POSC 100F Exam 3
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 12-16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Political participation
refers to a wide range of activities, designed to influence the government
Voting
most utilized type of participation throughout the world; cost efficient; only needs to meet certain requirements
Protest
a type of political participation in which citizens utilize dramatic and unconventional means to achieve policy change
Ex: Grocery store strikes, unfair wages, etc
Civil disobediance
a type of political participation where citizens intentionally break a law that they see is unjust
Ex: Rosa Parks sitting in the front of the bus.
Socioeconomic status
Higher: may donate more money, spend more time volunteering or campaigning, etc
Lower: may participate more in protests and civil disobedience
Whether political participation is higher among individuals with a higher or lower _________ depends on the type of political participation and the state of the world.
Rational voting
occurs when an individual utilizes logic when deciding who or what to vote for
Based on:
an individual’s opinion about the policy issue
a candidate’s opinion about the policy issue
a candidate that is most like you (their stances on issues)
an individual’s opinion about the ability of the candidate to govern
Benefits:
Restricts and monitors the government’s actions
Determines relelection
Winner-take-all system
because of this system whoever wins the most votes in the state gets all electoral votes which has lead to apathetic voters in some states
Proposition Initiative Voting
each vote directly impacts policy making
Tips to Intiative and Proposition Voting
Vote on the issues you care about
Vote on laws or/and constitutional amendments
Look who is backing the initiative/proposition
Examine nonpartisan views before making a decision
If uncertain about outcome, vote for the status quo (nothing to change)
Suffrage
an individual’s legal right to vote
Excludes: noncitizens, permanent residents, illegal immigrants, minors, convicted criminals (laws differ from state to state)
Political efficacy
the belief that ordinary citizens can influence policy making
Ex: Proposition and initivative voting
Civic duty
the belief that being part of a democratic government means that citizens have the duty to vote
Reasons People Do Not Vote
Lack of time
More time is needed for research
Apathy
Lack of impact
Ex: Winner take all system, non swing states have less of an impact in an election, etc
Absentee ballot
mail in ballot
Voter registration
A system in which voters are required to register prior to voting
Differs from state to state:
Same day registration
No need for registration
Online registration (15 days before an election)
Motor Voter Act
Allows eligible voters to register to vote by simply checking on their driver’s license application or renewal form
Electoral College
the way in which the president of the United States is elected into office
Each state’s electoral votes = 2 senators + House of Rep
270 votes needed to win
Process:
Electors meet in December, following the November election to cast their votes and the official presidential candidate is considered.
If there is NO WINNER, The House of Representatives will decide who becomes president from the top three candidates; each state will have ONE vote.
Nomination Campaign
a candidate running for political office must get the endorsement of the political party in which he/she is affiliated with (more difficult to win than the election campaign)
This campaign process includes:
The National Party Convention
Caucus
Primaries
National Party Convention
meets every four years to nominate the party’s candidates for president and vice president
An individual must receive majority of the delegates to win his/her party’s nomination
Delegates: amount is given to candidates based on votes recieved in the caucus and primaries
Most important structural element of party as an organization
Caucus
meetings run by political parties that are held at the county, district, or precinct level where individuals must attend and vote their preference for who should be selected as president (Iowa is first caucus)
Primaries
voters in each state vote for their preference on who should be president based on their party’s selection (Most important primary = New Hampshire)
Simpler system than a caucus and similar to that of a general election.
Election Campaign
one presidential nominee from each party, with the vice president nominee as running mate (Shorter process than a nomination campaign)
Problems (Caucuses and Primaries)
Too much attention to the first caucus/primary , negates others that occur in other states later on
Difficulty to hold office and run (Ex: Hilary Clinton was Senator of NY and running for office at the same time)
Money plays a big role in momentum (If political parties stop offering money, candidates will not want to run)
Does not represent voters at large (In order to vote for a primary or caucus, you must mark down your political party)
Requirements for an effective campaign
Hire a campaign manager
Get a research staff and policy advisors
Hire a pollster - interprets public polls for the President
Hire a press secretary
Get a website
Federal Election Campaign Act
ensure that reporting requirements of contributions are met and limit money contributions
Created the Federal Election Commission (FEC)
Federal Election Commission
administers campaign finance laws and compliances with requirements
FEC Requirements
Full financial disclosure - all money given and spent must be documented
Limit amount of money that can be contributed by individuals to a candidate and political party
Provide public financing
Provide full public financing for majority party candidates (Available but unlikely for a political party to accept because citizens may get upset that their tax money is being used to pay for a political campaign)
Buckley v Valeo
limitation on one's own money is violation of Freedom of Speech
However the SC can limit the amount of money that someone can give you
Soft money
monetary contributions that are used for party building such as distribution of campaign materials, signing up to vote are allowed (No limit)
527 groups
Independent groups that seek to influence the political process but do not directly seek the election of a particular candidate
No limit on spending
Independent from candidate
Ex: NRA can spend as much money as they want on an advertisement bashing a candidate but they have to disclose that the advertisement is NOT ENDORSED by any candidate/political party.
Political Action Committee (PAC’s)
these interest groups are able to contribute $5000 to a candidate and $15,000 to a party by forming a PAC and registering it with the FEC
Senate
upper chamber of Congress
2 senators in each state (100 total)
6 year term - no term limits
California senators: Laphonza Butler and Alex Padilla
Powers of the Senate
Approves all bills (House looks at bills first and if it passes the House then it is passed to the Senate)
Confirms presidential appointees on federal courts as well as ambassadors, cabinet, and top military positions
Ratifies treaties
Tries impeached officials (2 step process)
House: charges
Senate: convicts
Proposes constitutional amendments
Filibuster: Each senator is able to prevent the voting of a bill by using his/her right to an unlimited debate (60 senators needed to override filibuster)
Senate Leadership
President of Senate = Vice President → JD Vance
Votes in case of a tie in the Senate
President Pro Tempore → Chuck Grassley
Highest ranking official in the absence of the Vice President
Majority Leader = majority party in govt → John Thune
Powers/duties: scheduling floor activities, influencing committee assignments
Minority Leader = minority party in power → Chuck Shumer
Powers/duties: similar to that of the Majority Leader
House of Representatives
lower chamber of Congress (total of 435 members)
2 year term - no term limits
# of reps in each state is based on population
Powers (House of Representative)
Approve all bills (House looks at bills first and if it passes the House then it is passed to the Senate)
Decides who is president if neither candidates obtains the majority of the electoral college votes
Indicts (charges) federal officials (2-step process): looks at evidence to see if there should be a trial
House charges individual with the crime
Senate- act as a jury to convict
Propose constitutional amendments
Leadership of the House
Speaker of the House → Mike Johnson
Majority party in power
Second in line of succession
Powers/duties: can determine which bill reaches the floor, can help ensure that bills that are supported by his/her party passes
House Majority Leader → Steve Scalise
Majority party in power
Power/duties: scheduling bills, influencing committee assignments, garnering votes for party
House Minority Leader → Hakeem Jefries
Minority party in power
Power duties: similar to Majority Leader
Constitutional Requirements to Become President
Native born U.S. citizen
“Native” - interpretation made by the SC
Some meanings of Native:
Individual was born in the U.S.
Individual was born to parents who are U.S. citizens
At least 35 years of age
Reside in the U.S. for at least 14 years (with no gap)
22nd amendment
President is limited to 2 four year terms
25th amendment
President’s succession if they are unable to run or die
Vice President
Speaker of the House
President Pro Tempore of the Senate
If the President is unable to serve for a temporary period: the President must submit a letter to the Speaker of the House and President Pro Tempore and submit another document after to resume term
Conflict of Interest (Reason a President Can No Longer Serve in Office)
Ex: Terrorist group kidnaps the President’s daughter > Now the President may not act like a President but instead a grieving father
When the President is unable to serve his office and has given written declaration to the Speaker of the House(SOH) and President Pro Tempore (PPT), the VP becomes the acting President
Once the President submits written declaration to the PPT and SOH that he is now able to serve his office, he shall resume his duty as the President
Presidential Powers
Commander-in-chief of the military (can declare war)
Negotiates treaties
Nominates ambassadors
Presents information in the State of the Union address
Recommends legislation to Congress
Vetoes legislation
Executes laws
Grants pardons for federal offenses: can clear ones criminal offenses
Nominates federal judges
State of the Union Address
the President talks about important issues facing Americans and offers his ideas on solving the nation's problems, including suggestions for new laws and policies
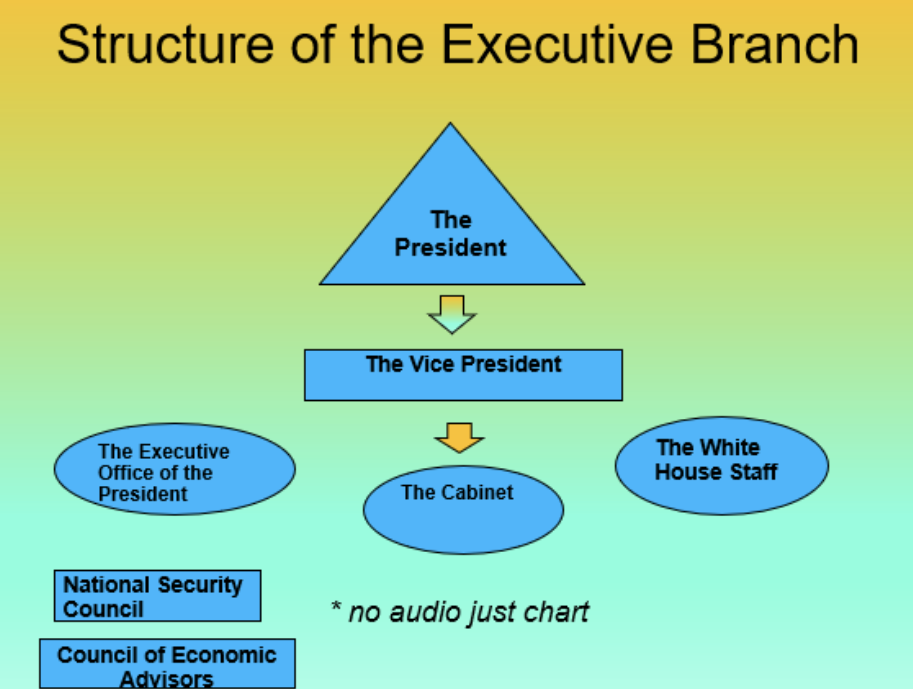
Structure of the Executive Branch
President → Vice President → The Cabinet
The Cabinet: departments and institutions created by past presidents (Ex: Treasury, Defense, Education, etc)
Executive Office of the President Includes:
National Security Council
Council of Economic Advisors
Office of Management and Budget
The White House Staff
National Security Council
advises the president on foreign and military practices
Council of Economic Advisors
advises the president of economic policy
Office of Management and Budget
advises the president to propose regulations and helps prepare the president's budget
White House Staff
aids and advises the president on a daily basis
Chief of Staff, Deputy Chief of Staff, National Security Assistant, Administrative and Political Assistants