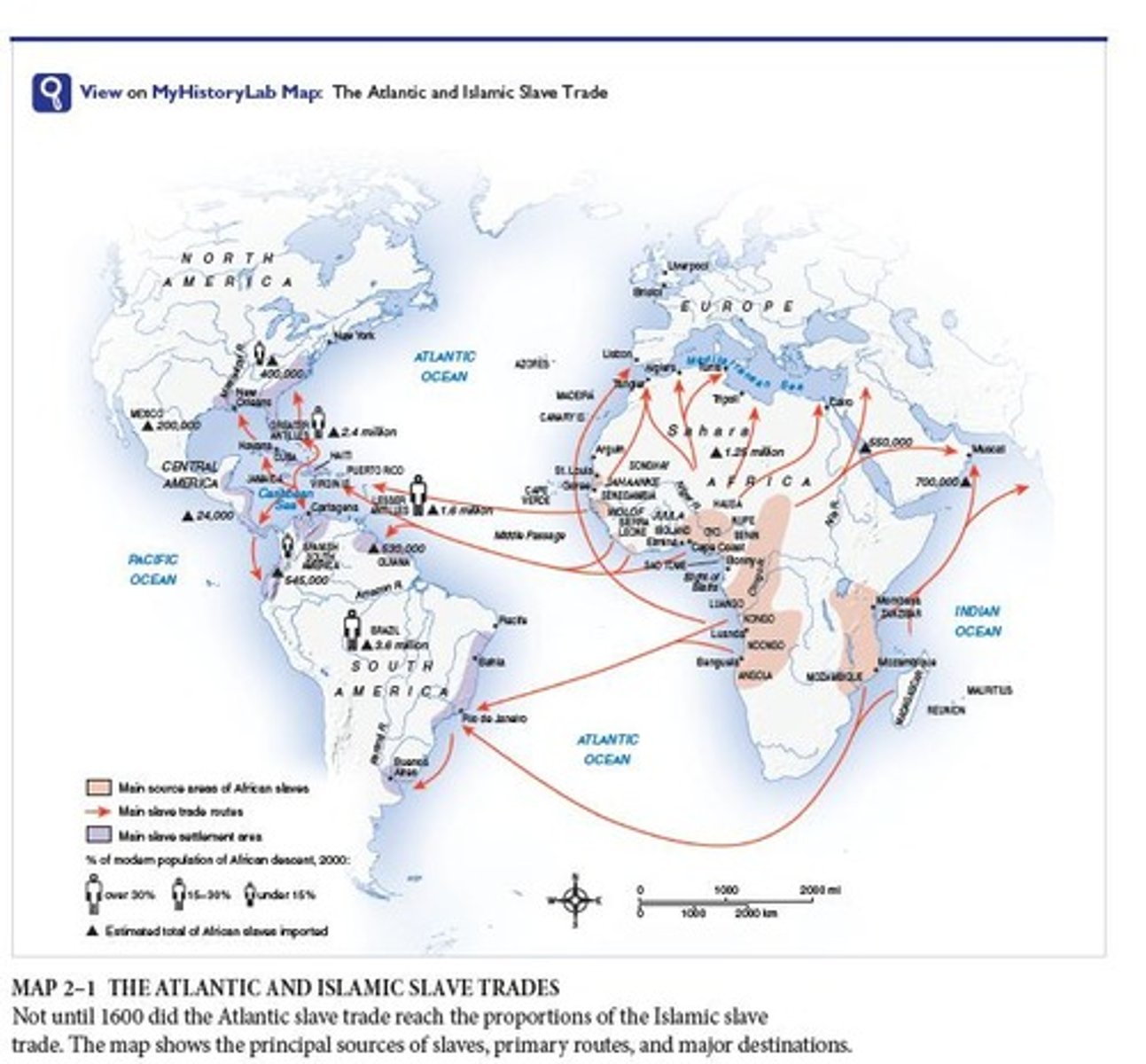
What was the 'Middle Passage'?
Learning Objective 2-4
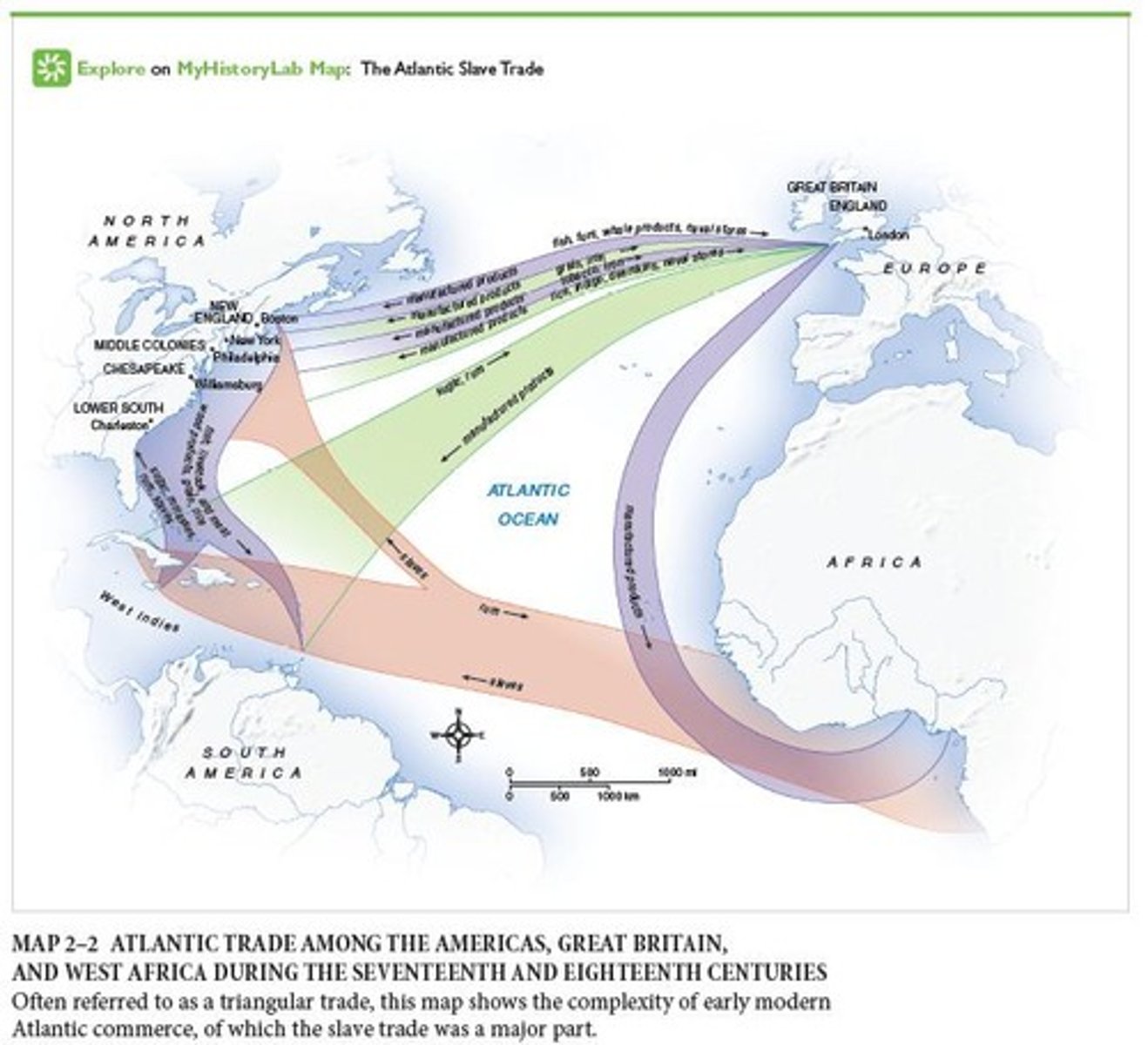
What was the relationship between the Atlantic slave trade and the Industrial Revolution?
Learning Objective 2-5
What happened to Africans after they crossed the Atlantic?
Learning Objective 2-6
How did Africans adapt to conditions in the Americas?
Learning Objective 2-7
What was 'seasoning'?
Learning Objective 2-8
How were slaves treated in the Americas?
Learning Objective 2-9
Why did the Atlantic slave trade end?
European Age of Exploration
European nations sought to colonize Africa.
Portugal's Role
Portugal led trade with African kingdoms.
Columbus's Journey
Columbus traveled west to reach Asia and accidentally landed in the Americas.
Indigenous Americans
Indigenous Americans died of diseases or fled.
Workforce Demand
Workforce demand caused the Atlantic slave trade.
Islamic Slave Trade
Sudanese conducted Islamic slave trade, which included blacks and whites, mainly women and children.
Trans-Sahara Slave Trade
Trans-Sahara slave trade made West African cities wealthy.
LO 2-1 Answer Options
A: a region to be converted to Christianity, B: a place to trade for various goods, C: a source of slaves for Europe, D: a place to send criminals and other exiles.
LO 2-1 True/False
Africa was more important as a source of trade and wealth than Asia during the fifteenth century.
LO 2-2 Answer Options
A: Christian Copts from Egypt, B: Berbers from North Africa, C: African forest dwellers, D: Islamic traders who sold Europeans as well as Africans.
LO 2-2 True/False
The trans-Sahara slave trade dealt mainly in men, who were in high demand as field workers.
Guinea Coast
The southward-facing coast of West Africa, from which many of the people caught up in the Atlantic slave trade departed for the Americas.
Indigo
A bluish-violet dye produced from the indigo plant.
Chattel
A form of slavery in which the enslaved are treated legally as property.
Asiento
The monopoly over the slave trade from Africa to Spain's American colonies.
Cash crop
A crop grown for sale rather than subsistence.
Industrial Revolution
An economic change that began in England during the early eighteenth century and spread to Continental Europe and the United States. Industry rather than agriculture became the dominant form of enterprise.
Bartolomeo Dias
An explorer whose voyages drastically changed the slave trade.
Vasco da Gama
An explorer whose voyages drastically changed the slave trade.
Christopher Columbus
An explorer whose voyages drastically changed the slave trade.
Antam Goncalvez
An explorer whose voyages drastically changed the slave trade.
Spain and Portugal
Countries that dominated the Atlantic slave trade.
Sugar cultivation
An extremely profitable agricultural practice in the Americas that increased the demand for slaves.
Tobacco
A crop that increased the demand for slaves.
Most slaves
The majority of enslaved individuals in the Americas were men or boys.
Slave trade profits
Financial gains from the slave trade that helped fund the Industrial Revolution.
Atlantic slave trade
A significant and tragic trade that grew huge as Europeans relied on it for labor.
Interethnic warfare
Conflict among different ethnic groups that produced slaves.
Racial solidarity
The lack of unity among Europeans and Africans regarding the slave trade.
Columbus's voyages
Events that drastically changed the dynamics of the slave trade.
Demand for labor
The enormous need for workers in gold and silver mines and sugar plantations during the sixteenth century.
Dutch
A group that shifted sugar production to the West Indies.
England and France
Countries that followed the Dutch in sugar production and slave trade.
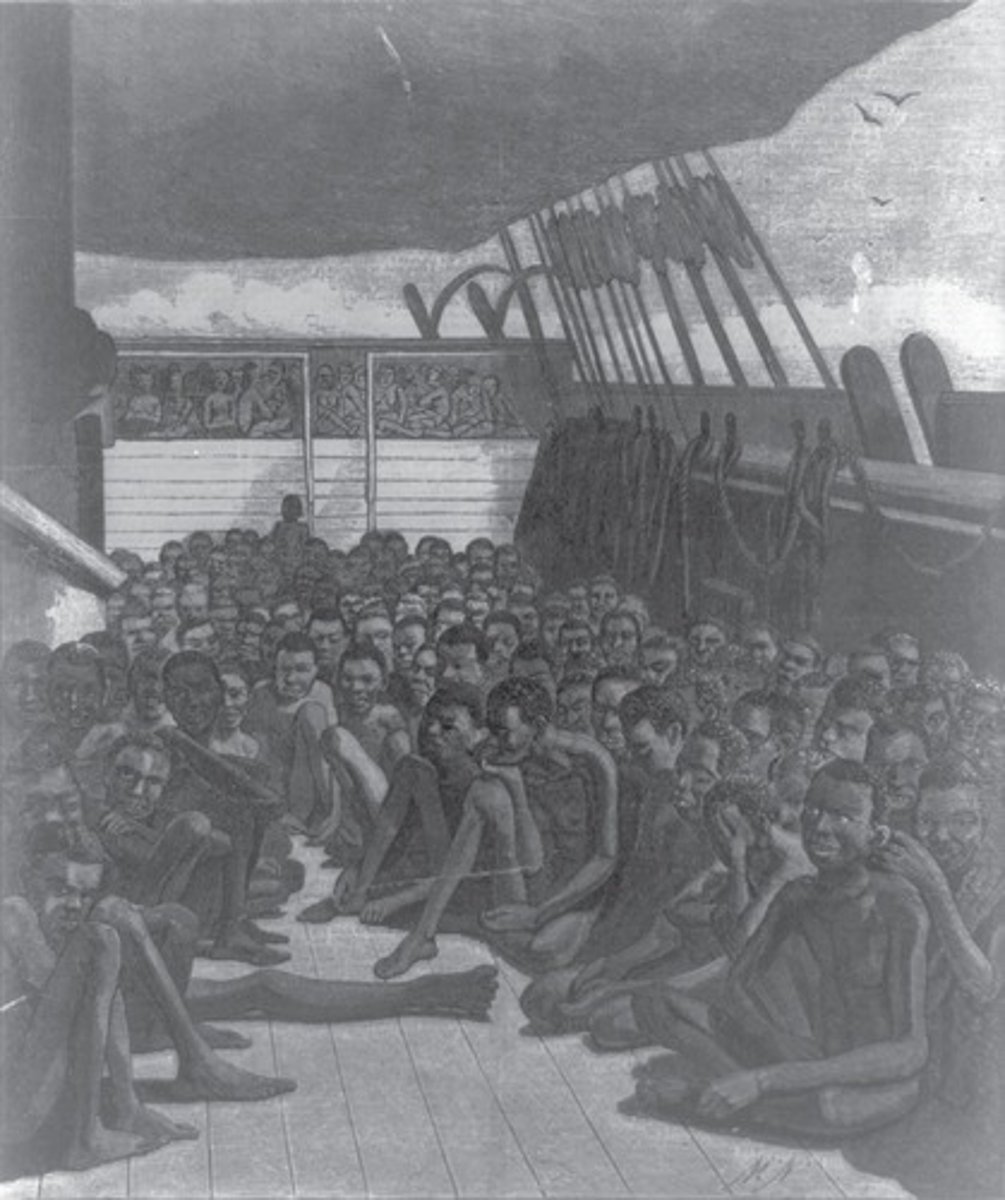
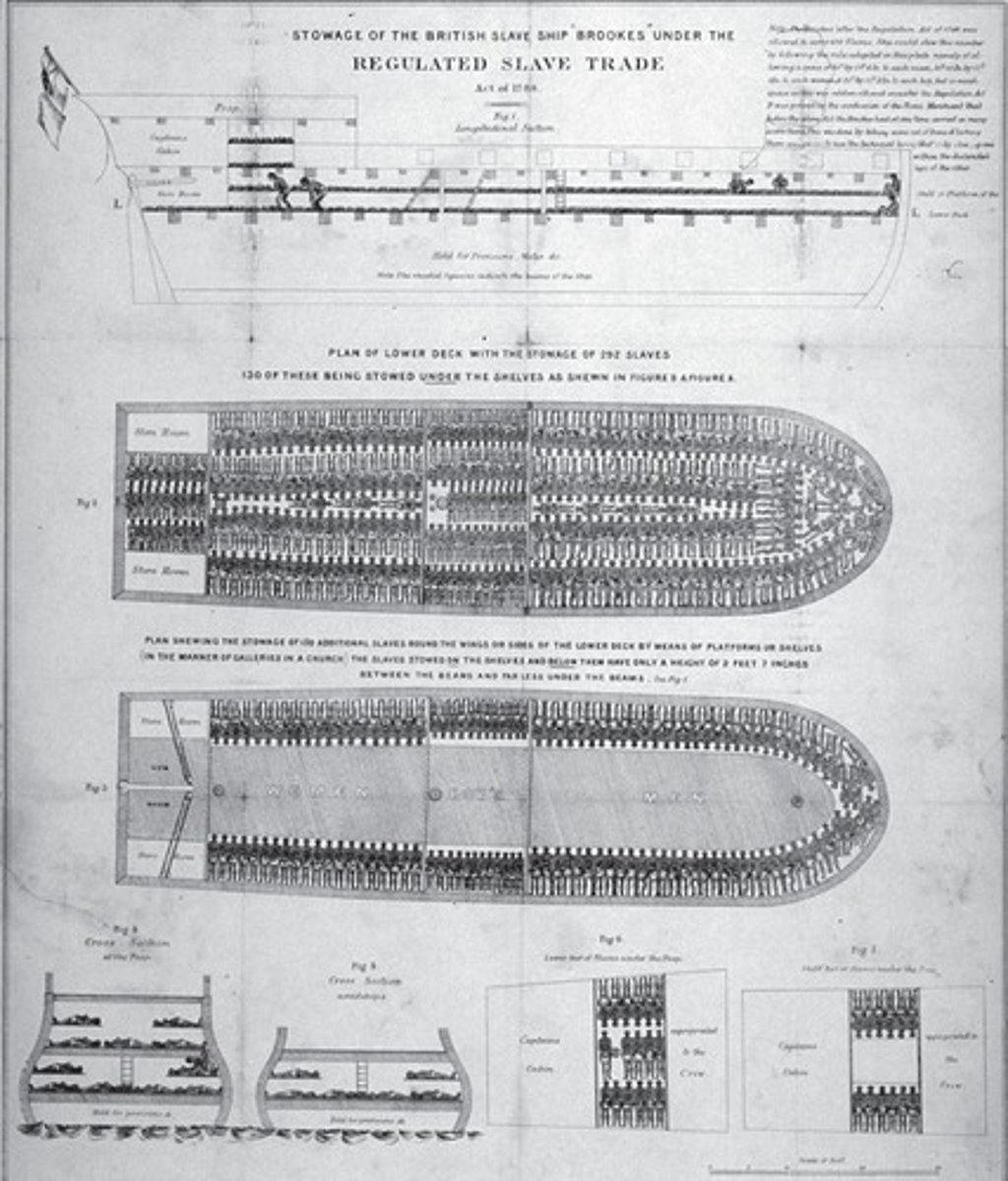
Slave deck of the Bark 'Wildfire'
A historical representation of the conditions aboard slave ships.

Atlantic slave trade profits
Delayed the Industrial Revolution by at least a century.
Factories
Headquarters for a European company that traded for slaves or engaged in other commercial enterprises on the West African coast.
The Crossing
Captives forced to leave native land; voyages lasted three to six months.
Causes of voyage delays
Human and natural causes such as piracy, hurricanes, and doldrums.
Slavers
Ships used to transport slaves from Africa to the Americas.
Mortality rate on slave ships
Seaboard epidemics caused high mortality rates.
Eighteenth-century slavers
Built to resist storms and better ventilated, included 'bondage hardware'.
Olaudah Equiano
Captured and sent to the West Indies; experienced overcrowding, unsanitary conditions, and darkness.
Desperation of captives
Some captives jumped overboard, preferring drowning to captivity.
John Newton
An indentured servant who became a crew member and then captain of a slaver; repented and wrote 'Amazing Grace'.
Indentured servant
A person who sold his or her freedom to a master for a term of years.
Provisions for the Middle Passage
Slave captains purchased African staples for slaves but skimped on supplies, leading to malnutrition.
Sanitation and disease on slave ships
Death rates were astronomical due to dysentery and smallpox.
Ships surgeons
Rewarded for delivering healthy slaves and regarded African remedies as superstitions.
Branded captives
Captives were branded like cattle.
European brutalization
Meant to destroy self-respect and identity of captives.
Voyage duration
Voyages from Africa to the Americas lasted three to six months.
Slave trade captives
African war captives fueled the slave trade.
European traders
Provided firearms to facilitate the capture of slaves.
Resistance and Revolt at Sea
Africans often rebelled rather than accept bondage.
Failed slave mutineers
Could expect harsh punishment.
Other slaves' resistance methods
Resisted captors by drowning, starving.
Cruelty in slavery
Debate among scholars about how much cruelty enslaved Africans suffered.
Primary cause of death at sea
Uncertain; could be epidemic disease, starvation, overcrowding, or harsh treatment and beatings.
Cultural strangers
Africans subjected to brutalization as they were seen as 'cultural strangers' to Europeans.
African Women on Slave Ships
Women worth half price of men.
Crew members' abuse
Crew members abused women sexually.
Separate compartments
Made women easy targets for abuse.
Primary cause of death at sea during the middle passage
Epidemic disease.
Slave rebellions and mutinies during the middle passage
Rare events; slaver crews generally felt safe.
Landing and Sale in the West Indies
Crew prepared human cargo for sale.
Cruelty, confinement, disease
Not easily remedied during the sale process.
Slaves at market
Suffer close inspection by buyers.
Buyers' actions
Grab and rope slaves they choose.
Martinique
An island in the eastern Caribbean Sea that was a French sugar-producing colony.
Barbados
An island nation in the Lesser Antilles, located to the southeast of Puerto Rico.
Physical inspections of Africans
Suggests the humiliation Africans endured before being sold.
Preparation for landing in the West Indies
Slaver captains cleaned, exercised, and rested slaves.
Selling cargo at first port of call
Slave ship owners sold their cargo to return to Africa as soon as possible.
True or False: Slave rebellions and mutinies were rare events
True.
True or False: Slave ship owners sold their cargo at the first port of call
True.
Seasoning
Disciplinary process to make slaves effective laborers.
Creoles
Persons of African or European parentage born in the Americas.
Acculturated
Change in individuals who are introduced to a new culture.
Survival
One of the primary criteria to assess successful seasoning.
Adaptation to new foods, climate, language
Criteria for successfully seasoning new slaves.
Slave society produced Africanized versions of French and English known as Creole dialects.
True or False question regarding the cultural impact of slavery.
English abolitionists crusade against slavery
Movement to end slavery in England.
Industrialized economy less dependent on slave trade
Economic shift that contributed to the abolition of slavery.
Britain abolished Atlantic slave trade
Legislation that ended the slave trade in Britain.
U.S. Congress outlaws Atlantic slave trade
Legislation that prohibited the slave trade in the United States.
Guinea, West Africa fought to keep trade going
Resistance from regions that benefited from the slave trade.
In the early 1800s, England's industrializing economy
Was less dependent on the slave trade.
The growing number of English abolitionists at the end of the 1700s had little effect on the slave trade.
True or False question regarding the impact of abolitionists.
Over three centuries, slavery brought 11 million Africans to Americas
Historical statistic on the transatlantic slave trade.
Most who survived came between 1701-1810
Timeframe indicating when the majority of enslaved Africans arrived in the Americas.