AP Unit 2 - Lesson 1 Enzymes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is an enzyme?
a protein that speeds up a chemical reaction without a temperature change
it is the site of a chemical reaction
it speeds up reactions without being used up or changed
it holds reactant molecules together long enough for them to react
What are the functions of an enzyme?
1) Maintaining Homeostasis (our body working normally)
living organisms regulate their internal environment - enzymes are needed for this
2) Metabolism
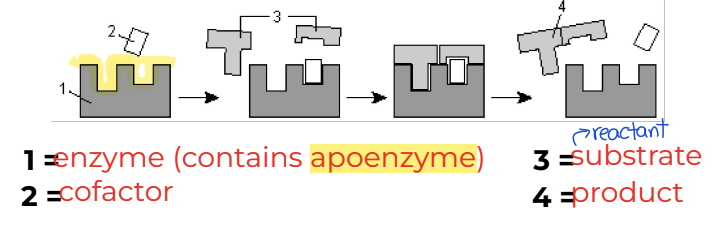
What are the components of an enzyme?
Substrates: reactants in an enzyme catalyzed reaction
Activate Site: location where substrate(s) bind an enzyme
Apoenzyme: protein part of enzyme, specific to substrate, where reaction is catalyzed
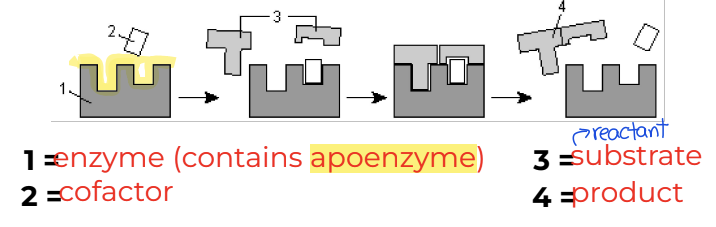
What are the components of an enzyme? pt. 2
Cofactor/Coenzyme: Organic/non-protein particle that helps an enzyme work by transferring ions to or from the substance the enzyme is acting on.
Vitamins: components needed for synthesis of cofactors
How do enzymes work?
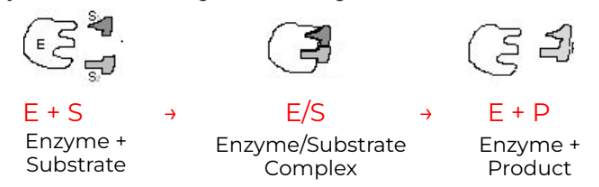
Induced Fit Theory: when binding to a substrate an enzyme will undergo a slight change in the shape of the active site
enzyme active site is not the exact same shape as the substrate (they don’t fit like a lock and key)
after the reaction the enzyme-substrate complex (structure formed when enzyme binds substrate) separates, the enzymes re-assumes its original shape, making it ready to catalyze another reaction
What is the equation for an Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction?
Enzyme + Substrate → Enzyme/Substrate Complex →Enzyme + Product
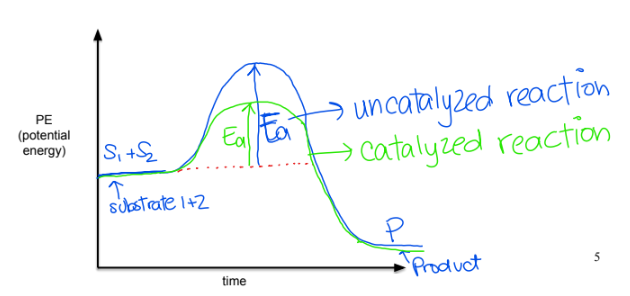
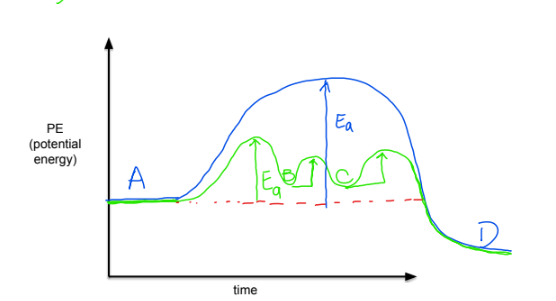
What is Activation Energy?
energy needed to form a reaction
How do enzymes affect activation energy?
enzymes lower activation energy by bringing the substrate molecules together and holding them together long enough for the reaction to take place
What is the Metabolic Pathway?
a step-wise series of chemical reactions from reactants to products where one reaction leads to the next (each step requires a specific enzyme)
it is not possible for biological systems to produce complex molecules from simple reactions
one path can also lead to several other paths (multiple bumps on the PE diagram)
having more than one step means more places where the overall reaction can be controlled
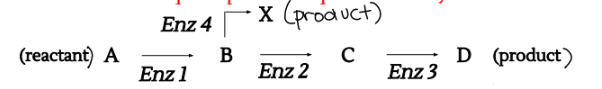
What are potential energy pathways?
one uncatalyzed reaction can turn into several other catalyzed paths (multiple bumps on PE diagram)
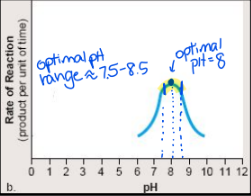
Which factors can affect enzyme activity?
1) pH: each enzyme works optimally in a preferred pH range
if pH is out of range (too high or too low) the enzyme denatures
Denaturing: loss of normal shape + ability to form an enzyme/substrate complex
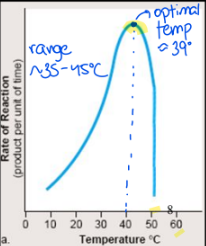
Which factors can affect enzyme activity? pt. 2
2) Temperature: low temperature slows the rate of reaction due to slowed collision rate of enzyme + substrate
very low temp will not normally denature enzyme
temperature greater than 45 degrees Celcius will denature enzymes
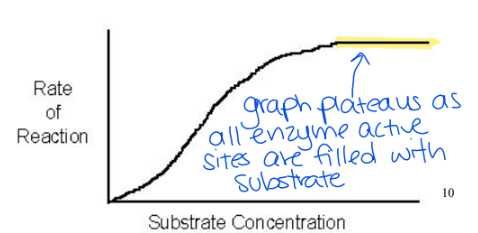
How does substrate concentration affect the reaction rate?
the higher the substrate concentration, the higher reaction rate (rate of the product formation)
after a certain substrate concentration is reached the reaction rate will not increase anymore
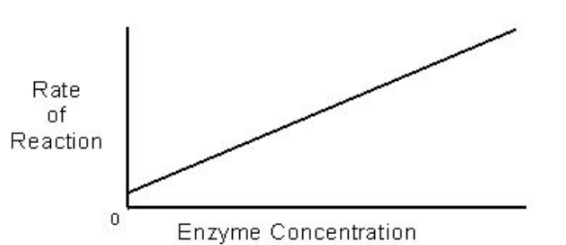
How does enzyme concentration affect the reaction rate?
there are typically millions more substrate molecules than enzyme molecules (no plateau)
increase in enzyme concentration = increased reaction rate vice versa
What are inhibitors?
Inhibitors are molecules that disrupt the formation of the E/S complex
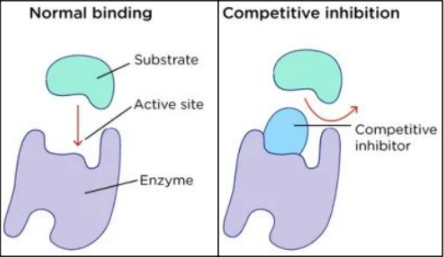
What is a Competitive Inhibitor (CI)
1) Competitive Inhibitor (CI): molecule that has a shape very similar to the actual substrate
blocks the actual substrate from binding in the active site
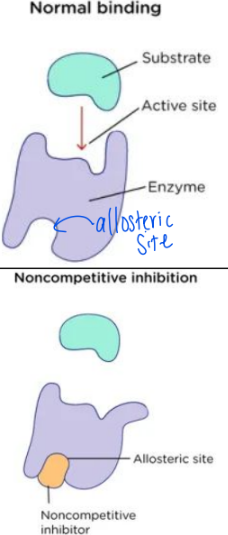
What is a Non-Competitive Inhibitor (NCI)
2) Non-Competitive Inhibitor (NCI): molecule that can look different from the substrate but is able to bind to the allosteric site on the enzyme
Allosteric Site: site that is not the active site but has binding ability for other molecules
binding at the allosteric site causes the whole enzyme to denature (change shape) so that the substrate cannot bind to the active site
What is Penicillin?
An irreversible competitive inhibitor of enzyme that aids in bacterial cell wall synthesis
What is Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)?
An irreversible competitive inhibitor of enzyme essential to proper mitochondria function in humans
What are Heavy Metals (such as lead, mercury, and cadmium)?
An irreversible non-competitive inhibitor of human enzymes