Mutualisms & Positive Interactions | Lecture 27
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mutualisms, Positive Interactions, Plant on Plant, Nurse Plants, parasitism, Commensalism, Mycoheterotrophy, Plant on Fungi, Plants & Animals/Pollination
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Positive Interactions
1 species is benefitting, no one is harmed
What are the two types of positive interactions?
mutualism, commensalism
Negative interactions include…
competition, disturbance, herbivory
What is a rare example of a pollinator species and a seed disperser species being the same organism?
wild bananas, bats
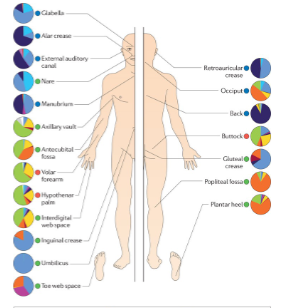
Describe the mutualisms that led to the human body:
cells: cooperation between eukaryotic host and descendant of prokaryote (mitocondria)
multicellularity: cells give up reproduction to specialize in function and benefit whole organism
Microbes: more prokaryotes than eukaryotes, cooperate with each other and eukaryotic cells for digestion, immune, and excretory

Forest Mutualisms Belowground
mycorrhizal fungi transfer nutrients & carbon with trees, ++ or +0

Forest Mutualisms Aboveground
animals carry pollen from 1 flower to another and disperse seeds, ++

Forest Mutualisms Per Individual Plant
cells cooperating, microbiota
Positive Interaction (2)
interaction between organisms where at least 1 benefits and no one is harmed
Symbiosis
two organisms living in close association, not mutualism
Both competition and mutualisms can be…
asymmetric
Describe what correlates to (+,+) and (+,0)
mutualism, strong symmetric, clearly benefit like mycorrhizal fungi
commensalism, one benefits and other is not affected, like epiphytes
Why are plant-on-plant positive interactions not common?
plants living in close enough for positive interactions also likely competing for same resources
What are 3 examples of positive interactions for plant-on-plant?
nurse plants, commensalisms (epiphytes), parasitism
Nurse Plants
improve conditions for another plant species even if still engaging in competition
In what kind of habitat are nurse plants thought to be important?
arid environments
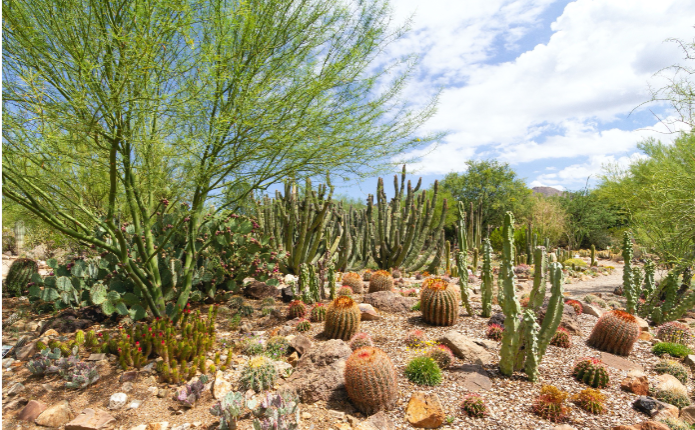

Explain how saguaro cacti use nurse plants to survive:
seedlings require shade, nurse plants Larrea and palo verde provide shade, cacti grow out
What is the cost of Saguaro cacti seedlings relying on nurse plants?
increase survival, growth rates decline by 33%
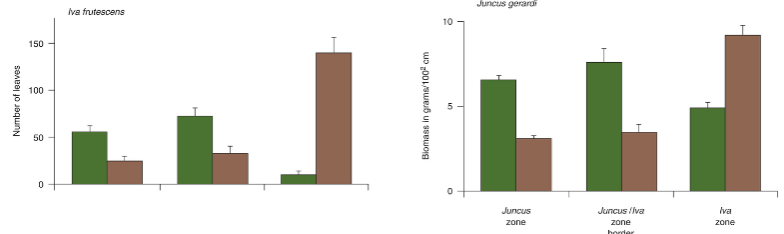
In the Juncus & Iva study, where did Iva grow best with and without neighbors?
iva grew best with neighbors in the middle zone, best without neighbors in the well-drained and low salintity soils
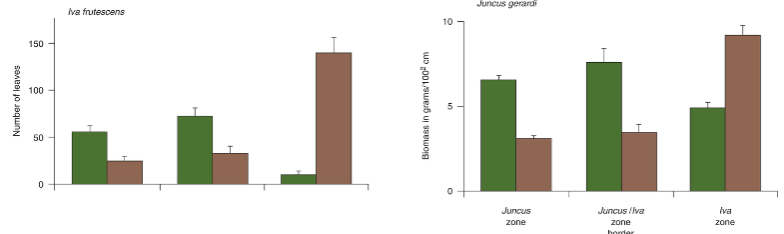
In the Juncus & Iva study, where did Juncus grow best with and without neighbors?
grew best with neighbors in middle zone and best without in well drained low salinity soils, but had higher biomass that iva in the waterlogged & saline soils
What determines the line between competition and facilitation in nurse plants?
stress gradients

Commensalism is _____ between plants
very common
What are two examples of commensalism in plants? (+, 0)
epiphytes, shade-dependent plants in understory
What is a less studied commensalism involving plants but not “plant on plant?”
mycorrhizal associations
Parasitic Plants
derive some or all their food from other plants or fungi
Hemiparasites
still photosynthesize to some degree, hemi-partial
Holoparasites
entirely reliant on stealing from host, holo-whole
Parasites make up ____ of angiosperm species
parasites
Parasitism evolved…
many times
Parasites can parasitize ___ and ____ of other plants
stems, roots
Haustoria
root-like projections that invade host tissues and extract water & nutrients
Mycoheterotrophy Parasite
type of plant that gives up photosynthesis to rely entirely on mycorrhizal associations
How is mycoheterotrophy indirectly plant-on-plant?
all the mycohetertroph’s biomass comes from the fungus, but all the fungi’s biomass came from a different plant
Mycorrhizae
fungi associated with plant roots
Describe the mutualistic interaction between mycorrhizae fungi and plants:
fungi gain carbon & stable environment in roots, plant gets nitrogen, phosphorus, and water
Mycorrhizae are found in _______ of plant species in most habitats
80-90%
Plants benefit _______ from interactions with animals
reproductively
What two positive interactions do animals have with plants?
pollination, seed dispersal
Generalist
interacts with a variety of species or functional types
Specialist
interacts with only 1 species or functional type
Describe how pollination and animals can be generalist:
pollination: plant welcomes many pollinators, focus on maximizing visits from most effective species and limiting ineffective pollinators
animals: visit many different species & flowers for rewards
Describe how pollination and animals can be specialists:
pollination: plant adapted for just 1 species to pollinate it
animal: only visits 1 flower/species
Most flowering plants are _____ pollinated and attract _____ pollinator(s)
animal, multiple, generalists
Animal pollination is ____ compared to wind pollination
more precise
What is an example of a generalist plant? How many pollinators visit it?
wild carrots, 334 pollinators
Most pollinators visit _____ plant species
multiple, generalists
What rewards do animals get from pollinating?
nectar/sugar/amino acids, pollen/protein, oils/fat
Pollen is both ____ and _____ by pollinators
eaten, transferred
What three things attract pollinators?
scent, pigments, pseudocopulation
What scents can attract pollinators?
sweet odor, pheromone mimics, dung/rotting meat odor
Carrion Plant/Starfish Flower:
attracts carrion flies, dead/rotting odor, covered in hairs