Sports Medicine III Final
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Bones that make up the ankle joint
Tibia, fibula, and talus
Main weight bearing bone of the lower leg
Tibia
Non-weight bearing bone of the lower leg
The fibula
Main weight bearing bone of the foot
Calcaneus
Tarsal bone of the medial side
Navicular
Tarsal bone on the lateral side
Cuboid
This forms the medial malleolus
Distal end of the tibia
Forms the lateral malleolus
Distal end of the fibula
What aspect of tibia lacks muscle protection?
Medial aspect
Bones that are labeled medial to lateral 1,2,3
Cuneiforms
Tibialis anterior, peroneus tertius, extensor hallucis longus, and extensor digitorum longus do what movement?
Dorsiflexion
Flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus brevis, and peroneus longus do what movement?
Plantar Flexion
Tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, gastrocnemius, and soleus do what movements?
Inversion
Peroneus Tertius, peroneus brevis, peroneus longus(note that the peroneus’ are listed from shortest to longest), and extensor digitorum longus do what movement?
Eversion
Anterior talofibular ligament connects what two bones?
Talus to the fibula(anterior aspect)
Special test for injury to the ATFL(anterior talofibular ligament)
Anterior Drawer
Calcaneofibular ligament is strictly injured by what movement?
Inversion of the ankle
Special test for injury to the CFL(calcaneofibular ligament)
Talar tilt
Special test for injury to the PTFL(posterior talofibular ligament)
Posterior Drawer
Medial side of the ankle is made up of what ligament
Deltoid ligament
Special test used for injury of the deltoid ligament
Talar tilt
What two ligaments make up the syndesmotic(high) ankle ligaments?
Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments
What two motions are the main MOI for a lateral ankle sprain?
Excessive inversion with plantar flexion
What special test is used to rule out fracture?
Squeeze or bump test
Hearing or feeling a crunching sound during palpitations
Crepitus
Medial tibial stress syndrome is also called…
shin splints.
The four grades of shin splints are…
Hurts after exercise
Hurts during and after exercise
Hurts before, during and after exercise
Hurts to the point you can’t compete
Fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal indicates what injury?
Jones fracture
Anterior compartment syndrome may require a surgery called…
fasciotomy.
The components of the anterior compartment are..
tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, deep peroneal nerve, and the anterior tibial artery.
The medial meniscus in the knee is ____ shaped and the lateral meniscus in the knee is ____ shaped.
“C” shaped and “O” shaped
Anterior Cruciate Ligament(ACL) prevents what movement?
Prevents the tibia from sliding too far forward in relation to the femur.
Special test for ACL injury are…
Anterior drawer, lachman’s, and lever sign.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament(PCL) prevents what movement?
Keeps the tibia from sliding too far back in relation to the femur.
Special tests for PCL injury are…
Posterior drawer and sag sign.
Medial Collateral Ligament(MCL) prevents what force?
Prevents valgus forces(direct blow to the lateral side of the knee) and external rotation.
Special test for MCL injury is…
Valgus stress test
Lateral Collateral Ligament(LCL) prevents what force?
Prevents varus forces(blow to the medial side of the knee)
Special test for LCL injury is…
Varus stress test
Quadricep muscle group does what movement with relation to the knee?
Extends the knee
The quadricep muscles are..
Vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius(can’t palpate), and rectus femoris.
Hamstring muscle group does what movement in relation to the knee?
Flexes the knee
The hamstring muscles are…
Biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus.
The unhappy triad consists of the…
the MCL, medial meniscus, and the ACL
What kind of injury is common in snow skiing?
LCL injury.
What meniscus is injured more frequently?
The medial meniscus
Meniscus injuries usually need surgery because of the lack of…
blood supply.
The term for the surgery of the removal of the meniscus is called…
a meniscectomy.
A patella is usually dislocated in what direction?
Laterally
To relocate the knee, slowly extend the leg while…
pushing medially on the patella.
Predispositions for patellar dislocations include…
Wide pelvis, genu valgum, increased Q angle, shallow femoral grooves, flat lateral femoral condyles, high-riding and flat patellas, and vastus medialis/ligamentous laxity.(Note that you only need to know genu valgum and two others)
What’s the term for softening of the articular cartilage on the underside of the patella?
Chondromalacia
This disease presents an apophysitis of the tibial tuberosity.
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Patella tendonitis is also called…
Jumper’s Knee
Patella tendonitis can lead to…
patella tendon degeneration.
A patella tendon rupture is characterized as…
the patella being in the thigh, and the athlete cannot extend the knee.
What is cranial nerve II? What does it do?
Cranial nerve II is the optic nerve. It helps with visual acuity. It’s classified as a sensory nerve.
What is cranial nerve VIII? What does it do?
Cranial nerve VIII is the vestibulocochlear nerve. It helps with hearing and equilibrium. It is is classified as a sensory nerve.
What is the minimum time that an athlete will more than likely have to stay out of the sport for after a concussion?
1 week.
What is the type of amnesia that is characterized by not remembering things after the injury?
Anterograde Amnesia
What is the type of amnesia that is characterized by not remembering what happened before the injury?
Retrograde Amnesia
A progressive degenerative disease of the brain found in athletes with a history of repetitive brain trauma caused by concussive or subconcussive hits to the head is called…
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy or CTE.
A nosebleed is called…
epistaxis.
Poor fitting teeth is a sign of…and is called…
a mandibular fracture…loss of normal occlusion.
Double vision is called…
diplopia.
What is cauliflower ear called? What is it?
hematoma auris. It’s fluid accumulation in the ear after trauma to the auricle(outer ear) tears away overlying tissue from the cartilage.(may not need to know the “What is it?” part)
What is swimmer’s ear called? What is it?
Otitis externa. It is an infection caused by bacteria growth in the ear canal. Water is then trapped in the ear canal.
The eardrum is also called the…
tympanic membrane.
What is pink eye called? What is it?
Acute conjunctivitis. It is the infection of the conjunctiva of the eye.
A sensitivity to light is called…
photophobia.
A scratch on the eye is called…
a corneal abrasion.
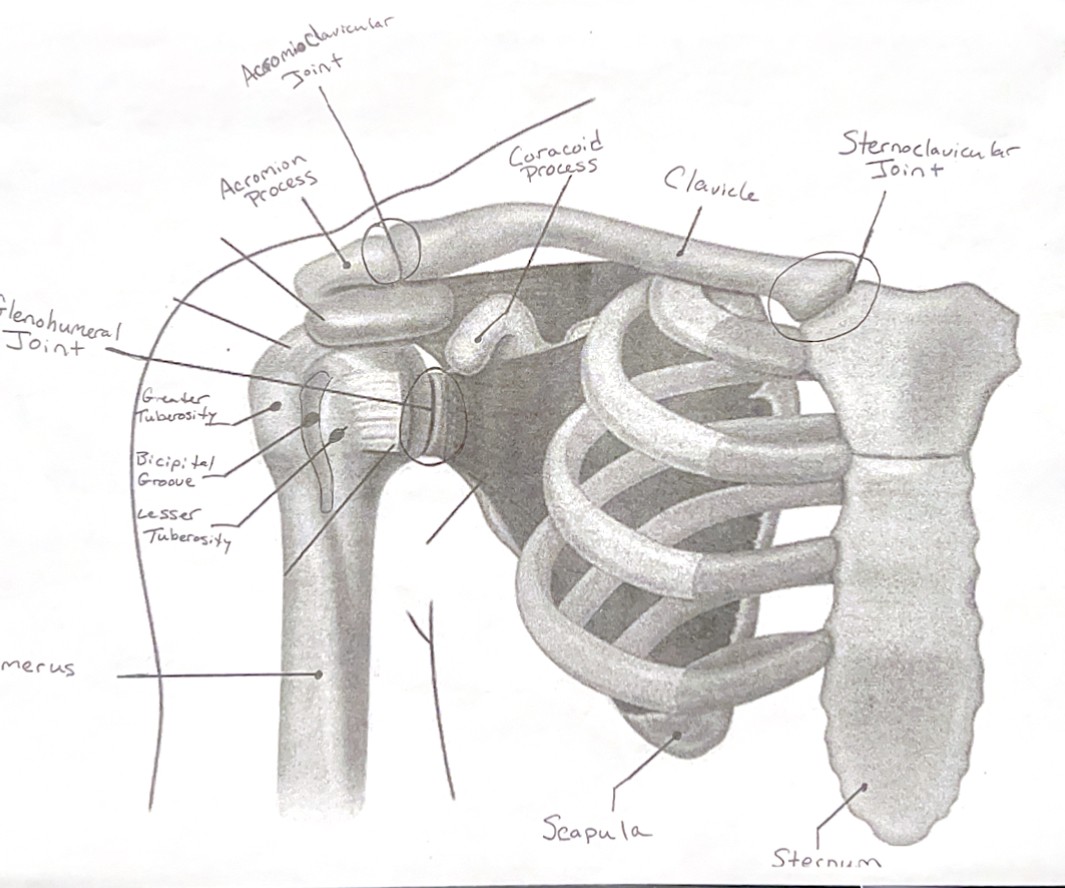
The shoulder joint(glenohumeral joint) is a…
ball and socket joint.
Which bone in the shoulder is S-shaped and has no muscle protection?
The clavicle.
The AC joint is where what two bones connect?
The distal end of the clavicle and the acromion process.
What muscle in the rotator cuff does abduction?
The supraspinatus.
The infraspinatus(part of the rotator cuff muscles) does what movement?
External rotation.
What rotator cuff muscle does external rotation?
Teres minor.
The subscapularis(part of the rotator cuff muscles) does what movement?
Internal rotation.
The clavicular fracture is one of the _____ common fractures in sports.
“most”
Someone with a clavicular fracture should be in a sling for how long?
6-8 weeks.
A Grade 1 acromioclavicular(AC) sprain should be in a sling for how long?
3-4 days.
9 out of 10 shoulder dislocations will dislocate in which direction?
Anteriorly.
You can palpate the head of the humerus in the…
axilla(arm pit).
The structures involved in a shoulder impingement are the…
supraspinatus tendon, subacromial bursa, and the biceps tendon.
Diagram of Shoulder Anatomy