Basics of Pharmacology
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
definition of a drug
a substance that changes a biological system by interacting with it
definition of medicine
a substance/mixture of substances used in restoring/preserving health
can be natural
regulated by medicines act (1968)
when does a drug become a medicine
when used to restore/preserve heath
BNF
British National Formulary
used to provide sound up-to-date information about the use of medicines
how many medicines are in BNF
over 1700
how to learn drugs
biochemical effect
physiological effect
the clinical effect of the pathology
targets of drug action
Regulatory proteins
RECI
Receptors
Enzymes
Carriers/Transporters
Ion Channels
How do drugs work
Bind to targets (RECI), changing function of physiological systems they regulate
What happens when a drug targets a Receptor
binds causing downstream change e.g. enzyme cascade, leading to physiological effect
what happens when drug targets ion channel?
binds to stop or increase ion flow
what happens when drug target a carrier/transporters?
binds to distrupt movement of other molecules
what happens when drug targets an enzyme?
modifies cell signalling causing a direct change of function
Inhibition- direct + rapid
Induction- gene effect+ delayed
what can drugs do at their targets?
activate
partially activate
block/inactivate/inhibit
functional effects of drugs
Biochemical
Cellular
Physiological
Structural
biochemical definition
chemical processes and substances which occur within living organisms
cellular definiton
relating to/consisting of living cells
physiological definition
relating to normal functions of living organisms and their parts.
structural definition
the composition and arrangement of the component parts of an organism or a device
temporal effects of drugs
Drug + target:
RAPID physiological response or Altered Gene expression
Physiological Response ⇌ Altered gene expression is SLOW
Altered Gene expression ⇌ Delayed Responses is SLOW (causes altered protein expression)
How do drugs interact with Receptors?
Exogenous ligands compete with Endogenous ligands causing downstream change, leading to a physiological effect
e.g. Beta blockers (e.g. bisoprolol) are adrenaline antagonists with high affinity for β1-adrenergic receptors in heart. Binding causes heart to beat slower and weaker.
Affinity
How avidly a ligand binds to a receptor
Efficacy
Magnitude of the effect once a ligand is bound
Ligands
molecules that bind to receptors and cause changes in cell signalling and hence cell behaviour or structure.
Agonists
Bind, activating receptor
Antagonists
Bind, inhibiting activation by preventing endogenous ligand binding
Receptors
protein molecules which recognise endogenous signals e.g. hormones, neurotransmitters, inflammatory mediators.
response- series of downstream reactions, causing physiological effect
Enzymes
biological catalysts
basis for intracellular signalling cascades
drug effects: inhibition- direct+rapid; induction- gene effect+delayed
How do drugs interact with enzymes?
Inhibition- direct + rapid
Induction- gene effect+ delayed
e.g. statins are HMG CoA reductase analogues, binding to HMG-CoA competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase binding, hence prevent conversion of HMG-CoA into mevalonate- slowing cholesterol production in the liver
Channel
Protein forming Lipid Bilayer pore
allows passive diffusion down concentration gradient for specific ions/molecules
e.g. Amlodipine binds to L-type calcium channels, stabilising channel in closed/inactive state, reducing influx of Ca2+ which inhibits release from SR and binding to myofilaments, reducing cardiac contractility, lowering blood pressure and reducing heart rate.
Exchanger (Antiporter)
moves two different ions across lipid bilayer in opposite directions. one down conc gradient and one up.
Co-transporter (Symporter)
moves two different ions/molecules across lipid bilayer in same direction.
One moves down conc gradient, and one up.
e.g. furosemide inhibits the Na⁺/K⁺/2Cl⁻ co-transporter, leading to increased urine production by blocking ion reabsorption at LoH in the kidneys.
specificity
the receptors ability to respond to a single ligand
effective drugs have high specifity, binding to other targets- side effects
Pharmodynamics
What the drug does to the body
effects of drug in body and mechanism of action
bioavailability
pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug
ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
ADME
pharmacokinetics- what the body does to the drug
Absorption- depends on administration route. passive/facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis. IV/PO. plasma drug conc
Distribution- drug nature lipo-/hydro- phillic. blood flow- brain vs skin. capillary permeability e.g. high in liver, low in brain. plasma+ tissue binding- e.g. albumin systemic availability lower
Metabolism- Liver. Phase I- Oxidation, hydrolysis or reduction by cytochrome P450s. Phase II if still lipophillic- glutathione conjugation, acetylation, sulfation, glucuronidation. makes drug more readily excretable.
Excretion- Renal (adjust if creatinine eGFR low), Bile (adjust dosage if LFT low)
A in ADME
Absorption
depends on route of administration
passive diffusion (most common) - down conc gradient
facilitated diffusion- requires specific membrane molecules
active transport- not conc dependent. uses transporters
endocytosis- rare, larger molecules
IV/PO
Plasma drug conc
Bioavailability
fraction of administered dose that reaches systemic circulation
determined by drug properties and route of administration
AUC PO/ AUC IV
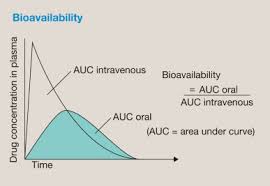
D in ADME
Distribution
NBCPT
Nature of drug- lipo-/hydro- phillic
blood flow- brain vs skin
capillary permeability- e.g. high in liver, low in brain
plasma+ tissue binding- e.g. albumin systemic availability low
M in ADME
Metabolism
makes drug more readily excretable
Liver
Phase I- oxidation, hydrolysis, reduction - by cytochrome P450s
Phase II if metabolites still lipophillic- gluthione conjugation, acetylation, sulfation, glucuronidation
Phase I of Metabolism
by cytochrome P450s
oxidation, hydrolysis, reduction
if still lipophillic goes to Phase II
Phase II of metabolism
if metabolism still lipophillic after Phase I by cytochrome P450s (oxidation , reduction, hydrolysis)
glutathione conjugation, acetylation, sulfation, glucuronidaton
E in ADME
Excretion
Renal (reconsider if creatinine/ eGFR low)
Bile (adjust dosage if LFT low)
Medicine classes
PoM- prescription only- from pharmacist with Rx from approved practitioner
Pharmacy only- purchased under supervision of a registered pharmacist
GSL- general sales list- can be bought from any outlet without Rx or pharmacist supervision
PoM
prescription only medicines
only from pharmacists with Rx from approved practitioner
pharmacy only medicine
bought under supervision of registered pharmacist
GSL medicines
General sales list
can be bought without Rx or pharmacist supervision
Medicines are regulated by
Medicines act (1968)
defines where which medicines can be obtained and where
components of Medicines in healthcare
PDAM
Prescribing
Dispensing
Administration
Monitoring
Prescribing
A Rx from a suitably-qualitied healthcare professional that authorises dispensing/administration of a medicine for a pt
Rx definition
a written order from a suitably-qualified healthcare professional (within scope of practice) that authorises the dispensing/administration of a medicine for a ppt
Dispensing
to make up + distribute medicines- especially on Rx
Primarily by pharmacists, also dispensing doctors + nurses
receive +validate Rx
understand + interpret
prepare + label
final check
record action
issue medicine with clear instructions + advice to pt
dispensing process
receive +validate Rx
understand + interpret
prepare + label
final check
record action
issue medicine with clear instructions + advice to pt
drug administration
giving a therapeutic agents to a pt e.g. by infusion, inhalation, injection, paste, suppository or tablet
primarily pts + carers. organisations- determined by local policy- self administration, appropriately trained + competent staff-mostly nurses, some doctors (emergency) and other practitioners
Check, Give, Record, Monitor
What to check when administering a drug
Identify pt
Rx
Consent
Allergies/ADR
identify meds + expiry date
storage compliance
not already given
give, record, monitor
What to check when monitoring a patients drugs
SEA, symptoms (hx), signs (exam), investigations
Safety- side effects (hx), exam, any side effect markers deteriorated)
Efficacy- feeling better (hx), improved signs, disease markers improved?
acceptability- Can they manage to take it?
interactions
How to check safety in drug monitoring
SIDE EFFECTS
any side effects in hx?
any signs of emerging side effects?
any side effect markers deteriorated?
how to check efficacy in drug monitoring
do they feel better?
have signs of disease improved?
have diseases markers improved?
how to check acceptability in drug monitoring
Can they manage to take the medicine?
Drug monitoring treatment regimen
Pt Tx goals/concerns
Best medication? - start additional drugs/ increase dose
anything to remove? stop/reduce dose- reduce harm/ treatment burden
How to make a therapeutic decision
Work out what is wrong- Presenting complaint, DDx
Identify right treatment- treat before if in emergency
start Tx + monitor
review + repeat
Pattern recognition- Hx, exam, inv, summarise, dx/ddx
How to work out what is wrong when making a therapeutic decision
p/c
DDx
Aims of treatment
Prioritised
Save life
relieve sxs
treat underlying disease cure for short term, control for long term
improve px- delay diseases progression, prolong survival
manage drug side effects
Social prescribing
lifestyle- diet, exercise, weight management. alcohol, smoking, illict drugs
MH- TThxm support+ counselling
social- housing, loneliness, isolation, family issues
medicines
interventions
surgery
Adverse drug reaction
unintended response in a patient resulting from medical intervention
prescribing should
Firstly do no harm
reduce mortality+ morbidity
basic duties of prescribing
Dukes and Seartz
restrictive use
careful choice
consultation and consent
Rx + recording
explanation
supervision
termination
conformity
drug use process
establish need- appropriate indication, address problems therapeutically, not prescribing is an option
select drug + regimen- factors- safety, tolerance, efficacy +price, pt factors, formulary alternative, risk:benefit
provide drug- dispensing, blister back etc
drug administration- appropriate devices + techniques
monitor- effectiveness/AEs, determine to maintain/modify/discontinue
counsel+closure- management plan to optimise care, identify ideas, concerns, expectations, establish responsibilities, safety net
Pt factors to consider when prescribing
coexisting disease- hepatic renal metabolism+excretion, cardiac/cancer side effects+ vulnerability, drug interactions, check BNF for dosage
pregnancy- malformation- T1 follic acid effects, T3
allergies
key steps in prescribing
STEP
safety
tolerability
efficacy - pt trust
Price
drug absorption methods
Oral
buccal
rectal
transdermal
nasal
lungs
intramuscular
subcutaneous
intravenous
intrathecal
oral absorption
enters bloodstream from digestive system
easy for pt compliance +administration
tablets, liquid
variable absorption, first-pass effect
buccal absorption
cheek
direct absorption into bloodstream through mucous membranes
rapid onset
avoiding liver metabolism
e.g. nitroglycerin for angina, buprenorphine for pain/opioid dependence
rectal absorption
when oral not possible- vomiting/ unconscious
localised effects in rectum
e.g. diazepam for seizures, acetaminophen
transdermal absorption
topical
continuous release- steady levels in blood, avoid frequent dosing
e.g. nicotine patch for smoking cessation
nasal absorption
rapid absorption through nasal mucosa
quick relief, emergencies
e.g. fluticasone for allergies, naloxone for opioid overdose
Lung absorption
inhalation
directly targets respiratory system for quick relief of symptoms w minimal systemic side effects
e.g. salbutamol for asthma
intramuscular absorption
relatively fast into bloodstream from muscle tissue
useful for larger volumes/ medications that irritate veins
e.g. epinephrine for anaphylaxis, vaccines
subcutaneous absorption
under skin
slower, sustained release into bloodstream
consistent levels over time
e.g. insulin for diabetes, heparin for thrombosis
Intravenous absorption
vein
direct into bloodstream, immediate effect + precise dosage control
ideal for emergency/ rapid action
e.g. morphine, antibiotics like ceftriaxone
intrathecal absorption
spinal canal
targets CNS directly by delivery into CSF- high local conc + reducing systemic side effects
e.g. morphine, methotrexate for certain cancers
Consider when prescribing to older people
reduced absorption- increased gastric motility
decreased intestinal/hepatic/renal blood flows (decreased renal clearance of digoxin and aminoglycosides)
reduced clotting factor synthesis -increased NSAID toxicity
anti-cholinergic, opiates, TCAD, antihistamines- constipation
anti-cholinergics- constipation, confusion
hypnotics, Beta blockers- confusion
fat soluble drugs- (increased sensitivity to benzodiazepine)
reduced hepatic clearance (increased level of benzodiazepine)
Stop Smoking advice
Ask status
Advice value of stopping
Assess intrest
Assist treatment options
Arrange follow up and monitor
Drugs
monitoring books of drugs
Steroid- Blue card
Warfarin- Orange book
Methotrexate/ Lithium- purple
Drugs with narrow therapeutic index
lithium
digoxin
theophylline
gentamicin
phenytoin
warfarin
drugs that require regular monitoring
morphine
insulin
neoplasia- chemo
digoxin
theophylline
hypoglycaemic agents- SU
epileptic treatments
gentamicin
anticoagulants- warfarin
anti-psychotics- lithium