Molecular Structure, Orbitals, and Bonding Theories in Chemistry
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What does Lewis theory predict?
Connectivity by converting molecular formulas into Lewis structures.
What are the limitations of Lewis theory?
It cannot predict the 3D shape of molecules and does not account for the role of orbitals.
What theory minimizes electron pair repulsions to determine molecular structure?
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR).
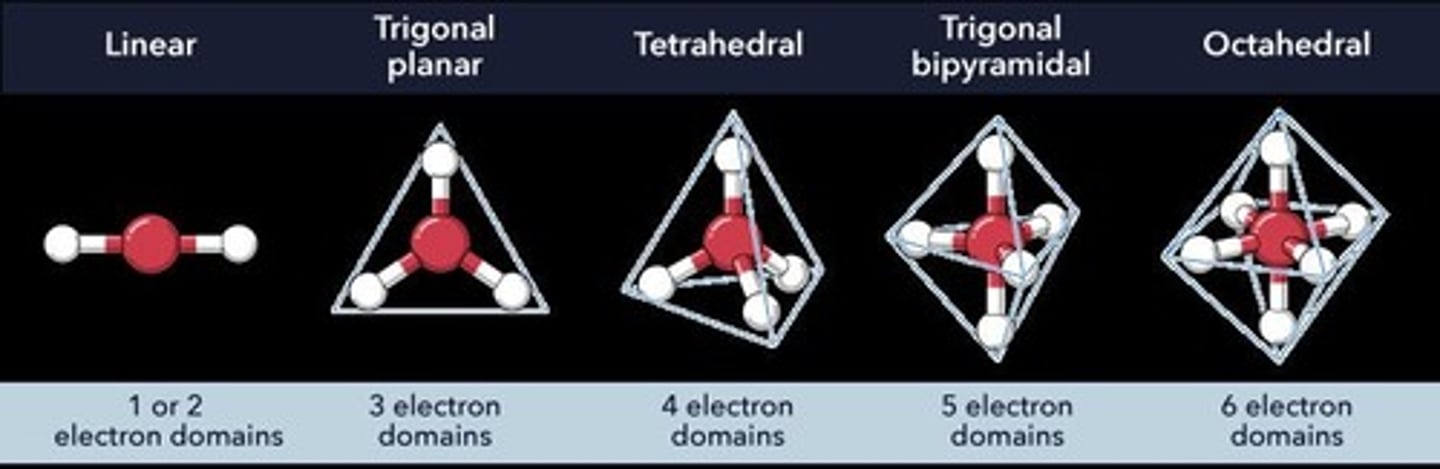
What is the steric number for a linear structure?
Steric number 2, as seen in BeCl2.
What molecular structure does a steric number of 3 indicate?
Trigonal planar structure, as seen in BH3.
What is the molecular structure for a steric number of 4?
Tetrahedral structure, depending on the number of real bonds.
How do lone pairs affect bond angles?
Lone pairs need more space than bonding pairs, compressing the angles between bonding pairs.
What is the problem-solving strategy for applying the VSEPR model?
Draw the Lewis structure, count electron pairs, arrange them to minimize repulsion, determine atom positions, and name the molecular structure.
How does the VSEPR model treat double bonds?
A double bond is considered as one effective pair of electron density.
What is a dipole moment?
A molecule with a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge, represented by an arrow pointing to the negative charge center.
What do electrostatic potential diagrams represent?
Dipole moments, showing variation in charge distribution with colors indicating electron-rich and electron-poor regions.
What determines the molecular polarity of a molecule?
The arrangement of individual bond polarities; if they cancel each other out, the molecule may not exhibit a dipole moment.
What is hybridization in chemistry?
The mixing of native atomic orbitals to form special orbitals for bonding, depending on the electron pair arrangement of the central atom.
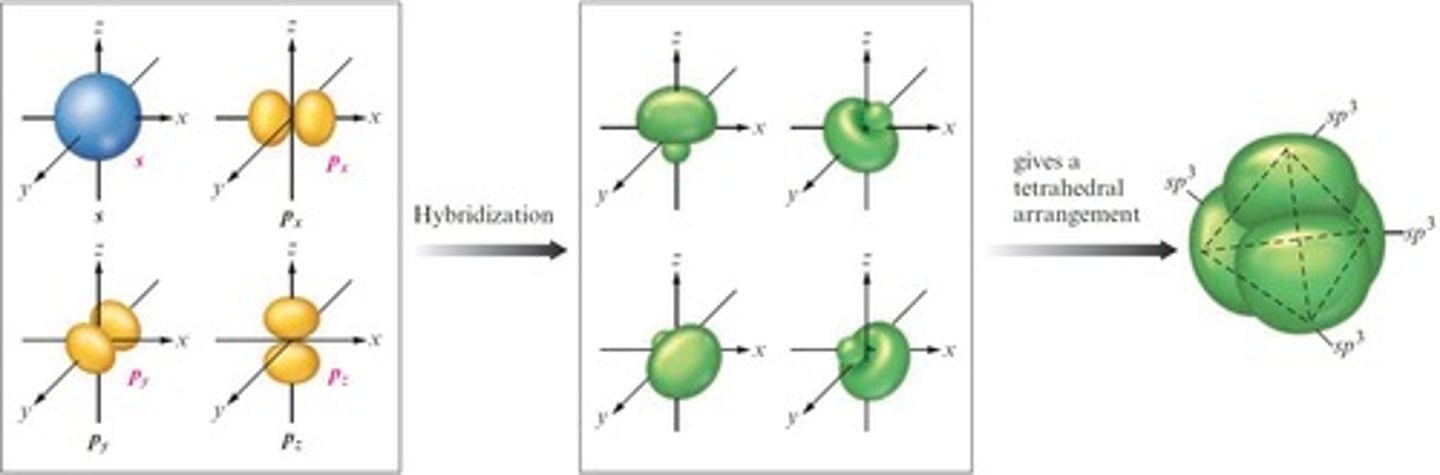
What hybridization occurs when an atom requires equivalent tetrahedral atomic orbitals?
sp3 hybridization.
What is the steric number for a structure with five electron pairs?
Steric number 5, which can lead to various molecular shapes.
What is the significance of resonance structures in molecular structure prediction?
Any one of the resonance structures can be used to predict molecular structure using the VSEPR model.
What are the bond angles for phosphine (PH3) and ammonia (NH3)?
PH3 has a bond angle of 94 degrees, while NH3 has a bond angle of 107 degrees.
What does a molecule with polar bonds exhibit?
A dipole moment, unless the bond polarities cancel each other out.
What is the molecular structure of sulfur dioxide (SO2)?
A bent molecular structure predicted using the VSEPR model.
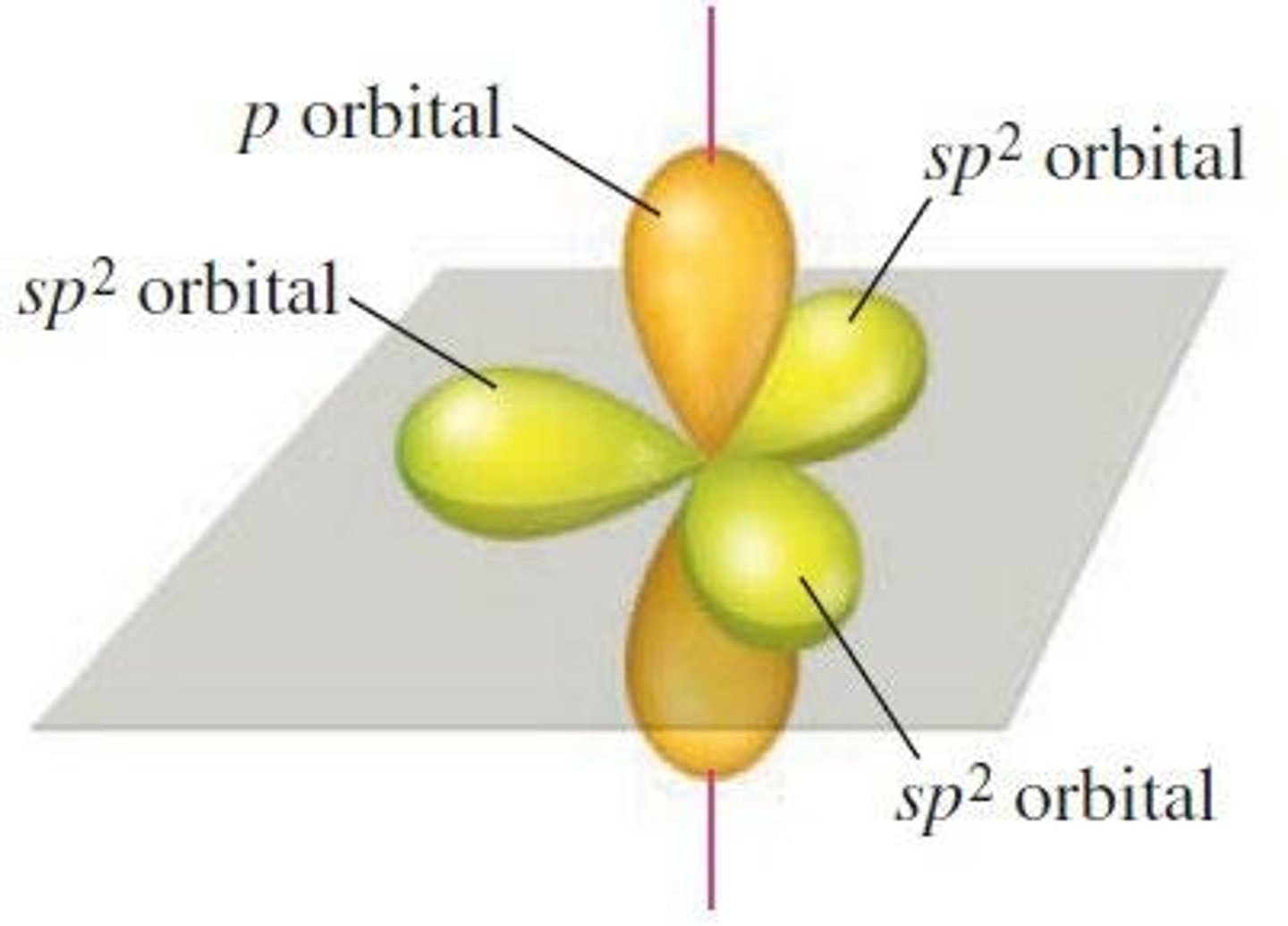
What is the arrangement of atomic orbitals in sp2 hybridization?
Trigonal planar with bond angles of 120 degrees.
What orbitals combine to form sp2 hybrid orbitals?
One 2s and two 2p orbitals.
What type of bond is formed by the sharing of an electron pair in an area centered on a line between atoms?
Sigma (σ) bond.
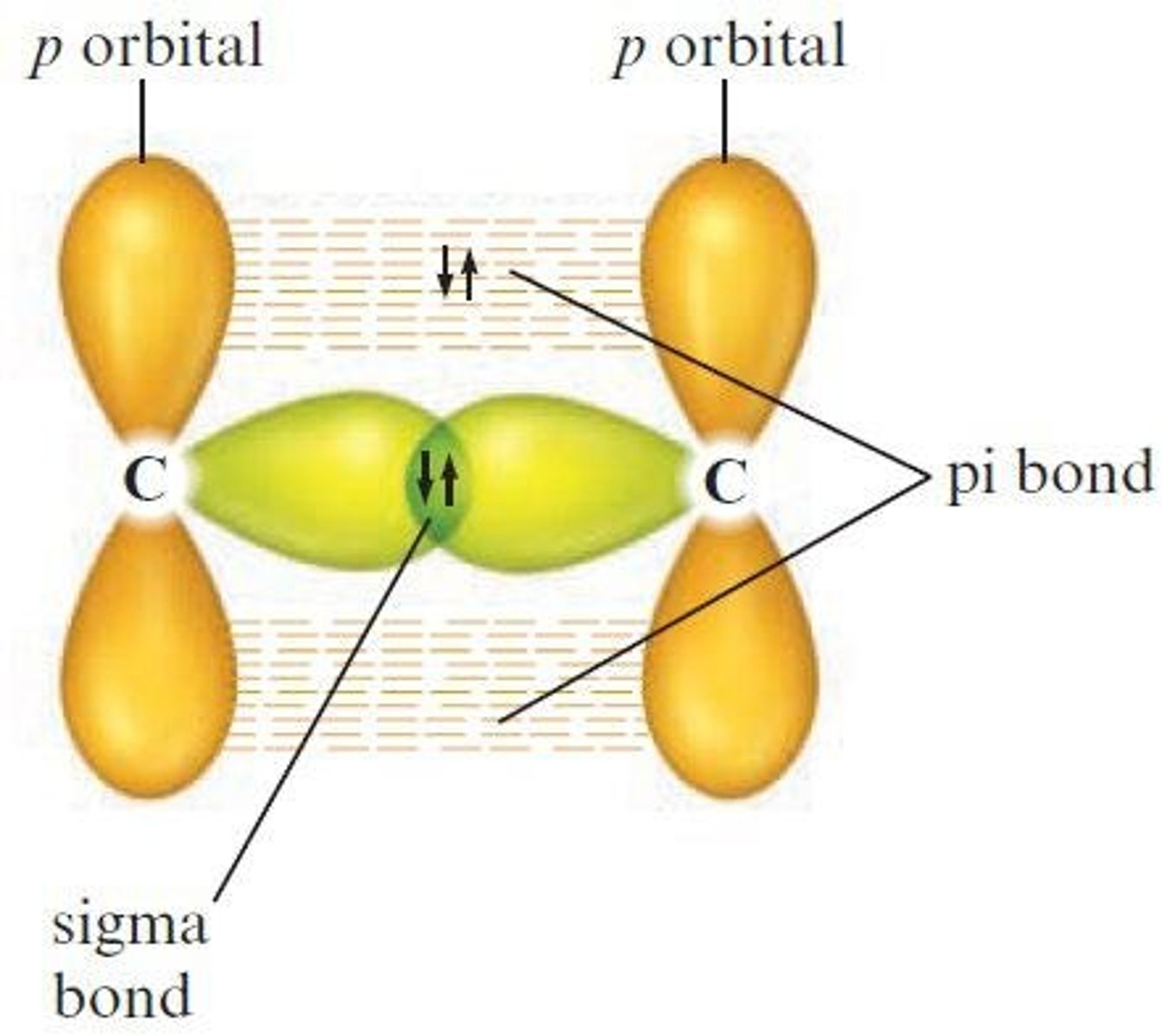
What type of bond forms double and triple bonds using unhybridized p orbitals?
Pi (π) bond.
What is required for an atom surrounded by three effective pairs?
A set of sp2 hybrid orbitals.
What is the arrangement of atomic orbitals in sp hybridization?
Linear arrangement.
What orbitals combine to form sp hybrid orbitals?
One s and one p orbital.
What is the hybridization for an atom with two effective pairs?
sp hybridization.
What is the arrangement of orbitals in dsp3 hybridization?
Trigonal bipyramidal arrangement.
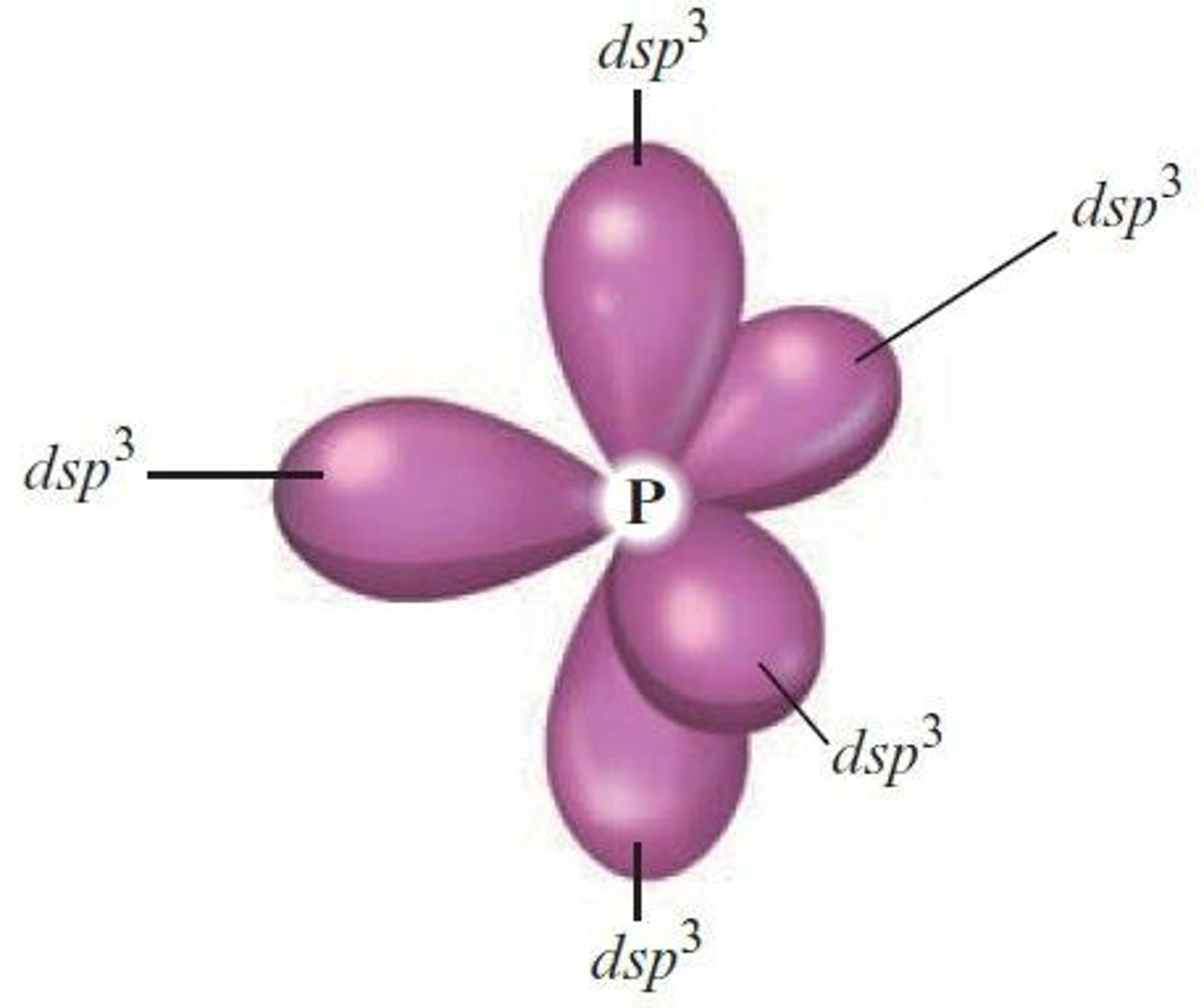
What orbitals combine to form dsp3 hybrid orbitals?
One d, one s, and three p orbitals.
What is the arrangement of orbitals in d2sp3 hybridization?
Octahedral arrangement.
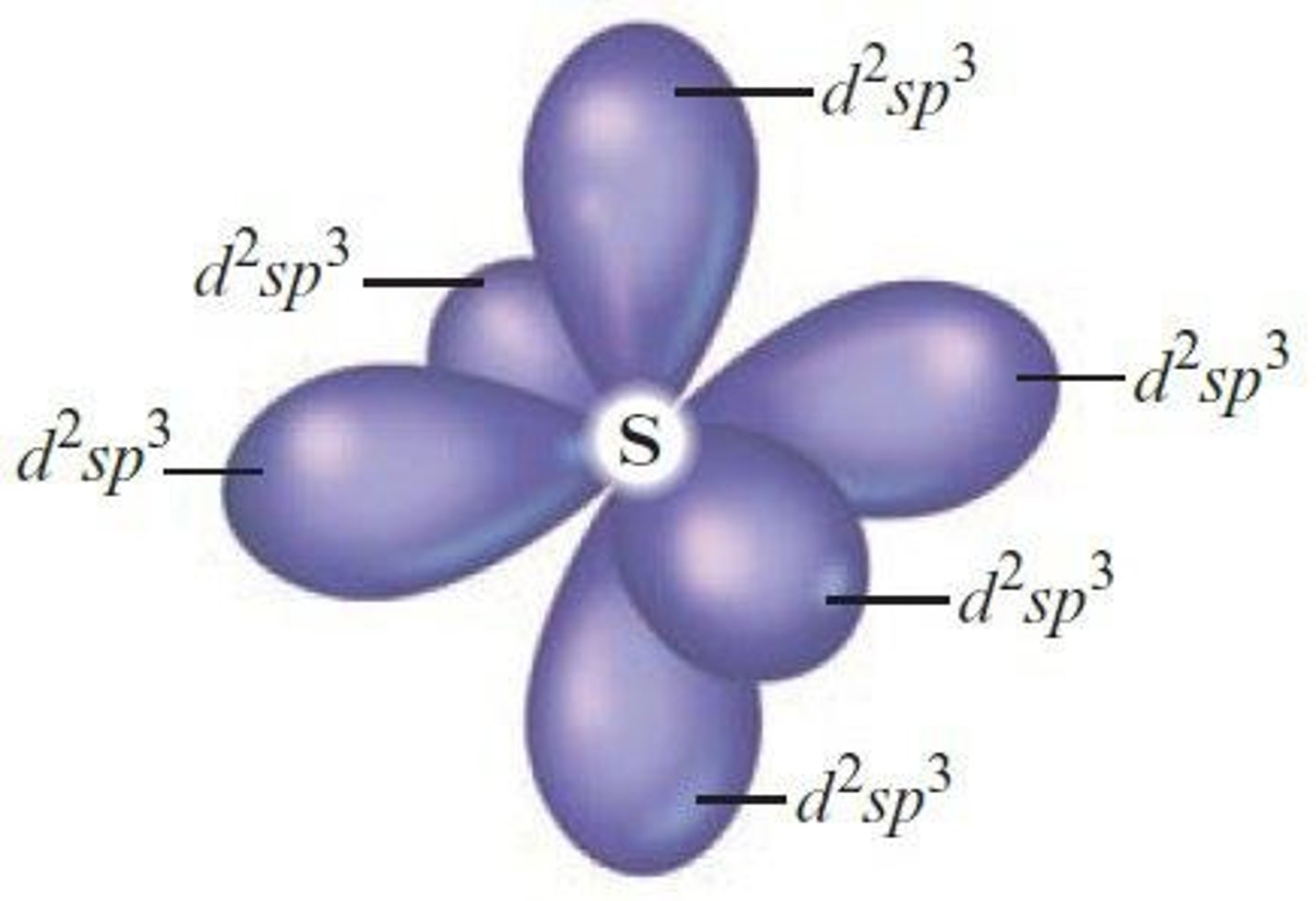
What orbitals combine to form d2sp3 hybrid orbitals?
Two d, one s, and three p orbitals.
What does bond order represent?
The difference between the number of bonding electrons and antibonding electrons divided by 2.
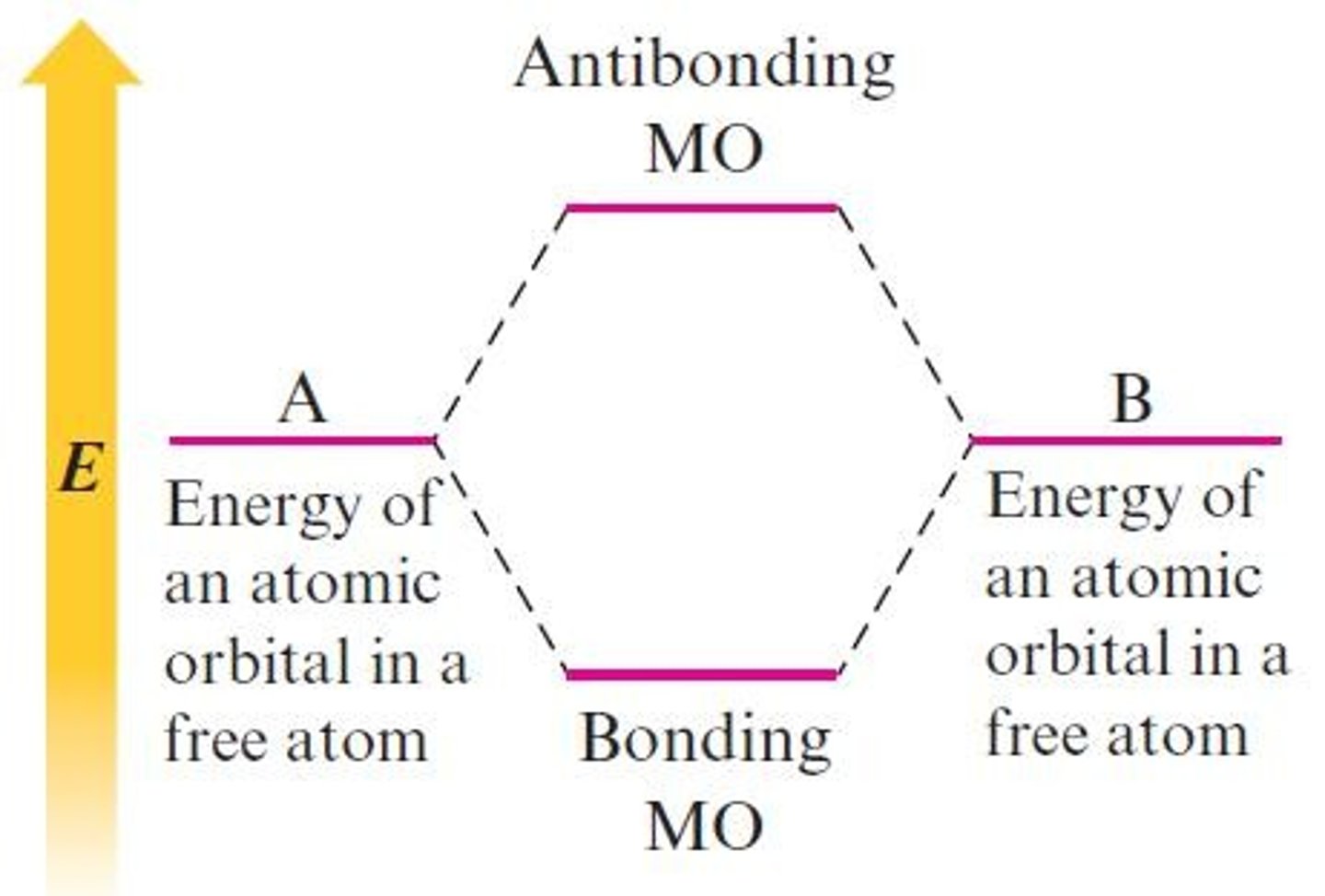
What is a characteristic of bonding molecular orbitals?
They are lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are composed.
What is a characteristic of antibonding molecular orbitals?
They are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they are composed.
What is the significance of the number of molecular orbitals?
It is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals used to construct them.
What causes paramagnetism?
The presence of unpaired electrons.
What causes diamagnetism?
The presence of paired electrons.
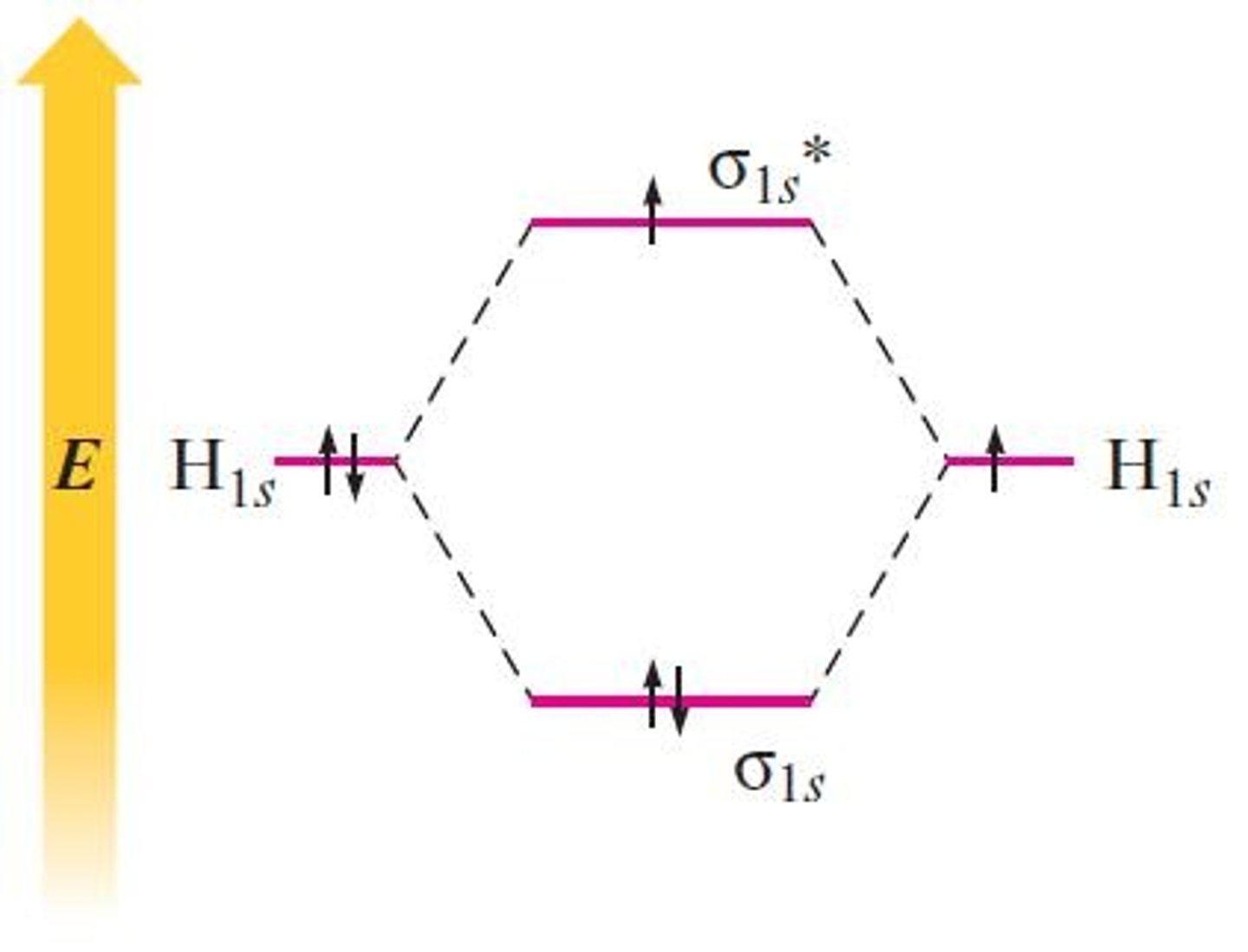
How does the molecular orbital model predict the stability of H2?
By analyzing the bond order and the presence of unpaired electrons.
What is the electron probability distribution in homonuclear diatomic molecules?
High above and below the line between the nuclei.
What does the molecular orbital diagram for HF indicate about electron sharing?
The σ MO shows higher electron probability closer to fluorine.
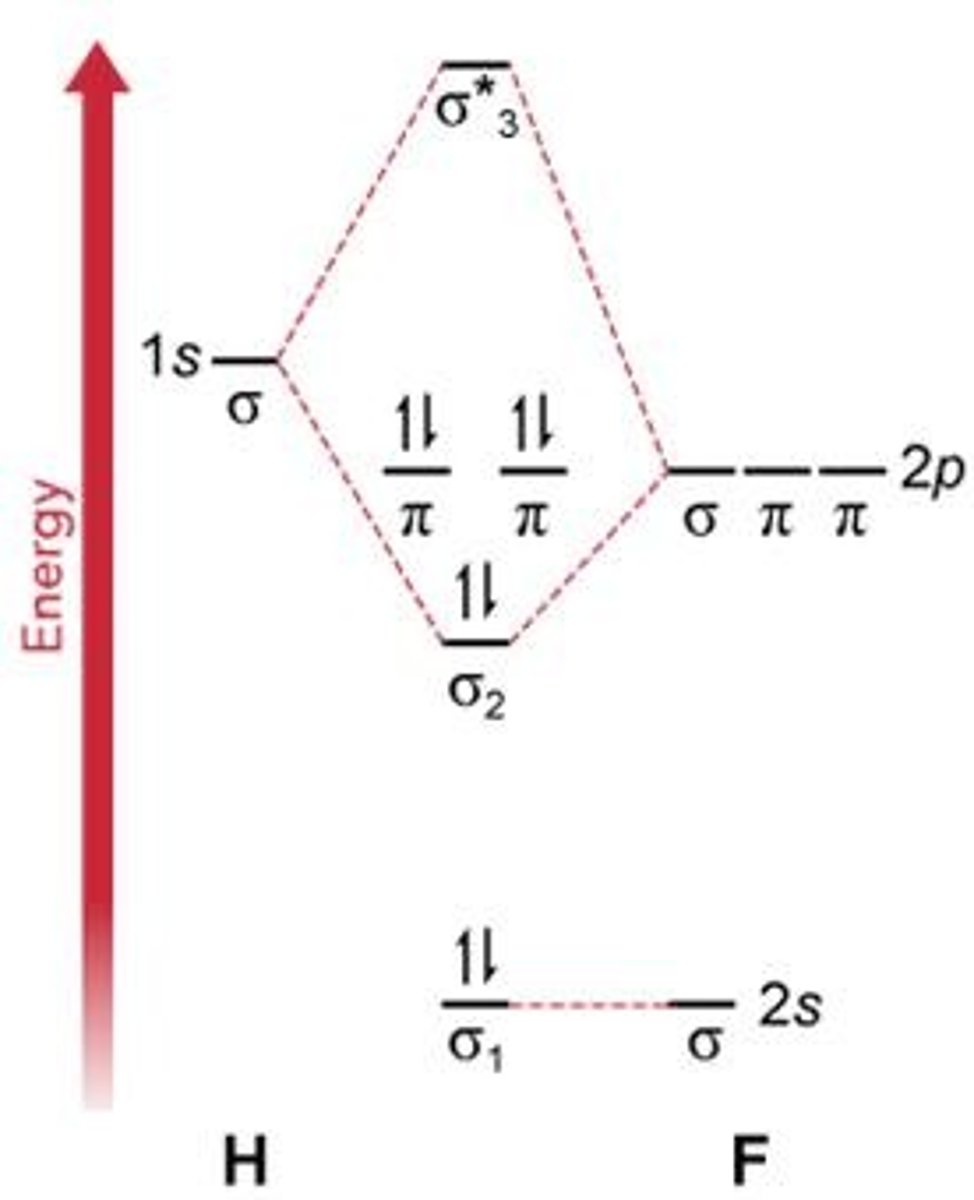
What is the bond order for a molecule with 4 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons?
1 (calculated as (4-2)/2).
What is the relationship between bond order and bond strength?
Larger bond order generally indicates greater bond strength.
What is the hybridization of the central atom in CO2?
sp hybridization.
What is the hybridization of the central atom in SO2?
sp2 hybridization.
What is a chemical bond?
The force that holds atoms together.
How is a covalent bond formed?
When atoms share electrons.
What is a molecule?
A collection of atoms.
Name three ways to represent molecular structures.
Chemical formula (e.g., CO2), Structural formula (e.g., H—O—H), Condensed formula (e.g., CH3CH2CHBrCH3).
What does a space-filling model indicate?
The relative sizes of the atoms and their orientation in the molecule.
What is the ball and stick method?
A three-dimensional model using spheres and rods to represent molecules.
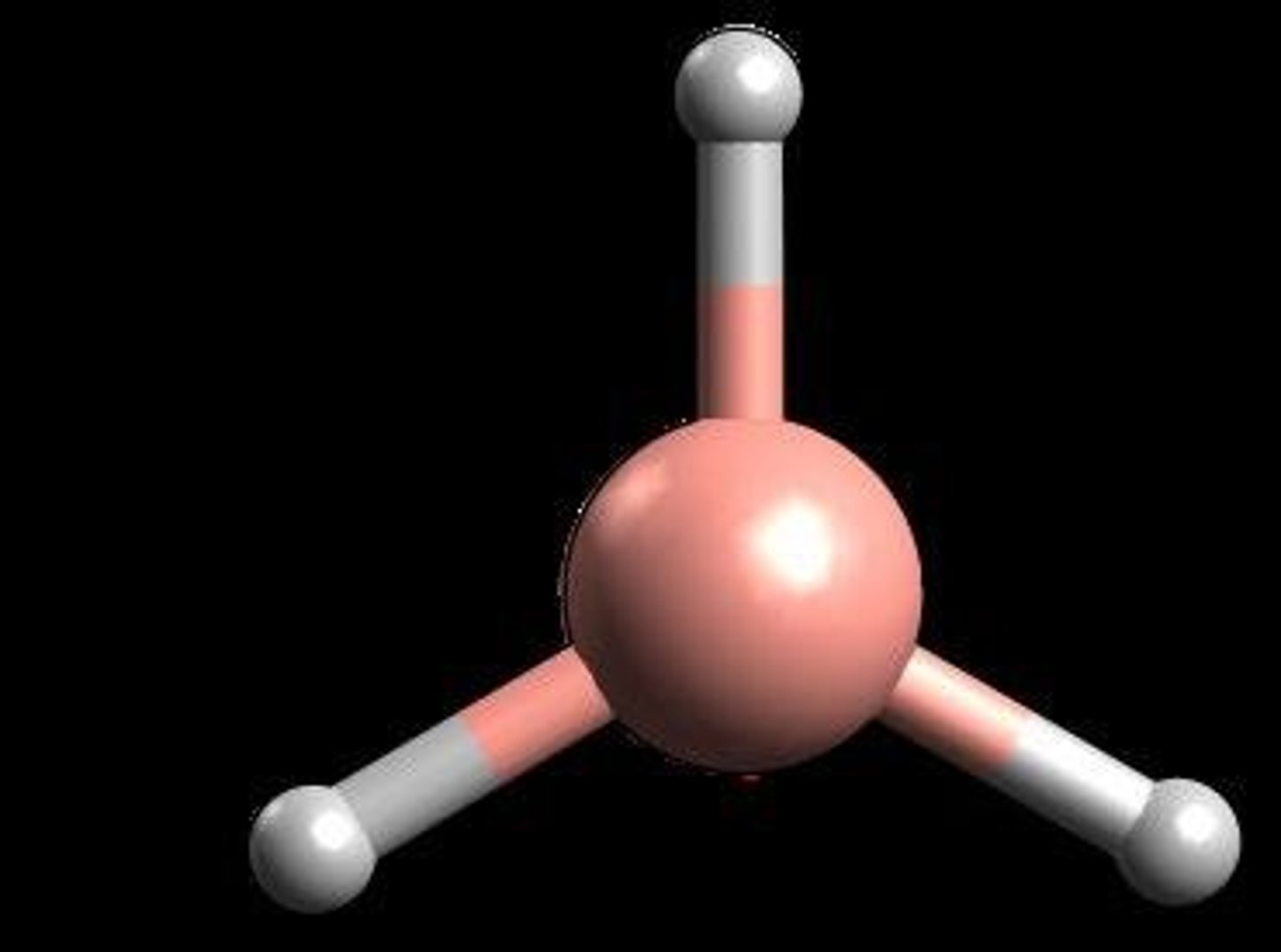
List some attributes of molecules.
Physical properties, melting point, boiling point, electrical and thermal conductivity, solubility, electric charge, and bond energy.
What is ionic bonding?
Occurs between an atom that easily loses electrons and an atom that has a high affinity for electrons.
What types of elements typically form ionic compounds?
Metals react with non-metals.
What is covalent bonding?
Occurs between atoms that prefer to share electrons, typically non-metals.
What happens to electrons in the H2 molecule?
Electrons reside in the space between the two nuclei, leading to increased stability.
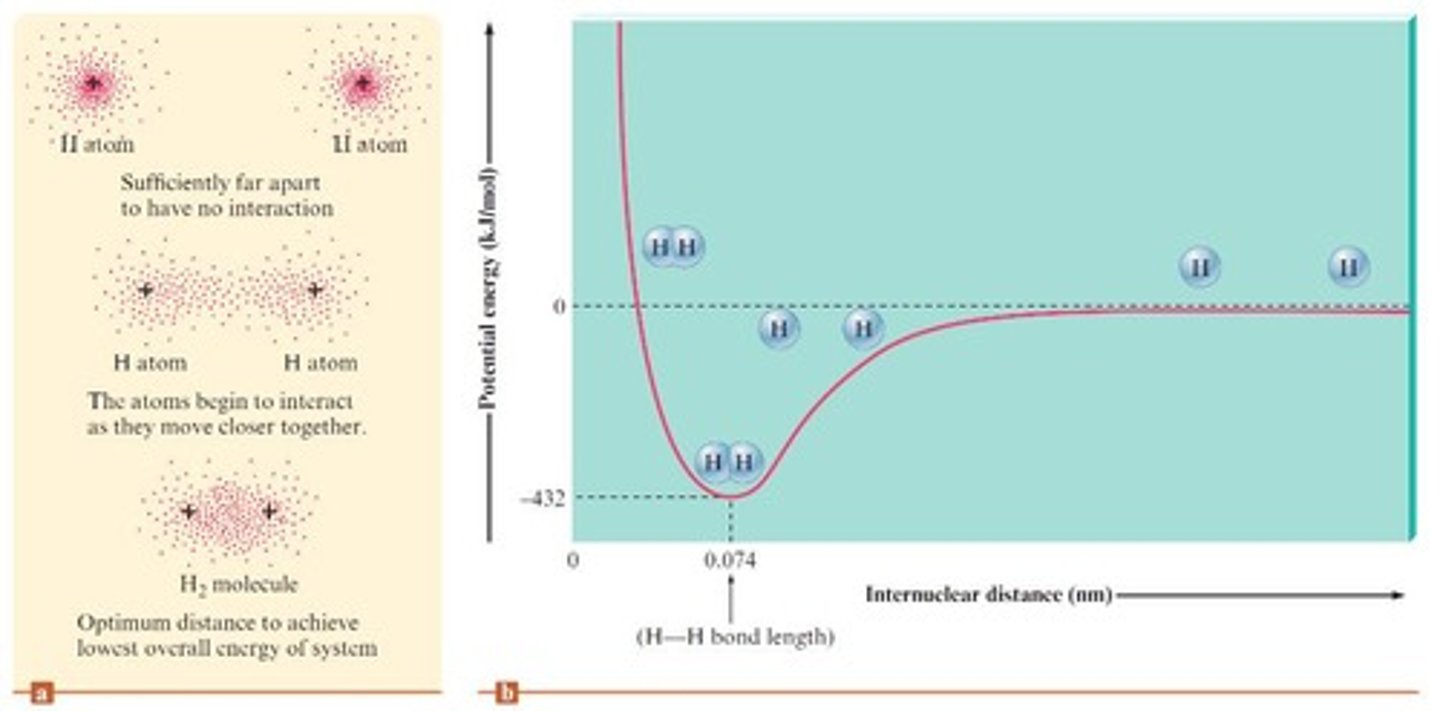
Define electronegativity.
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself.
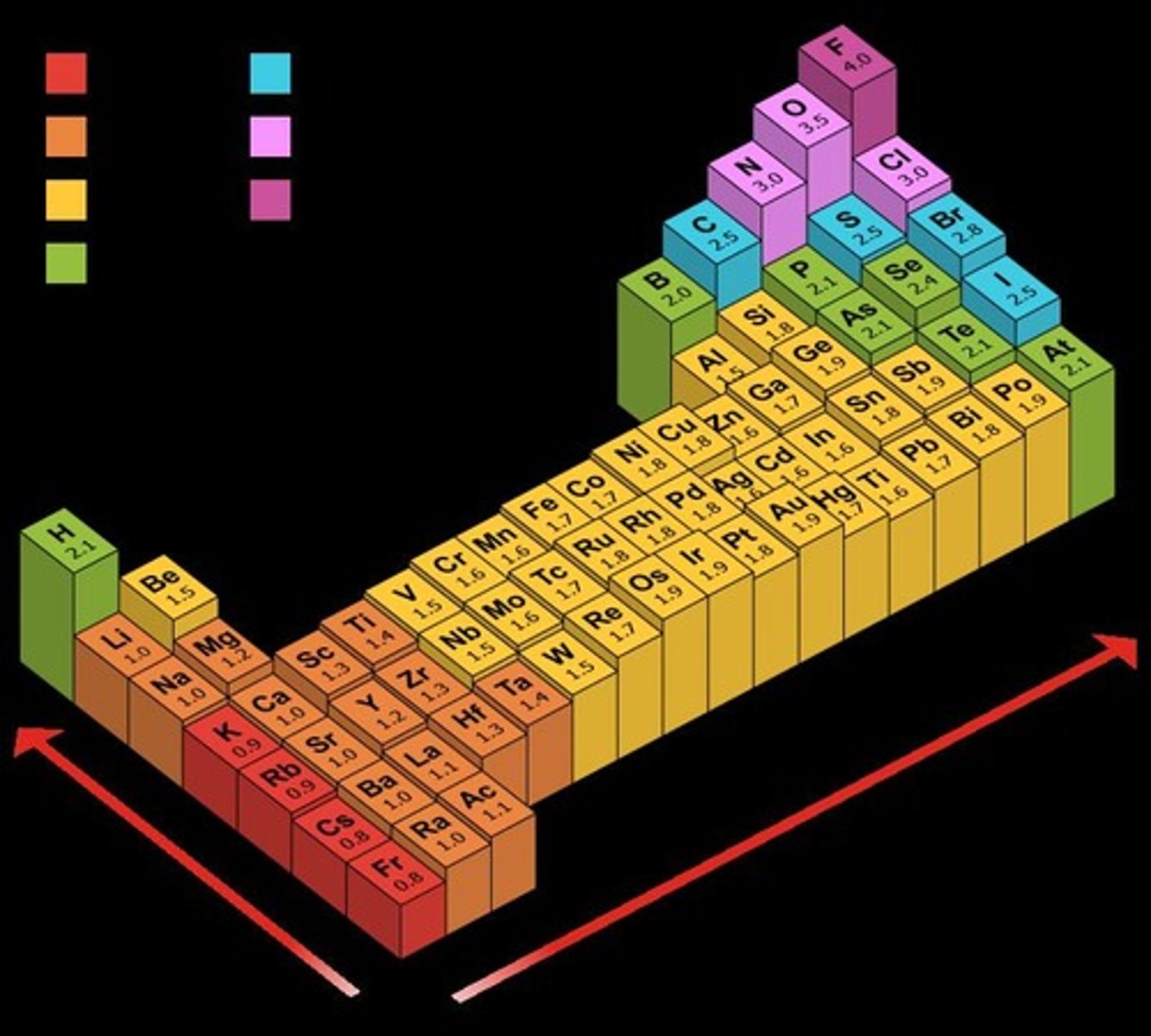
What is the significance of Linus Pauling's method?
It determines the relative electronegativities of atoms by comparing bond energies.
Order the following bonds according to polarity from least to most electronegative: H—H, O—H, Cl—H, S—H, F—H.
H—H < O—H < Cl—H < S—H < F—H.
What occurs in a reaction between two nonmetals?
Electron sharing ensures complete valence electron configuration of both atoms.
What is formed in a reaction between a nonmetal and a representative-group metal?
A binary ionic compound.
What is an ionic compound?
Chemists' term for compounds in solid state, formed by the attraction between positive and negative ions.
What is the significance of noble gas configurations in ionic bonding?
They are generally stable and guide predictions of compound formation.
What is an important fact about chemical compounds?
They are always electrically neutral.
What is the empirical formula of the compound formed between calcium and oxygen?
CaO.
What is a recommended method for naming compounds?
Learn the basic rules, practice daily, and use index cards with formulas and names.
What is the general structure of binary ionic compounds?
They possess a cation in the formula followed by an anion.
How do you name a binary ionic compound?
The cation is named first, followed by the anion, which takes the root of the element name and adds -ide.
What is a common example of a monatomic anion?
O2- is known as peroxide.
What is the formula for Calcium chloride?
CaCl2
What is the formula for Potassium iodide?
KI
What is the formula for Calcium oxide?
CaO
What is the formula for Gallium bromide?
GaBr3
What is the naming convention for metals that form more than one type of positive ion?
The higher charge ends in -ic, and the lower charge ends in -ous.
What is the systematic name for NiCl2?
Nickel(II) chloride
What is the systematic name for FeBr3?
Iron(III) bromide
What is the systematic name for CoCl2?
Cobalt(II) chloride
What is the systematic name for AgCl?
Silver chloride
What is the systematic name for MnO?
Manganese(II) oxide
What is the systematic name for Vanadium (V) fluoride?
Vanadium(V) fluoride
What is the systematic name for N2O?
Dinitrogen monoxide
What is the common name for NO2?
Nitrogen dioxide
What is the naming convention for oxyanions with fewer oxygen atoms?
They end in -ite.
What is the naming convention for oxyanions with more oxygen atoms?
They end in -ate.
What is the name for Ba(OH)2•8 H2O?
Barium hydroxide octahydrate
What is the name for CuSO4•5 H2O?
Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
What is the prefix for indicating 5 in Greek nomenclature?
Penta-
How is an acid named if the anion ends in -ide?
The acid is named with the prefix hydro- and the suffix -ic.
What is the name of the acid derived from the anion chlorate?
Chloric acid (HClO3)
What is the general formula for alkanes?
CxH2x+2
What suffix is used when naming alkanes?
'ane'
What is the prefix for a 1-carbon alkane?
meth-
What is the molecular formula for methane?
CH4
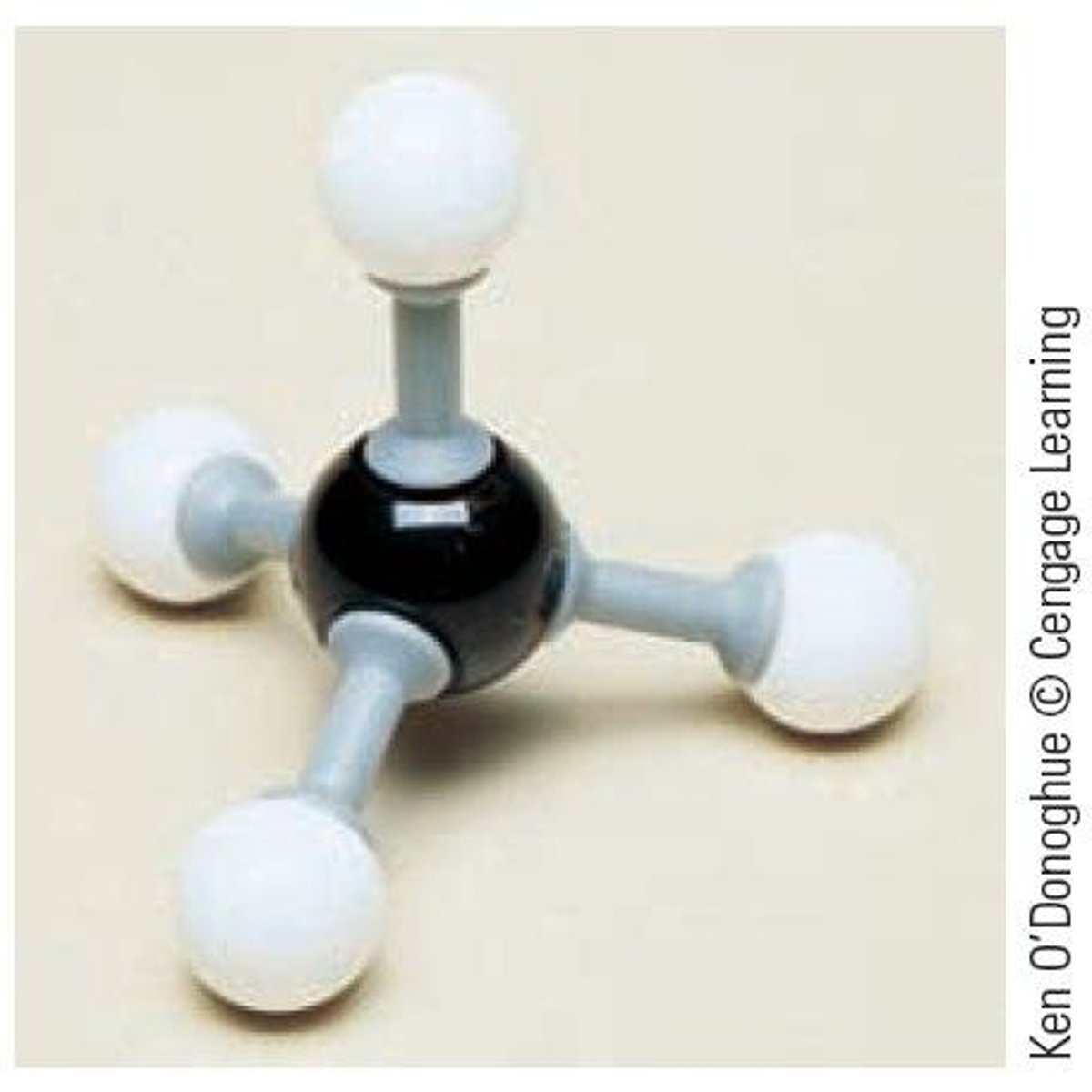

What is the prefix for a 2-carbon alkane?
eth-
What is the molecular formula for ethane?
C2H6
What is the prefix for a 3-carbon alkane?
prop-
What is the molecular formula for propane?
C3H8
What is the prefix for a 4-carbon alkane?
but-
What is the molecular formula for butane?
C4H10
What is the prefix for a 5-carbon alkane?
pent-
What is the molecular formula for pentane?
C5H12