Biology - B5 (Genes, Inheritance and Selection) *GCSE OCR HIGHER*
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Active Site
The part of the enzyme which is specific to the substrate and has a complementary shape to it
Allele
A version of a gene (also known as variant)
Antibiotic
A type of medication that helps cure bacterial disease by killing infective bacteria inside the body
Antibiotic Resistance
- The ability of a bacteria to become resistant to the treatment that is being used to kill it, i.e. antibiotics
- This provides evidence for evolution.
Artificial Classification
- The classification of organisms based on observable characteristics (appearance)
- Advantage: It is quick
- Disadvantage: It isn't accurate
Asexual Reproduction
A form of reproduction that only involves a single parent and creates genetically identical offspring ( a clone)
Biodiversity
The variety of different organisms living in an ecosystem
Chromosome
A long, coiled molecule of DNA that carries genetic information in the form of genes
Continuous Variation
Variation that can take any value between two extremes, e.g. height or weight
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- A polymer that is made of two strands twisted around each other forming a double helix
- It contains all the genetic information
Diploid
When a cell has a full set of chromosomes (46 chromosomes)
Discontinuous Variation
Variation that can only take discrete values, e.g. eye colour
Dominant Gene
- An allele that is always expressed when present
- It is represented by a capital letter (B)
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions
Evolution
A gradual change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time, through the process of natural selection, which may result in the formation of new species
Extinction
When all the members of a species have died
Fossil Record
- The remains or impressions of dead organisms found in rocks that are millions of years old
- They provide evidence for evolution since the rock layers allow for the showing of a gradual change over time
Gamete
- Sex cells (sperm and egg cells) with half the usual number of chromosomes (23 chromosomes)
- They are involved in reproduction.
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific amino acid sequence which is polymerised to make a specific protein
Genetic Variation
- The variation in the genes of a species
- Different forms of a gene (alleles) show up in an organism's phenotype if they are present in the genetic material
- BB = homozygous dominant
- bb = homozygous recessive
- Bb = heterozygous
Genome
The entire genetic material of an organism
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism
Haploid
When a cell has half the number of chromosomes (23 chromosomes), seen in ova and sperm
Heterozygous
When an individual has two non-identical alleles of a gene e.g. Bb
Homozygous
When an individual has two identical alleles of a gene e.g. bb or BB
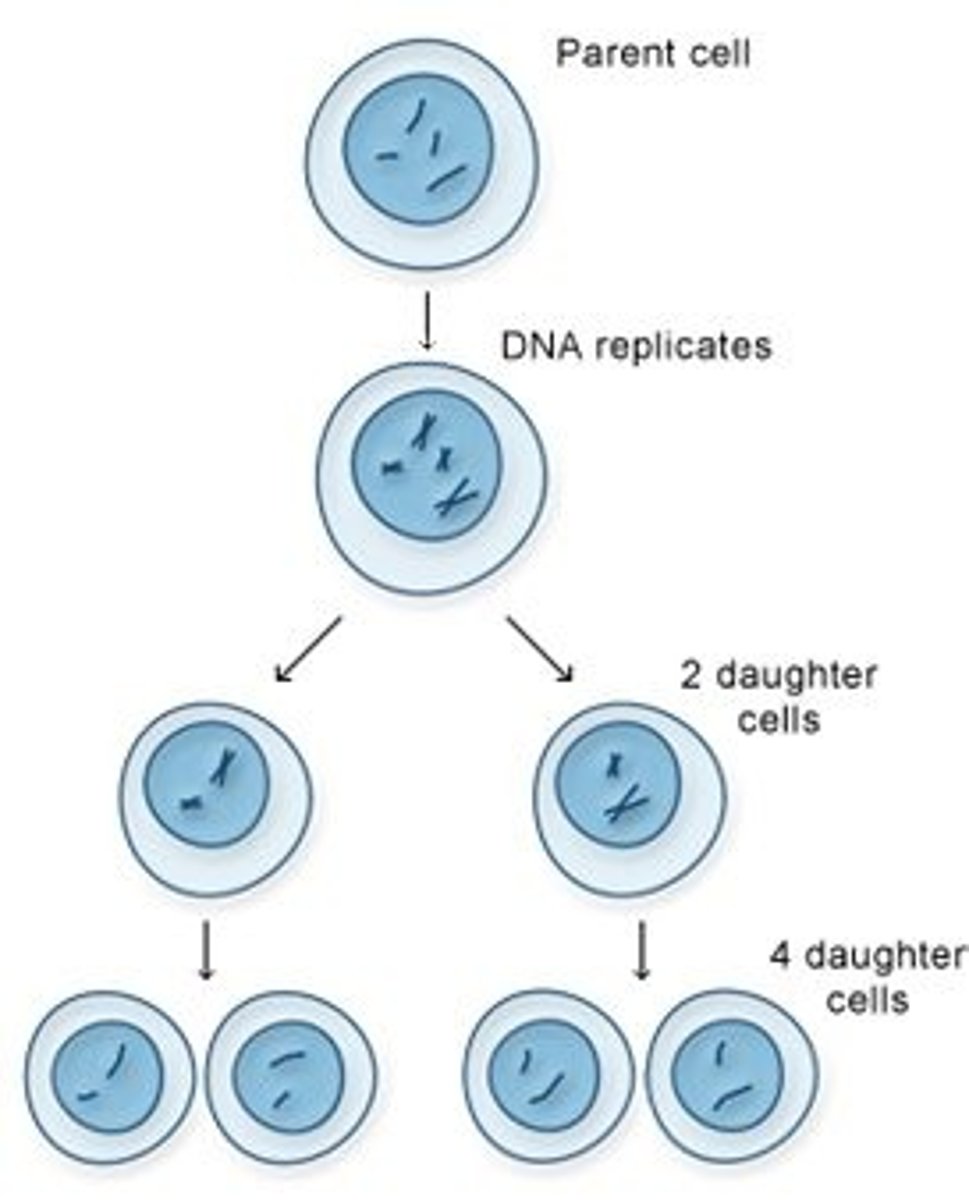
Meiosis
- A form of cell division that produces gametes (4 haploid cells from one diploid cell)
- They are not genetically identical and contain half the number of chromosomes
1. Chromosomes are copied and line up along the middle of the cell in pairs
2. One member of each pair is pulled to the opposite side
3. Cell divides in two
4. Chromosomes line up along the middle of the new cell
5. Chromosomes are pulled in half and a single copy goes to each end
6. Each cell divides in two resulting in 4 haploid cells
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
An RNA subtype that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
Molecular Phylogenetics
- Finding evolutionary relationships between organisms on the basis of their DNA
- This method can only be used in fossils that have DNA present
- It studies similarities in DNA between species
Mutation
- A random change in DNA which increases variation
- The sequence of DNA bases is altered creating a different version of an allele
- Mutagens are radiation / chemicals which are mutagenic
- They may have a neutral, beneficial or damaging effect on the phenotype
Natural classification
- The classification of organisms based on their evolutionary relationships (DNA)
- Advantage: Its accurate
- Disadvantage: It takes time
Natural selection
- The process by which advantageous alleles are passed down to offspring over many generations, increasing the allele frequency
- These alleles give rise to phenotypes best suited to the environment meaning less adapted organisms die
- This process repeats over many generations
Nucleus
An organelle found in most eukaryotic cells that contains the cell's genetic material and controls the activities of the cell
Phenotype
- The physical characteristics of an organism
- It is due to interactions between the genotype and the environment
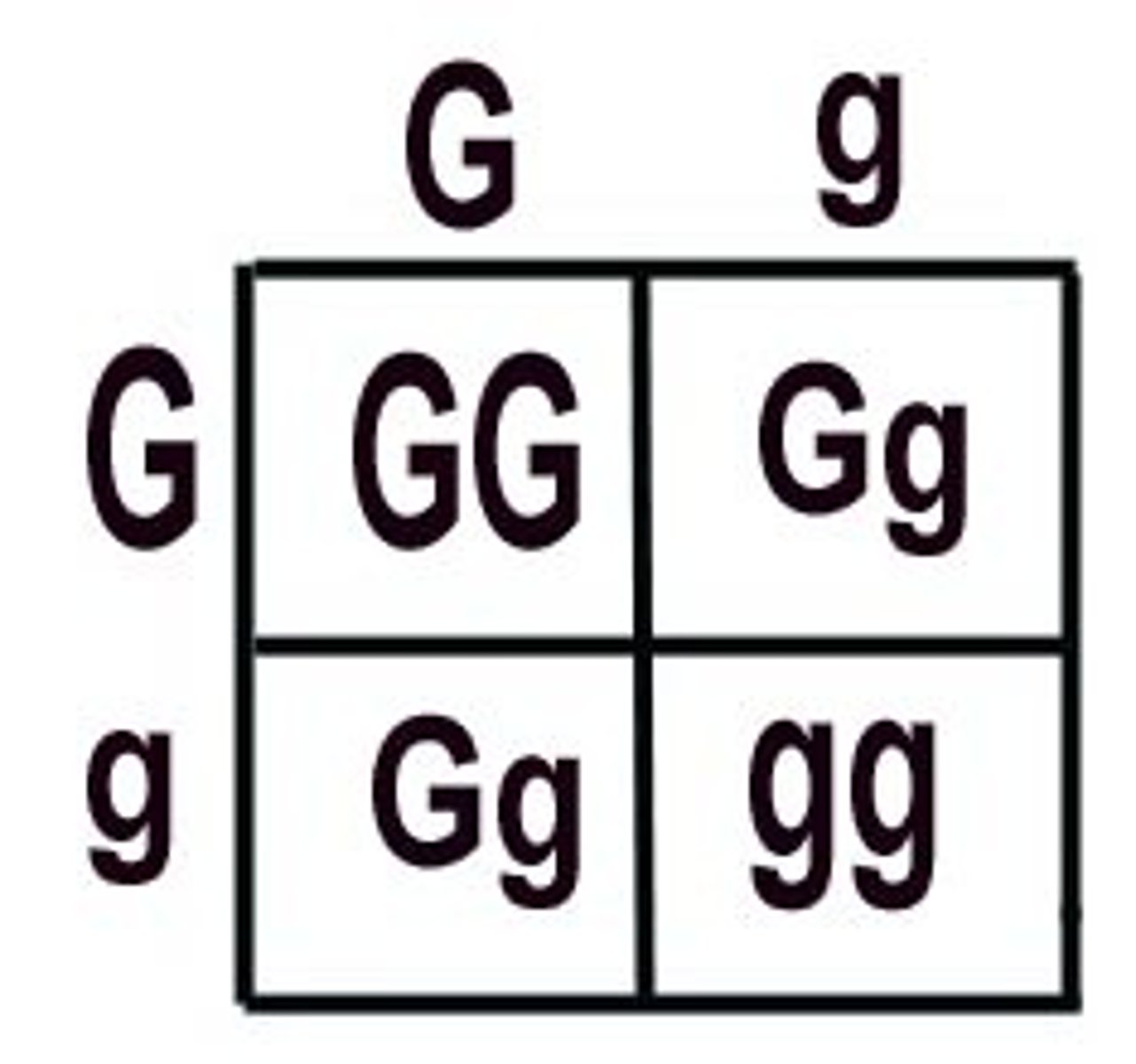
Punnett Square
A grid used to determine potential outcomes of a genetic cross
Recessive
- An allele that is only expressed if two copies are present
- It is represented by a small letter (b)
Seedbank
A place where seeds are preserved in order to preserve genetic diversity
Sexual Reproduction
- Reproduction that involves the fusion of male and female gametes
- This method of reproduction produces genetic variation due to genetic information being taken from two parents
Single Gene Inheritance
Inheritance of characteristics that are controlled by a single gene
Speciation
- The formation of new species due to the evolution of two reproductively separated populations
- This is usually due to geographic isolation.
Transcription
The unzipping of the DNA molecule around the gene, copying it to mRNA in the nucleus
Translation
Translating the mRNA sequence to an amino acid sequence during protein synthesis
Classification
- The action or process of classifying something according to shared qualities or characteristics
- By using one classification system, all scientists understand the research

Asexual Reproduction - Advantage
- If parent is well adapted, the offspring will be too
- Only one parent is needed
- Reproduction is faster
- More offspring
Asexual Reproduction - Disadvantage
- Changes to the biotic or abiotic factors can destroy the species
- Reduction in the gene pool
Sexual Reproduction - Advantage
- Variation leads to adaptions required to cope with environmental pressure
- More genetic variation
Sexual Reproduction - Disadvantage
- Reproduction requires to parents
- Reproduction is slower
- Less offspring produced
Fossils
- The organism dies and rots, leaving the skeleton
- The skeleton is covered in sand / soil / clay and is protected for millions of years
- The skeleton mineralises and turns into rock
- The rock shifts in the earth with the fossil trapped inside
- Eventually the fossil emerges as the rocks move and erosion takes place
Evidence for Evolution
- The fossil record
- Extinction of species that don't adapt
- Molecular comparison (similarities in DNA of humans and chimpanzees)
- Rapid changes in a species (seen in bacteria which replicates rapidly)
Theory of Evolution
- It states that organisms change and develop over time to adapt an increase rate of survival
- Charles Darwin went to the Galapagos Islands where he made his observations on the Finches
- Different Islands had different Finches depending on what food was available
- Darwin called this natural selection
- Alfred Wallace was working on his theory of evolution at the same time
- Both had similar ideas so they did a joint presentation
- Darwin published a book "On the origins of species" which was very controversial at the time as it conflicted with the idea of God
Genetic Over Time - 1866
Discovery that certain characteristics are inherited
- Grégor Mendel carried out experiments on peas.
- He noticed that = Characteristics in Plants where determined by genes (hereditary units)
= Hereditary units are passes from both parents (one unit each)
= Hereditary units are dominant or recessive
Genetic Over Time - 1869
Nucleon discovered
- Fredrich Miescher discovered an acidic substance in the nucleus (DNA)
Genetic Over Time - 1944
Genes can be transferred from on generation to the next
- Oswald Avery transferred DNA between bacteria
- This passed the disease from one strain to another then to the offspring
Genetic Over Time - 1950
DNA base pairs discovered
- Edwin Chargaff found all DNA contains equal quantities of Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine
Genetic Over Time - 1952
DNA crystals photographed
- Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin imaged DNA crystals using x-rays
Genetic Over Time - 1953
Double helix structure of DNA identified
- James Watson and Francis Crick publish their description of DNA
Genetic Over Time - 1953 to 2000
Scientists identify individual genes that code for genetically inherited disorders (e.g. cystic fibrosis)
Genetic Over Time - 2003
Scientists identifies and sequenced 24,000 genes. The complete set of genes in the human body